Skills Exam 2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
89 Terms
1
New cards
Phlebitis:
- inflammation of a vein
2
New cards
- Inspect for localized redness, tenderness, and swelling over vein sites.
How to assess for phlebitis:
3
New cards
- Stop infusion and discontinue intravenous therapy; Restart new intravenous line if continued therapy is necessary
- Place moist, warm compress over area
- Place moist, warm compress over area
How to treat phlebitis:
4
New cards
- blood clots/emboli (thrombophlebitis)
What can phlebitis cause?
5
New cards
Infiltration:
- occurs when IV catheter becomes dislodged and vein ruptures so IV fluids inadvertently enter subcutaneous tissue around the IV site
- potentially dangerous
- potentially dangerous
6
New cards
Fluid overload:
- hypervolemia
- too rapid administration
- excessive amount of fluids (edema)
- can lead to vascular congestion impairing body’s ability to deliver oxygen to tissues
- swelling, bloating, headache
- treat with diuretic
- too rapid administration
- excessive amount of fluids (edema)
- can lead to vascular congestion impairing body’s ability to deliver oxygen to tissues
- swelling, bloating, headache
- treat with diuretic
7
New cards
Diuretics:
- given PO, IV, IM
- decreases BP, Na, Cl, K, weight, I&O, dehydration, hyperglycemia
- furosemide, aldactone, kayexalate
- decreases BP, Na, Cl, K, weight, I&O, dehydration, hyperglycemia
- furosemide, aldactone, kayexalate
8
New cards
Aldactone:
- saves the potassium
- gets rid of water and sodium
- blocks aldosterone in kidneys
- watch for headache, diarrhea, hyperkalemia, electrolyte imbalance, fatigue, and GI disturbance
- can cause weakness in heart muscles
- gets rid of water and sodium
- blocks aldosterone in kidneys
- watch for headache, diarrhea, hyperkalemia, electrolyte imbalance, fatigue, and GI disturbance
- can cause weakness in heart muscles
9
New cards
kayexalate:
- PO or enema
- need to get rid of potassium or it can kill you
- watch for constipation, gastric irritation, diarrhea, sodium retention, and hypokalemia
- watch heart rate and sodium levels
- need to get rid of potassium or it can kill you
- watch for constipation, gastric irritation, diarrhea, sodium retention, and hypokalemia
- watch heart rate and sodium levels

10
New cards
furosemide:
- PO or IV
- potassium wasting
- loop diuretic
- used for edema, hypertension, and ascites
- side effects: decreased BP, photosensitivity, hyperglycemia, decreased potassium
- potassium wasting
- loop diuretic
- used for edema, hypertension, and ascites
- side effects: decreased BP, photosensitivity, hyperglycemia, decreased potassium
11
New cards
- through lab work
Best way to assess fluid and electrolyte imbalances:
12
New cards
hyperkalemia:
- potassium level 5.1 or higher
- need kayexalate
- look for peaked T waves and dysrhythmias
- abdominal dissension
- muscle weakness, cramps, irritability anxiety, low BP, pins and needles sensation
- need kayexalate
- look for peaked T waves and dysrhythmias
- abdominal dissension
