M.7 Weekly Quizzes
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
M.7, W.1-4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What is the definition of protraction in relation to the forelimb of the dog?
A. Movement of the limb cranially relative to the trunk
B. Movement of the limb caudally relative to the trunk
C. Rotation of the limb
D. Folding or shortening of the limb
E. Movement of the limb towards midline
Movement of the limb cranially relative to the trunk
What type of bone is the patella?
A. Short
B. Sesamoid
C. Irregular
D. Long
E. Flat
Sesamoid
When performing radiography, what is the effect of increasing kVp on the resulting x-ray beam?
A. Increased x-ray beam penetration
B. Decreased speed of x-ray photons
C. Decreased x-ray beam intensity
D. Diffraction of x-ray beam
E. Increased mass of x-ray photons
Increased X-ray beam penetration
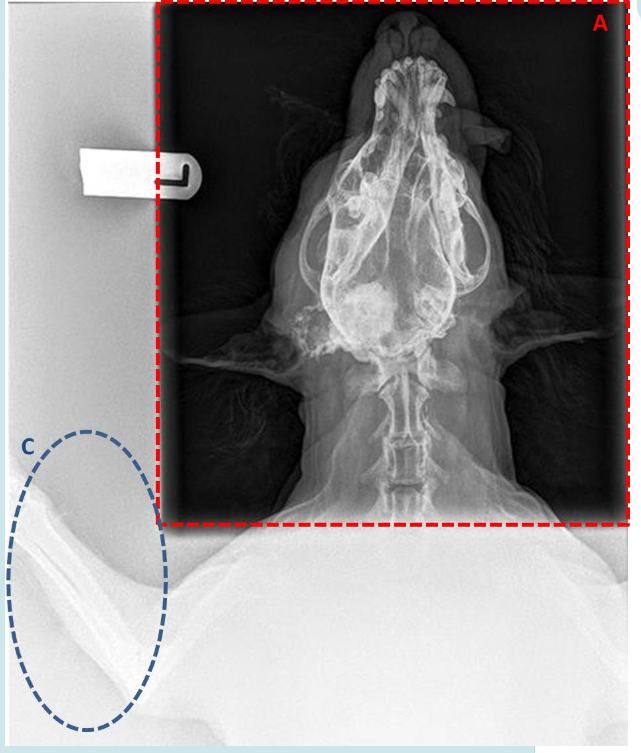
A. Is the image in the area marked A created by the primary or secondary x-ray beam?
B. Will protective clothing (gloves, gowns) stop X-rays within area A?
C. What effect is mainly responsible for producing the image seen in Area C?
D. What piece of equipment can be used to reduce the production of images such as that seen in area A, while maintaining a diagnostic image in area A?
A. Primary
B. No
C. Compton Effect
D. Grid
What is the principal cell type associated with the stratum basale?
A. Langerhans Cells
B. Merkel Cells
C. Basal Cells
D. Melanocytes
E. Corneocytes
Basal Cells
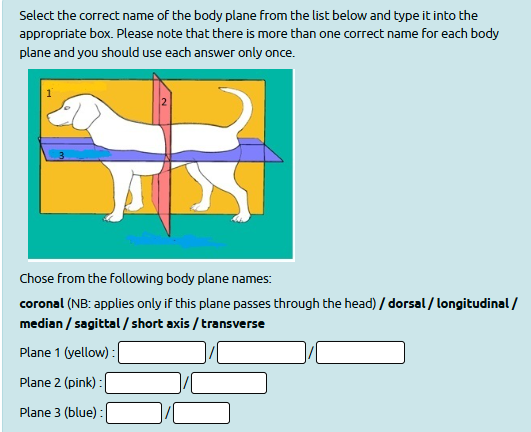
Plane 1: sagittal / median / longitudinal
Plane 2: transverse / short axis
Plane 3: dorsal / coronal
Identify the extrinsic forelimb muscle that originates on the axial skeleton (cervical and thoracic vertebrae) and inserts on the scapular spine, resulting in a primary function of abduction of the limb
A. Brachiocephalic muscle
B. Latissimus dorsi
C. Pectoral muscles
D. Serratus ventralis muscle
E. Trapezius muscle
Trapezius muscle
In cursorial vertebrates, the vertical and lateral orientation of the scapula and the resulting relatively lower position of the shoulder joint contribute to which primary functional outcome during normal locomotion?
