Section 2: Digital Transformation in Non-IT industries; Managing IT Crisis
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What is supply chain management (SCM)?
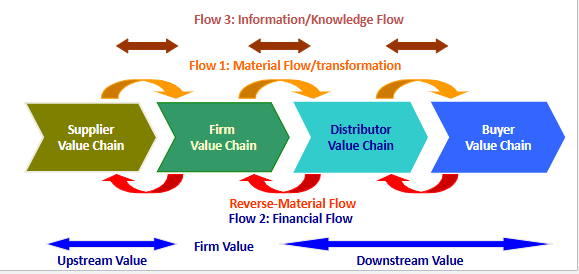
Coordination and integration of all activities and flows (material, information, and financial) in the value system that includes suppliers and customers to maximize the firm's benefits
Material: movement of raw materials and goods
From Suppliers → to the Firm (manufacturer) → to the Distributor → to the Buyer (customer).
Information: orders, inventory levels, customer preferences
Customer preferences go upstream (from Buyer → Firm), while delivery updates go downstream (Firm → Buyer).
Financial: payments, credit, invoices (backwards)
The Buyer pays the Distributor, who pays the Firm, who then pays the Supplier
Upstream value - value gained from the suppliers and what the firm receives
Value of car company comes from steel manufacturers
Downstream value - value delivered to customers through distribution and final sales
What you create for your final customer
What are the key challenges of SCM?
Uncertainty
Demand (customer preferences, obsolescence, technology shifts)
Supply (quality and performance of suppliers)
Process (breakdowns, catastrophic events)
Coordination
Complexity (multiple agents)
Inappropriate business processes and metrics
Lack of standards
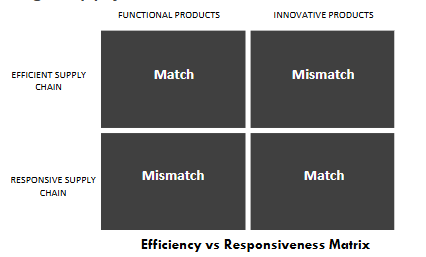
What is an efficient supply chain?
Predict demand and supply efficiently at the lowest cost
Maximize capacity utilization
Suppliers selected based on cost and quality
Minimize costs for predictable and stable demand.
What is a responsive supply chain?
Respond quickly to demand changes
Minimize lead time aggressively
Selected based on speed, flexibility, and quality
Built for flexibility and speed when demand is volatile.
When given certain features of a product or an industry, be able to match it with the right supply chain strategy.
Functional (predictable demand, low customization, and low margins) → Efficient SC (e.g., groceries) (less variable demand)
Innovative (unpredictable demand, high margins, and high customization) → Responsive SC (e.g., fashion, tech) (more variable demand)
What is the conventional supply chain structure in the fashion industry? What are the major benefits and drawbacks for such a supply chain structure?
Most outsource to contract manufacturers (cheap labor, long lead times, low flexibility)
Benefits: cost efficiency, specialization, scalability
Drawbacks: 6 months to design a new collection and 3 months to manufacture, unable to customize and respond, less control over the products, disruptions
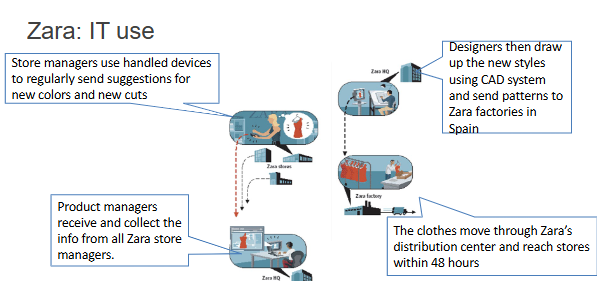
What is the difference between Zara’s supply chain and the conventional supply chain in the fashion industry?