- muscle weakness, cramps, irritability anxiety, low BP, pins and needles sensation
13
New cards
hypokalemia:
- potassium level 3.5 or below
- administer potassium rich diet
- arrhythmia (thready pulse), tachycardia
- weakness, fatigue, intestinal mobility decreases, drowsiness
- metabolic alkalosis
- administer potassium rich diet
- arrhythmia (thready pulse), tachycardia
- weakness, fatigue, intestinal mobility decreases, drowsiness
- metabolic alkalosis
14
New cards
potassium deficiency symptoms:
- alkalosis
- shallow respirations
- irritability
- confusion
- weakness
- arrhythmias
- lethargy
- thready pulse
- shallow respirations
- irritability
- confusion
- weakness
- arrhythmias
- lethargy
- thready pulse
15
New cards
hypernatremia:
- sodium level above 145 in blood
- rehydrate
- rehydrate
16
New cards
hyponatremia:
- sodium level below 135 in blood
- fluid restriction
- water intoxication
- fluid restriction
- water intoxication
17
New cards
hypercalcemia:
- loop diuretics
- increase hydration
- synthetic calcitonin
- monitor I&O, vitals, and HR
- administer diuretics (kayexalate)
- constipation
- increase hydration
- synthetic calcitonin
- monitor I&O, vitals, and HR
- administer diuretics (kayexalate)
- constipation
18
New cards
hypocalcemia:
- give foods high in calcium with vitamin D supplements
- watch for bleeding gums and mucus membranes
- chvostek's sign
- trousseau's sign
- watch for bleeding gums and mucus membranes
- chvostek's sign
- trousseau's sign
19
New cards
factors contributing to fluid loss:
- vomiting
- diarrhea
- bleeding
- sweating
- diarrhea
- bleeding
- sweating
20
New cards
alkalosis:
- pH above 7.45
- kicking up the pH
- kicking up the pH
21
New cards
acidosis:
- pH below 7.35
- sliding the pH down
- sliding the pH down
22
New cards
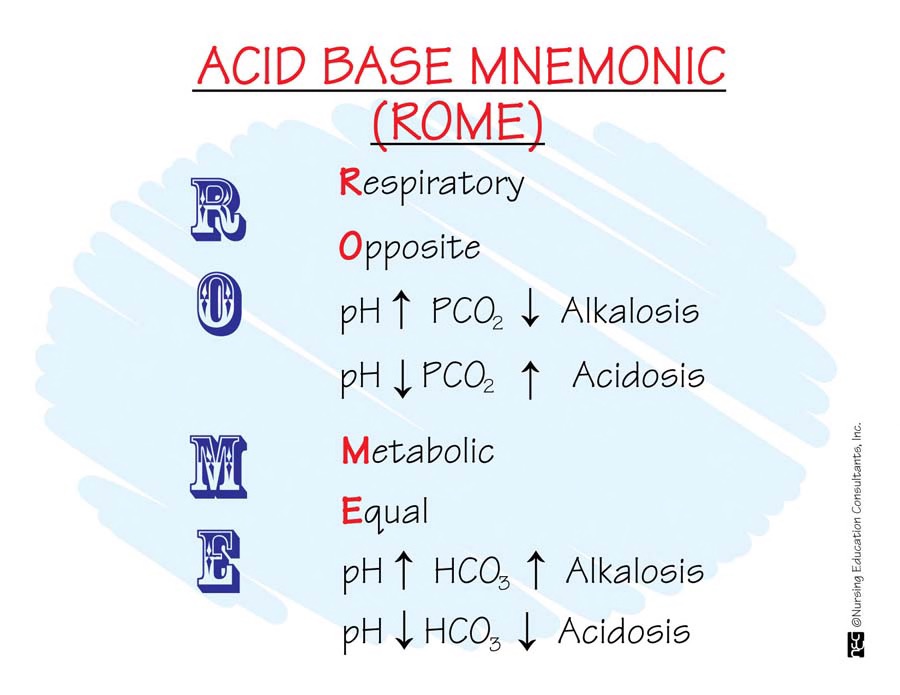
R.O.M.E. acronym
- Respiratory Opposite:
---------high pH=low CO2, low pH=high CO2
- Metabolic Equal:
---------high pH=high HCO3, low pH=low HCO3
---------high pH=low CO2, low pH=high CO2
- Metabolic Equal:
---------high pH=high HCO3, low pH=low HCO3
23
New cards
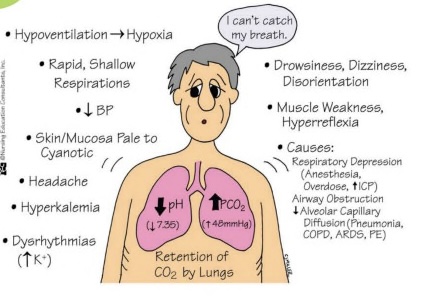
respiratory acidosis:
- low pH, high CO2
- hypoventilation, hyperkalemia, shallow respirations, nausea and vomiting, numbness and tingling
- use ventilator
- causes: COPD, pneumonia, atelectasis
- hypoventilation, hyperkalemia, shallow respirations, nausea and vomiting, numbness and tingling
- use ventilator
- causes: COPD, pneumonia, atelectasis
24
New cards
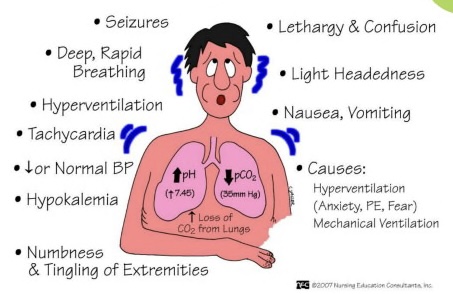
respiratory alkalosis:
- high pH, low CO2
- hyperventilation, hypokalemia, deep respirations, muscle weakness, cyanotic pale skin
- causes: hyperventilation (stress), mechanical ventilation
- hyperventilation, hypokalemia, deep respirations, muscle weakness, cyanotic pale skin
- causes: hyperventilation (stress), mechanical ventilation
25
New cards
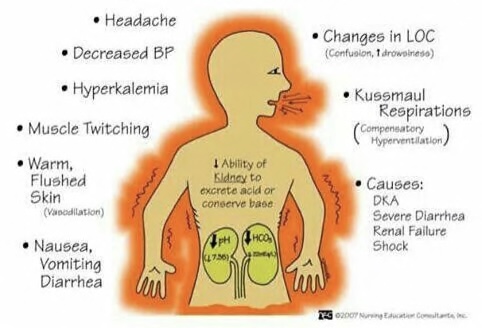
metabolic acidosis:
- low pH, low HCO3
- hyperventilation, hyperkalemia, muscle twitching, increased body temp.
