APUSH Period 2 1607-1754
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Spanish Goals
Mainly Religious & Economic Motives
Tight control, sought wealth for gold & silver, later sugar & tobacco
Conversions to Christianity
Dutch and French Goals
Economic/Trading Motives
Fewer settlers, trade alliances, intermarried even for fur trades
Few converts
Religious Freedom (Puritans & Seperatists)
British Goals
Did NOT want anything to do with natives
Settled for Social Mobility
Heavy reliance on agriculture for cash crops, hostile relationships with natives
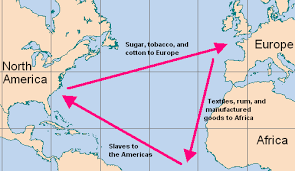
Atlantic Trade
Cause by a lack of indentured servants
Demand for goods
Desire for more lands
Passive forms of resistance (breaking tools)
New England
Puritans, longer life expectancy, mixed economy (agriculture & trade)
Plymouth Colony (Mayflower Compact), New Hampshire (Political independence from Masachusetts)
Massachusetts Bay Colony ( Family based), Rhode Island (Religious Dissenters)
Middle Colonies
Diverse, Mix of agriculture & trade, Religious Tolerance
Sea Ports & Fertile soil
Pennsylvania- (William Penn) Refuge for Quakers / Religious dissenters, diverse population
New York ( Duke of York granted land), New Jersey (Split from NY, Freedom of religion)
Delaware - Part of Pennsylvania, became seperate by 1704
Chesapeake & Northern Carolina Colonies
Relied on indentured servants, later slavery, diseases raptured the colonies
Goal for money
Growing sugar & rice with heavy use of slavery
Jamestown 1607
Maryland - early religious toleration (only for Christians)
Cecil Calvert & Second Lord Baltimore
Virginia - Jamestown 1607, grew from the growth of tobacco
1619 - Slaves & House of Burgesses
Southern & BWI Colonies
Highest Concentration of Enslaved Labor (Black to white 4:1), Social Hierarchy, dependence on cash crops like tobacco, indigo and rice
S. Carolina (Split in 1712) - Mirrored BWI
British West Indies - Barbados Slave Code (Formalized chattel slavery)
Pueblo Revolt (1680)
Spanish sought to suppress Native practices to convert to Christianity
Advocated for religious assimilation of NativesNative American warfare became more destructive
Advocated for religious assimilation of Natives
Native American warfare became more destructive
Metacom’s War / King Philip’s War 1675
Massasoit maintained peace with New Englanders, his son became chief in 1662 and is called King Philip by colonists
Detrimental effects on Natives, they were sold into slavery and forced to become servants.
Continued colonial expansion
Salutary Nelect
British’ loose supervision of laws on colonies, self governance flourished within the colonies
Navigations Acts (1651)
Everything has to go through England, travel on English vessels, when seized, 1/3 goes to the governor of the land, 1/3 goes to authorities, and 1/3 goes to the crown
Mercantilism
Exports > Imports
Colonies exist to benefit mother country
Bacon’s Rebellion (1676)
Led by Nathaniel Bacon, rebellion by lower classes
Led to racial divide to prevent future uprisings and stricter laws on enslaved people
Leisler’s Rebellion 1689-1691
New York - Rebellion held by Jacob Leisler after the Glorious Revolution where King James II was overthrown
Rebelled to make a representative government
Enlightenment (1685)
A period where reason, science, and individual rights were promoted over tradition.
(Natural rights, freedom of speech/religion, separation of powers, social contract)
1st Great Awakening (1730s-1740s)
A period where religion was “revived”, it was a very emotionally charged event that spread throughout the colonies & Europe
(George Whitefield, Jonathon Edwards)
Old light & New light views
John Winthrop
Puritan, “City on the hill” guy
George Whitefield
Main preacher in Great Awakening
Toured colonies, was a minister, founders of methodism & evangelical movement
Jonathon Edwards
“Sinners in the Hand of an Angry God” Sermon
Played a big role in religious revival
Roger Williams & Anne Hutchinson
Founder of Rhode Island, Exiled from MA ;
earliest feminist, challenged Puritan leaders in MA, also exiled from MA
William Penn
English Quaker Leader, Founded Pennsylvania to make it a safe haven for those of different race/religion
Glorious Revolution (1688-1689)
Deposition of Catholic King James II, He gets replaced by Protestant daughter
Outcome: Parliament gains more power, similar to a democracy
Puritans
Wanted to “purify” the Church of England
Separatists
Wanted to break off from the Church of England