19. Retinal pigment epithelium physiology
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
What prevents photo-oxidative damage in the RPE?
Antioxidants: glutathione, catalase, ascorbate, superoxide dismutatse.
High capacity for cell repair
What are melanosomes?
An organelle derived from late endosomes that form during development. They prevent light reflection back to photoreceptors and absorb light and heat.
What is a key enzyme to produce melanin?
Tyrosinase
What do mutations in tyrosinase cause?
Lead to albinism
Affect melanosomes and can cause ocular albinism
Development of RGC is closely associated with what?
RPE during axon elongation.
How does ocular albinism disrupt binocular vision?
Albinism leads to improper routing of ganglion cells through the optic chiasm. Fewer ipsilateral projections of RGC axons.
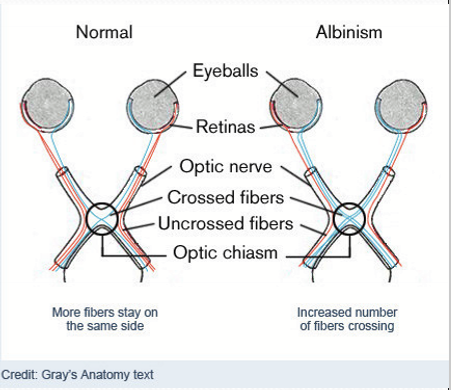
What fails to develop without melanosomes in the eye?
The fovea. It ranges in severity, reduced/variable cone density, reduced visual acuity, and delay in visual maturation.
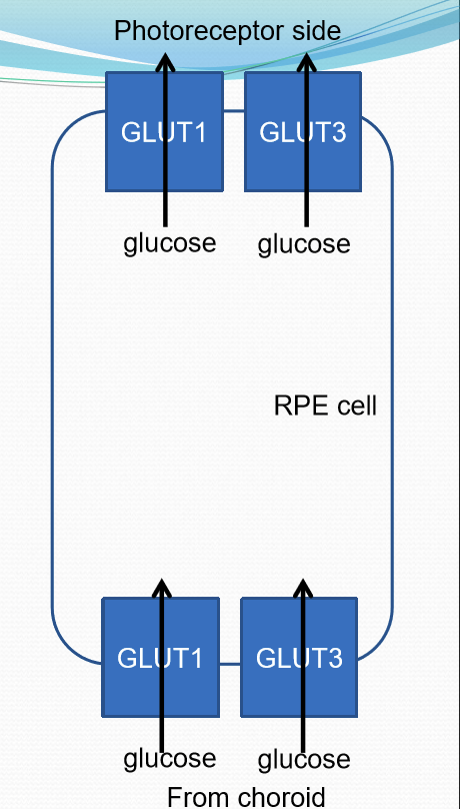
How does RPE cells transport glucose from the choroid to the outer retina?
GLUT1 and GLUT3. Reduced O2: more GLUT transport. More O2: less GLUT transport.
What do RPE cells use for energy?
lactate
What do neuronal cells produce due to their high metabolic activity?
Large amounts of water and accumulation of lactate.
How does the eye prevent water accumulation in the RPE?
RPE transcellularly transports ions from the subretinal space, through RPE cytoplasm, and out through the basolateral membrane. Chloride ions are the main driving force.