- check renal labs
- causes: DKA, severe diarrhea, renal failure, shock
- hyperventilation, hyperkalemia, muscle twitching, increased body temp.
- check renal labs
- causes: DKA, severe diarrhea, renal failure, shock
26
New cards
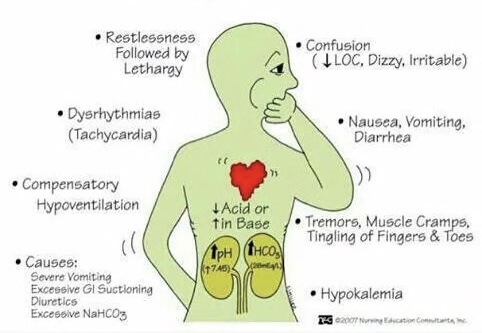
metabolic alkalosis:
- high pH, high HCO3
- hypoventilation, hypokalemia, tremors/cramps/tingling, nausea
- causes: severe vomiting, excessive GI suctioning, diuretics, excessive NaHCO3
- hypoventilation, hypokalemia, tremors/cramps/tingling, nausea
- causes: severe vomiting, excessive GI suctioning, diuretics, excessive NaHCO3
27
New cards
BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen)
- indicates renal function and hydration status
28
New cards
10-20 mg/dL
Normal range of BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen):
29
New cards
above 100
Critical range of BUN (Blood Urea Nitrogen):
30
New cards
symptoms of increased BUN:
- dehydration
- impaired renal function
- excessive protein intake
- impaired renal function
- excessive protein intake
31
New cards
symptoms of decreased BUN:
- malnutrition
- overhydration
- liver damage
- overhydration
- liver damage
32
New cards
when to take a patients weight:
- at the same time every day with the same circumstances
- indicates fluid status
- its a gold standard
- indicates fluid status
- its a gold standard
33
New cards
- Normal saline IV solution
What type of solution is hung with blood?
34
New cards
- 30 minutes from the blood bank
- 2-4hr infusion rate
- 2-4hr infusion rate
How long do you have to hang a bag of blood for a blood transfusion?
35
New cards
- "Y" tubing
- for the blood and saline
- change after 4 hours
- for the blood and saline
- change after 4 hours
What tubing is used for blood transfusions?
36
New cards
- based on hospital policy
- when any change occurs
- stay with patient for the first 15 minutes
- when any change occurs
- stay with patient for the first 15 minutes
when to take vitals during blood transfusions?
37
New cards
Febrile reaction to blood transfusion:
- chills, fever, headache, flushing, tachycardia, increased anxiety
38
New cards
allergic reaction to blood transfusion:
- mild: hives, pruritis, facial flushing
- severe: shortness of breath, bronchospasm, anxiety
- severe: shortness of breath, bronchospasm, anxiety
39
New cards
Hemolytic transfusion reaction:
- Low back pain, hypotension, tachycardia, fever and chills, chest pain, tachypnea, hemoglobinuria, may have immediate onset
40
New cards
- stop transfusion immediately and notify the prescriber
- change the IV tubing
- treat symptoms if present (O2, fluids, epi)
- change the IV tubing
- treat symptoms if present (O2, fluids, epi)
what to do when complications arise during a blood transfusion?
