AP Psych - Biological Basis of Behavior
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Myers Psychology 9th Edition - modules 4-6
Last updated 3:23 PM on 7/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
1
New cards
Neuron
nerve cell, building block of the nervous system
2
New cards
sensory neurons (afferent)
carry incoming information from sensory receptors to brain and spinal cord
3
New cards
motor neurons (efferent)
carry outgoing information from brain and spinal cord to muscles and glands
4
New cards
interneurons
only in brain and spinal cord, communicate internally between sensory inputs and motor outputs
5
New cards
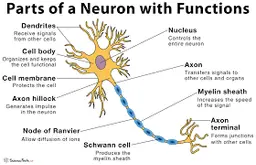
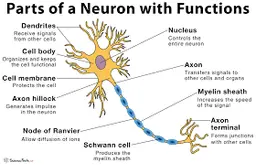
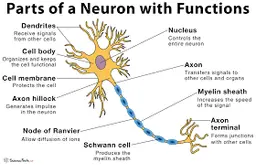
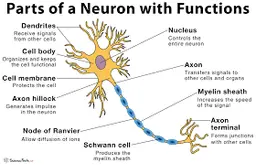
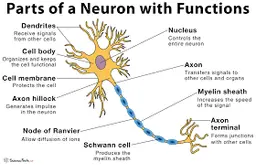
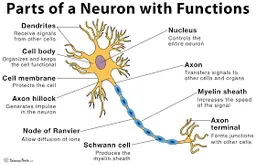
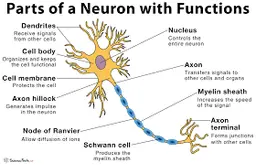
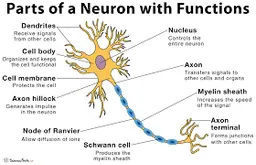
diagram of a neuron
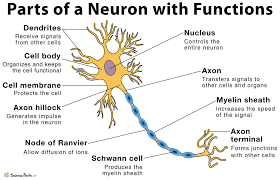
6
New cards
dendrites
receive information and conduct it towards cell body
7
New cards
soma (cell body)
contains **nucleus**
8
New cards
nucleus
has genetic material
9
New cards
axon
transfers electrochemical messages
10
New cards
myelin sheath
layer of fat that speeds up transmission
11
New cards
node of ranvier
gaps in **myelin sheath** that sped up transmission
12
New cards
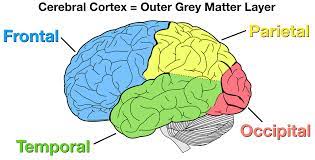
schwann cell
produces **myelin sheath**
13
New cards
axon terminal (synaptic knobs, etc.)
very end of **axon**
14
New cards
synapse
allow for communication between nerve cells
15
New cards
action potential