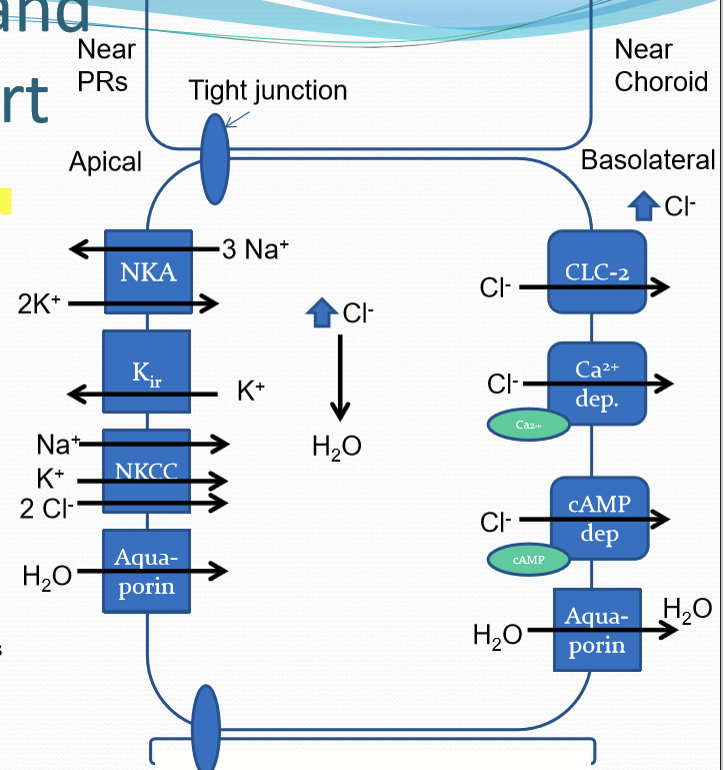
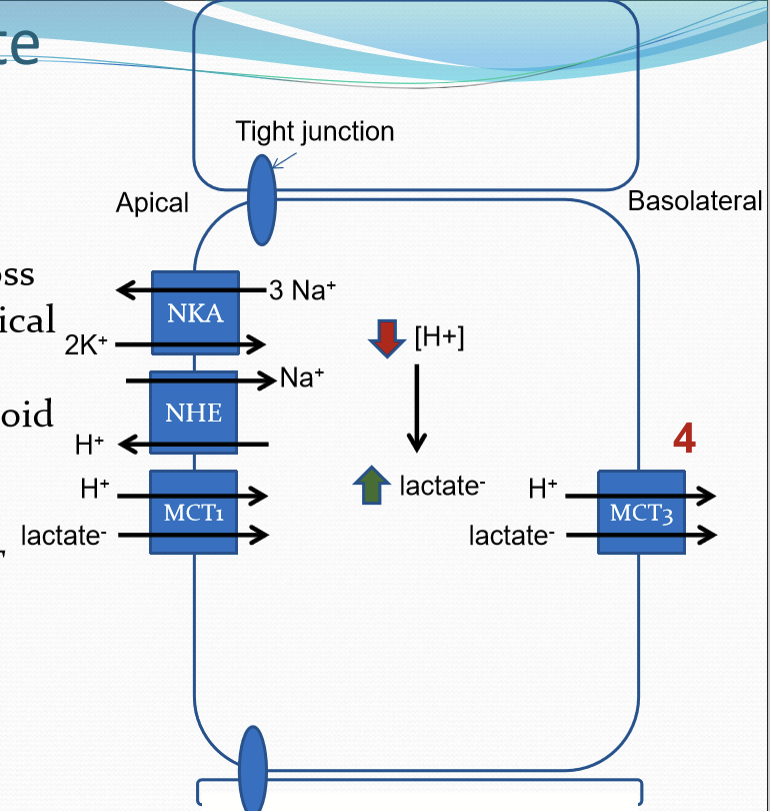
How is lactate transported by the RPE?
Lactic acid is transported across RPE from PR/apical side to basolateral/choroidal side
Utilizes NKA/NHE/MCT
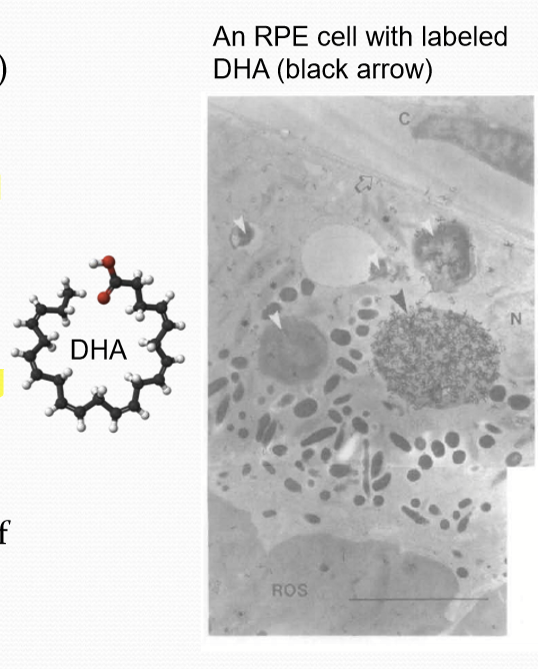
What is Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA)?