41
New cards
5 mL
1 tsp = ___ mL
42
New cards
ways to transfer a patient:
- gait belt
- pivot
- cane
- crutches
- if patient is obese, utilize equipment!!!
- pivot
- cane
- crutches
- if patient is obese, utilize equipment!!!
43
New cards
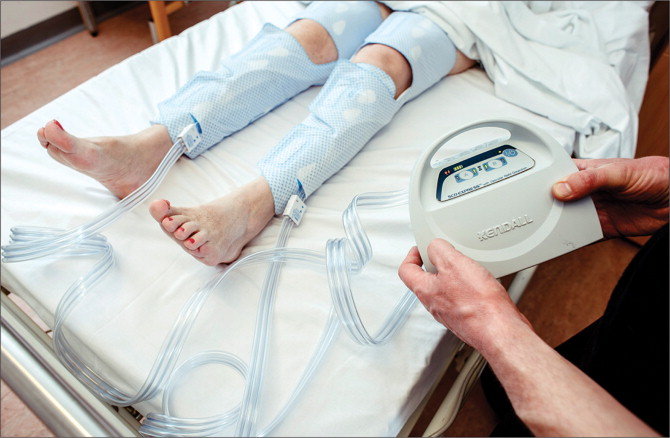
sequential compression devices
SCDs
44
New cards
- promote venous return as a prevention of DVT
What do SCDs do?
45
New cards
how to open an ampule:
- break away from body with gauze
- use filter needle to extract meds
- use filter needle to extract meds
46
New cards
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
- promotes retention of water by kidneys
- when we are low on volume
- released from pituitary gland
- helps control blood pressure
- KEEP 1
- when we are low on volume
- released from pituitary gland
- helps control blood pressure
- KEEP 1
47
New cards
renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS)
- a hormone cascade pathway that helps regulate blood pressure and blood volume
- watches fluid levels and helps protect volume through the kidneys
- sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion
- watches fluid levels and helps protect volume through the kidneys
- sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion
48
New cards
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)
- causes sodium loss and inhibits the thirst mechanism
- influences sodium and water release
- hormone secreted in response to atrial stretching and an increase in circulating blood volume
- RELEASE 2
- influences sodium and water release
- hormone secreted in response to atrial stretching and an increase in circulating blood volume
- RELEASE 2
49
New cards
what do you do if a patient is trying to get out of bed, but the doctor will not order restraints?
- try to distract with videos, puzzles, toys, etc.
- bed alarm
- move close to nursing station
- bed alarm
- move close to nursing station
50
New cards
how to start an IV:
- Inform client about procedure and indication
- Gather supplies
- Wash hands and Wear gloves
- Apply tourniquet
- Locate vein
- Clean area with alcohol
- Position and insert needle-looking for a flash of blood
- Advance catheter
- Release the tourniquet
- Remove the needle
- Secure the catheter and start IV fluid if ordered
- Document
- Gather supplies
- Wash hands and Wear gloves
- Apply tourniquet
- Locate vein
- Clean area with alcohol
- Position and insert needle-looking for a flash of blood
- Advance catheter
- Release the tourniquet
- Remove the needle
- Secure the catheter and start IV fluid if ordered
- Document
51
New cards
- only LICENSED personnel
- not us
- not us
who can start and IV?
52
New cards
hypertonic solutions:
- sodium and volume replacement
- used for hypernatremia (water insufficiency)
- go slow
- cells shrink
- used for hypernatremia (water insufficiency)
- go slow
- cells shrink
53
New cards
hypertonic IV solution examples:
- D5 ½ NS
- D5 NS
- D5 NS

54
New cards
hypotonic solutions:
- isotonic until INSIDE the body
- used for hyponatremia (water excess) and hypoglycemia
- don't give to infants or head injury patients (cerebral edema may occur)
- cells swell
- used for hyponatremia (water excess) and hypoglycemia
- don't give to infants or head injury patients (cerebral edema may occur)
- cells swell
55
New cards
hypotonic IV solution example:
- D5W

56
New cards
isotonic solutions:
- fluid resuscitation
- expands the volume, dilutes medications, and keeps veins open
- same osmolarity as body fluid
- expands the volume, dilutes medications, and keeps veins open
- same osmolarity as body fluid
57
New cards
isotonic IV solution examples:
- lactated ringers
- NS 0.9% NaCl
- NS 0.9% NaCl
58
New cards
Subcutaneous injection sites:
- upper arms, back, abdomen, top of legs.
