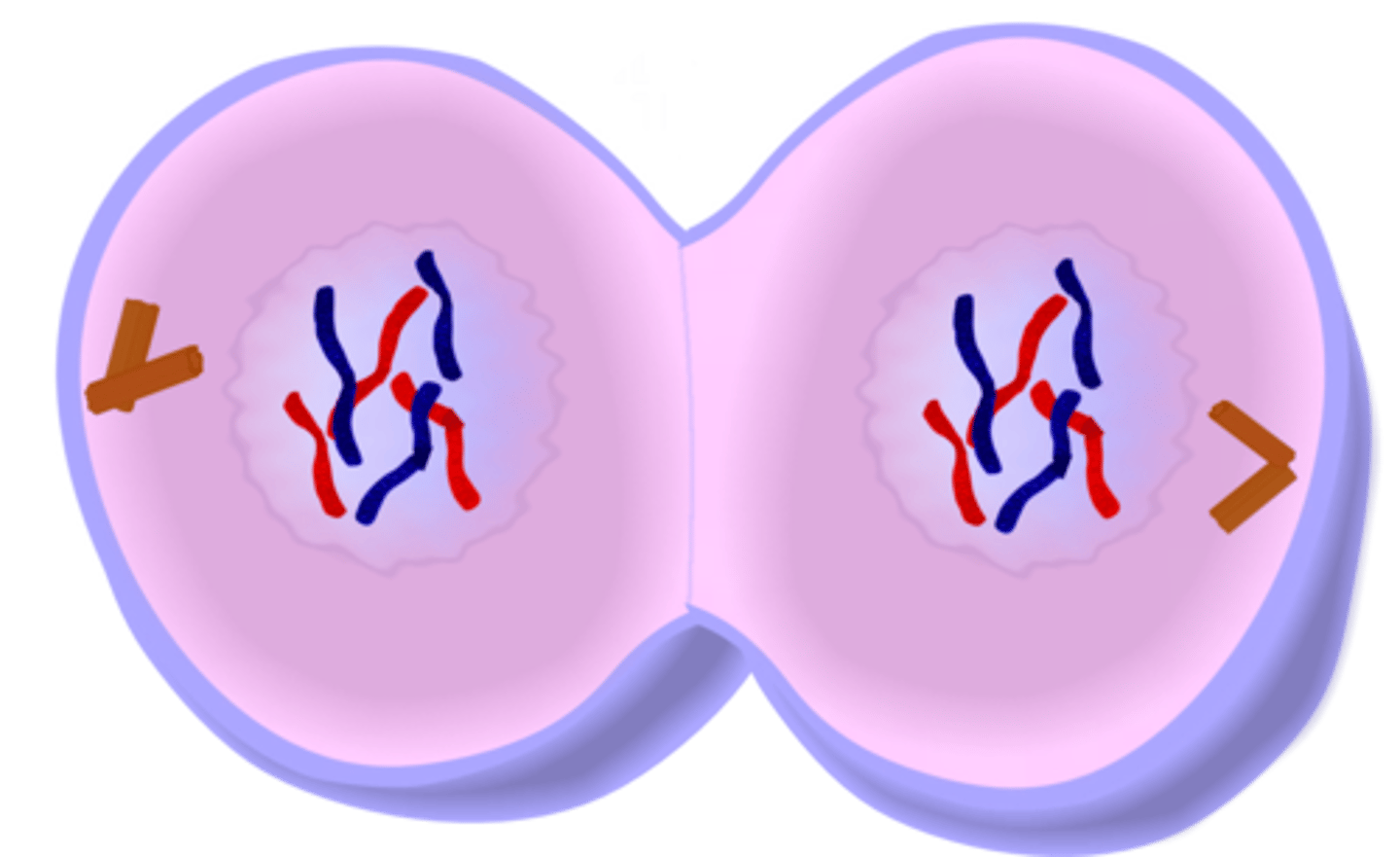
Mitosis and Meiosis
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
meiosis
type of cell division that results in 4 daughter cells that each have half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.

Diploid
A cell containing two full sets of chromosomes 2n=46.