a. Restriction of movement to the shoulder joint, limiting overall stride length
b. Increased limb length, which allows for increased stride length and ultimately more ground covered
c. Enhanced lateral movement (abduction/adduction) due to the reduced pectoral skeleton
d. Increased stability resulting from the presence of a large, functional clavicle
e. A decrease in scapular glide, minimizing energy expenditure
Increased limb length, which allows for increased stride length and ultimately more ground covered
Which cells produce histamine in response to trauma, cold, or heat?
A. Basophils
B. Endothelial cells
C. Mast cells
D. Neutrophils
E. Platelets
Mast cells
What are the three main phases of tissue repair?
a. Angiogenesis, collagen synthesis, progressive vascular regression
b. Haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation
c. Inflammation, angiogenesis, remodelling
d. Inflammation, contraction, maturation
e. Inflammation, proliferation, remodelling
Inflammation, proliferation, remodelling
Which muscle has an action that is antagonistic to the triceps brachii?
a. Extensor carpi radialis
b. Teres major
c. Latissimus dorsi
d. Pectoral
e. Biceps brachii
Biceps brachii
Which nerve(s) is/are responsible for contraction of the muscles providing lateral collateral support to the shoulder joint?
a. Subscapular nerve
b. Suprascapular nerve
c. Axillary nerve
d. Median and ulnar nerves
e. Radial nerve
Suprascapular nerve
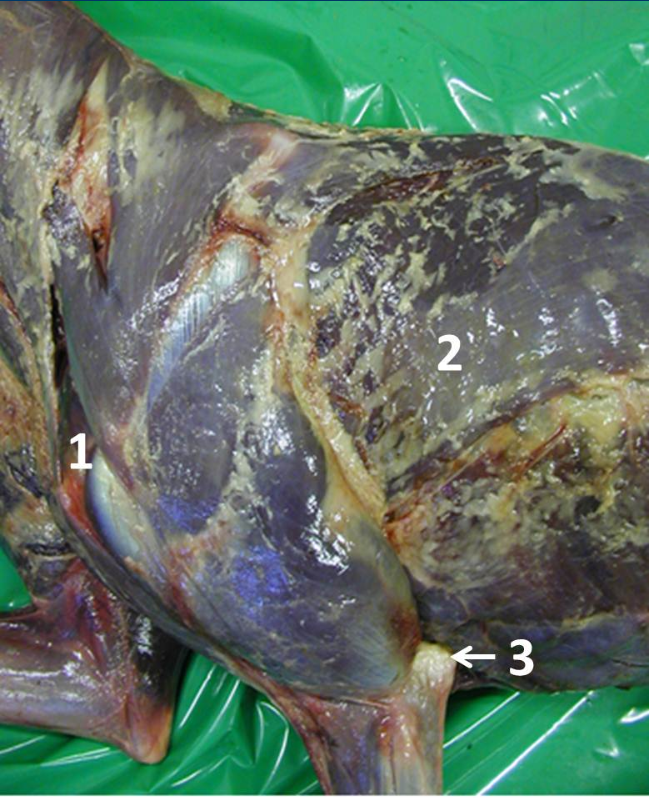
Identify joint 1
Identify muscle 2
Identify bony landmark 3
What is the function of the soft tissue structures that insert onto 3
Shoulder Joint
Latissimus dorsi
Olecranon process (of ulna)
Extension of the elbow joint
Describe the main anatomical difference(s) between the radius and ulna in the dog versus the horse. (2 marks) Briefly explain the functional significance of this.
