2. Immune ch18-21
1/146
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
147 Terms
What happens after “innate immune response by infected cells and local macrophages via PRRs.”
activated DCs process and present viral antigens, while migrating to LNs
What happens after “activated DCs process and present viral antigens, while migrating to LNs”
DCs interact with naive T cells to initiate the adaptive response.
What happens after “DCs interact with naive T cells to initiate the adaptive response.”
Effector and memory T and B lymphocytes are generated.
what happens after “Effector and memory T and B lymphocytes are generated.”
Cells go to the lung to fight infection
What happens after “cells go to the lung to fight infection.”
Memory T cells specific for COVID antigens remain in the lung as first responders in case of a re-infection.
What does CTL stand for
cytotoxic T lymphocytes
What is the two mechanisms of CTLs
Release of cytotoxic granules, Fas-FasL interactions
What is the first step of CTL-mediated killing of target cells
MHC I dependent target recognition
What is the second step of CTL-mediated killing of target cells
Formation of a cell-cell conjugate is formed with a “kiss of death”
What is the third step of CTL-mediated killing of target cells
a Ca2+ triggering and reorganization of the microtubule organizing center
What is the fourth step of CTL-mediated killing of target cells
release of granules via exocytosis
What is the fifth step of CTL-mediated killing of target cells
CTL dissociate and moves on
What is the sixth step of CTL-mediated killing of target cells
CTL can kill multiple cells through serial engagement
perforin
a pore-forming protein
granzymes
serine proteases
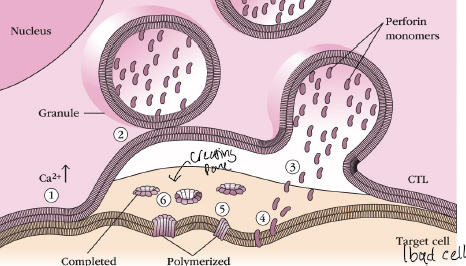
What is the 1 in the picture
TCR-dependent Ca2+ triggering
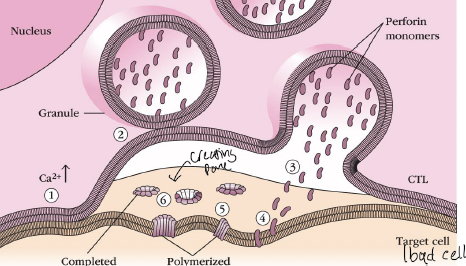
What is the 2 in the picture
granules are delivered to the site of cell-cell interaction
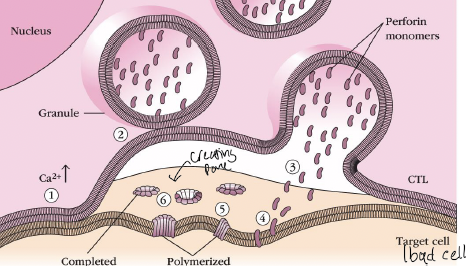
what is the 3 in the picture
In presence of Ca2+, perforin monomers are inserted into the target membrane
What pathway, of CTLs kill target cells, activate apoptosis
Both pathways
active caspases induce
apoptosis
both granzymes and FAS induce cleavage of
pro-caspases to generate active caspases
caspases are normally present in
inactive forms (pro-caspases)
anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies can release the brakes off…
CD8 T cells (checkpoint blockade therapy)
Th1 effector cells are critical for control of intracellular pathogens. what is the primary function of Th1 cells
to activate infected macrophages by contact-dependent on target delivery of IFNy and CD40L
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). Generation of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species (NO and O2)
Th1
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). Phagosome acidification.
Th1
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). Elicits heighted microbial intracellular killing
Th1
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). Additional production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines
Th1
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). __ cells recruit and activate M2 macrophages via IL-4 and IL-13, which increase smooth muscle contraction and enhance tissue remodeling and repair
Th2
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). __ cells produce IL-13 which induces epithelial cell repair and mucus. which increase cell turnover and movement helps shedding of parasitized epithelial cells
Th2
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). IL-13 produced by __ increase smooth muscle contractility that enhances worm expulsion, which increased contractility of mucosal smooth muscle enhances worm explusion.
