IB HL Biology 4.3 Carbon Cycling 4.4 Climate Change
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:34 PM on 5/29/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
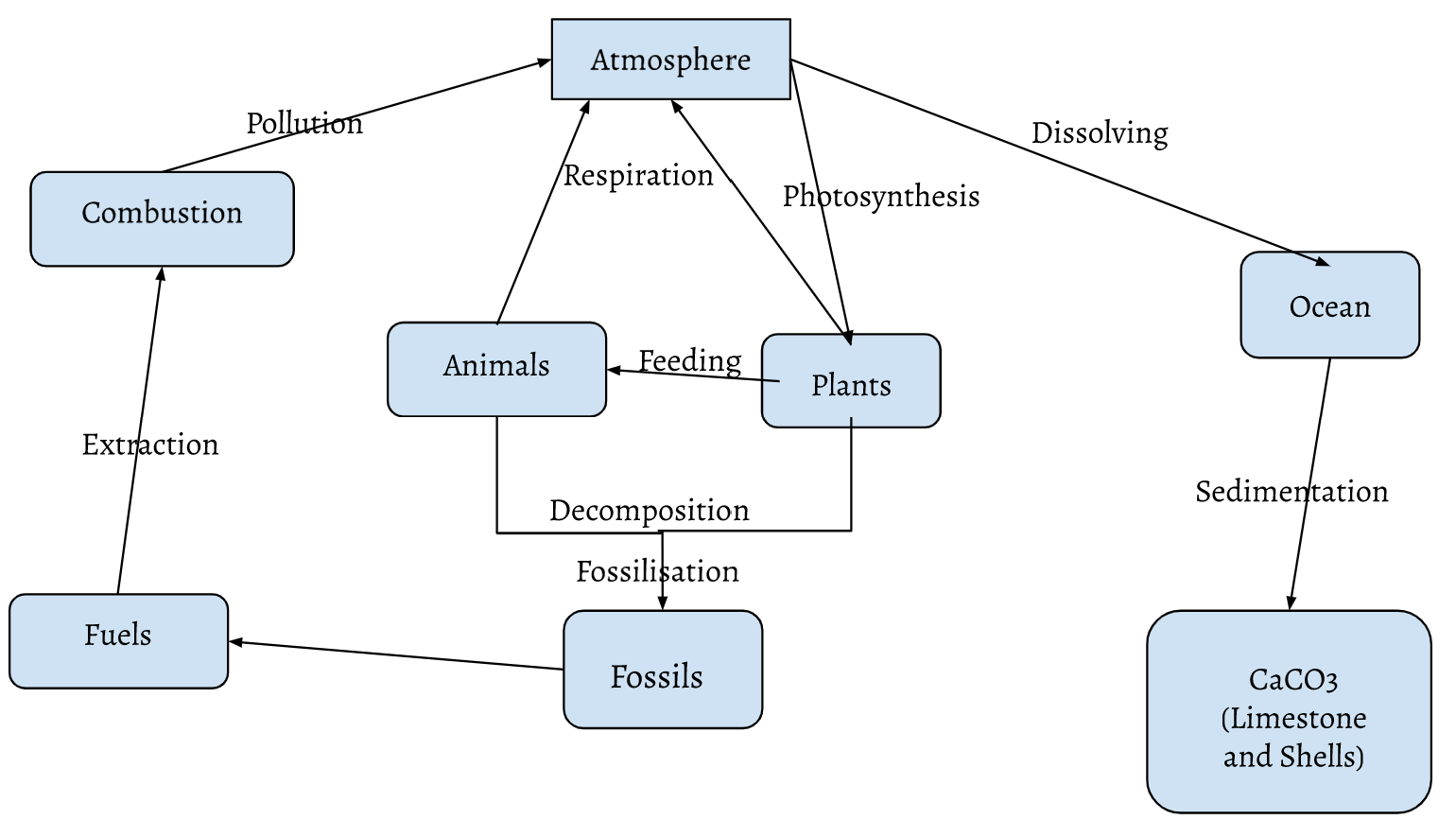
Carbon Cycle
Sinks: Fuels, fossils, animals, plants, ocean, CaCO3, atmosphere
Fluxes: Pollution, respiration, photosynthesis, dissolving, extraction, feeding, sedimentation, decomposition, fossilisation
Fluxes: Pollution, respiration, photosynthesis, dissolving, extraction, feeding, sedimentation, decomposition, fossilisation
2
New cards
Sink
Store of carbon
3
New cards
Flux
Movement of carbon between sinks and the atmosphere(e.g. respiration, photosynthesis, combustion), measured in gigatonnes(GT)
4
New cards
Spheres
Atmosphere(air), lithosphere(earth), hydrosphere(water), biosphere(living things)
5
New cards
Methanogenic Archaea
extremophiles, live in the guts of ruminants + waterlogged areas + deep ocean sediment, convert acetic acid into methane
6
New cards
Peat
Organic matter is not fully decomposed in waterlogged soils, carbon-rich molecules remain in the soil and form peat
7
New cards
Combustion
A chemical process in which a hydrocarbon-rich substance exothermically reacts with oxygen to produce water and carbon dioxide
8
New cards
CaCO3
CO2 dissolves in water to form carbonic acid(H2CO3), which dissociates to form bicarbonate ions and hydrogen, carbonate ions in the ocean are used to build shells and skeletons for organisms, excess hydrogen ions react with carbonate ions and remove them from the environment
9
New cards
Warming Impact
* How much long-wave radiation it absorbs compared to CO2 as 1(methane 21, NOx 310)
* The greater the concentration of a gas, the greater its warming impact will be within the atmosphere
* The concentration of a gas will be determined by both its rate of release and persistence within the atmosphere
* Atmospheric lifetime(water vapour 1-5 days, methane 12 year, NOx 120 years)
* The greater the concentration of a gas, the greater its warming impact will be within the atmosphere
* The concentration of a gas will be determined by both its rate of release and persistence within the atmosphere
* Atmospheric lifetime(water vapour 1-5 days, methane 12 year, NOx 120 years)
10
New cards
Wavelength
Earth absorbs short-wave energy from the sun and re-emits longer wavelengths
11
New cards
Pre-Industrial CO2 Levels
280ppm