Produce the fabrics and merch in-house
More quality control over the distributors and retailers
Vertical integration (design, production, distribution)
Shorter lead times + more responsive
15 days from idea to appearance
Tech-enabled manufacturing with robots (fabric is cut and dyed + half is undyed for fashion shifts)
Factory → global distribution center → flagship stores
Why is Zara able to offer fast fashion?
Zara is responsive to the changes in customer demand
Dyed thing is huge (keep half undyed to respond to changes)
Data driven-analysis - how many of which items in which sizes should be delivered to which stores?
Small batch production too + rapid designing and prototyping
2x weekly shipment to the stores
Uses IT and direct feedback from the store to make changes to the designs
What is omnichannel?
Seamless and effortless, high-quality customer experiences that occur within and between contact channels. (in store, mobile, website, and social media)
Integrated distribution center - heart of omnichannel that handles: i) shipping to online orders ii) shipping to stores
Flagship stores - stock room, stock floor, online order prep, collection area for these online orders
Orders can be shipped from these integrated distribution centers or even flagship stores
Better customer experience
Higher conversion rates
Real-time inventory management
How does Zara’s online store change its supply chain structure?
The distribution centers and stores work together
Integrated inventory across all channels
Lot’s of data and customer feedback
Fulfillment of orders in store and then also online
Shorter lead times overall (tight control over production)
Why does Zara want to build an integrated offline and online store model?
Seamless customer experience (shop in one channel and finish in the other)
Aggregates demand to manage uncertainty on demand
allocation
Enables inventory pooling and reduces inventory costs (product doing bad in store can be sold online)
Creates flexibility (fulfill from store or DC)
Reduces logistics and reverse logistics costs (click and collect —> pick up in store) (in-store returns of online orders)
Data explosion, experiments (lots of customer data!)
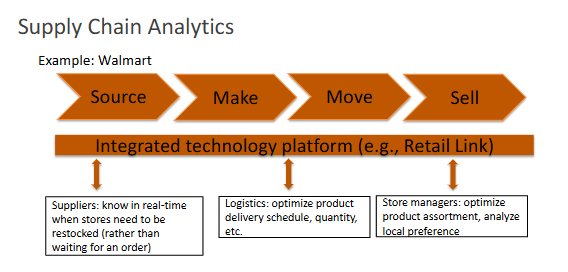
What are the potential data sources for supply chain analytics?
Used for prediction, optimization, and simulation.
POS devices
Social media feeds
ERP and other enterprise software systems
Mobile devices or GPS
RFID chips - tracks inventory without scanning
Automatic and no manual labor needed
Doesn’t need to be visible on the outside
Less affected by dirt
Store more data
Be able to identify applications of analytics in supply chains
Source:
supplier risk, product type, sourcing options, supplier deals
Make:
inventory levels, capacity limits, factory location, workforce planning
Move:
distribution, transport methods, delivery routes, scheduling, maintenance
Sell:
location-based ads, in-store behavior, customer segments
Used to optimize sourcing, production, logistics, and sales.
What is blockchain and what are its key characteristics?
New platform technology to verify and record transactions among an interconnected set of users.
Transaction = block
Cumulative transactions = chain
Data is not changeable (transparent and traceable)
No central coordinating entity
Broadcasted across network to be verified and validated (decentralized trust)
What are the key differences between permissioned and permissionless blockchain?
Permissioned blockchain (private blockchain): Only a restricted set of users have the rights to validate transactions and create smart contracts
Permissionless blockchain (public blockchain): Anyone can join the network, trade assets, validate transactions, and/or create smart contracts.
What is bitcoin? What factors contribute to the volatility of bitcoin?
Digital currency that relies on encryption techniques to regulate the number of digital coins generated and to verify the fund transfers.
Volatile due to speculation, low liquidity (limited supply), lack of intrinsic value, media influence
What are smart contracts? Understand how smart contracts can be used in logistics and supply chain areas.
Event triggered automated pieces of computer code intended to facilitate, verify, and enforce the negotiation or performance of a contract.