Th2
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). IL-5 produced by Th2 cells recruits and activates eosinophils, which produce MBP that kill parasites and also mediate ADCC using parasite-specific ig
Th2
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). IL-17 and IL-22 produced by __ induce the production of antimicrobial peptides by epithelial cells, which direct killing/growth inhibition of bacteria attached to the epithelium
Th17
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). IL-17 produced by __ cells activates stromal cells and epithelial cells to produce chemokines that recruit neutrophils, which recruitment of neutrophils to the site of infection
Th17
Match descriptions to the effector cells (Th1, Th2…). IL-22 produced by ___ increase epithelial cells turnover, which increase epithelial cell division and shedding impairs bacterial colonization
Th17
What does T regulatory cells (Treg) do
competition with Teff for pep-MHC, stealing CD80/86 from DCs surface, steal IL-2 from T cells, secrete regulatory cytokines (TGFb, IL-10), generate adenosine (anti-inflammatory), treg expansion, convert more T cells into Tregs
antibody isotypes are
encoded in Fc regions of the antibody
Isotype switching is
regulated by the inflammatory cytokines that B cells sense during activation (many come from TfH)
Isotypes determine
the effector functions of the antibodies
Neutralization is a type of antibody-mediated effector functions. what is it?
blocks ability of pathogens or toxins to target and infect cells
Opsonization is a type of antibody-mediated effector functions. what is it?
promotes and/or enhances the engulfment of antigens by phagocytes
Complement Activation is a type of antibody-mediated effector functions. what is it?
results in the generation of the membrane attack complex (MAC), creates pores in pathogen membranes and killing the microbes.
ADCC is a type of antibody-mediated effector functions. what is it?
activates the killing activity of several types of cytotoxic cells (NK cells)
What does ADCC stand for
Antibody-Dependent Cell-mediated Cytotoxicity
Antibody-dependent degranulation and mediator release is a type of antibody-mediated effector functions. what is it?
triggers mediator release from granulocytes
FcR signaling through ITAMs (activation)/ITIMs (inhibition)
see T/B signaling - elicits different functions
what does ITAMs do
activation
what does ITIMs do
inhibition
Degranulation
crosslinkinh of FceR on mast cells elicits granule release
Opsonization
FcyR expressed on macrophages binds to complexed IgG or IgA. induces phagocytosis
Mother/Fetus interface