neural impulse, brief electrical charge that travels down the **axon**
16
New cards
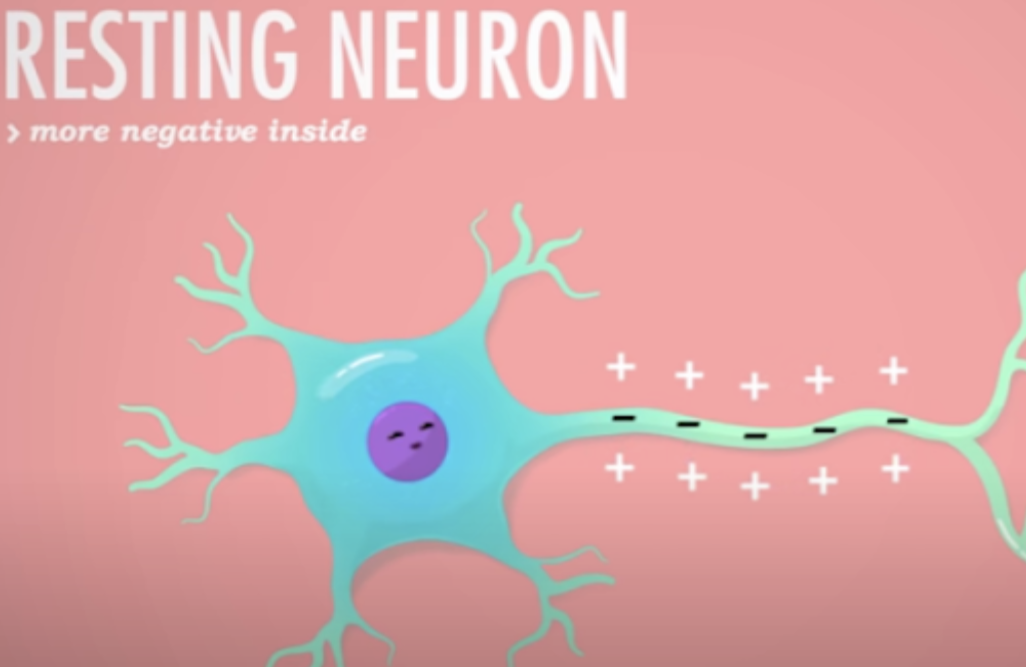
resting potential
* outside has more positive sodium ions, inside has more negative ions
* polarized
* polarized
17
New cards
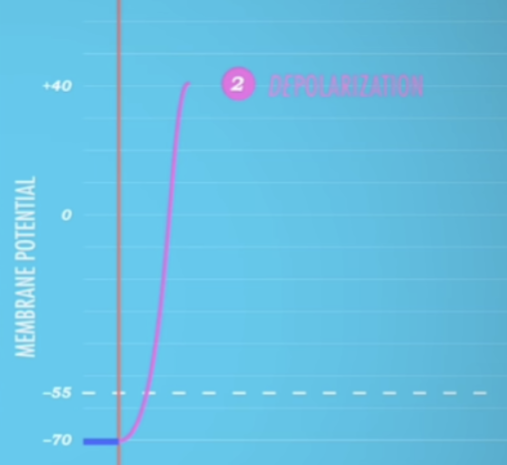
depolarization
positive Na+ ions enter cell
18
New cards
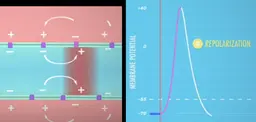
repolarization
return of + outside, - inside
19
New cards
excitatory signals
push charge above -70mv
20
New cards
inhibitory signals
push charge below -70mv
21
New cards
refractory period
the time in which a nerve cell is unable to fire an **action potential** (nerve impulse)
22
New cards
threshold
about -55 mv
23
New cards
"all or none" phenomenon
the **action potential** either fires or it doesn't, no middle ground
24
New cards
When action potential reaches knoblike terminals at end of axon, triggers release of...
chemical messages called **neurotransmitters**
25
New cards
Neurotransmitter: Acetylcholine (ACh)
* Function: enables muscle action, learning, memory
* Examples of malfunction: Alzheimer's - ACh producing neurons deteriorate
* Examples of malfunction: Alzheimer's - ACh producing neurons deteriorate
26
New cards
Neurotransmitter: Dopamine
* Function: influences movement, learning, attention, emotion
* Examples of malfunction:
* Excess dopamine receptor activity is linked to Schizophrenia.
* When starved of dopamine, the brain produces tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson's.
* Examples of malfunction:
* Excess dopamine receptor activity is linked to Schizophrenia.
* When starved of dopamine, the brain produces tremors and decreased mobility of Parkinson's.
