AP Euro Topic 3.4 Economic Development and Mercantilism Terms/Names (Amsco Bolded)
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower. (cotton, sugar, tobacco, for example).
West Indies
Caribbean Islands
Spice Islands
Europeans' name for the Moluccas, islands rich in cloves and nutmeg-- modern day Indonesia south of Asia.
Demographics
the characteristics of a population with respect to age, race, and gender.
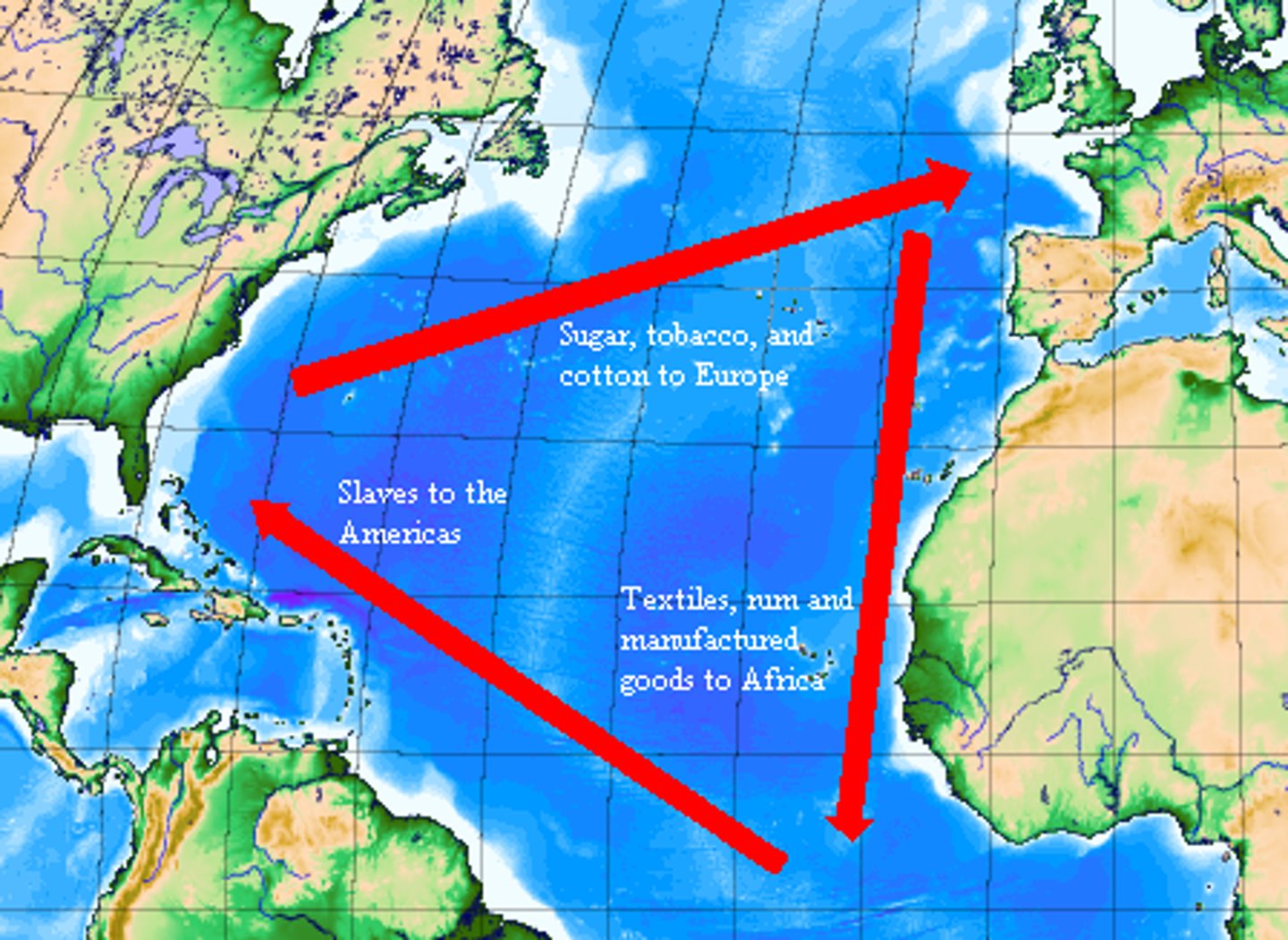
Triangle Trade
the extensive exchange of slaves, sugar, cotton, and furs between Europe, Africa, and the Americas that transformed economic, political, and social life on both sides of the Atlantic
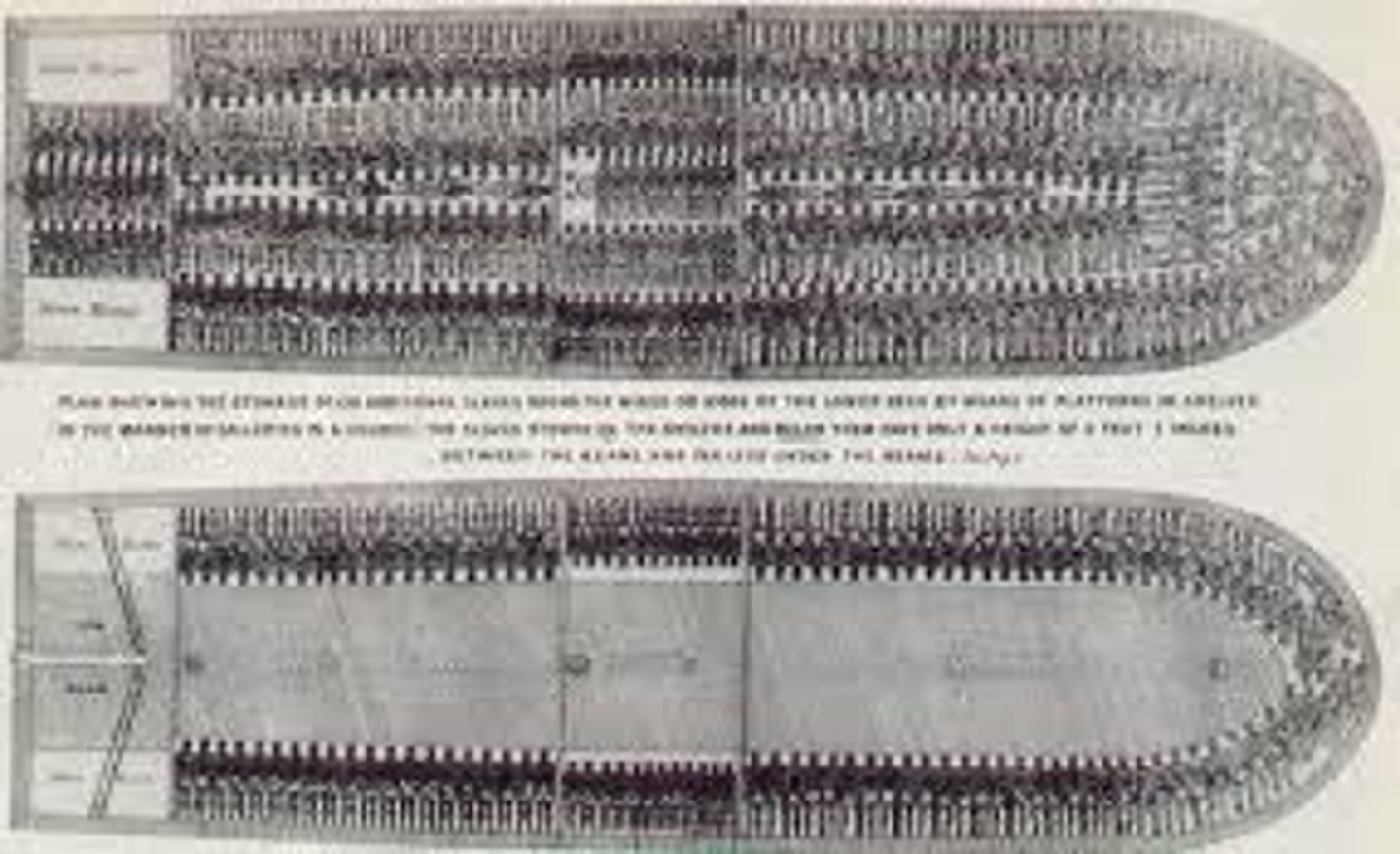
Middle Passage
the horrific sea journey undertaken by slave ships from West Africa to the West Indies.
Forced Migration
Human migration flows in which the people moving are not doing so because of their own choice (such as the slave trade).
Chattel Slavery
A system of bondage in which a slave has the legal status of property and so can be bought and sold like property.
Commercial Revolution
A dramatic change in the economy of Europe at the end of the Middle Ages. It is characterized by an increase in towns and trade, the use of banks and credit, and the establishment of guilds to regulate quality and price.
Mercantilism
An economic policy under which nations sought to increase their wealth and power by obtaining large amounts of gold and silver and by selling more goods than they bought
colonization
The expansion of countries into other countries where they establish settlements and control the people
Plantation
A large farm in tropical and subtropical climates that specializes in the production of one or two crops for sale, usually to a more developed country.
Navigation Acts
Laws that governed trade between England and its colonies. Colonists were required to ship certain products exclusively to England.
Joseph Marie Jacquard
French inventor of a loom that could automatically weave complicated patterns (1752-1834)
John Rolfe
Jamestown colony leader who showed that tobacco could be grown successfully in Virginia