FcRn(neonatal) expressed on placental cells transports IgG into the fetal circulation
ADCC
FcyR expressed on NK cells binds on IgG bound to surface of infected cells and elicits NK mediated killing
Transport into mucosa
Poly-Ig receptor expressed on mucosal epithelial cells transport IgA into mucosal lumen (gut, airways)
Fc receptors distinguish free antibodies from those bound to a pathogen via
aggregation and cross-linking, lead to ITAM activation (phosphorylation) and signaling
IgG can
stays in the circulation to protect against dissemination and transferred across the placenta via the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn)
IgA can
transported into the lung mucosa via pIgR for immediate protection and transferred to the newborn via breast milk
IgE can
bound to mast cells and eosinophils localized in barrier surfaces
What are two types of diversity generated BEFORE exposure to antigen (during b development)
combinatorial diversity (VDJ recombination) and Junctional diversity (random nucleotides added (TdT))
What are the types of diversity generated AFTER B cell development
IgM vs IgD surface expression, surface expression vs secretion, affinity maturation through somatic hypermutation, isotype class switching
What does RNA processing determine
IgM vs IgD and membrane vs secreted
What does DNA mutation determine
hypermutation
What does DNA rearrangement determine
class switching
Alternative polyadenylation regulates
production of IgM vs IgD
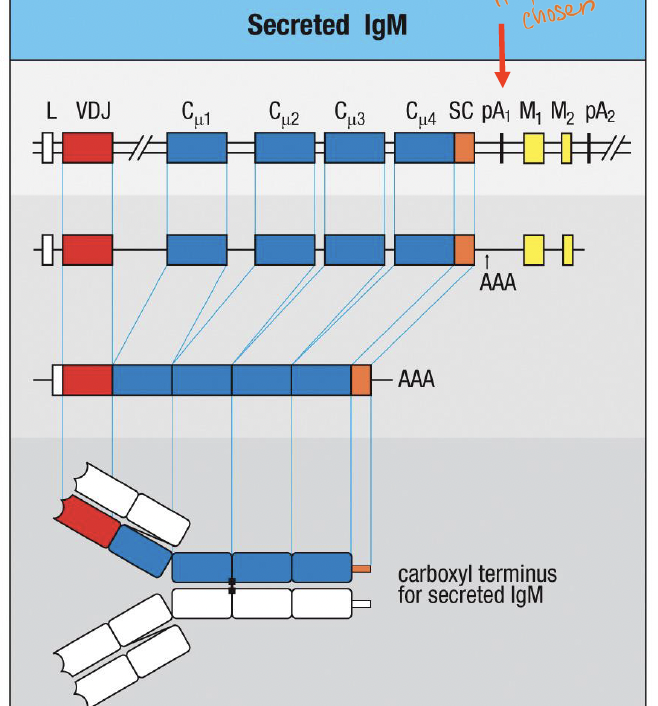
What determines if a Ig is a transmembrane IgM
pA2; yellow membrane coding (MC) exons encode a hydrophobic transmembrane domain not present in the orange secretion coding (SC) exon
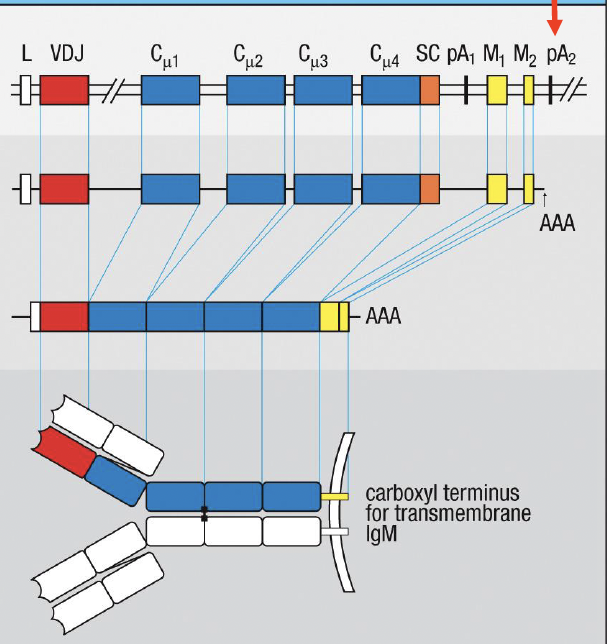
What determines if a Ig is secreted Ig
pA1 ;regulated use of an “internal” polyadenylation site that precedes the exons encoding the transmembrane domain
What are the three ways to modify DNA of rearranged Ig locus
somatic hypermutation, class switching recombination, and gene conversion
What is somatic hypermutation (SHM)
single base pair mutation in V genes, can change receptor affinity for Ag
what is class switching recombination
replacement of constant genes encoding one isotype, modify effector function, but not Ag specificity.
Gene conversion
only for birds? DNA sequnce replace a similar one, causing them to be identical
CSR and SHM occur only after
B cell get “help” from tfh.
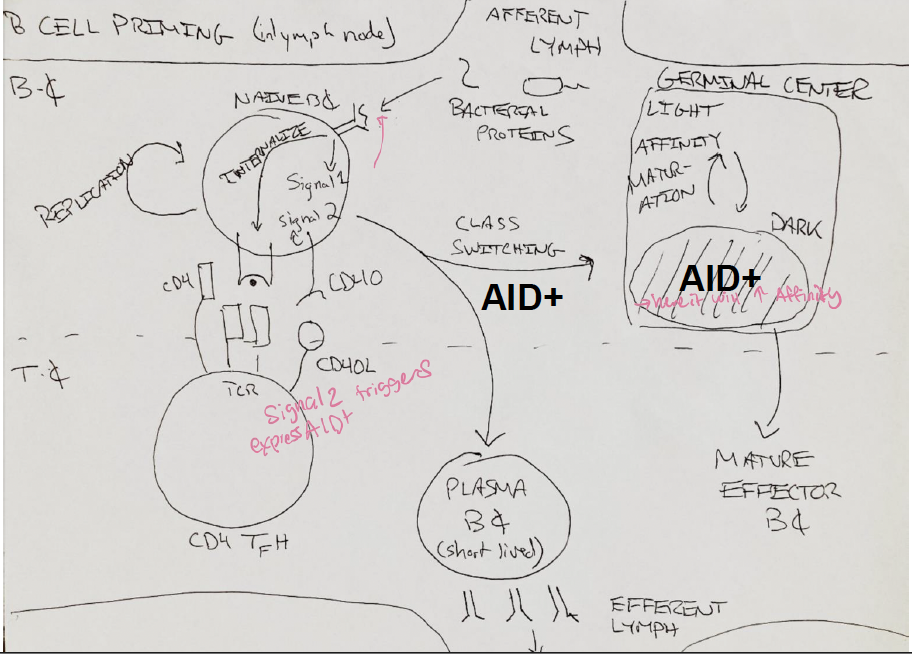
B cells express AID only after
they get “help” from Tfh cells
What does AID stand for
Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID)
What does AID do
initiates both somatic hypermutation and class switch recombination