In dogs the radius and the ulna appear as paired bones which are completely separate structures.
In horses these two bones are fused together (0.5 mark) with the ulna fusing with the radius at its proximal end.
Functionally this means that in the dog there is a degree of rotation possible at this level whereas in the horse no rotation is possible between these two bones.
What is the name of the cells that produces the osteoid in bone?
a. Osteoblasts
b. Osteoclasts
c. Chondrocytes
d. Osteocytes
e. Osteophytes
Osteoblasts
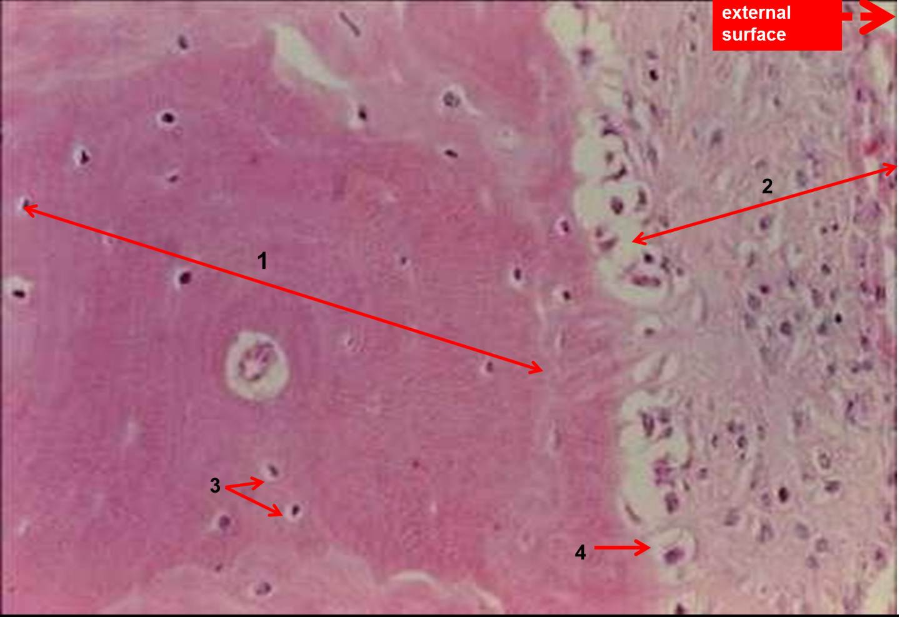
1. What special name is used to describe the functional unit of compact bone indicated by arrow 1?
2. What specific name is given to the tissue that covers the outer surface of compact bone - labelled 2?
3. Identify and name the cells embedded in the osteoid -labelled 3?
4. What is the precise functional role of the cells labelled 4
Haversian system or osteone
Periosteum
Osteocytes
Produce the osteoid (extracellular matrix) which subsequently becomes mineralized to form bone
what does the presence of hyaline cartilage in a callus during fracture healing indicate?
a. Blood supply is less than optimal.
b. The patient is young.
c. The patient is old.
d. Fracture is infected.
e. Fracture is unstable.
blood supply is less than optimal
fracture is unstable
which of the following characteristics is unique to cartilage?
a. It contains collagen fibers
b. It is classified as a supportive connective tissue
c. The extracellular matrix consists of glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans
d. It contains cells that produce and subsequently maintain the extracellular matrix
e. It is avascular
It is avascular
What type of tissue replaces articular cartilage at sites of full thickness loss?
a. Fibrocartilage
b.Trabecular bone
c. Hyaline cartilage
d. Dense fibrous tissue
e. Elastic cartilage
Fibrocartilage
What is the most common route of entry to the joint for bacteria causing infectious arthritis? Two answers correct!
a. Hematogenous
b. Joint injection, e.g. nerve block
c. Spread from adjacent soft tissues
d. Traumatic wound
e. Surgical procedure
traumatic wound
hematogenous