A polyunsaturated omega-3 fatty acid that is essential for the renewal process of the photoreceptor outer-segment membrane. It is required for efficient phototransduction
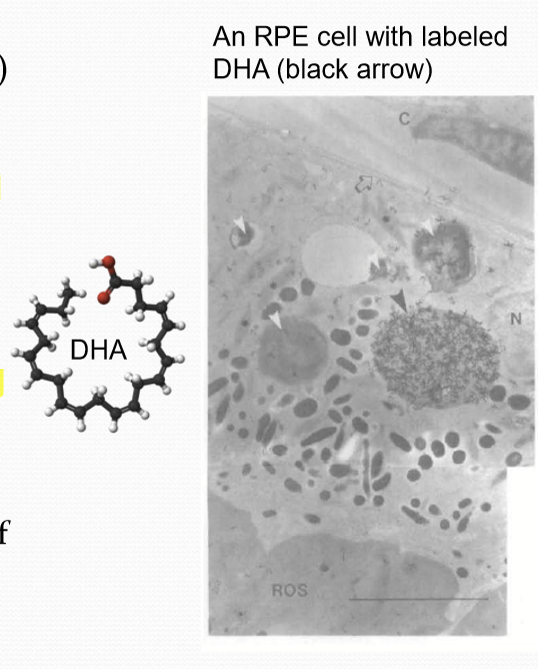
Where is DHA syntehsized?
In the liver, not in retina
How is Vitamin A uptaked?
Through a transmembrane protein STRA6 expressed in RPE cells.
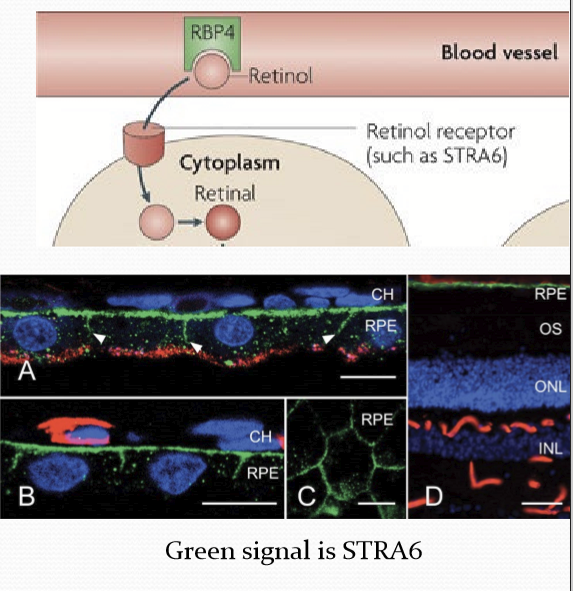
Disruptions to STRA6 gene in humans result in what?
Ocular pathology from minor vision problems to anophthalmia.
How does all-trans-retinal get converted back to 11-cis-retinal?
Retinol dehydrogenase in the RPE.