AID initiates a
nucleophilic attack on the pyrimidine ring of cytidine
What are things that happen in the DNA that causes SHM
replication, mismatch repair, base excision repair
What enzyme does mismatch repair use to excision
MSH 2/6
What is the enzyme used in Base excision repair
UNG
what can happen to the DNA for class switching to occur
single strand cut by enzyme APEI
What does switch regions do
they determine where AID generates nicks, are CG-rich stretches of DNA in the intron just upstream of the first exon of each Ch gene (except Cs)
In class switching, cytokines signals determines which
switch regions are activated at the level of transcription (IL-4 opens Se)
In class switching, where do the cytokines come from
CD4 T cells, which have been trained by DCs about the nature of the pathogen
which enzymes introduce clustered nicks on both strands of DNA
APE1, UNG, AID
Coordinated deamination at donor and acceptor switch regions by
AID-UNG-APE1, which results in double stranded DNA breaks (DSBs)
Only these events of diversity can be reversible
IgM vs IgD expression, and the membrane vs secreted form
Pt with AID deficiency have
hyper-IgM syndrome type 2, which include no class switching, no somatic hypermutation, lymph node hyperplasia d/t enlarged germinal centers, recurrent infection with pathogens
Deficiency in ___ also causes hyper-IgM syndrome
CD40L (X-linked)
plasmodium is a type of parasite and can stimulate germinal center and cause
chronic (but asymptomatic) infection in endemic regions, lives in the blood, so there’s tons of antigen available for B and T cells, and periodically changes the antigens on the surface of the infected RBC, so antibody response needs to keep evolving
Evidence of gene conversion in humans
pt infected with malaria found that 5-10% of them have antibodies that include part of the LAIR1 protein in the heavy chain, which is good at binding to RIFIN proteins that malaria inserts on the surface of infected RBC
Malaria + Epstein barr virus (EBV) + AID =
Burkitt’s lymphoma
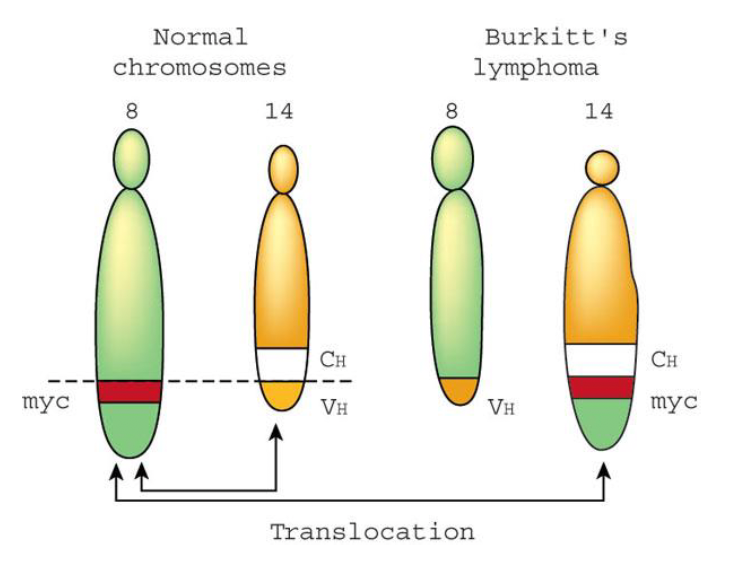
Plasmodiumin burkitt’s lymphoma
drives long-lasting germinal centers filled with AID-expressing B cells
EBV (epstein barr virus) in burkitt’s lymphoma
specifically and persistently infects B cells and can replace the survival signals normally provided by BCR signaling
AID in Burkitt’s lymphoma
off-target activity can cause chromosomal translocations, such as insertion of the myc oncogene into the BCR locus, which is the hallmark of burritt’s lymphoma
with the important exception of the skin, most immune responses occur
at mucosal surfaces
Intestinal Orientation. where is the lumen?