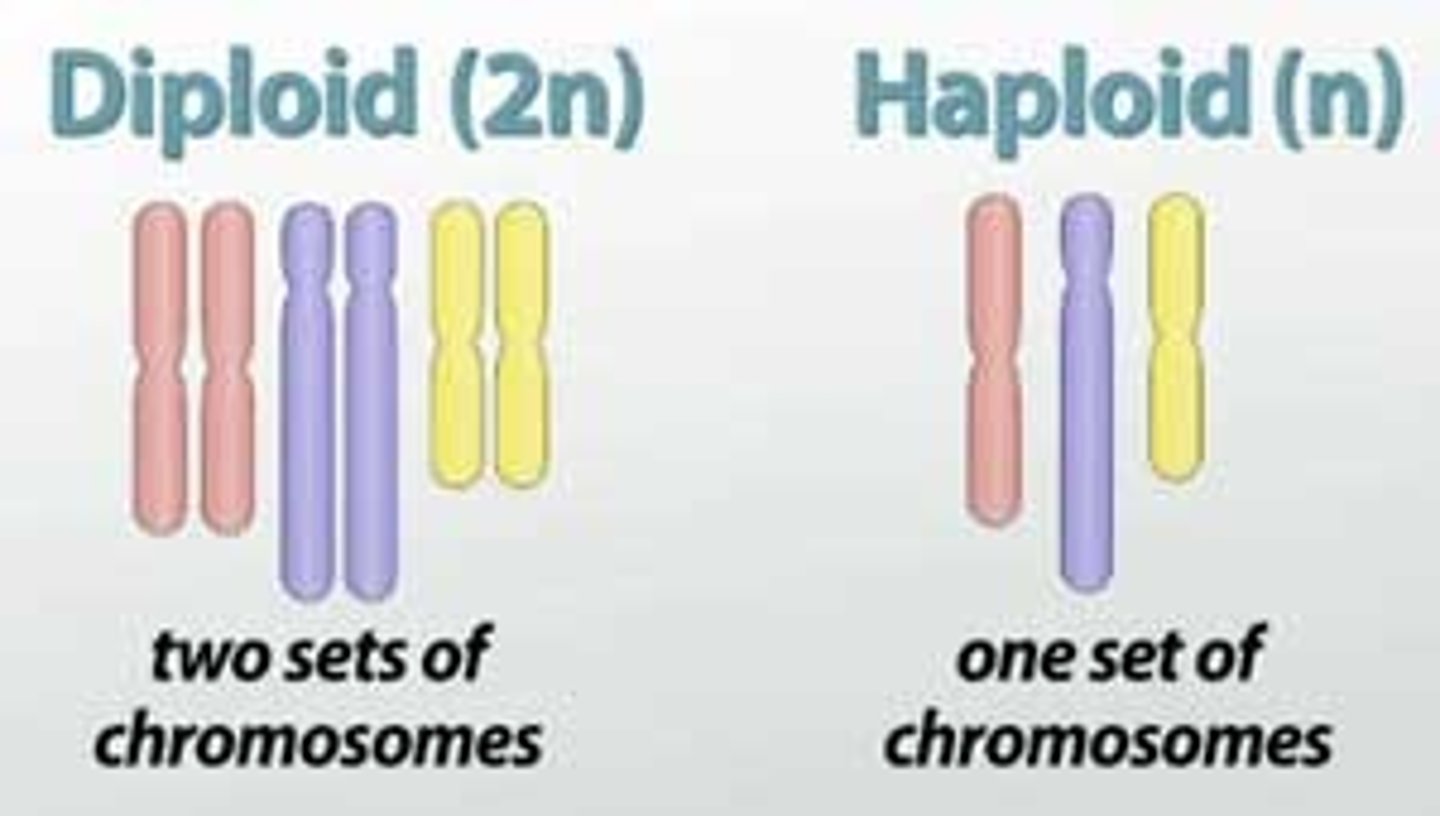
Haploid
A cell containing a single/ half set of chromosomes n=23
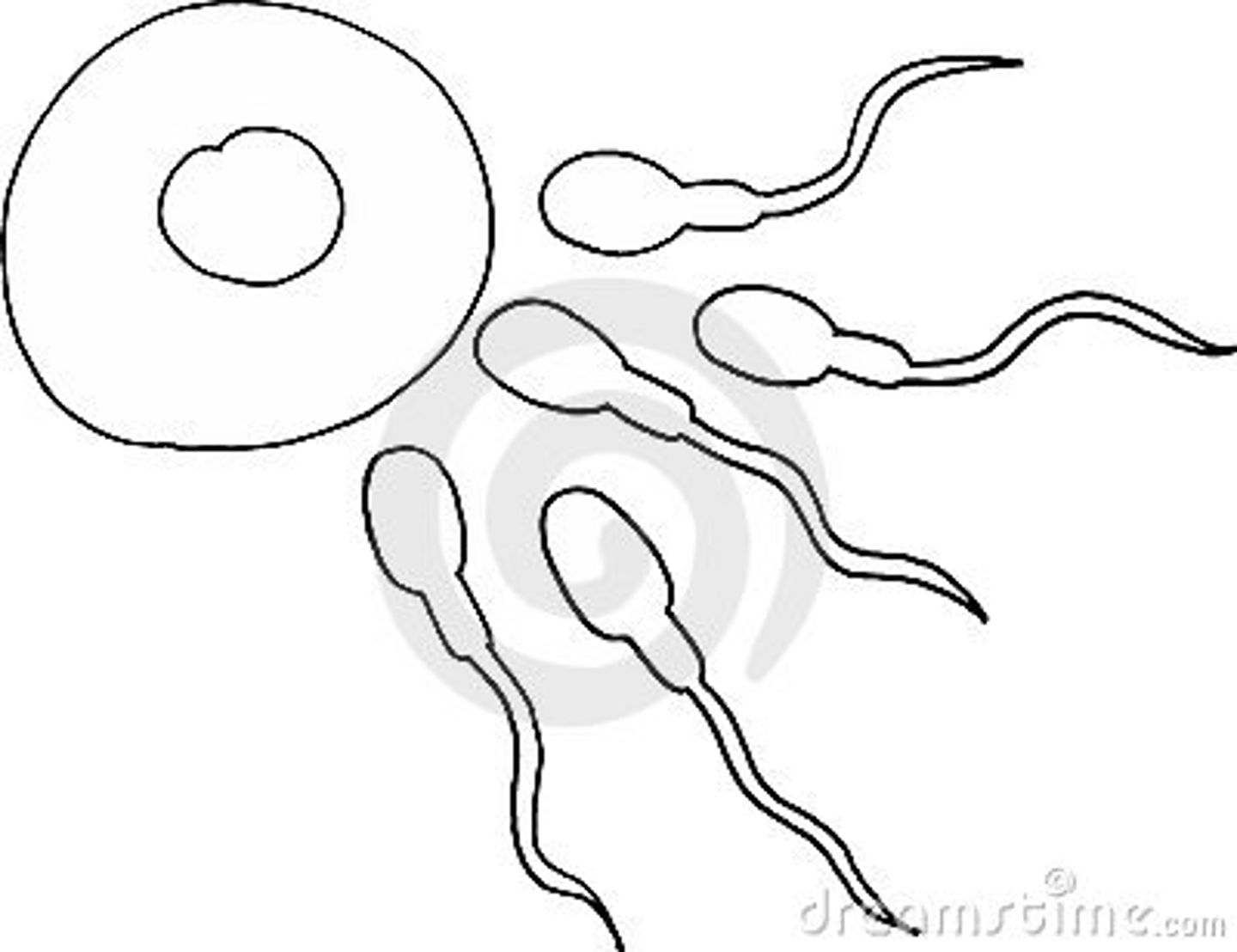
Gametes
A haploid male or female germ cell (e.g. sperm and egg) produced via meiosis
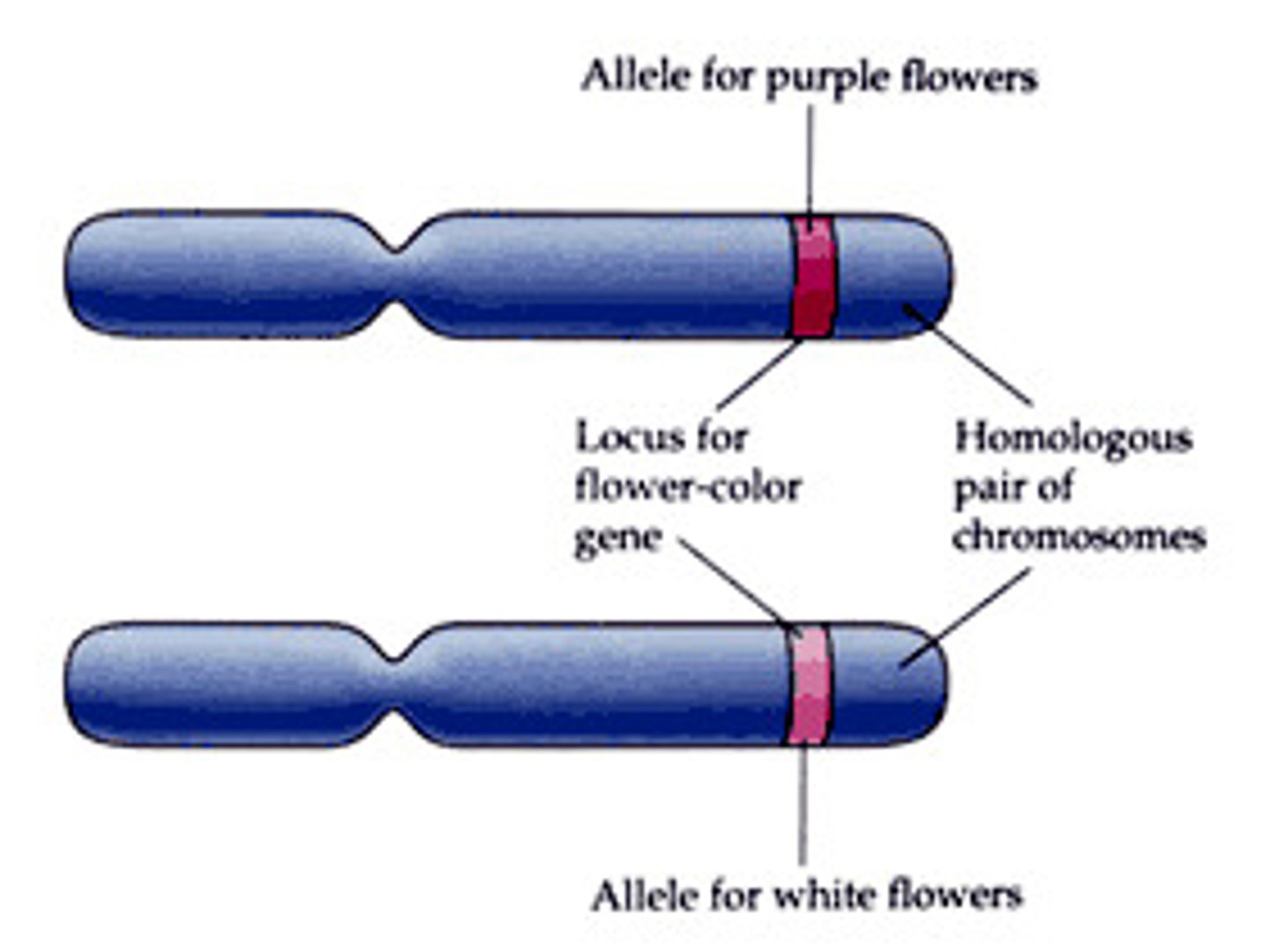
gene