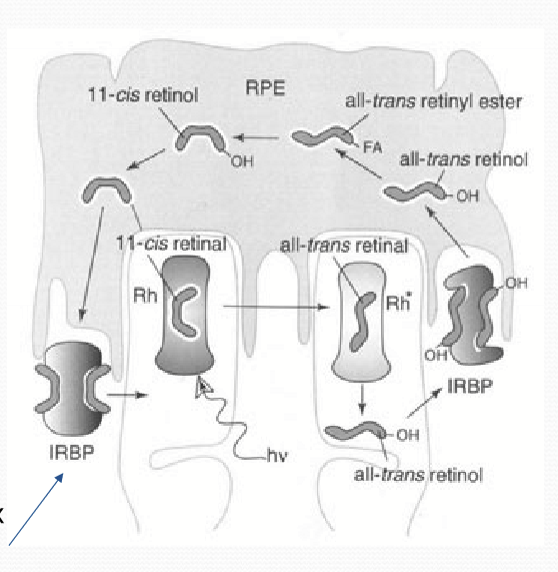
The rod visual cycle
11-cis retinal is converted all-trans retinal by light
all-trans retinal converted to all-trans retinol in outer segment
all-trans retinol is transported to RPE via IRBP
all-trans retinol is converted to 11-cis retinol in RPE
11-cis retinol is converted to 11-cis retinal in RPE
11-cis retinal is delivered back to outer segment via IRBP
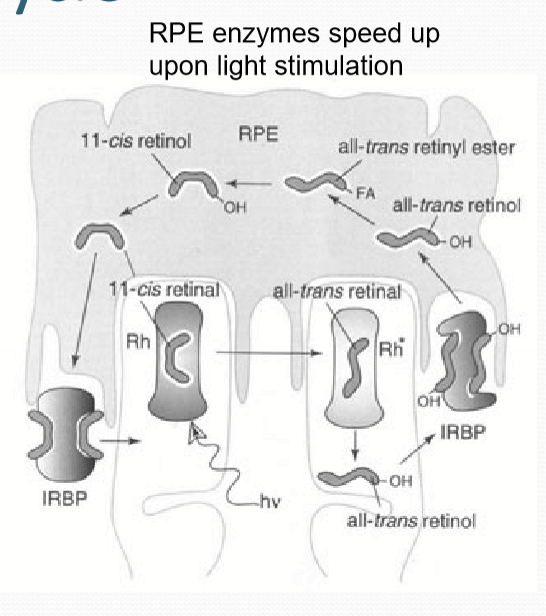
What is different about cones vs rods for the visual cycle?
Cones receive 11-cis retinal from RPE, 11-cis retinol from muller cells, and can convert 11-cis retinol to 11-cis retinal themselves.
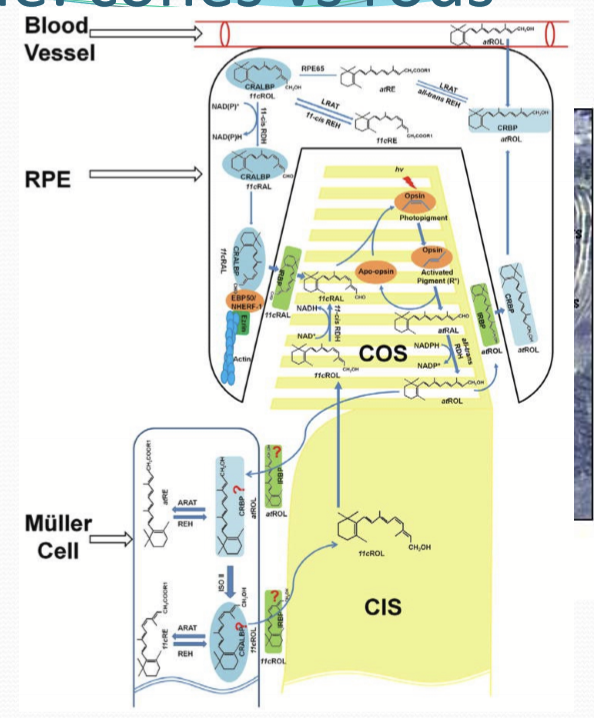
Why is the cone visual cycle different?
Higher demand: cones need faster chromophore regeneration
Competition with rods: rods dominate the RPE visual cycle
Greater RPE distance: cones, especially in the fovea, are farther from RPE
What is lipofuscin?
Vesicles are found within the RPE that are composed of incomplete degradation of internalized macromolecules from visual cycles.
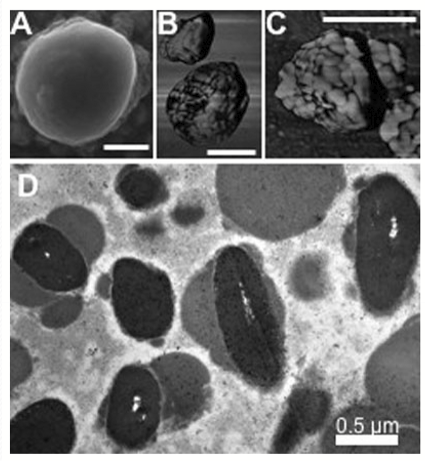
What happens with lipofuscin with age?
