BC.09 Weak bonds and Van der Waals forces
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
1
New cards
Describe at which geometry is a hydrogen bond at its strongest.
When the participating three nuclei (hydrogen-acceptor, hydrogen and hydrogen-donor) of a hydrogen bond lie in a straight line.
2
New cards
What is the other (weak) rule that determines the stability and strength of a hydrogen bond?
Dipoles of the hydrogen bond align which provides mor stability.
3
New cards
What type of dipoles do Van der Waals interactions involve?
Transient (induced) dipoles
4
New cards
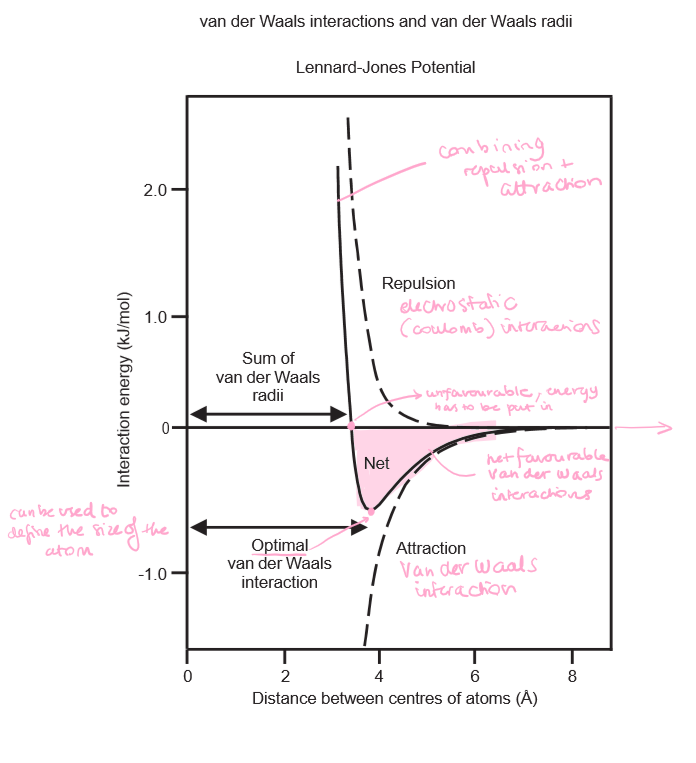
Explain the Lennard-Jones potential graph.
* As you bring two atoms closer together, they begin to induce dipoles in each other resulting in attraction (Van der Waals interactions)
* However, the nuclei and electron clouds are also being brought closer, resulting in repulsion (electrostatic Coulomb repulsion)
* Initially, the interaction gets better, but then quickly becomes unfavourable
* However, the nuclei and electron clouds are also being brought closer, resulting in repulsion (electrostatic Coulomb repulsion)
* Initially, the interaction gets better, but then quickly becomes unfavourable
5
New cards
Draw a Lennard-Jones potential graph and note the **net favourable Van der Waals interactions**, the **optimal Van der Waals interactions** and the **sum of the Van der Waals radii.**
6
New cards
Precisely, when does steric clash occur?
When atoms are brought closer than the sum of Van der Waals radii.
7
New cards
Water forms a clathrate around hydrophobic substances, why is this unfavourable?
Disorganised water molecules are more favourable than organised water molecules due to entropy.
8
New cards
Compare the energies (KJ/mole) of covalent and hydrogen bonds, Van der Waals interactions and rotational conformations.
Covalent bonds = 350
Hydrogen bonds = 5-20
Van der Waals = 0.2-2
Rotational conformations = 10
Hydrogen bonds = 5-20
Van der Waals = 0.2-2
Rotational conformations = 10