a section of the DNA (chromosome) that codes for a specific trait (e.g. eye color or hair color)
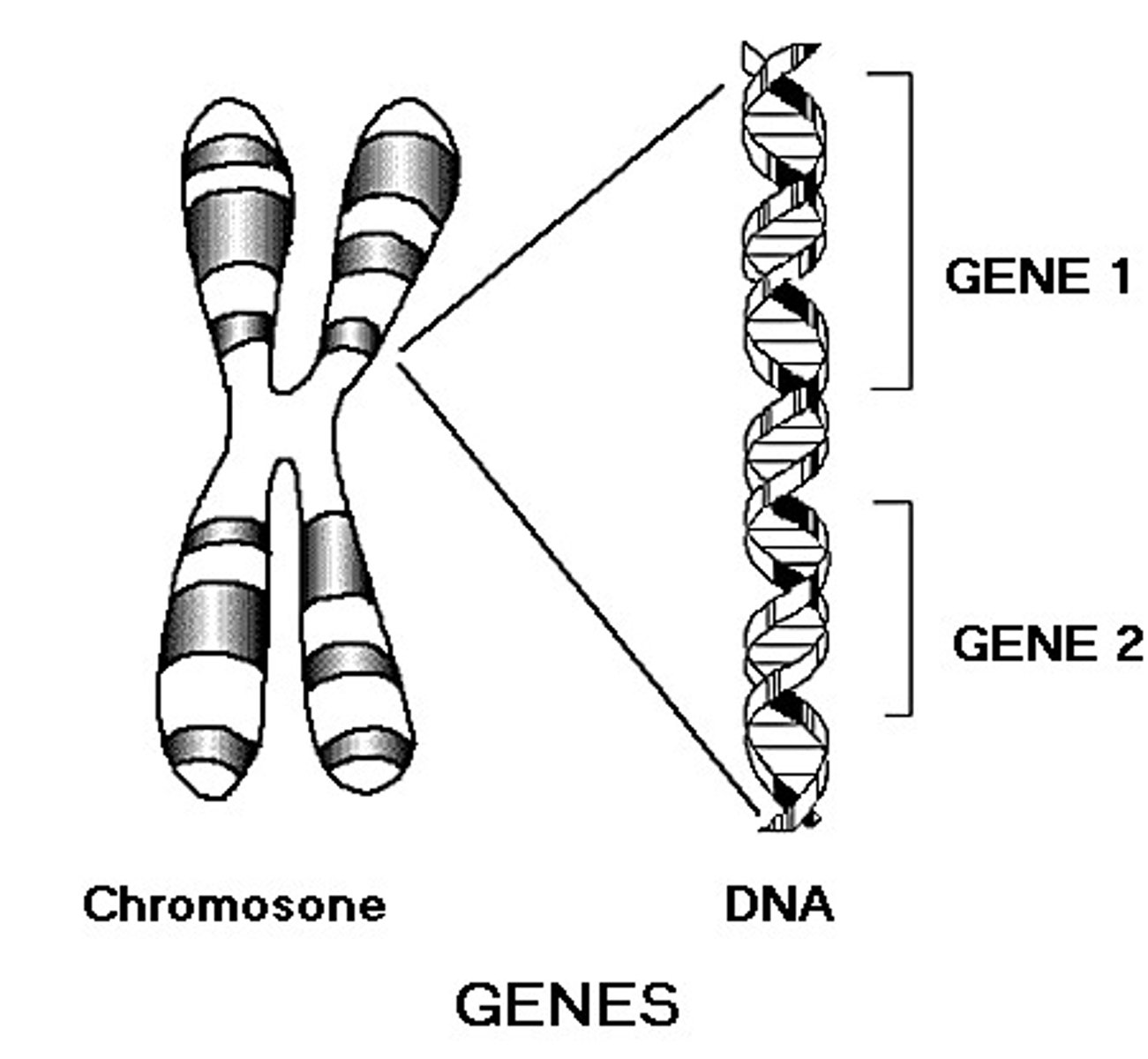
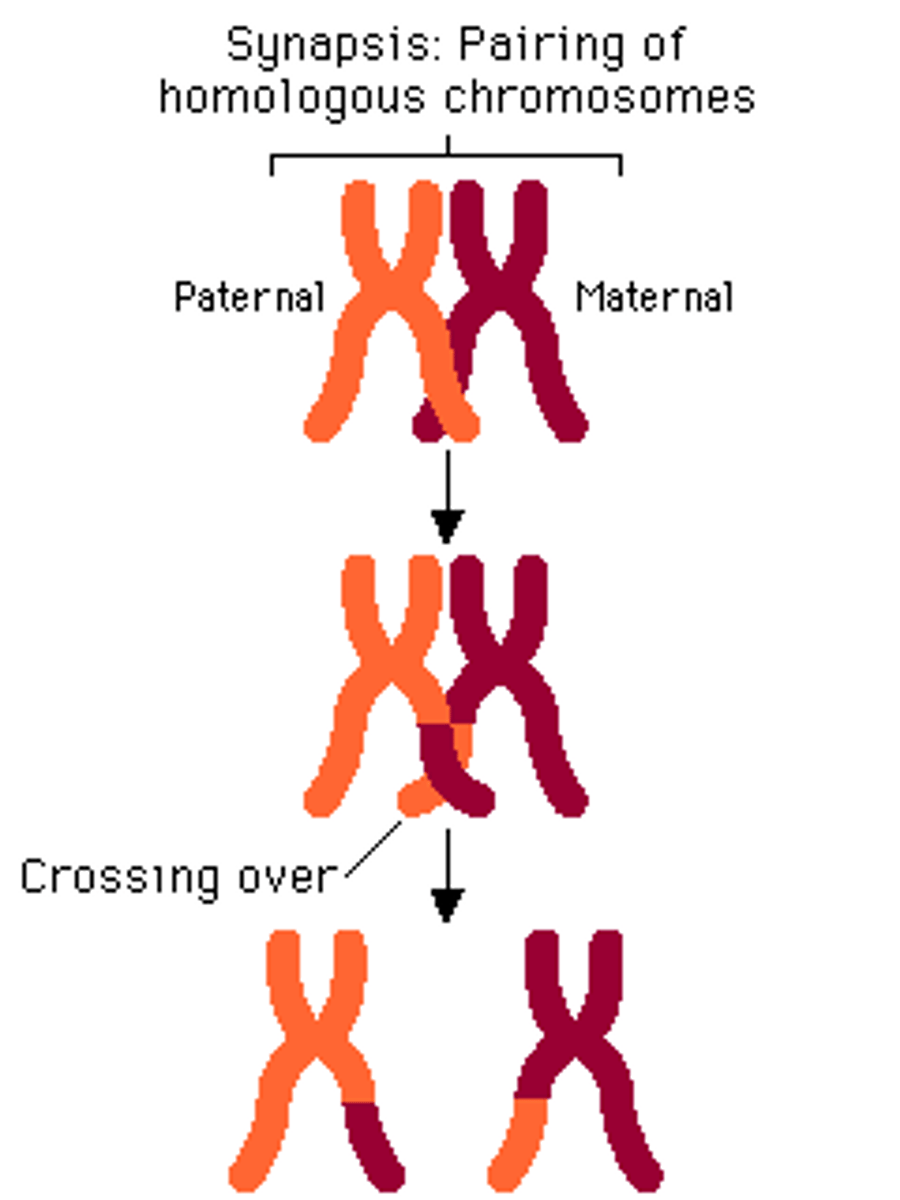
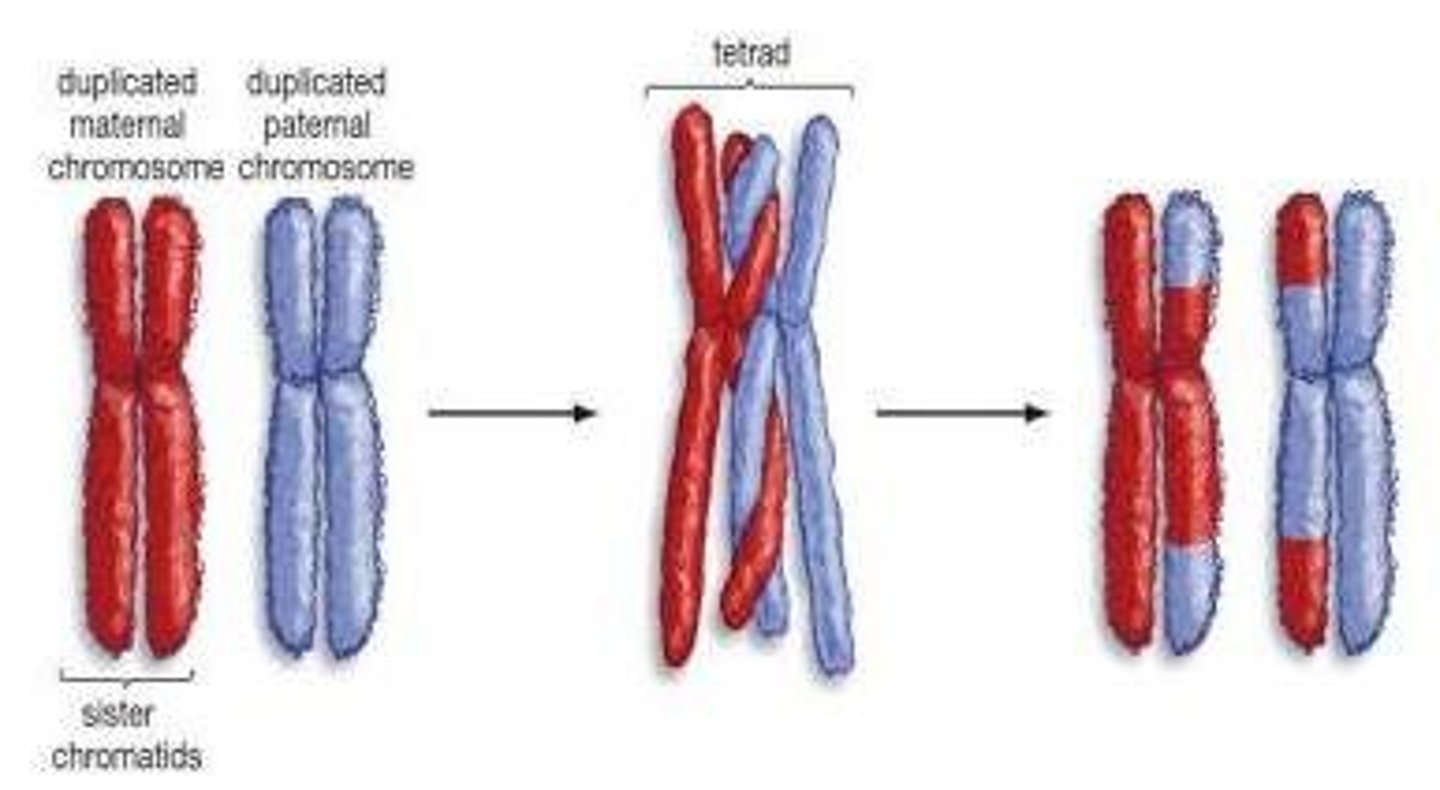
crossing over
when homologous chromosomes exchange genes during Prophase 1 creating new mixture of parent traits in their offspring
