Memory and encoding
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This unit was aight
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Memory
The persistence of learning over time through encoding, storage, and retrieval of information
Essential to human functioning and is needed to complete the simplest of tasks
Studied from various different perspectives, including how we make, forget, and the significance of it to us.
Recall
A person must retrieve information learnt earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test.
Most difficult and can be limited with the passage of time
Recognition
A measure of memory in which a person identifies items previously learnt, as on a multiple choice test
Quicker and easier, and persists over greater time periods
Relearning
A measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning the same material again
Distributed practise can help strengthen memories and decrease the amount of time needed to relearn information in the future
Encoding
The process of getting information into the memory system like by extracting meaning through visual, auditory, and semantic information
Storage
The process of getting information out of memory storage
Information is stored in multiple levels of storage based on capacity and duration
Retrieval
The process of getting information out of memory storage
At some point, information that is stored long-term needs to be retrieved in order to be of use
Parallel processing
Processing of multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously
Sensory memory
The immediate, very brief recording of sensory information in the memory system
All sensory stimuli briefly passes through our sensory memory but not all of it is moved further into the system
Only information we pay attention to and encode further will move into short-term memory
Short-term memory
Briefly activated memory of a few items (such as digits of a phone number while calling) that is late stored or forgotten
Limited duration and capacity
Information is often held here for us to use but then forgotten if further encoding doesn’t occur
Any semantically encoded information will make its way to the long-term storage for us to retrieve later
Long-term memory
The relatively permanent, limitless archive of the memory system. Includes knowledge, skills, and experiences
Working memory
A newer understanding of short-term memory
Conscious, active processing of both incoming sensory information and information retrieved from long-term memory
Selective attention helps us to focus when integrating new information with long-term memories in working memory
Central Executive
A memory component that coordinates the activities of the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad
Phonological loop
A memory component that briefly holds auditory information
Visuospatial sketchpad
A memory component that briefly holds information about objects’ appearance and location in space
Neurogenesis
The formation of new neurons
Long-term potentiation
An increase in a nerve cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
When new information is learnt or old information is retrieved and used, new neural connections are created and strengthened
A neuron’s potential to fire is linked to learning and memory, and specific areas of the brain play roles in memory
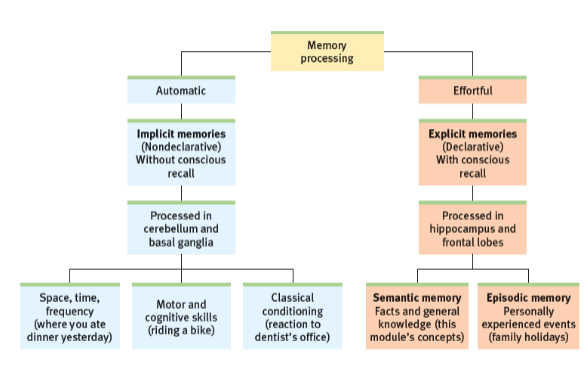
Explicit/Declarative memory
Retention of facts and experiences that we can consciously know and “declare”
Effortfully encoded and retrieved by our conscious mind, and facts we can “declare” we know are considered it
Some things are explicit at first but get implicit over time and habit
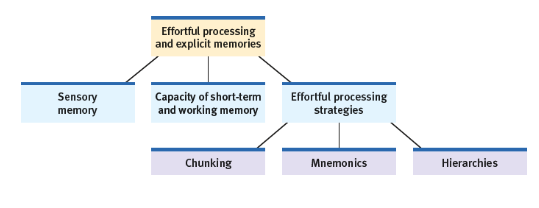
Effortful processing
Encoding that requires attention and conscious effort
Automatic processing
Unconscious encoding of incidental information, such as space, time and frequency, and of familiar or well-learnt information such as sounds, smells, and word meanings
Implicit/nondeclarative memory
Retention of learning skills or classically conditioned associations independent of conscious recollection
They are encoded and stored by the unconscious track
Controls procedural skills
Classically conditioned
Iconic memory
A momentary sensory memory of visual stimuli; a photographic of picture-image memory lasting no more than a few 10ths of a second.
