3.2.1.7 Applications of conservation laws
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/5
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
1
New cards
Beta decay occurs because of what interaction?
Beta decay occurs because of the weak interaction between quarks.
2
New cards
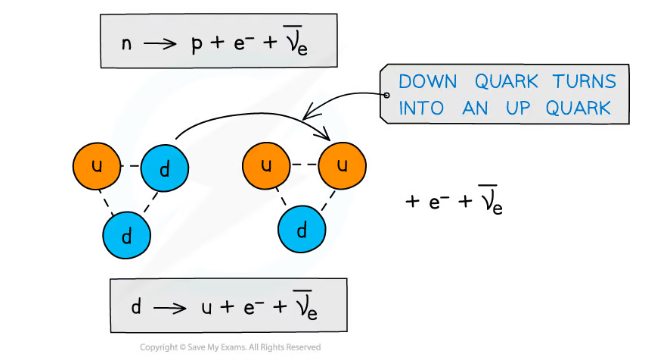
Why does a neutron turn into a proton in beta minus decay?
A neutron turns into a proton because a down quark turns into an up quark.
3
New cards
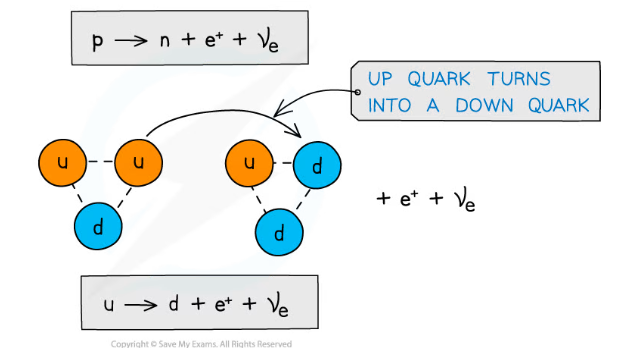
Why does a proton turn into a neutron in beta plus decay?
A proton turns into a neutron in beta plus decay as an up quark turns into a down quark
4
New cards
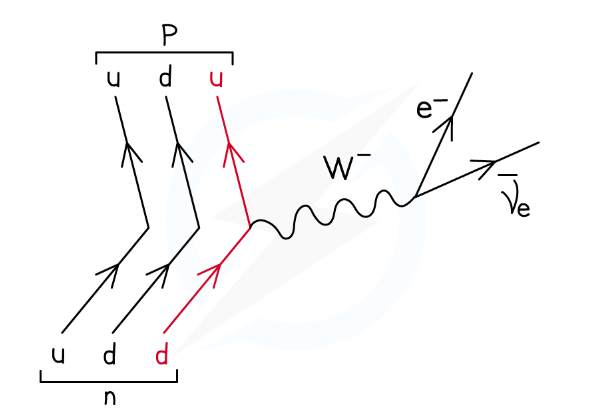
What does the W^- boson do in beta minus decay?
The W^- boson ‘carries away’ the negative charge of the down quark (that turns into an up quark) which provides the negative charge for the electron and antineutrino.
5
New cards
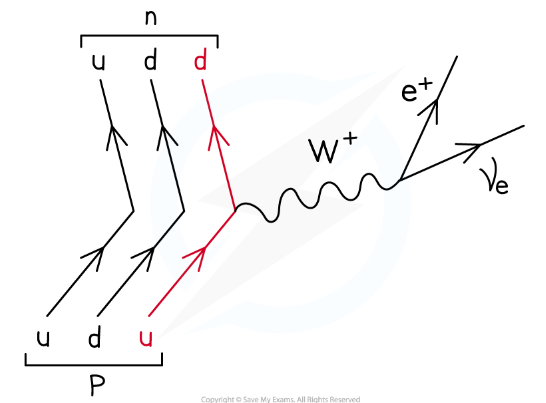
What does the W^+ boson do in beta plus decay?
The W+ boson ‘carries away’ the positive charge of the up quark (which turns into the down quark) which provides the positive charge for the positron and neutrino.
6
New cards
What four things are always conserved in an interaction?
Things that are conserved in an interaction:
* baryon number
* lepton number
* energy
* momentum
* baryon number
* lepton number
* energy
* momentum