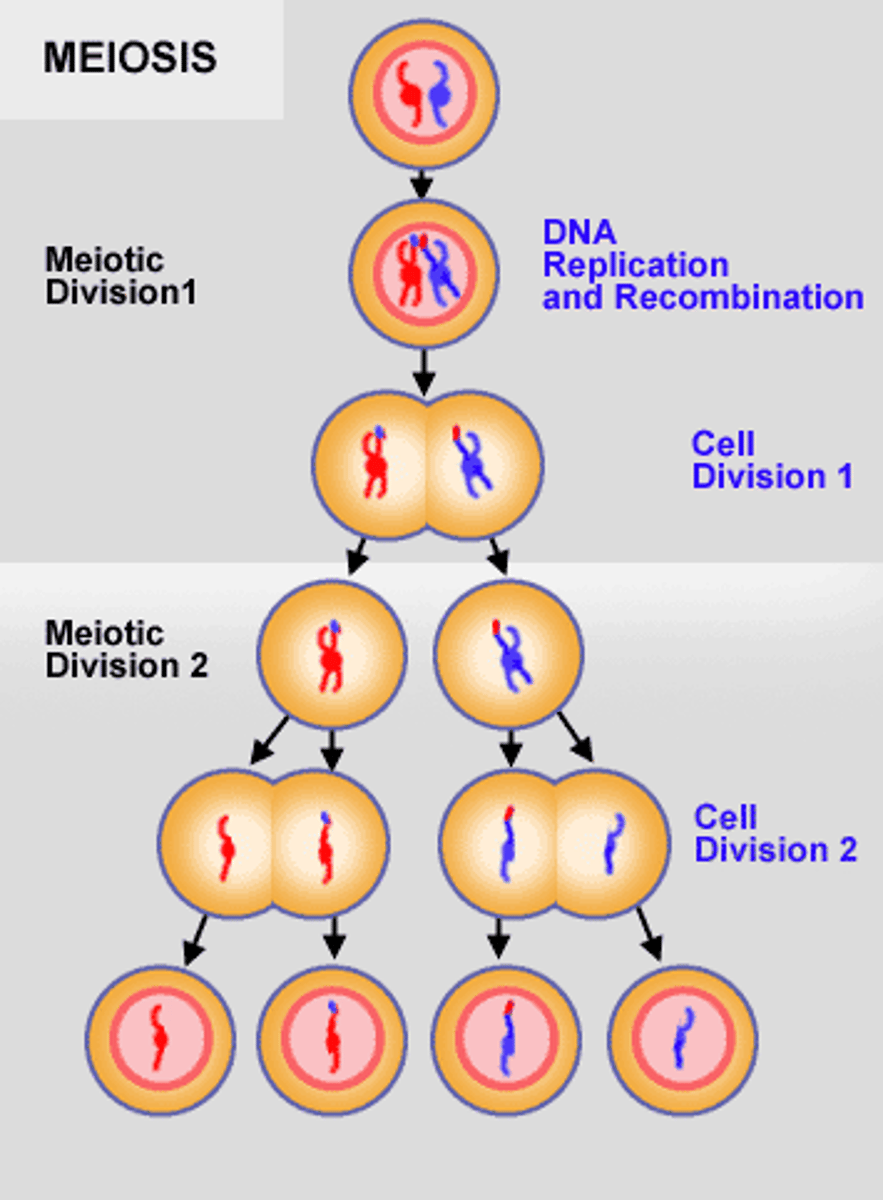
Meiosis I
PMAT I: The first cell division of meiosis when the homologous pairs are split up into two separate cells.
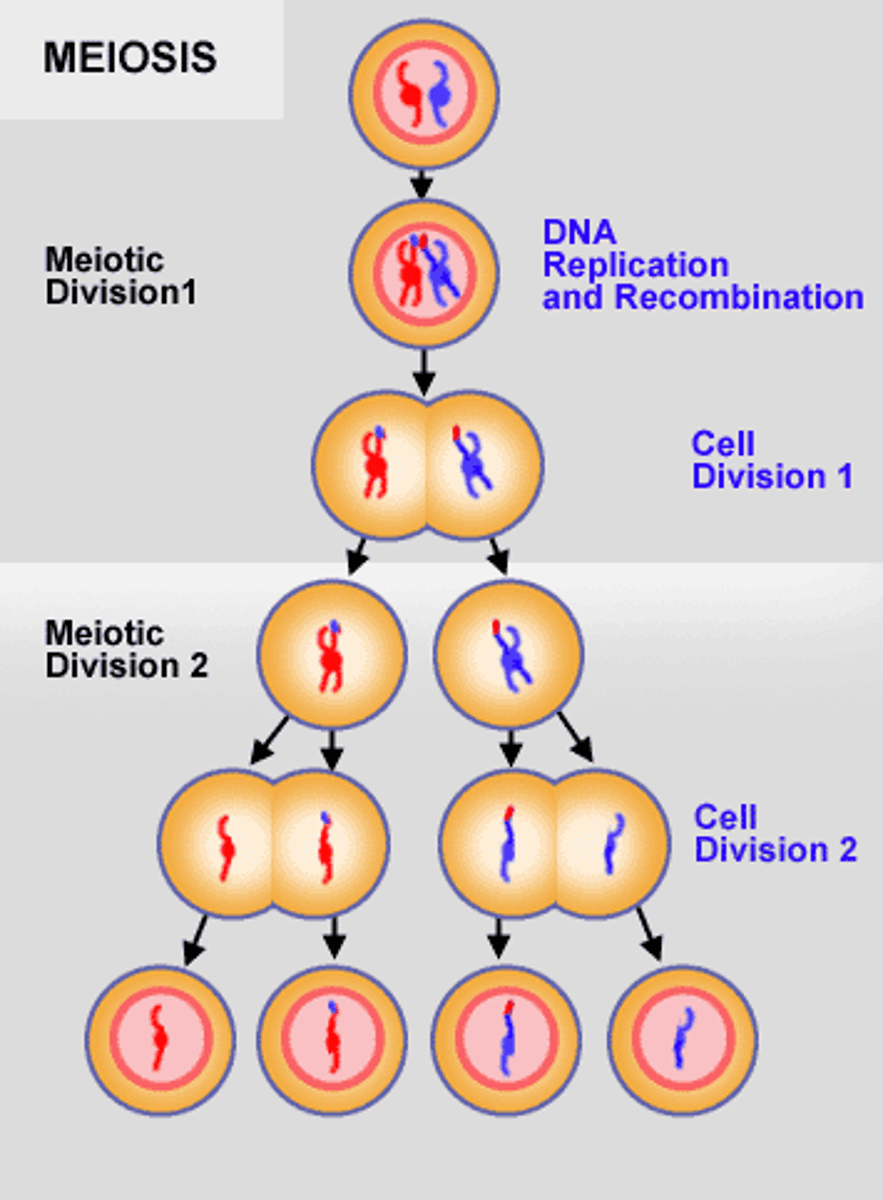
Meiosis II
PMAT II: The second cell division of meiosis. This is when the sister chromatids are split up into two separate cells.