“Ship product when we get paid”
Payment triggers upon the delivery of a product with no disputes
What is the major problem faced by the container shipping industry? How can blockchain be used to address this problem?
Lacks efficient collateral for booking deposit, caused long-lasting shipper no-show and cargo roll-over problems (cargo gets left behind)
Shippers reserve space but don’t show up because there is no penalty or deposit.
Both have a tokenized deposit (shipper and carrier) —> if the smart contract this broken then the other party gets the tokens is
300cubits used blockchain and smart contracts to “lock in” shipping agreements with digital deposits (TEU tokens), solving the trust problem behind cargo no-shows and rollovers.
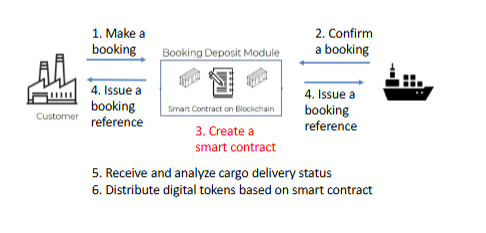
What are the main challenges faced by 300cubits for its blockchain applications?
New system requires coordination of different stakeholders + changes in existing systems
Two-sided platform that is subject to network effects
No laws regulate the implementation of smart contracts
Poor ICO performance
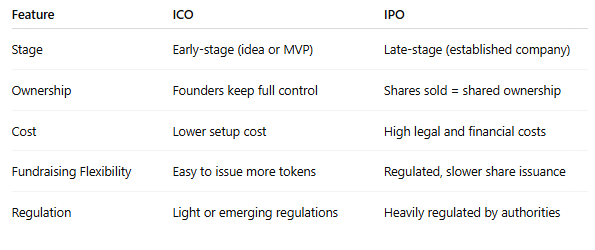
What is Initial Coin Offering (ICO)? How does it differ from Initial Public Offering (IPO)?
A mechanism for new projects to raise funds by selling their underlying crypto tokens in exchange for fiat currencies, Bitcoin and/or Ether (selling tokens in exchange for crypto); not regulated!
IPO - this is moreso selling shares of a company to raise money; regulated
What are the advantages provided by ICO to raise funds?
Funds can be raised at the early stage of projects
Entrepreneurs still have full ownership and control over the company
More cost effective than an IPO
More flexibility by issuing more tokens
What are the potential participants on 300cubits blockchain platform? How would you help 300cubits to attract more participants to the platform?
Users: shippers (use the tokens), carriers (use the tokens), investors (equity and crypto investors who use the tokens as an investment)
Attend industry events to promote the TEU tokens (gain access to key players)
Educate shippers and shipping companies on the system and how it can solve their problems
Crypto up (focus on selling to the crypto investors) // crypto down (focus on selling to the users - the shippers and carriers)
Why did Walmart want to adopt blockchain technology for its logistics?
Discrepancies in the invoice and payment processes (errors in the invoices)
There was a lack of integration and everything was messy
Blockchain: capture information at every step from the tender offer from the carrier to the proof of delivery and approval of the payment
<1% of the invoices being disrupted
When given an example of blockchain implementation, be able to analyze the challenges faced by the focal company.
see image
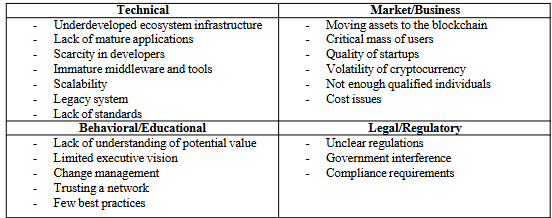
When given an example of blockchain implementation, be able to provide recommendations for the focal company
Education for the users who are going to be using these tokens
Focus on the crypto market trends to attract investors
Regulatory compliance and attract mass users!
What is industry 4.0? What are the digital technologies that could be included in Industry 4.0?
Convergence and application of various digital technologies.
IoT, AI, digital twins, AR/VR, robotics, and analytics
What is the Internet of Things?
Connects smart devices to gather and act on real-time data.
