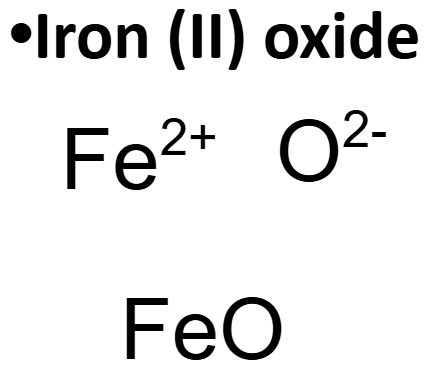Unit 4 Part I IB Chem
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Physical Properties of Ionic Compounds
Solids are usually hard & brittle
Typically soluble in water
Do conduct electricity in aqueous or molten state
Molten = melted
Do NOT conduct electricity as solids
Melting points and boiling points are usually HIGH
Ionic bonding
Ionic bonds form between a metal & a non-metal
Electrons are transferred from the metal to the non-metal
In an ionic bond, a cation and an anion have an electrostatic attraction
The cation is the metal, loses electrons and is a positive ion
The anion is the non-metal, gains electrons and is a negative ion
Ionic Bonding Facts
Large electronegativity difference
>2.2 between ions
Forms crystal lattice structure
Ionization of Sodium
metal
Valence Shell - 3s1
loses electron
isoelectronic with Neon
becomes Na+(cation)
Ionization of Chlorine
Chlorine
nonmetal
Valence Shell - 3s23p5
gains electron
isoelectronic with Argon
becomes Cl- (anion)
How to write chemical formulas
Ions have charges based on their valence electrons
Ions combine in the smallest ratio to make a net charge of zero
Positive charges and negative charges must cancel out.
Roman Numeral
Number | Roman Numeral |
1 | I |
2 | II |
3 | III |
4 | IV |
5 | V |
6 | VI |
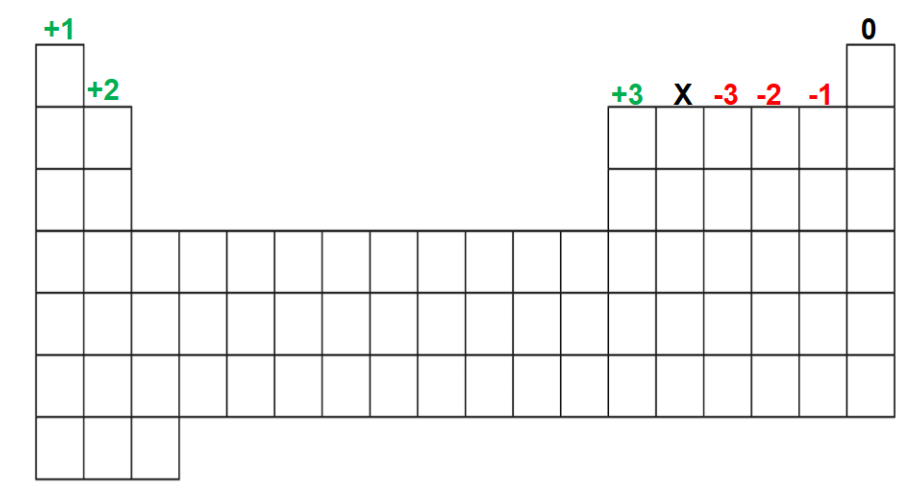
Naming Ionic Compounds with Transition Metals
Silver (Ag) always has a 1+ charge
Ag+
Zinc (Zn) is always 2+
Zn2+
No roman numeral is needed for Ag, Zn, Al, group 1 and group 2
Naming Acids
All acids have a Hydrogen in them
All acids will start with H
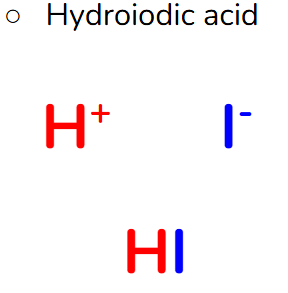
Naming Monatomic Acids
Acids with a monatomic anion
Use the prefix “hydro”
Use the name of the anion
but change the ending to -ic
Add the word acid at the end
Example:
HBr
Hydrobromic Acid
Naming Acids with Polyatomic Ions
Acids with a polyatomic ion
NO “hydro”
If the polyatomic ion ends in
“ate” → “ic”
“ite” → “ous”
Add the word acid at the end
Example:
H2SO4
Sulfuric acid
Example of Ionic Compound Formula
Calcium and Fluorine
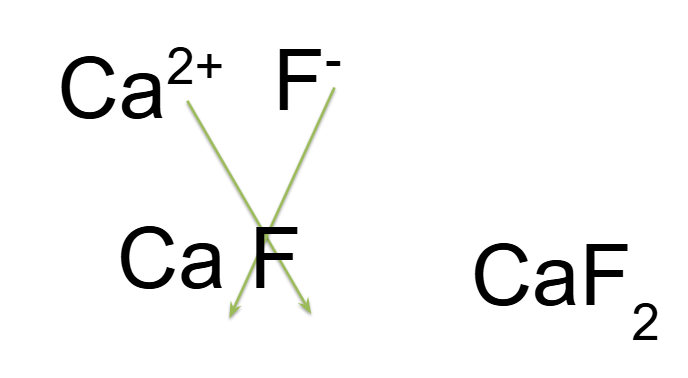
Example of Ionic Bond w/a transition metal