Mitosis
Produces cells almost genetically identical
46 pairs of chromosomes
How many pairs of chromosomes present in humans
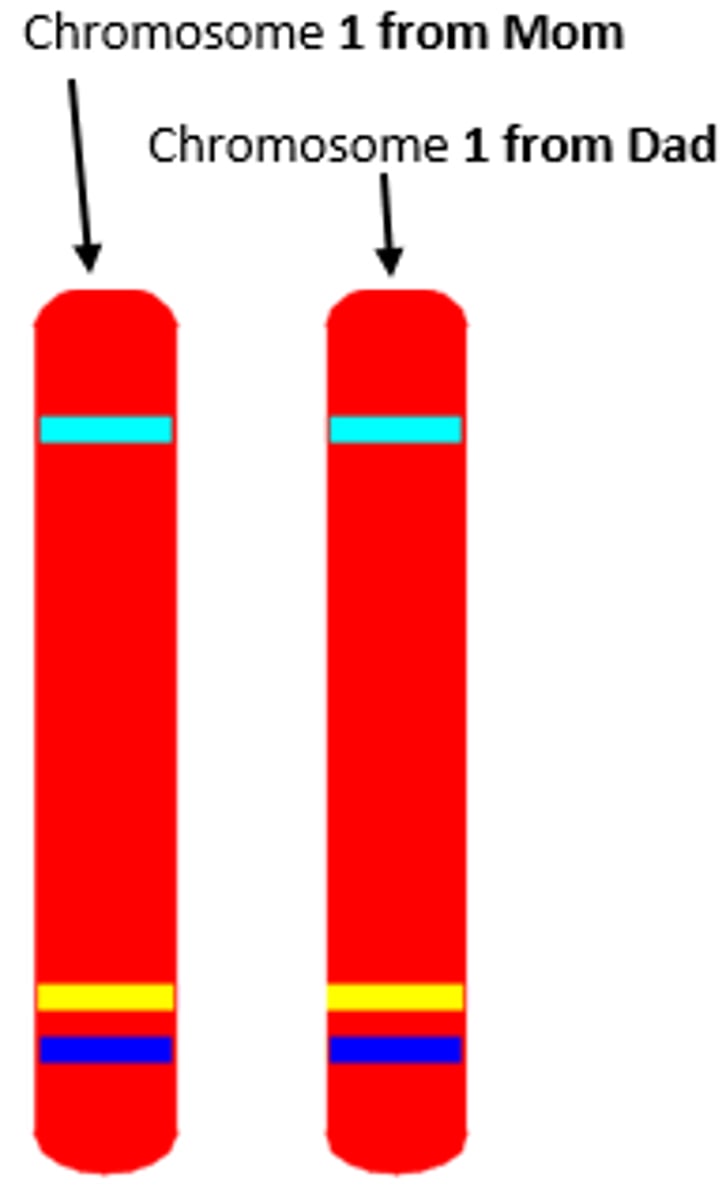
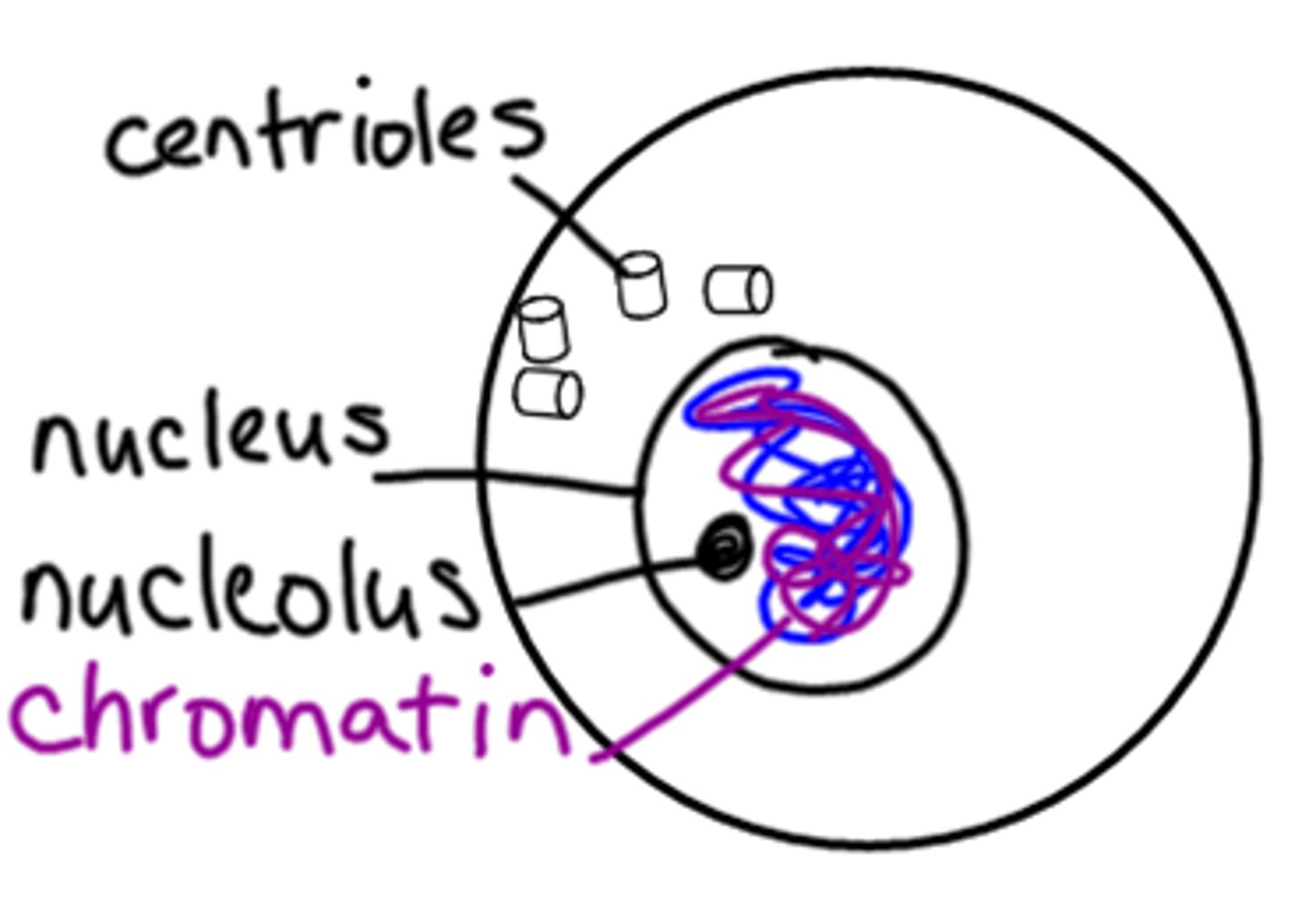
Chromosome
Coiled up DNA
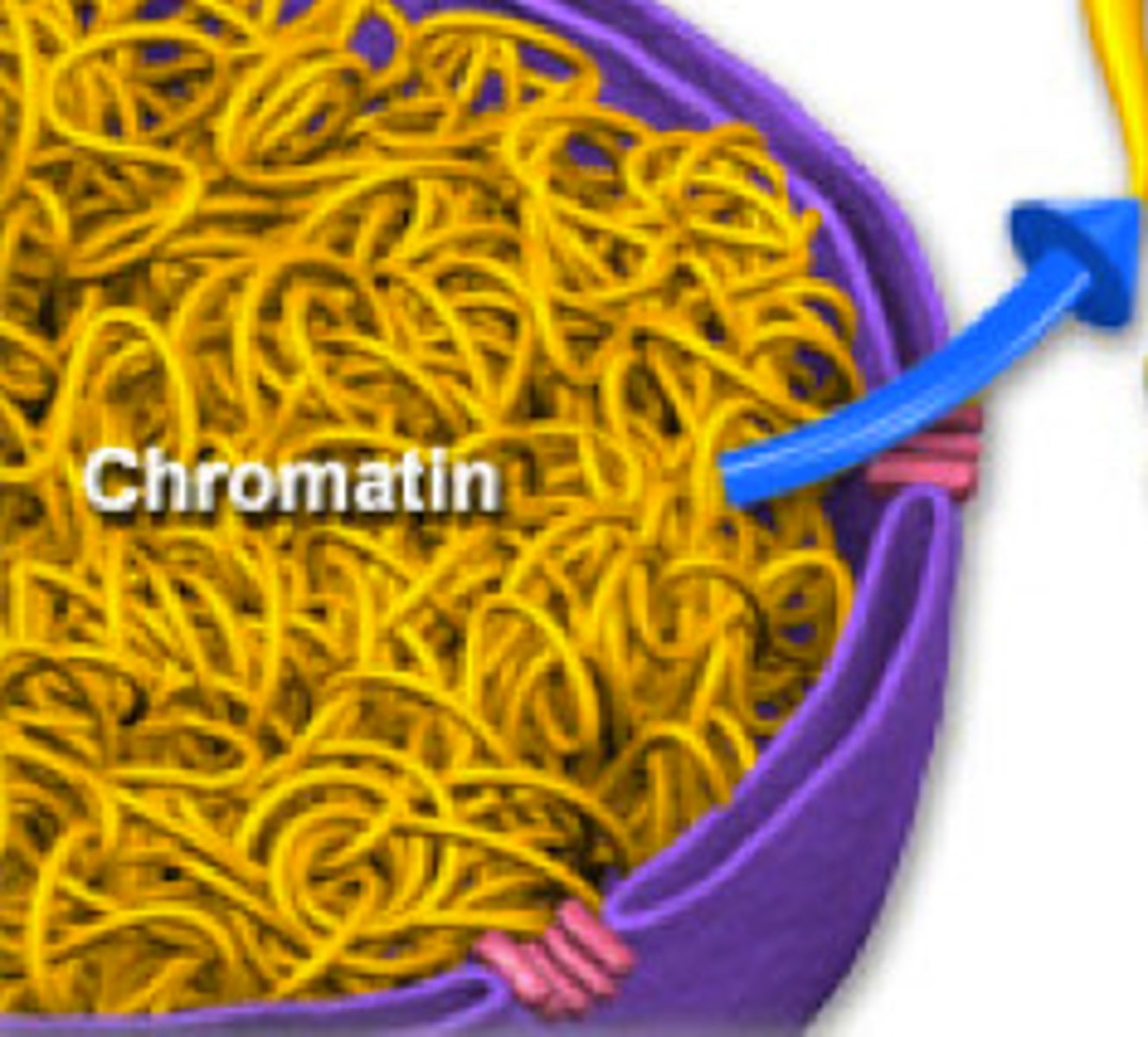
Chromatin
Uncoiled DNA. Present in interphase
Somatic
Body cells (liver, skin, etc), The type of cells that undergo mitosis
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosomes of the same size and length that carry the same type of information (gene for hair color), one from mom and one from dad
Function and location of Mitosis
Cell division for growth, repair or maintenance. Occurs in somatic cells.