Echoic memory
A momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli; if attention is elsewhere, sounds and words can be recalled within 3 to 4 seconds
Chunking
Organising items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
Mnemonics
Memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organisational devices
Retain more information but require more effort to practice
Mental images and organisation can also be very helpful
Spacing effect
The tendency for distributed study of practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through mass practice or study
Testing effect
Enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading information
Shallow processing
Encoding on a basic level, based on the structure or appearance of words
Focus on sound or sight of words
Deep processing
Encoding semantically, based on the meaning of words; tends to yield best retention
Focus on meaning and context of words by rewording or summarising into your own words
Semantic memory
Explicit memories of facts and general knowledge; one of 2 conscious memory systems
Episodic memory
Explicit memory of personally experienced events; other of 2 conscious memory systems
Hippocampus
Neural centre located in the limbic system; helps process explicit/conscious memories of facts and events for storage
Memory consolidation
The neural storage of a long-term memory
Prefrontal cortex plays a role by sending older memories into short-term to help process new information
Works with help of hippocampus and is improved through better sleep
Flashbulb memory
A clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event
Stress hormones triggered by emotional events influence memory formation
They signal the brain through glucose energy
Stress provokes amygdala to initiate a memory trace
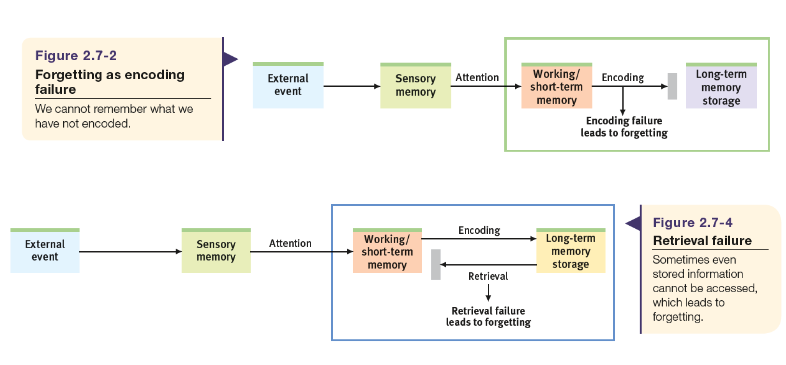
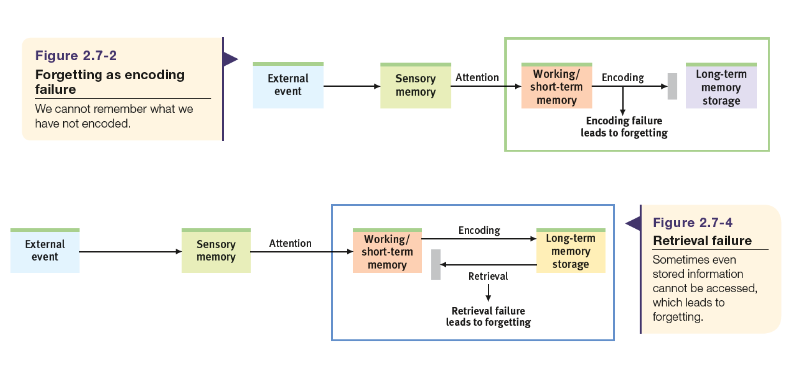
A good picture of a flowchart
Priming
The activation, often unconsciously, of associations in memory
A variety of retrieval cues can help bring information out of long-term storage
Other bits of info like surroundings, time, people, and place can serve as retrieval cues
The more retrieval cues the easier it is to retrieve
Encoding specificity
The idea that cues and context that are specific to a particular memory will be the most effective in helping us recall it.
Context plays a role in helping retrieval (EX: being back in the same environment as the original memory)
Specific cues trigger retrieval better than other cues
Serial position effect
Our tendency to recall best the last items in a list (recency) and the first items in a list (primacy)
Interleaving
A retrieval strategy that involves mixing the study of different topics
Monitor and evaluate learning and identify what knowledge is missing
Test yourslef repeatedly
Study many subjects within a class or among multiple classes can boost memory
Anterograde amnesia
An inability to form new memories
Retrograde amnesia
An inability to remember past information
Ebbinghaus curve
Forgetting occurs rapidly at first and then decreases and tapers off
Forgetting is also connected to retrieval failure rather than decay
Proactive interference
The forward-acting disruptive effect of older learning on the recall of new information
New memories may be hard to locate because of stronger and older memories (thinking of the previous year whenever in a new year)
Retroactive interference
The backward-acting disruptive effect of newer learning on the recall of old information
Repression
In psychoanalytical theory, the basic defence mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety arousing thoughts feelings and memories
Reconsolidation
A process by which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again
Memories constantly revised and it can change every time it recalls
Memories aren’t visual recordings of an event or face, but a constructed version influenced by our perception and expectations
Misinformation effect
Occurs when a memory has been corrupted by misleading information
Receiving misleading information can alter the way in which we remember an event in a phenomenon
Children’s memories are more malleable and often incorrect
Elizabeth Loftus
Leading researcher on the factors that lead to reconstruction in our memories
Source amnesia
Faulty memory for how, when or where information was learnt or imagined (misattributing of a wrong source) and is at the heart of many false memories
Déjà vu
“I’ve experienced this before“
Cues from the current situation may unconsciously trigger the retrieval of an earlier experience
How to do better in your classes
Rehearse repeatedly using distributed practise to benefit from the spacing effect
Make material meaningful to you, personalised to create better retrieval cues and make more associations
Activate retrieval cues by using context-dependent memories by mentally replicating the environment and mood in which you originally learnt the information
Use mnemonic devices like narratives and acronyms to help store large amounts of information to be more easily retrieved later
Minimise proactive and retroactive interference by scheduling study topics
Sleep more, as REM sleep helps with consolidation of memories (impossible cuz KatyISD schools start at 7:15AM and we can’t do nothing about it)
Test your recall, to both rehearse as well as create stronger memories