Lipofuscin vesicles accumulate with age.
What does an increase in lipofuscin strongly correlate with?
Cellular dysfunction and contributes to retinal aging and degeneration. High abundance is a feature of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
What is lipofuscin?
Lipofuscin is a byproduct of the visual cycle, formed from the accumulation of fluorescent compounds in the RPE.
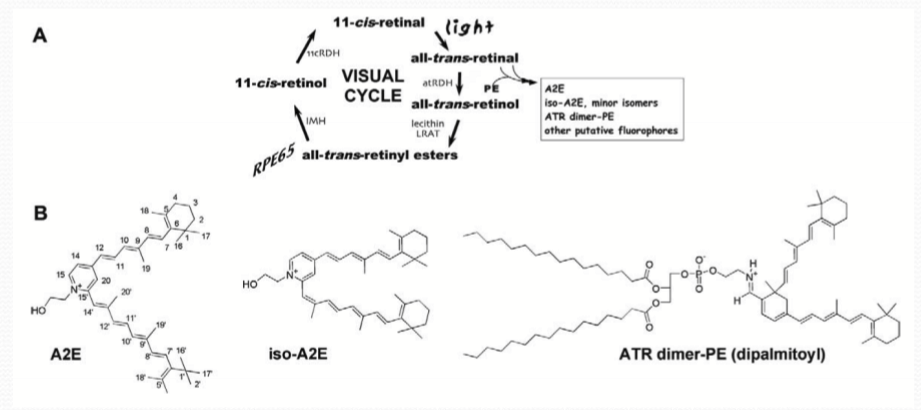
What molecule from the visual cycle can react with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE)?
All-trans retinal
What does all-trans retinal react with to form fluorophores?
It reacts with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), a major lipid in photoreceptor disc membranes.
What is the name of the major fluorophore that accumulates in lipofuscin?
A2E (N-retinyl-N-retinylidene ethanolamine)
What does A2E do?
It is a source of autofluorescence in confocal laser scanning ophthalmoscopy (Fundus autofluorescence, FAF).
What happens when A2E-epoxides from exposure to blue light?
Damaged DNA, leading to RPE cell death, leading to photoreceptor death.
What is retinitis pigmentosa?
Mutations in rhodopsin gene, producing destabilized protein => reduced function/transport => photoreceptor cell death
What is Stargardt’s Macular degeneration?
Due to accumulation of fluorescent lipfuscin pigments in RPE, RPE degenerates and photoreceptor cell dies. ABCA4 mutation encodes disk membrane protein required for rod visual cycle.
Leber’s congenital amaurosis?
Caused by mutations in RPE65, which encodes a RPE protein required for rod visual cycle.
Why do PRs generate new membrane discs?
The focus of light energy onto retina and increased formation of ROS exposes photoreceptors outer segments to toxic compounds.
How does membrane discs regeneration occur?
In a circadian manner, with highest phagocytotic activity in morning and peaks in 1-2 hours.
How many days is required for a whole length of a photoreceptor outer segment to be renewed?
11 days
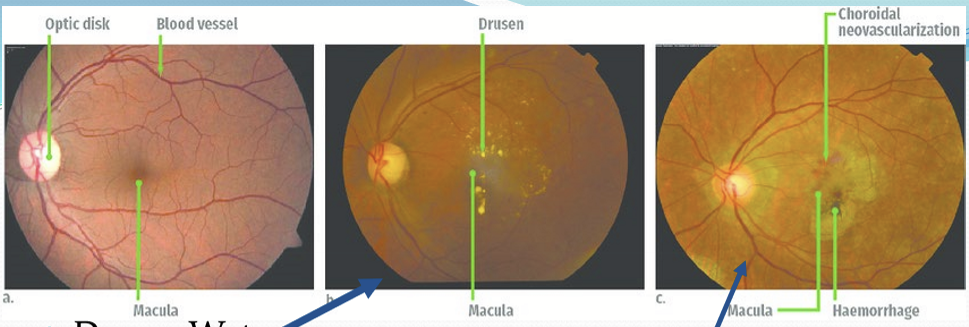
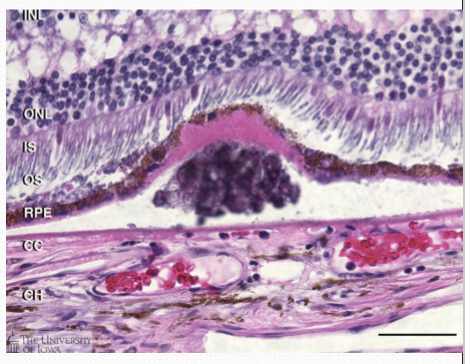
What is RPE Drusen?