27
New cards
Neurotransmitter: Serotonin
* Function: affects mood, sleep, hunger, arousal (consciousness)
* Examples of malfunction: undersupply linked to depression
* Examples of malfunction: undersupply linked to depression
28
New cards
Neurotransmitter: Norepinephrine
* Function: helps control alertness and arousal
* Examples of malfunction: undersupply can depress mood
* Examples of malfunction: undersupply can depress mood
29
New cards
Neurotransmitter: GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
* Function: major inhibitory neurotransmitter
* Examples of malfunction: undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia
* Examples of malfunction: undersupply linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia
30
New cards
Neurotransmitter: Glutamine
* Function: major excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in memory
* Examples of malfunction: oversupply can overstimulate brain, producing migraines or seizures
* Examples of malfunction: oversupply can overstimulate brain, producing migraines or seizures
31
New cards
Neurotransmitter
* chemical messengers
* Fit receptor site much like a key fits a lock
* Fit receptor site much like a key fits a lock
32
New cards
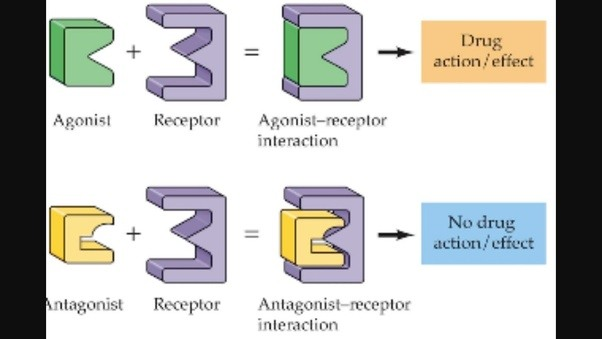
Agonist
__Excites__, similar enough in structure to fit neurotransmitter and mimic effects of neurotransmitter on receiving neuron
(ex. nicotine)
(ex. nicotine)
33
New cards
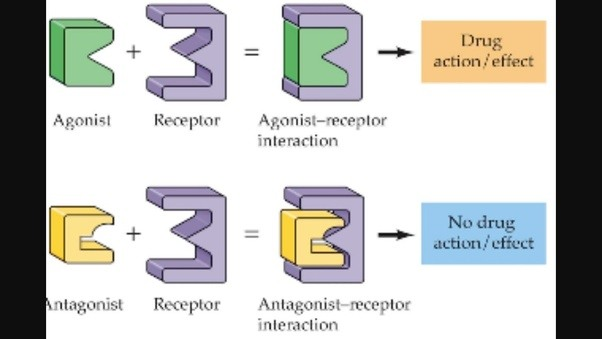
Antagonist
__Inhibits__, similar enough structure to occupy receptor site but not similar enough to stimulate receptor
(ex. beta blockers)
(ex. beta blockers)
34
New cards
reuptake inhibitors
block reabsorption of neurotransmitters into sending neurons
(ex. SSRIs or cocaine)
(ex. SSRIs or cocaine)
35
New cards
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
* nerves connecting **CNS** to muscles and organs
* **sensory** (afferent) and **motor** (efferent) neurons
* **sensory** (afferent) and **motor** (efferent) neurons
36
New cards
Central Nervous System (CNS)
* contains interneurons (basically can't regenerate)
* brain and spinal cord
* brain and spinal cord
37
New cards
Somatic (skeletal)
Part of PNS
- nerves to voluntary muscles and sensory receptors
- both voluntary and reflex movements
- nerves to voluntary muscles and sensory receptors
- both voluntary and reflex movements
38
New cards
Autonomic
Part of PNS