Allows for digital transformation of previously analog machine and service operations
What are smart, connected products? What benefits can smart and connected products bring to a focal company and its customers
IoT refers to smart, connected, products. They typically have smart components (software, sensors) and connectivity components (enable wireless connections). Allows for autonomous product operation.
Company: efficiencies (real-time data), cost reduction, product innovation, scalability
Customers: control/customization, reliability (products can fix issues before failure), convenience (less manual operation), lower maintenance, integrated products
What are digital twins? How are digital twins related to but different from simulations?
True-to-reality virtual representation of a real world physical asset or system which is continuously updated. Used for monitoring, diagnostics, and predictions.
Send data from the real-world product to the digital model with continuous updates.
Contains: 1) physical products in real space 2) virtual products in virtual space 3) connections of data and information that ties the virtual and real products
Simulations are more static, whereas digital twins are continuously updated.
Be able to list example applications of digital twins in certain industries or scenarios.
Manufacturing - monitoring, simulating, and optimizing production lines and factory equipment
Mirror machines or entire factories
Autonomous Vehicles - simulate road conditions and vehicle behavior to improve the autonomy
Healthcare - diagnosing and treating heart disease; replicas of organs, patients, or hospital systems
Supply chain and logistics - end-t-end of goods, assets, or logistics (Ashok Leyland uptime + maintenance tracking)
What is Metaverse? How are digital twins related to but different from Metaverse?
Collection of virtual shared space connected to many aspects of the physical world, including people, places, things, enabling shared experiences.
Both digital twins and Metaverse use Cloud, IoT, VR/AR, AI/ML.
Digital twins - focused on industrial and business applications, used for engineering and process optimization
Metaverse - moreso focused on human entertainment and the experience (gaming, social, and virtual events)
What motivated Ashok Leyland to leverage digital twins for business model innovation?
Realized that vehicle sales only captured 7-8% of the total cost of ownership. Most of the expenditures for these purchasers came form things like paying for operations/maintenance. Weren’t earning more as the time went on.
Increased the share of wallet - enabling value-added services + revenue.
What are the possible ways for Ashok Leyland to monetize digital twins?
Subscription basis
Additional solutions - pay more for
Data as a service - Remotely track/manage a vehicle, report a stolen vehicle, or
bring a moving vehicle to an immediate halt from the control
center
Give predictive maintenance plans - driver informed about the defects in real time
Recommendation systems for sales
Remote fleet control services
Should we always add as many sensors to a product as possible? Explain your answer
Not necessarily - it can be very costly; instead use things that add value.
When given a traditional industry, be able to discuss how to make digital transformation for companies in the industry, as well as the potential challenges associated with such digital transformation
Adoption of IoT, cloud computing, data analytics
Used to reduce downtime and optimize productions
Cost is very high, skills gaps, system integration, and cybersecurity risks
When given a specific scenario, be able to discuss key challenges of implementing Industry 4.0 in such a scenario?
Outdated infrastructure
Lack of skilled workers
Data integration issues
Cybersecurity risks
What is a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack? Why is it not an intrusion?
Cyber attack in which the hacker seeks to disrupt a machine or network resource to make it unavailable to its intended users. (lock-out)
Done by sending requests to overload the systems and prevent legitimate requests from being fulfilled.
Does not break into the systems or access data - intrusion = breach.
Reflecting on your IT management simulation, how should you respond to an IT crisis like the one experienced by OnlineRetailCo (ORC)
Diagnose first (don’t assume hackers)
Prioritize: Protect data, restore ops
Call key roles in order: CEO → Security → Legal → Fulfillment → Tech
Stay calm, flexible in explanation
How should you manage external communication during an IT crisis similar to the one faced by ORC in the simulation?
Keep statements truthful and avoid saying more than you can be sure of
Avoid making statements that invite follow-up or hard to answer questions
Avoid statements that hackers might consider to be a challenge and come back to you
Keep it rational and avoid panic or fear