Chemistry
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:47 AM on 2/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
1
New cards
Open System
Allows energy and matter to cross the systems boundary (tree)
2
New cards
Closed System
Allows only energy but no matter to cross the boundary (earth)
3
New cards
Isolated Systems
Allows neither energy nor matter to flow across the boundary
4
New cards
Atmosphere's layers
troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere, thermosphere
5
New cards
Troposphere
Lowest layer of the atmosphere where we find weather
6
New cards
Stratosphere
10-50 km above sea level, has the Ozon layer (protects organisms)
7
New cards
Mesosphere
50-80km
8
New cards
Thermosphere
80+km
9
New cards
Lithosphere
Is the solid portions of earth (above semi fluid upper mantle)
10
New cards
Hydrosphere
All water of earth (on the surface area and underground)
11
New cards
Biosphere
Absorbs energy
12
New cards
Reflection
Change the sun ray's direction
13
New cards
Absorption
Energy is converted into another form of energy
14
New cards
Albedo
Ability of a surface to reflect light (higher the Albedo the more it reflects)
15
New cards
Net radiation budget
Difference between the amount of incoming and outgoing radiation (net budget \= incoming - outgoing)
16
New cards
How much solar energy is absorbed by land and ocean
49%
17
New cards
How much solar is absorbed reflected and scattered
42%
18
New cards
reflected by earths surface
9%
19
New cards
gases that absorb infrared radiation
water, co2, ch4 (methane), n20 (nitrous oxide), ozon, halocarbon
20
New cards
Photosynthesis
carbon is absorbed through plants
21
New cards
cellular respiration
carbon released into the atmosphere by terrestrial and aquatic living
22
New cards
Photosynthesis (compound)
carbon dioxide + water = glucose + oxygen
CO2 + H2O = C6H12O6 + O2
CO2 + H2O = C6H12O6 + O2
23
New cards
Cellular respiration (compound)
Glucose + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
C6H12O6 + O2 = CO2 + H2O
C6H12O6 + O2 = CO2 + H2O
24
New cards
combustion (compound)
Methane + oxygen = carbon dioxide + water
CH4 + O2 = CO2 + H2O
CH4 + O2 = CO2 + H2O
25
New cards
Dalton
Believed all atoms are smart particles of matter. Billiard ball model
26
New cards
Bohr
electrons surrounded the nucleus in specific (quantized) energy levels
27
New cards
JJ Thomson
Atoms are positive spheres embedded with negative charged atoms (plum pudding model)
28
New cards
Ruther Ford
Gold foil experiment. Believed most atoms are empty space with tiny positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons orbit the positively charged nucleus (planetary model)