* nerves to heart, blood vessels, etc.
* involuntary functions (heartbeat, blood pressure, respiration, etc.)
* nerves to heart, blood vessels, etc.
* involuntary functions (heartbeat, blood pressure, respiration, etc.)
39
New cards
Sympathetic
Part of Autonomic
* "Fight or flight:
* "Fight or flight:
40
New cards
Parasympathetic
Part of Autonomic
* "rest and digest"
* "rest and digest"
41
New cards
X-ray
Black/white
Captures structure
Captures structure
42
New cards
EEG (electroencephalogram)
Black/white (pen + paper)
Captures activity/function
Most commonly map altered states of consciousness (REM)
Captures activity/function
Most commonly map altered states of consciousness (REM)
43
New cards
CAT (or CT)
Black/white
Captures structure
Composite view of x-ray photos
Captures structure
Composite view of x-ray photos
44
New cards
PET (positron emission tomography)
Color
Captures activity/function
Displays brain activity, shows where radioactive form of glucose goes
Captures activity/function
Displays brain activity, shows where radioactive form of glucose goes
45
New cards
SPECT
Color
Captures activity/function
Displays brain activity, shows where radioactive substance goes
Captures activity/function
Displays brain activity, shows where radioactive substance goes
46
New cards
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
Black/white
Captures structure
Captures structure
47
New cards
fMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging)
Color
Captures activity/function
Revels blood flow (thus brain activity) by comparing successive MRI scans
Captures activity/function
Revels blood flow (thus brain activity) by comparing successive MRI scans
48
New cards
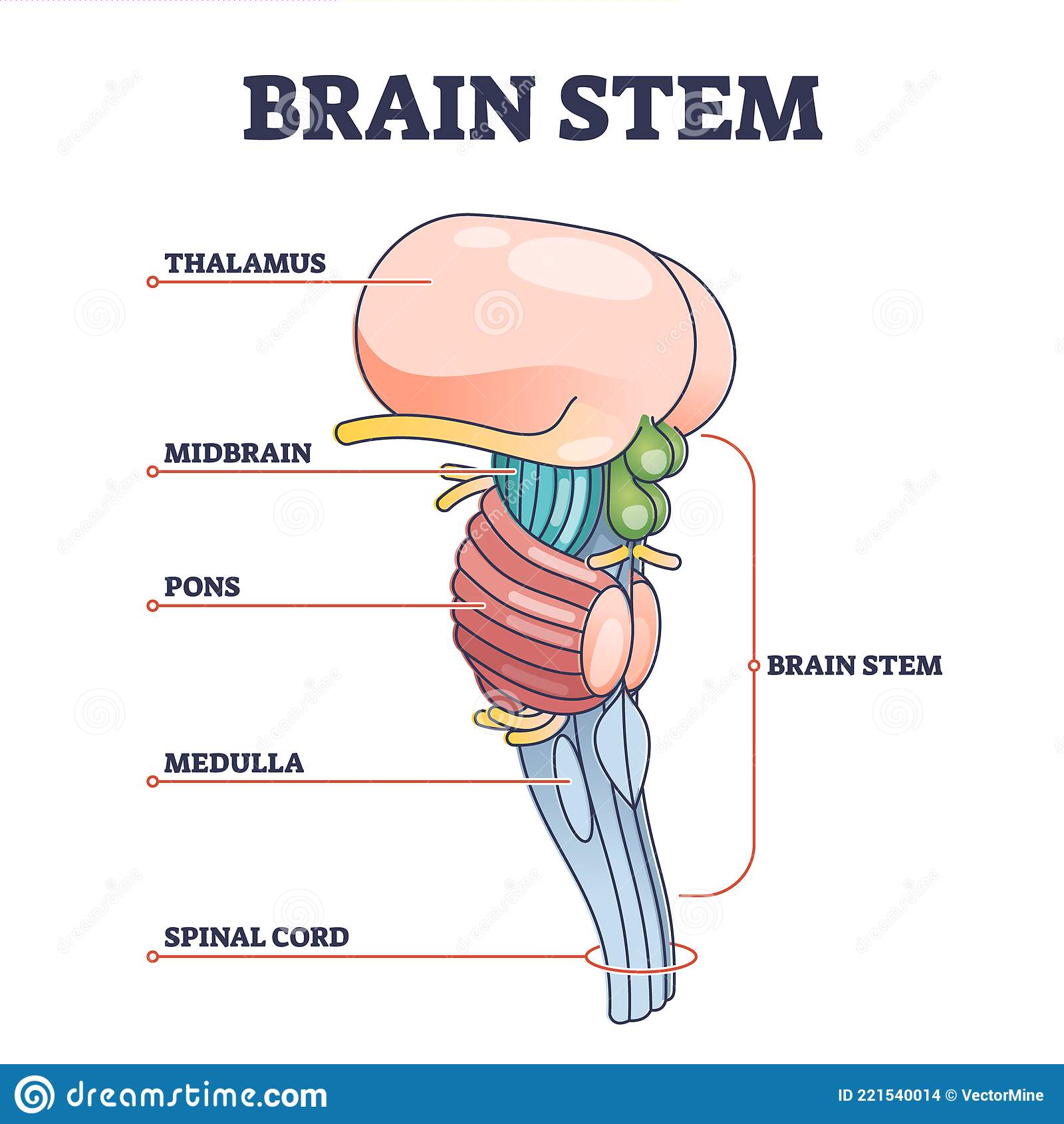
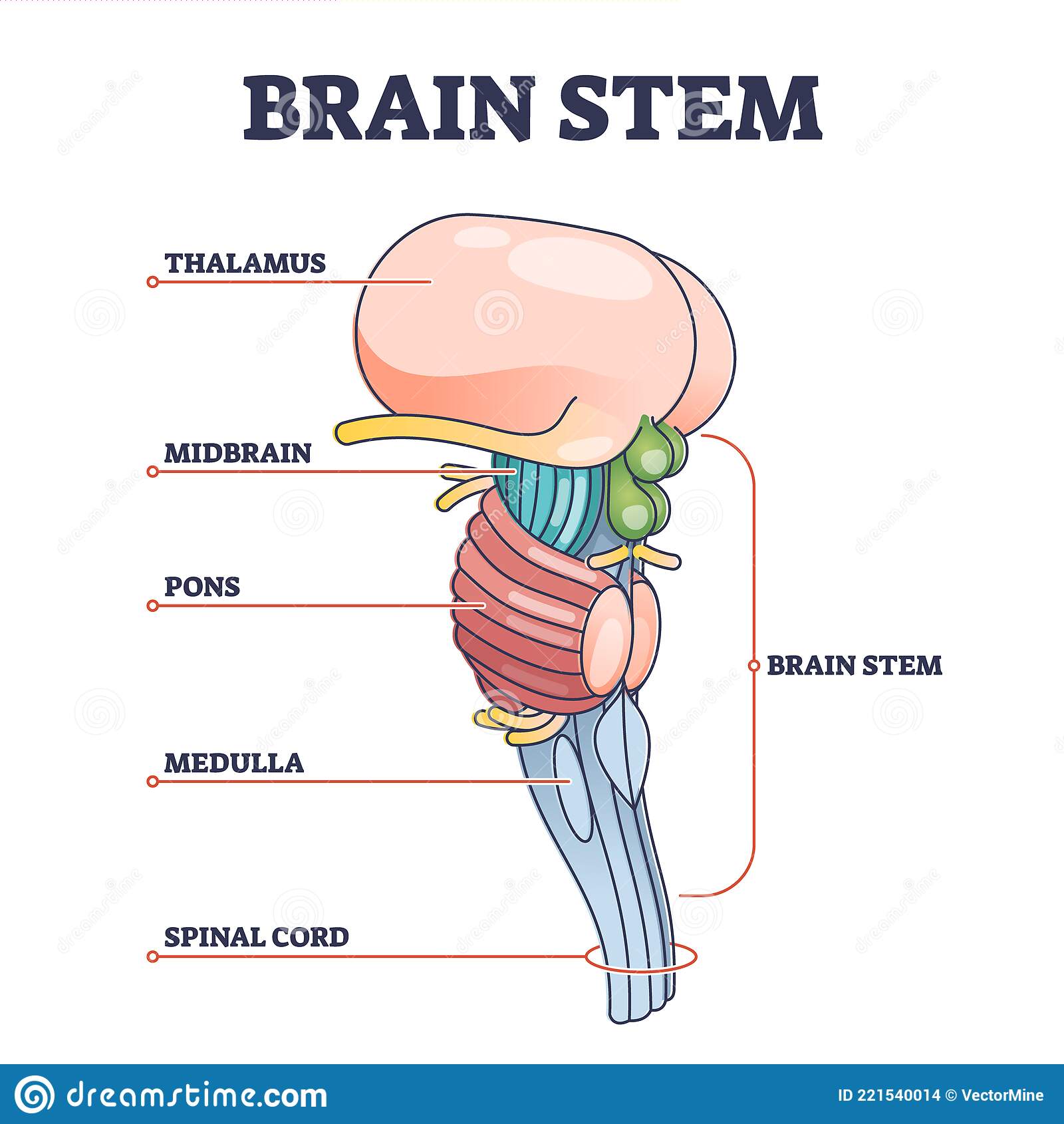
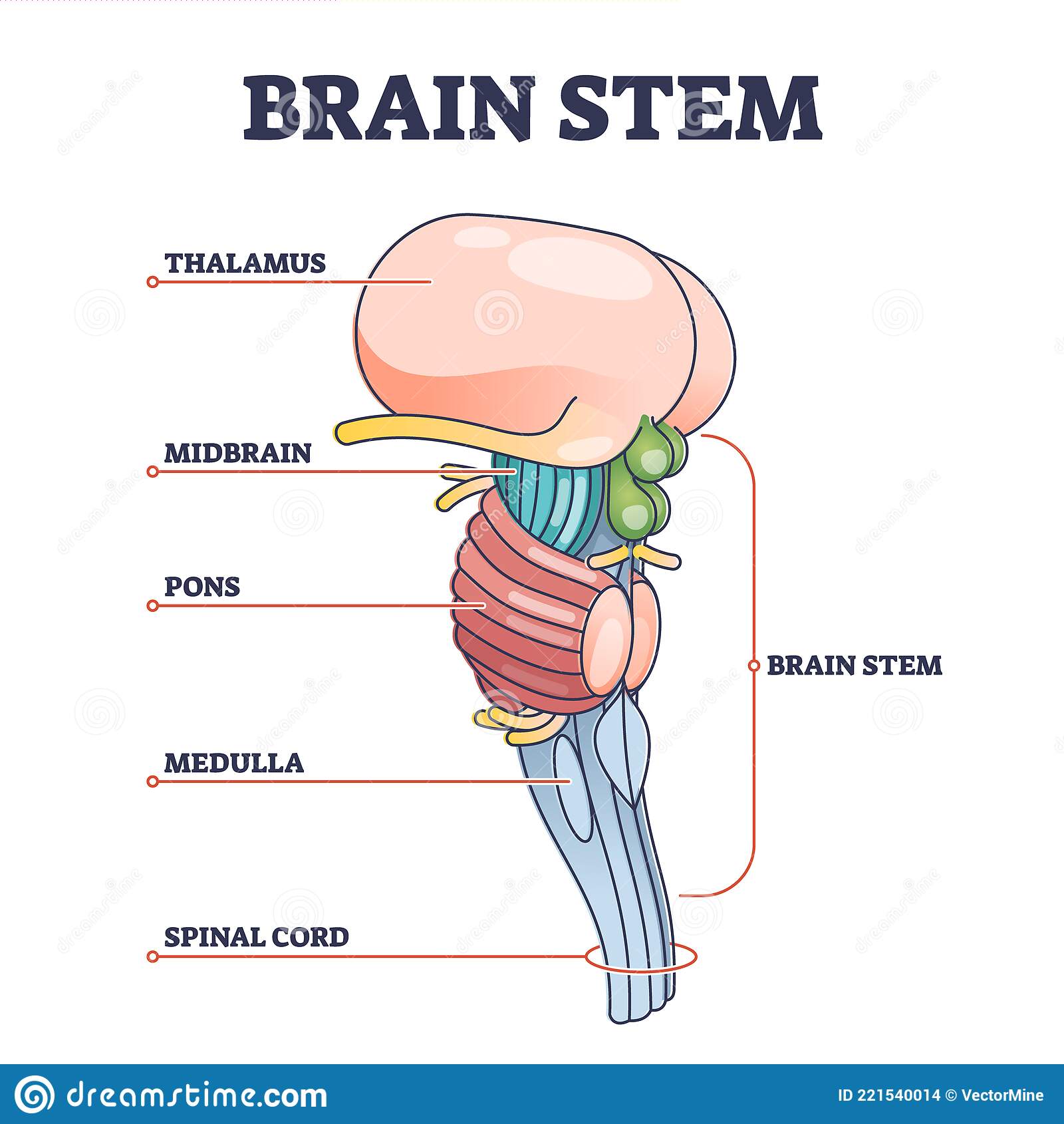
Brainstem
* Oldest part of brain, central core, responsible for automatic survival functions
* Contains **medulla**, **pons**, **reticular formation**
* Contains **medulla**, **pons**, **reticular formation**
49
New cards
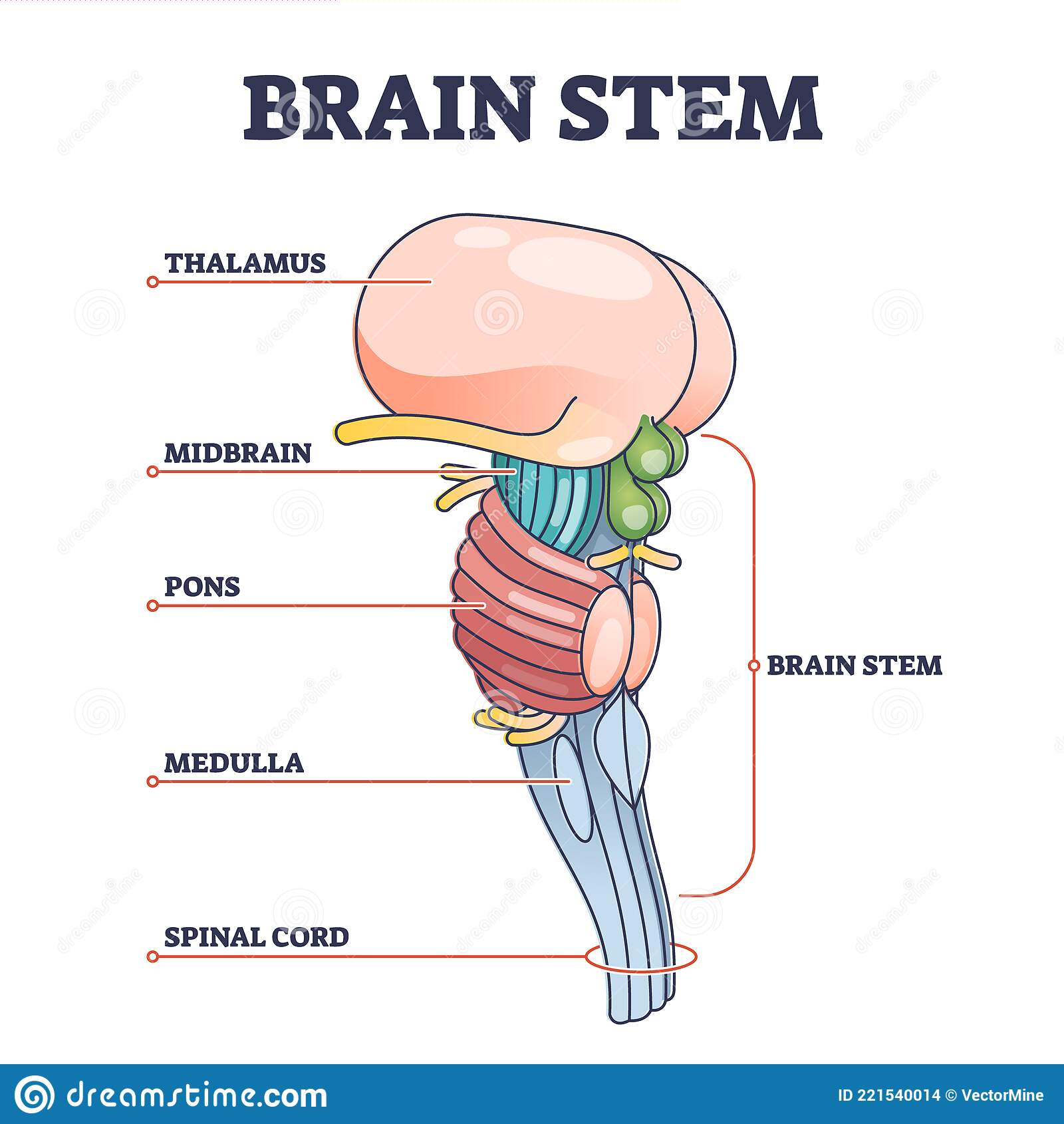
Medulla
* Base of **brainstem**
* Heartbeat and breathing
* Heartbeat and breathing
50
New cards
Pons
* Above **medulla**
* breathing, motor control, sleep and dreams
* breathing, motor control, sleep and dreams
51
New cards
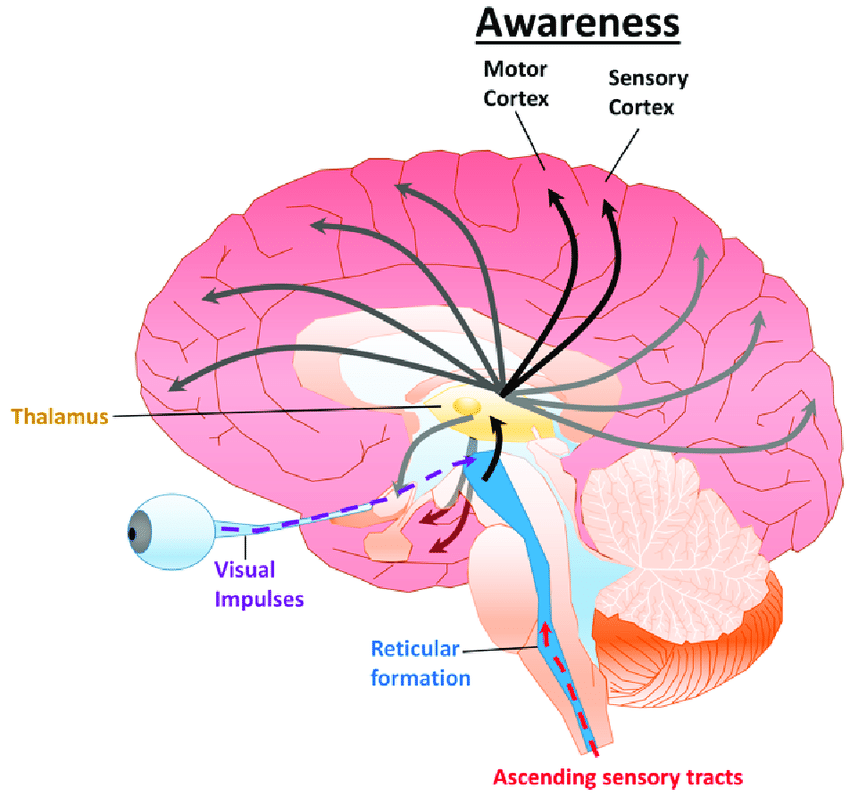
reticular formation
nerve network that controls arousal
52
New cards