PMAT
Function and location of Meiosis
Cell division for gamete production (sperm and eggs). Happens in gonads (ovaries and testes).
PMATPMAT
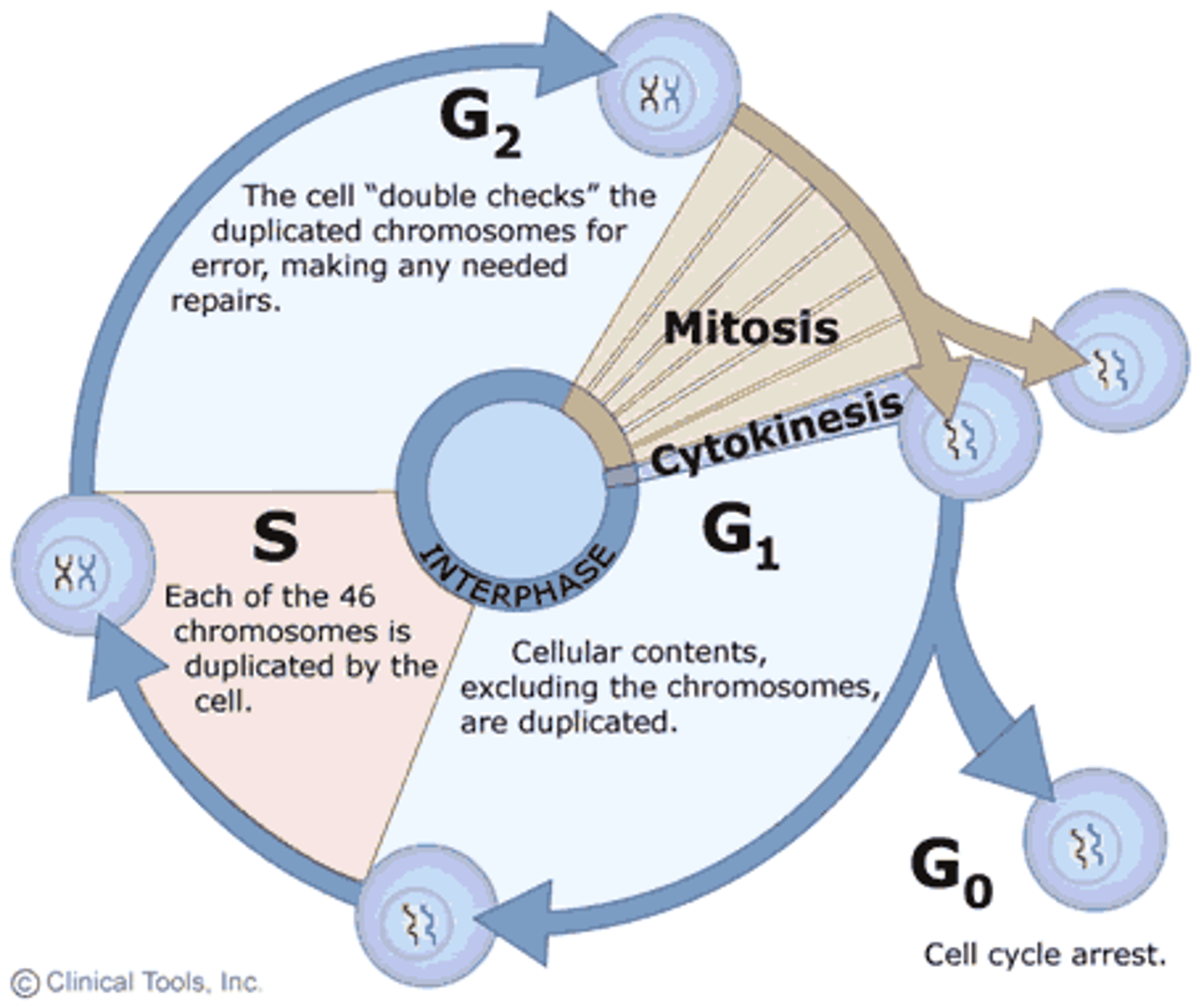
Phases of the Cell Cycle
1. Interphase (G1, S, G2)
2. Mitosis (PMAT)
3. Cytokinesis (cell division)
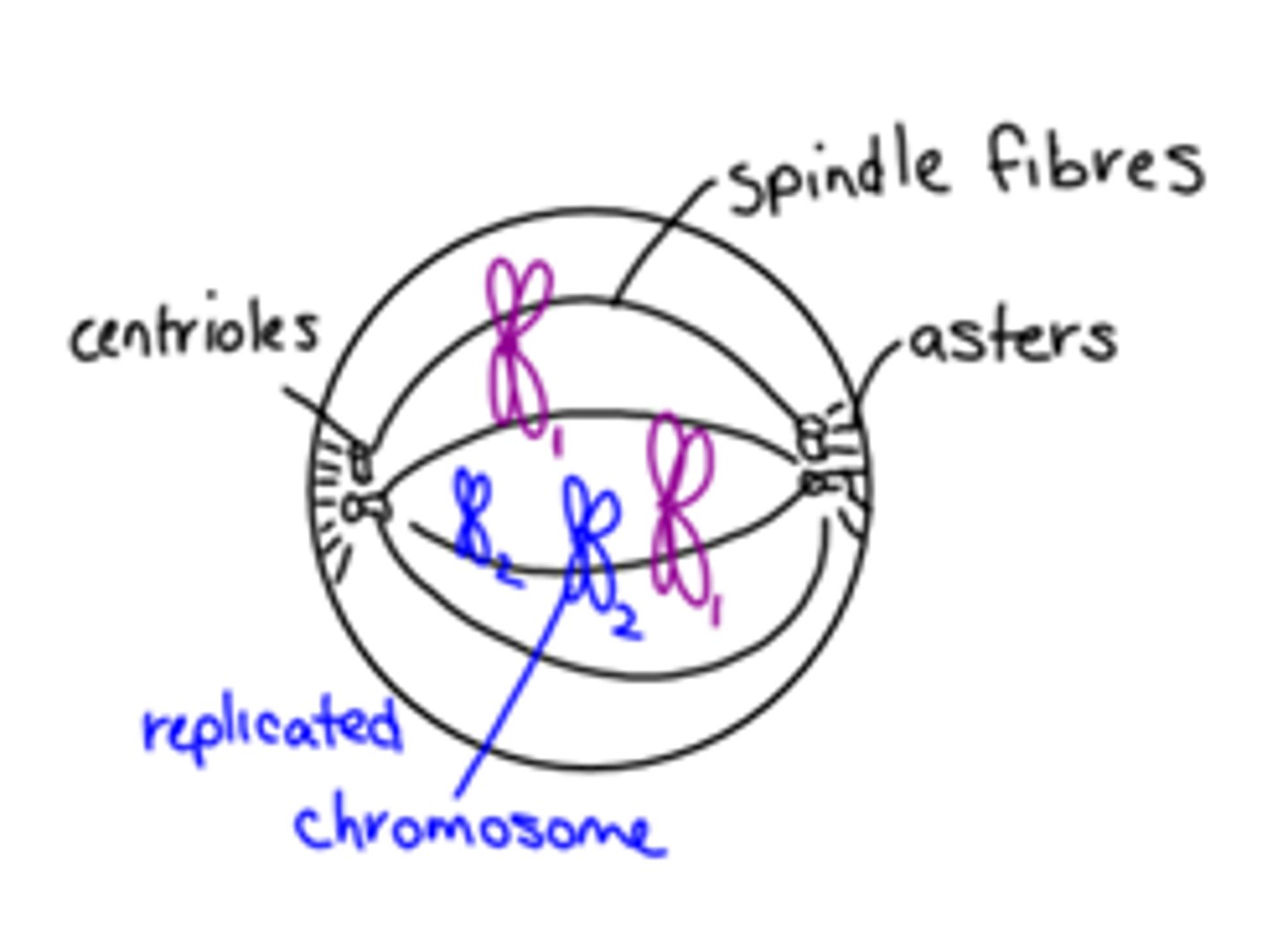
Events in Prophase
Chromatin coils up into chromosomes.
