BIOL2021: Chapter 11
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
What does diffusion across the membrane depend on?
Size and hydrophobicity
How well do hydrophobic molecules diffuse through the cell membrane?
Pass through very easily
How easily do small, uncharged polar molecules diffuse through the membrane?
Require facilitation to permeate
How easily do large, uncharged polar molecules diffuse through the membrane?
Cannot diffuse and require transport
How easily do ions diffuse through the membrane?
Cannot diffuse, require transporters
What do membrane transport proteins create to allow solutes through?
A hydrophilic pathway
What are the 2 main classes of membrane transport proteins and what differentiates them?
Transporters/carriers/permeases; move solute via conformational change and have specific binding sites
Channels; forms a pore, does not change conformation to move solute but can open/close (minimal solute interaction)
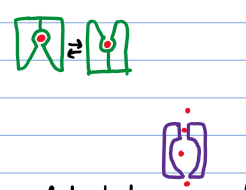
What type of transporters use diffusion passive transport?
All channels and some transporters
What do concentration gradients provide for diffusion?
Energy
How high are typical Na+ concentrations in the cytoplasm?
Low
How high are typical K+ concentrations in the cytoplasm?
High
How high are Cl- concentrations in the cytoplasm
Low
What is membrane potential/potential difference?
The difference between the inside and outside charges (always a negative value)
What does charged solute (ion) movement depend on?
Concentration gradient
Electrical/membrane potential
What is the electrochemical gradient?
The combination of ion concentration gradient and electrical/membrane potential
What do cells use electrochemical gradients for?
Transport
Signaling (action potentials)\
ATP production
other (ex. stomata open/close)
What is the typical animal cell electrical potential?
-20mV to -120mV
What type of transport do transporters use?
Passive or active
What is a uniporter?
A transporter that transports 1 solute
How do transporters and channels kinetics compare?
Transporters have similar rates to an enzyme-substrate reaction
Channels rates are directly proportional to solute concentration
What is Vmax?
The point at which all solute bonding sites are occupied; Max rate of a single transporter
What is Km?
The binding constant; Affinity for the solute
What are GLUT transporters?
A family of passive transporters for glucose
GLUT 1: RBC’s and other tissues
GLUT 2: Liver, gut epithelium
Which direction does solute move in active transport?
Against the concentration gradient
Where does the energy for active transport come from?
Ion gradient
ATP
Light
Redox reactions
What do coupled transporters do?
Couple uphill transport of 1 solute to downhill transport of another solute (ion)
What is a symporter?
Transporter that transports molecules in the same direction
What is an antiporter
Transporter that transports molecules in the opposite direction
How do Na+-glucose cotransporters work?
Symporter
Moves glucose against concentration gradient
uses Na+ gradient as energy
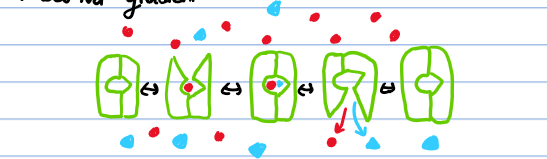
How do Gut epithelial cells transport glucose?
transport glucose from lumen to extracellular space
Gut → cell; Na+ glucose transporter
Cell → extracellular space; GLUT2 transporter
What regulate the pH of cytosol?
Coupled-transporters
Sodium-proton exchanger moves Na+ in and H+ out
Na gradient puts NaHCO3 in and HCL out
What are ATP-driven transporters?
Pumps that couple transport of solute against the concentration gradient of ATP hydrolysis
What are the 3 classes of ATP driven pumps?
P-type
ABC
V-type
What are the key features of P-type ATP pumps?
Phosphorylated by ATP during pumping cycle
Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation drives conformational change
Moves ions against concentration gradient
Primary transport
What are the main roles of P-type ATP pumps?
maintains low Ca2+ levels in cytoplasm
Na+/K+ gradients in animal cells
H+ gradient in plants and fungi
Maintain trace metal ions
Drug targets
What is SR Ca++ P-type ATPase?
Transporter in muscle cells
Triggers muscle contraction
Releases Ca++ from sarcoplasmic reticulum (modified ER)
Na+ channels respond to action potential propagates
composed of 10 transmembrane alpha-helices (binds to ions) and 3 cytosolic domains
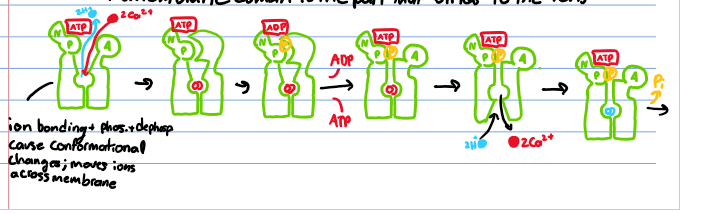
What does the Na+- K+ pump do?
Moves 3 Na+ and 2 K+ against the concentration gradient
Forms electrochemical gradient in animal cells
What does the H+-ATPase (proton pump) do?
Creates gradients across cell membranes
In plant, fungi, protozoal, archaeal, and bacterial
What does the Gastric H+/K+ ATPase in the stomach lining do?
Acidifies the stomach during digestion
What are pantoprazole, omeprazole, esomeprazole, and lansoprazole examples of?
Proton pump inhibitors
What is the largest family of membrane transporters?
ABC (ATP-Binding Cassette) transporters
What do ABC transporters do?
Pump small molecules across cell membranes
What are the 2 highly conserved domains in ATPase called and what side of the cell are they on?
ATP binding cassettes
On the cytoplasmic side
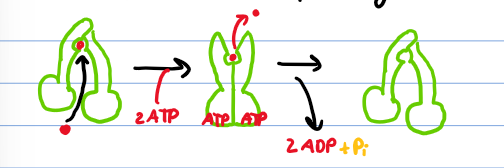
How does the ABC transporter mechanism work?
Solute binds to the transporter
2 ATP bind, causing a conformational change
solute is released to the other side
ATP is hydrolyzed and ADP + Pi is removed
Transporter assumes original conformational change
What medical relevance do ABC transporters have?
Pump drugs out of cells
ex. Cancer cells pump out cancer drugs
ex. Antimalarial drug resistance
ex. Bacterial antibiotic resistance
What are F-type ATPases, what pump type are they related to, and what do they use for energy?
ATP synthases
Structurally related to V-type proton pumps
Uses H+ gradient for ATP synthesis