- insulin and heparin
- 45 degree angle
- insulin and heparin
- 45 degree angle
59
New cards
Intramuscular injection sites:
- deltoid, ventrogluteal, vastus lateralis
- vaccines
- 90 degree angle
- aspirate except for deltoid
- vaccines
- 90 degree angle
- aspirate except for deltoid
60
New cards
Heparin needle size and length:
- 27G x 1/2"
- 1mL syringe
- 1mL syringe
61
New cards
Insulin needle size and length:
- 31G
- 1mL syringe
- 1mL syringe
62
New cards
IM needle size and length:
- 23G x 1"
- 3mL syringe
- 3mL syringe
63
New cards
anions:
- negatively charged ions
- bicarbonate and phosphate
- bicarbonate and phosphate
64
New cards
cations:
- positively charged ions
- magnesium, sodium, and potassium
- magnesium, sodium, and potassium
65
New cards
Nasogastric tube:
- tube inserted through the nose into the stomach
- short term use only
- short term use only
66
New cards
- to prevent gastric dilation, vomiting and paralytic ileus (intestinal muscle paralysis)
why is a NG tube inserted?
67
New cards
- drink water
What should you instruct a patient to do when inserting a NG tube?
68
New cards
urinary incontinence
- inability to control urination
- pregnancy and old age
- functional, overflow, reflex, stress, urge
- pregnancy and old age
- functional, overflow, reflex, stress, urge
69
New cards
colostomy:
- creation of an artificial opening into the colon
- opening is called a stoma which is at the end of the colon protruding through the skin
- ileocecal valve allows food to pass from small intestine to large
- opening is called a stoma which is at the end of the colon protruding through the skin
- ileocecal valve allows food to pass from small intestine to large
70
New cards
UTI:
- E. coli
- common in females due to shorter urethra
- common in females due to shorter urethra
71
New cards
micturition:
- urination
72
New cards
PACO2
- 35-45mmHg
- how well lungs excrete CO2
- how well lungs excrete CO2
73
New cards
HCO3
- 21-28meq/L
- how kidneys excrete metabolic acid
- increased means not enough metabolic acid
- how kidneys excrete metabolic acid
- increased means not enough metabolic acid
74
New cards
PAO2
- 80-100
- how well gas exchange occurs in alveoli
- how well gas exchange occurs in alveoli
75
New cards
ABG’s
- ph 7.35-7.45
- measures blood acidity
- PACO2, HCO3, PAO2
- measures blood acidity
- PACO2, HCO3, PAO2
76
New cards
Aldosterone
- keeps sodium, releases potassium
- KEEP 1 RELEASE 1
- KEEP 1 RELEASE 1
77
New cards
Fluid overload values:
- hemoglobin
- blood glucose
- hematocrit
- BUN
- blood glucose
- hematocrit
- BUN
78
New cards
Fluid overload
- give sodium
- give diuretic
- edema and crackles
- give diuretic
- edema and crackles
79
New cards
Abnormal fluid output:
- wound drainage
- vomiting
- hemmorage
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- hemmorage
- diarrhea
80
New cards
Carbonic acids:
- Respiratory
81
New cards
Cardiac rhythms
82
New cards
Dehydration
- sodium, specific gravity, hemaocrit go up
83
New cards
Overhydration
- sodium, specific gravity, and hematocrit go down
84
New cards
Angiotensin II
- vasoconstriction (increases BP)
- kidneys retain sodium and water
- stimulates aldosterone from adrenal cortex
- KEEP 2
- kidneys retain sodium and water
- stimulates aldosterone from adrenal cortex
- KEEP 2
85
New cards
Functional Incontinence
- inability of urethral sphincter to function properly
86
New cards
overflow incontinence
- bladder holds so much
- only 1000mL
- only 1000mL
87
New cards
Reflex incontinence
- hands in water and feeling the need to urinate
88
New cards
Stress incontinence
- increased urination pattern
89
New cards
Urge incontinence
- disease process
- neuromuscular and obesity
- neuromuscular and obesity