Extracellular lipid deposits, derived from remnants of RPE phagocytosis of photoreceptors.
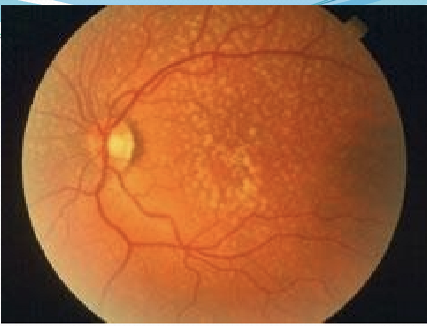
What layer is drusen located in?
Between the basal lamina of the RPE and the inner collagenous layer of Bruch’s membrane.
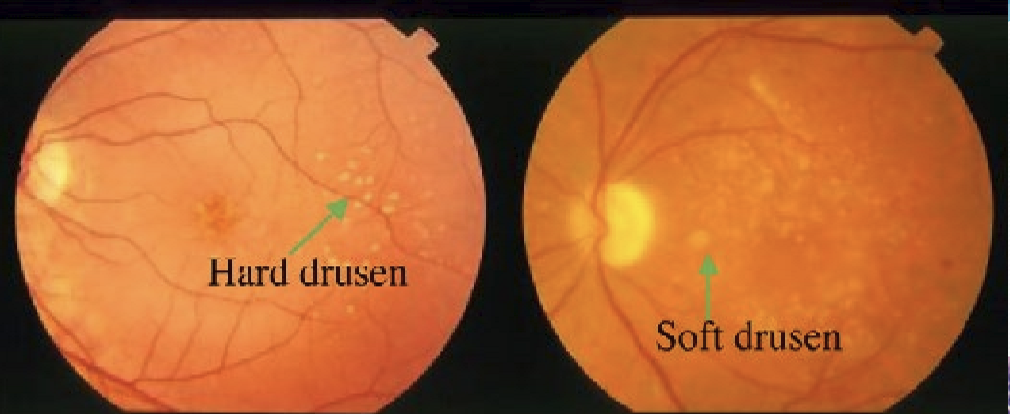
What is the difference between Hard vs Soft Drusen?
Hard: does not usually affect vision. Soft: increases risk of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
What are the characteristics of AMD?
Greatest risk factor is age. Damage/reduced RPE function leads to insufficient photoreceptor support, which leads to photoreceptor death.
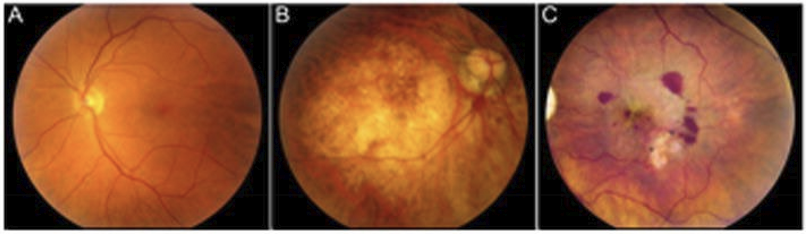
What is the difference between dry vs wet AMD?
Dry:
early-intermediate : fuzzy/distorted vision
advanced: loss of RPE in macular region: leads to loss of photoreceptors central vision loss
Wet: advanced neovascular stage
growth of choroidal vasculature into normally avascular sub-RPE and suv-retinal regions
loss of more RPE/photoreceptors/central vision