AP psych - consciousness
4.5(2)Studied by 91 people
0%Unit Mastery
0%Exam Mastery
Build your Mastery score
Supplemental Materials
Card Sorting
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:12 AM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
1
New cards
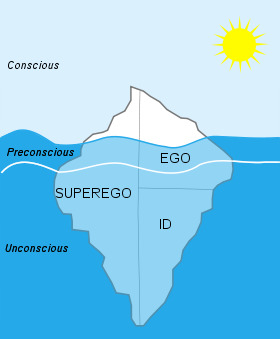
Awareness
1. sensory
2. self
-emotions
-feelings
3. Freud stuff
2. self
-emotions
-feelings
3. Freud stuff
2
New cards
Altered States
-when asleep -> less aware of self
-sleeping, dreaming, drug use, hypnosis
-sleeping, dreaming, drug use, hypnosis
3
New cards
Why sleep?
1. it allows us to conserve energy, repair damage to the body, and store and organize information.
2. rid waste - in the brain -> if not asleep, not able to "rid waste"
-physical
-mental
3. immune system - sick; injured
2. rid waste - in the brain -> if not asleep, not able to "rid waste"
-physical
-mental
3. immune system - sick; injured
4
New cards
How? (much)
1. Babies = 10-14 hours (maybe 20)
2. Adults = 7-9 hours
3. Sleep Debt - hard to get rid of
2. Adults = 7-9 hours
3. Sleep Debt - hard to get rid of
5
New cards
Circadian Rythms
1. 24 bio clock
2. jet lag
3. melatonin (hormone) - sun -> hypothalamus -> pineal gland
4. manage what time we go to bed
2. jet lag
3. melatonin (hormone) - sun -> hypothalamus -> pineal gland
4. manage what time we go to bed
6
New cards
Sleep Stages
brain waves
1. Stage 1 - alpha waves: neural activity decreases
2. Stage 2 - sleep spindles: neural activity decreasing. Easily woken up.
3. Stage 3 & 4 - "deep sleep" - delta waves : brain is least active. Feel worse after getting 8 hrs. of sleep.
4. REM
1. Stage 1 - alpha waves: neural activity decreases
2. Stage 2 - sleep spindles: neural activity decreasing. Easily woken up.
3. Stage 3 & 4 - "deep sleep" - delta waves : brain is least active. Feel worse after getting 8 hrs. of sleep.
4. REM
7
New cards
REM
- "Paradoxical Sleep": Brain extremely active -> body is "locked down"; body doesn't move.
- Dreaming
- Rapid eye movement
- Dreaming
- Rapid eye movement
8
New cards
Cycles
20 minute nap = coffee; 6-8 hrs. of energy; Stage 1 & 2
90 minutes = more energy (boost); Awake -> REM
Stage 3 & 4 - danger zone
1. 3/4 -> REM; REM increases the longer you sleep
2. REM Rebound - put body in REM earlier & stay in longer
3. Most in stage 2
90 minutes = more energy (boost); Awake -> REM
Stage 3 & 4 - danger zone
1. 3/4 -> REM; REM increases the longer you sleep
2. REM Rebound - put body in REM earlier & stay in longer
3. Most in stage 2
9
New cards
Dreaming
Pons
1. Evolution
-threat perception
2. Biological
-long-term potentiation/info processing (memory consolidation)
-Activation Synthesis
3. Psychoanalytic (Freud)
-unconscious: work through conflicts in a safe way through dreaming
-manifest vs. latent content
4. Psychodynamic (Carl Jung)
-collective unconscious
1. Evolution
-threat perception
2. Biological
-long-term potentiation/info processing (memory consolidation)
-Activation Synthesis
3. Psychoanalytic (Freud)
-unconscious: work through conflicts in a safe way through dreaming
-manifest vs. latent content
4. Psychodynamic (Carl Jung)
-collective unconscious
10
New cards
memory consolidation
rerunning routs in brain
11
New cards
threat perception
fear, loneliness, embarrassment, etc.