Cerebellum
* "little brain" attached to back of **brainstem**
* voluntary movement, balance, implicit procedural memories
* voluntary movement, balance, implicit procedural memories
53
New cards
Thalamus
* above **brainstem**
* brain's sensory switchboard, directs messages to **sensory cortex** and transmits replies to **cerebellum** and **medulla**
* brain's sensory switchboard, directs messages to **sensory cortex** and transmits replies to **cerebellum** and **medulla**
54
New cards
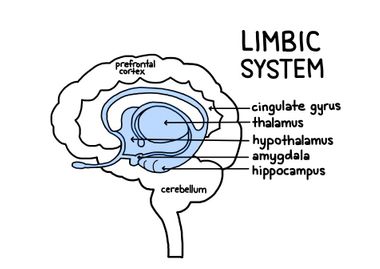
Limbic system
* emotion
* contains **hippocampus**, **amygdala**, **hypothalamus**
* contains **hippocampus**, **amygdala**, **hypothalamus**
55
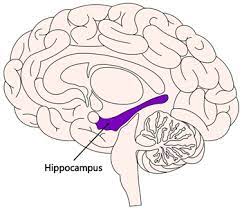
New cards
hippocampus
* part of **limbic system**, hook like structure
* responsible for storage and process of explicit memory
* responsible for storage and process of explicit memory
56
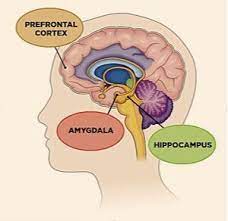
New cards
amygdala
* part of **limbic system**, almond shaped neural clusters
* linked to emotion (fear and aggression)
* linked to emotion (fear and aggression)
57
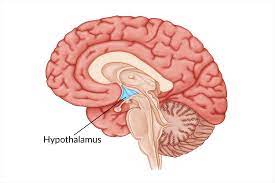
New cards
hypothalamus