the outside near apical membrane
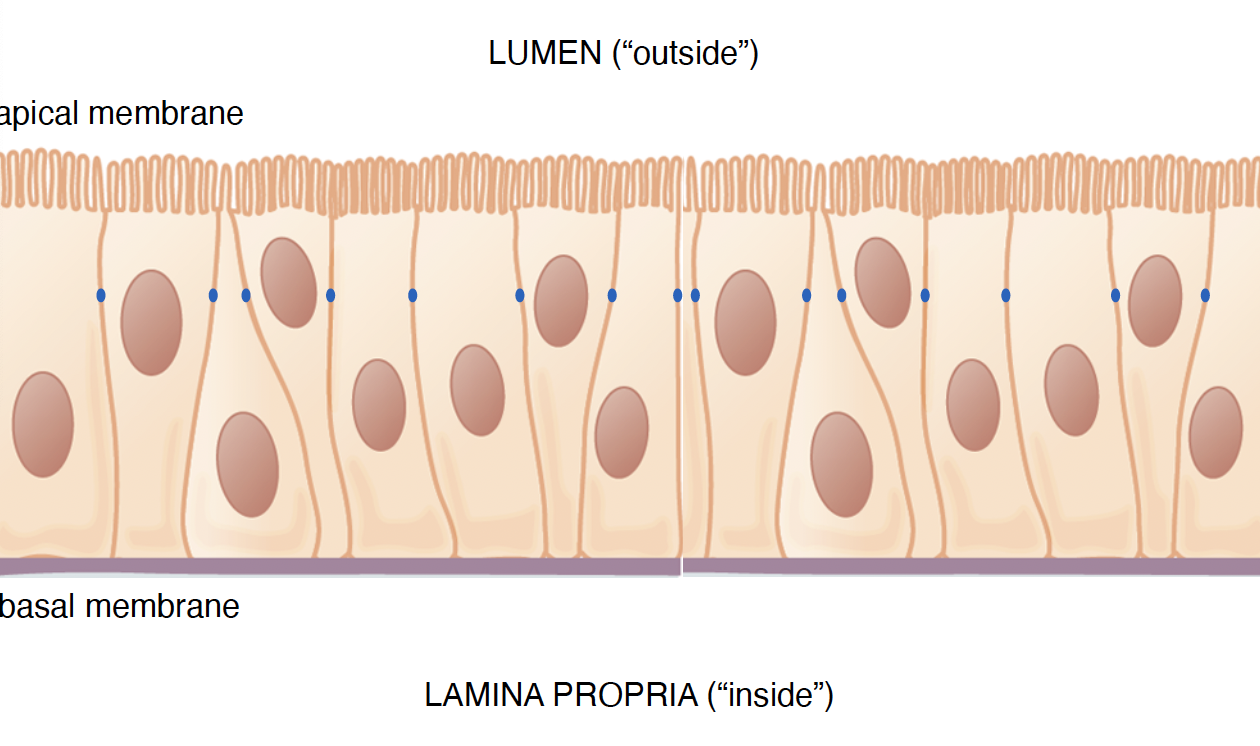
Intestinal orientation. where is the lamina propria?
Inside near the basal membrane
the microbiome helps us synthesize and extract nutrients from our diet because
commensal bacteria express enzyme that we lack.