12
New cards
activation synthesis
random things in dream
13
New cards
manifest content
story of the dream - part you remember
14
New cards
latent content
hidden meaning of a fantasy or dream
15
New cards
collective unconscious
cloud; google doc; Things are connected in a universal way. Things are the same to everybody
16
New cards
where does dreaming occur in the brain?
pons
17
New cards
how many sleep cycles does a person go through each night
5-6
18
New cards
Sleep Disorders
1. Insomnia & Depression
2. Sleep Apnea
3. Narcolepsy
4. Somnambulism
5. Night Terrors
6. Sleep Paralysis
2. Sleep Apnea
3. Narcolepsy
4. Somnambulism
5. Night Terrors
6. Sleep Paralysis
19
New cards
Insomnia & Depression
can't sleep (SSRI, therapy, sleep hygiene)
20
New cards
Sleep Apnea
stop breathing -> wake up (sent to stage 1-2) (snore)
mask send oxygen to lungs (c - pap)
mask send oxygen to lungs (c - pap)
21
New cards
Narcolepsy
random fall asleep midday (sleep attack)
destruction of cells in hypothalamus
simulant drugs
destruction of cells in hypothalamus
simulant drugs
22
New cards
Somnambulism
sleep walk / talk (stage 4)
23
New cards
Night terrors
sleep screaming / crying
24
New cards
Sleep Paralysis
REM; body on lockdown but you are aware; hallucinate
25
New cards
Ambien & Lunesta
drugs that cause sleep walking and talking
26
New cards
Hallucinogens
alter serotonin levels (happy)
1. marijuana
2. LSD/ACID
3. Psilocybin/Shrooms
1. marijuana
2. LSD/ACID
3. Psilocybin/Shrooms
27
New cards
marijuana
THC (paranoia)
28
New cards
LSD/ACID
dunk paper in acid and let dry; consume
29
New cards
Psilocybin / Shrooms
vomit (eat) Perception is altered
30
New cards
Stimulants
dopamine, adrenaline -> give you boost
1. Caffeine
2. Nicotine
3. Cocaine -> crack
4. Amphetamines -> meth
5. MDMA/Ecstasy
1. Caffeine
2. Nicotine
3. Cocaine -> crack
4. Amphetamines -> meth
5. MDMA/Ecstasy
31
New cards
Caffeine & Nicotine
increase heart conditions (cancer, heart attack, etc.)
32
New cards
Cocaine
coca leaves; stimulant
33
New cards
Amphetamines
Narcolepsy prescribed
34
New cards
MDMA/Ecstasy
touch, handsy, lights and music look and sound different
35
New cards
Depressants
GABA (increases) inhibitor heart rate/respiration slows
1. Alcohol
-slur speech
-cerebellum
-hippocampus (memory)
2. Opiates (+endorphins)
-morphine; heroine
3. Barbiturate's/Benzodiazepines
-Anti-anxiety
-think less
-Xanax
1. Alcohol
-slur speech
-cerebellum
-hippocampus (memory)
2. Opiates (+endorphins)
-morphine; heroine
3. Barbiturate's/Benzodiazepines
-Anti-anxiety
-think less
-Xanax
36
New cards
Alcohol
Decrease frontal lobe activity & nervous system
37
New cards
Addiction
1. Tolerance
2. Dependence
3. Withdrawal
2. Dependence
3. Withdrawal
38
New cards
Tolerance
how much/need to take
39
New cards
dependence
don't feel right without it
40
New cards
withdrawal
negative effects of not having it
41
New cards
Relaxed but not awake
consciousness narrows
42
New cards
suggestion
post hypnotic suggestion
placebo effecting
placebo effecting
43
New cards
role playing
naturalistic (actor playing)
44
New cards
Samesies
relaxed but not awake
45
New cards
Biofeedback
measure heart rate/blood pressure