29
New cards
Democritus
Proposed the idea that matter was made up of tiny particles that could not be further subdivided
30
New cards
Aristotle
Proposed (all matter) was made up of four elements. He also proposed matter was infinitely divisible
31
New cards
Mixture
Matter that can be separated by physical means, does not have a definite composition
32
New cards
Heterogeneous
(Mechanical mixtures) Different components of mixtures are visible. Component is variable (salad dressing)
33
New cards
Homogeneous
(solution) -different components are not visible (ice tea)
34
New cards
pure mixture
matter that has a definite composition (chem formula)
35
New cards
Element
Cannot chemically be broken down (is on period table) nor further broken down
36
New cards
Compound
Two or more elements that are chemically combined (can be
separated into simpler substances)
separated into simpler substances)
37
New cards
Monatomic
Element type: Single atoms (Li, Na, Mg)
38
New cards
Molecular
Combination of two or more atoms (P4, S8, I2, Br2)
39
New cards
Compound
Two or more elements chemically combined. Different properties than elements
40
New cards
Law of definite proportions
Always has same ratios of atoms (water is always H2O and never anything else)
41
New cards
Parts of Atom
Proton, Neutron, Electron
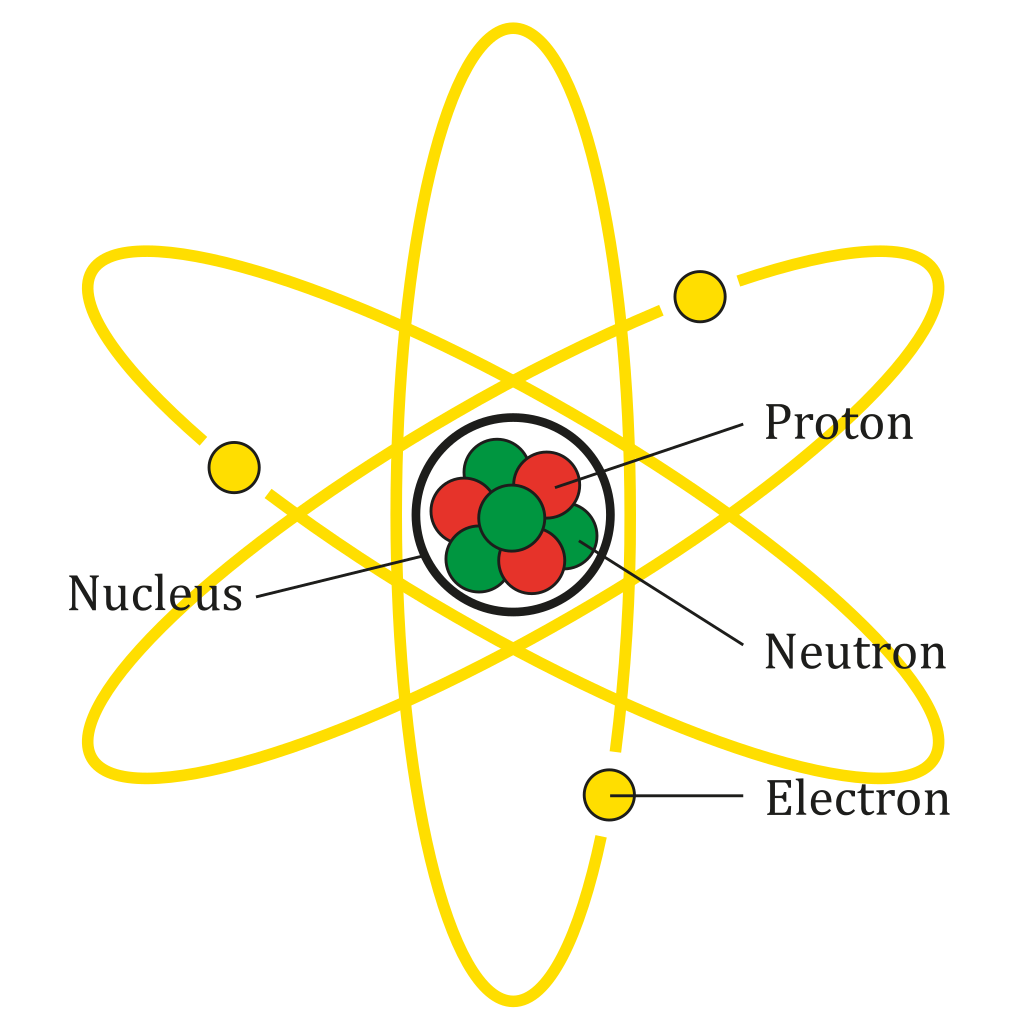
42
New cards
Metalloids
Have properties between metal and non metals
43
New cards
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different number of neutrons ( C-12, C-13, C-14)
44
New cards
Ions
stable, unequal # of P+ and E- there are
two types Cation and anions
two types Cation and anions
45
New cards
Atoms
Unstable (want to be stable),
equal #p+ and e-
form ion naturally by losing or gaining e-
equal #p+ and e-
form ion naturally by losing or gaining e-
46
New cards
outlet rule
They form ions in order to have a stable outtering
47
New cards
Ionic
Complete transfer of 1 or more electron from one atom to another
48
New cards
Covalent
some valence electrons are shared between atoms
49
New cards
Metallic
Holds atoms of metal together
50
New cards
ionic bonds
usually solid at room temp
formed by a transfer of e- from one atom to another
between metals and none metals
formed by a transfer of e- from one atom to another
between metals and none metals
51
New cards
Charged atom
when a atom gains or loses a e- they become charged
52
New cards
metal atoms/ions
loses e- and become positively charged
53
New cards
non metal atoms/ions
gain e- and become neg charged called ANION