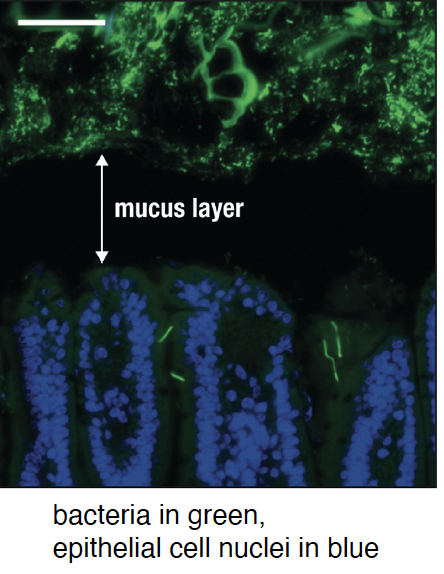
Mucosal defense: mucus. microbes are restrained from
encroaching through the mucus layer
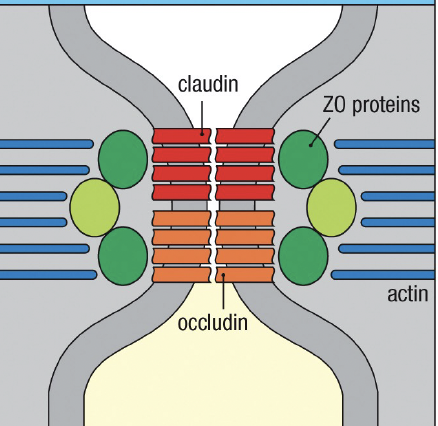
Mucosal defense: epithelium. what transmembrane proteins interact with actin cytoskeleton to regulate the permeability of tight junctions
claudin and occludin associated with zonulin(ZO)
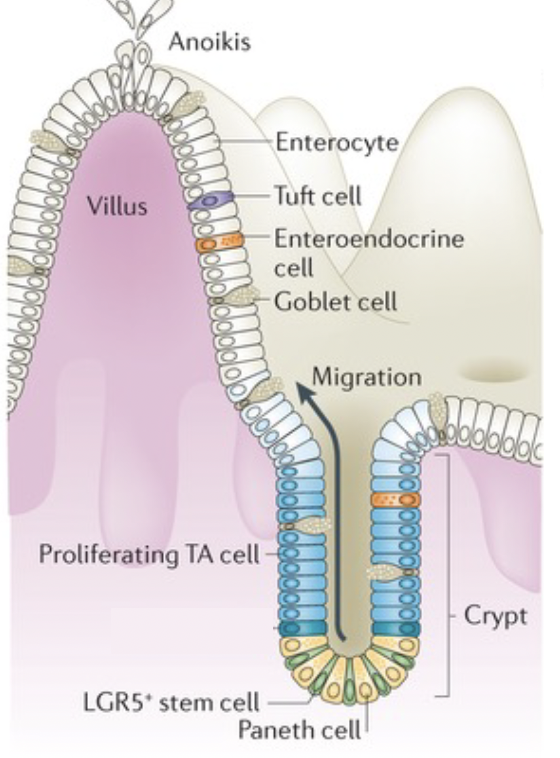
mucosal defense: epithelium. What is Enterocytes
absorptive cells of the intestine (most abundant)
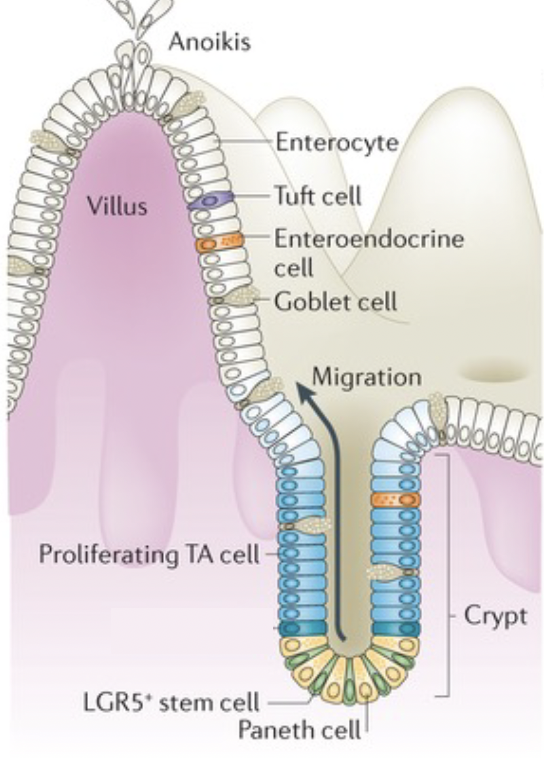
mucosal defense: epithelium. what is goblet cells
make the vast majority of the mucus