eating, drinking, body temperature, helps to govern endocrine system
58
New cards
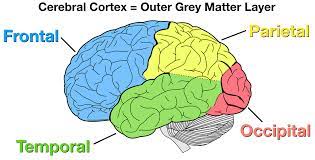
cerebral cortex (neocortex, cerebrum)
contains **frontal** lobe, **parietal** lobe, **occipital** lobe, **temporal** lobe
59
New cards
glial cells
cells in nervous system that support, nourish, protect neurons
60
New cards
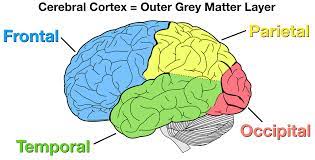
frontal lobe
speaking, muscle movement, plans and judgements
* **broca's** **area** - speaking
* **motor** **cortex** - back of ______ lobe, voluntary movement
* **prefrontal** **cortex** - plans and judgements
* **broca's** **area** - speaking
* **motor** **cortex** - back of ______ lobe, voluntary movement
* **prefrontal** **cortex** - plans and judgements
61
New cards
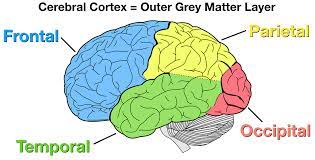
parietal lobe
**sensory cortex** (somatosensory) front of _______ lobe, registers and processes body sensations
62
New cards
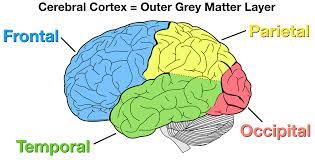
occipital lobe
the ______ lobe contains the **visual cortex**
63
New cards
temporal lobes
the ______ lobe contains the **auditory** **cortex**
64
New cards
corpus callosum
large band of neural fibers that connect the two hemispheres and carry messages between them