Centrioles move to poles.
Spindle fibres and asters form. Nucleus and nucleolus
disappear.
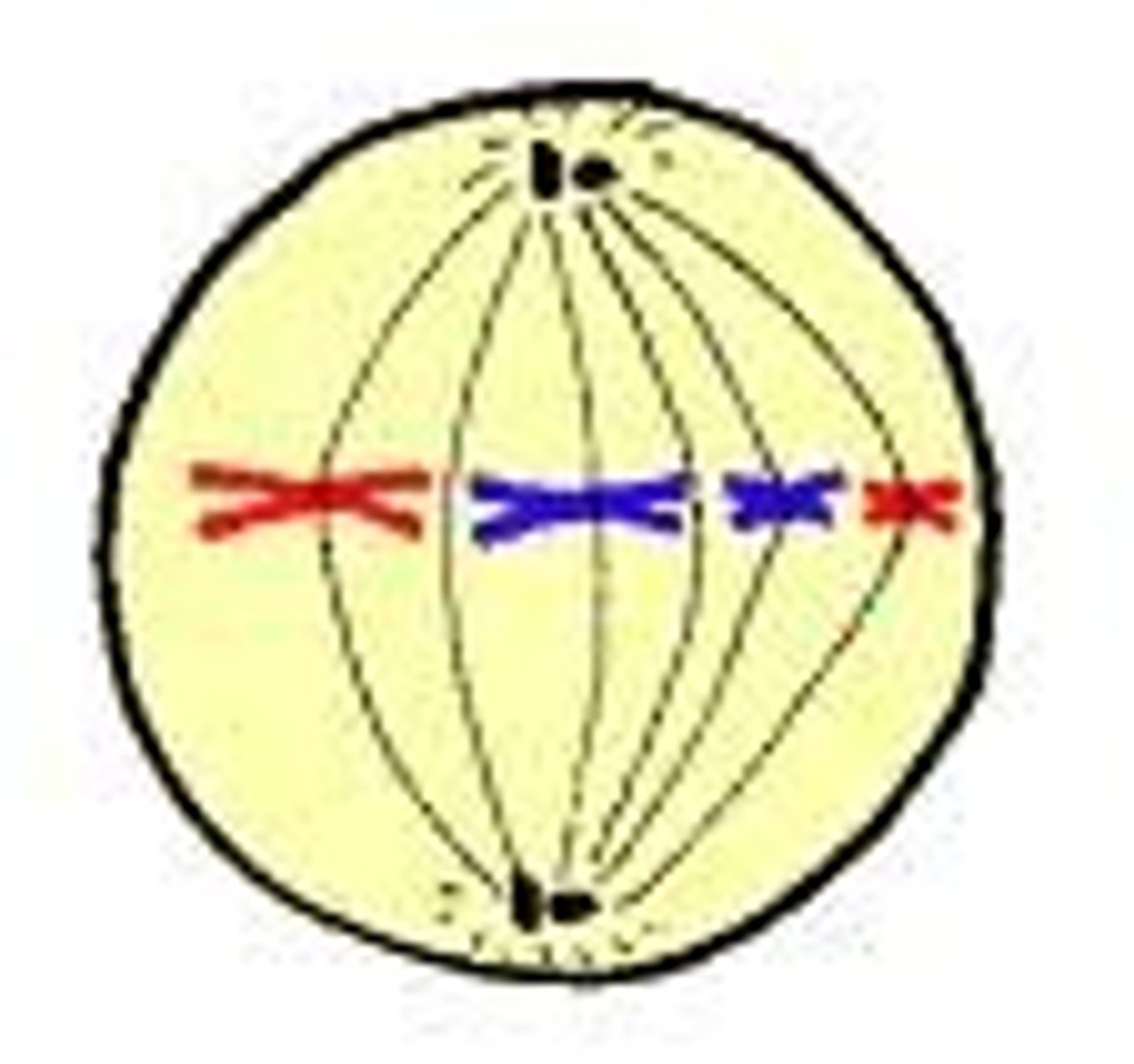
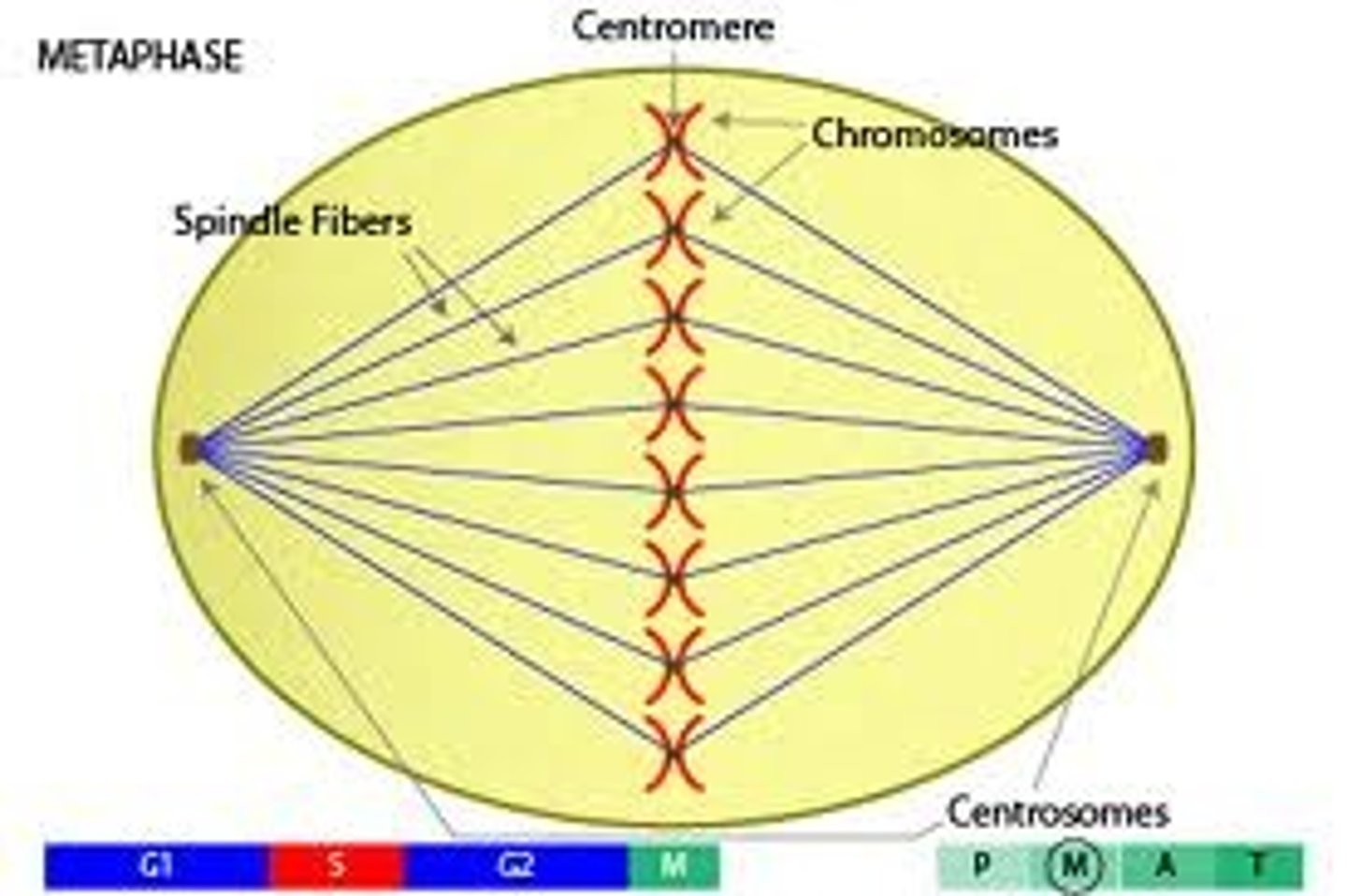
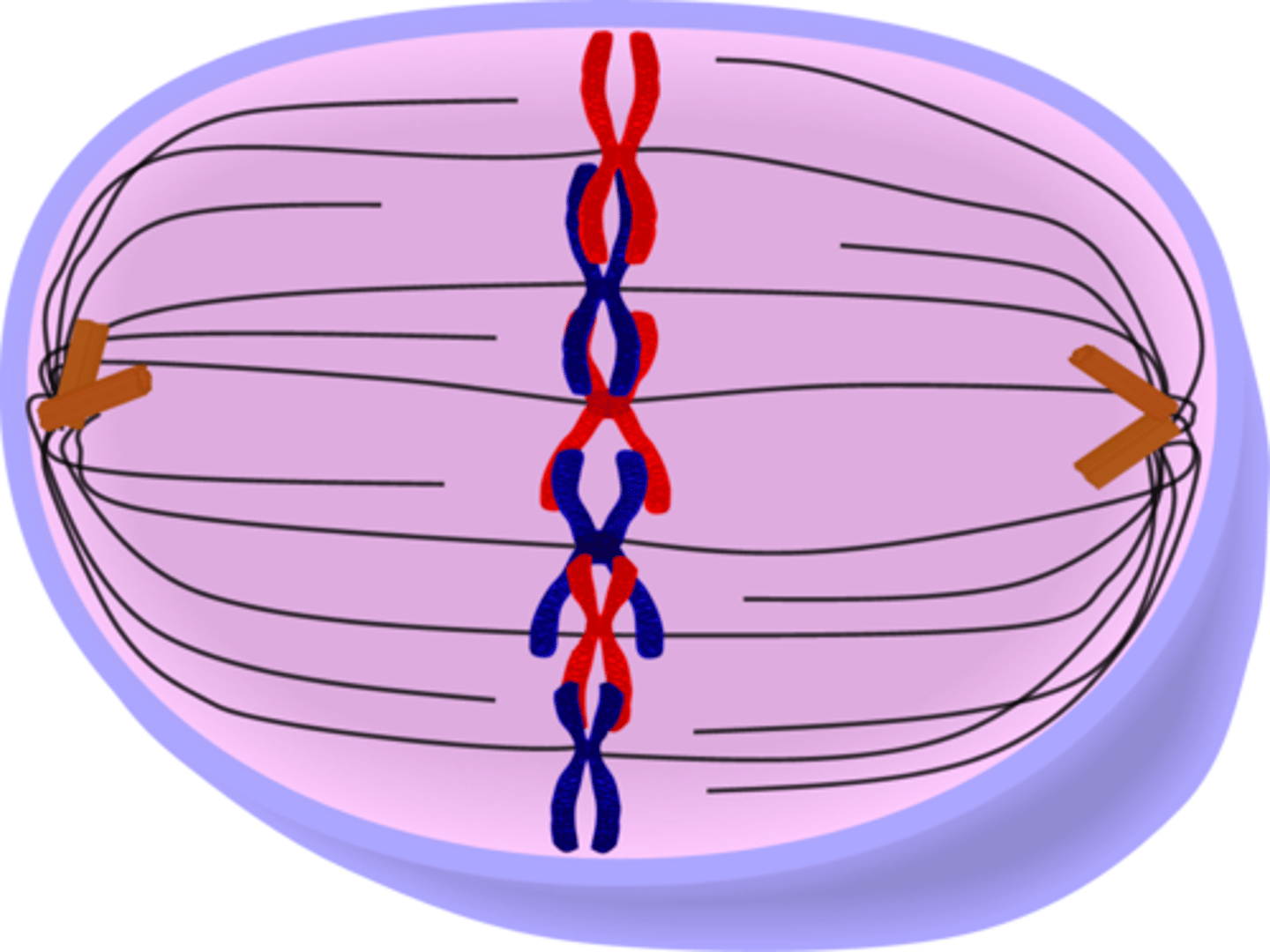
Events in Metaphase
Chromosomes line up at the metaphase plate.
MIDDLE
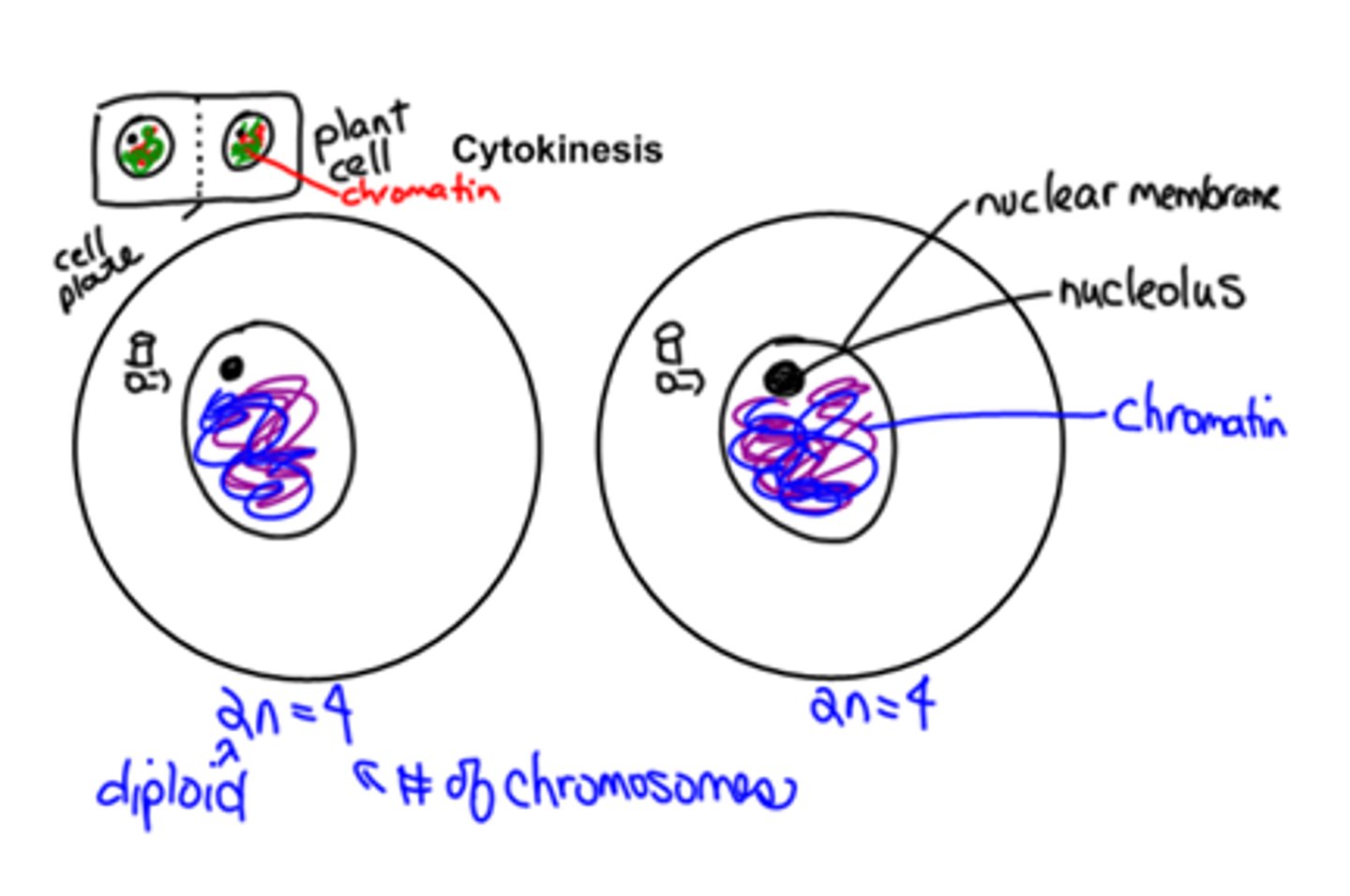
Cytokinesis
Cell divides into two. Cell plate forms in plant cells.
Cancer cells
Cells that keep reproducing. Can move and grow in another part of the body - metastasis. Don't specialize
Sexual Reproduction
Requires male and female gametes. Variation.
Asexual Reproduction
One parent only. (cloning)
Mitosis.
Parthenogenesis in reptiles.
Crossing over
Homologous chromosomes may exchange genetic material during prophase I.
Occurs more often in genes that are further apart.
Interphase I
G1 - growth, protein synthesis
S - DNA replicates
G2 - growth, protein synthesis
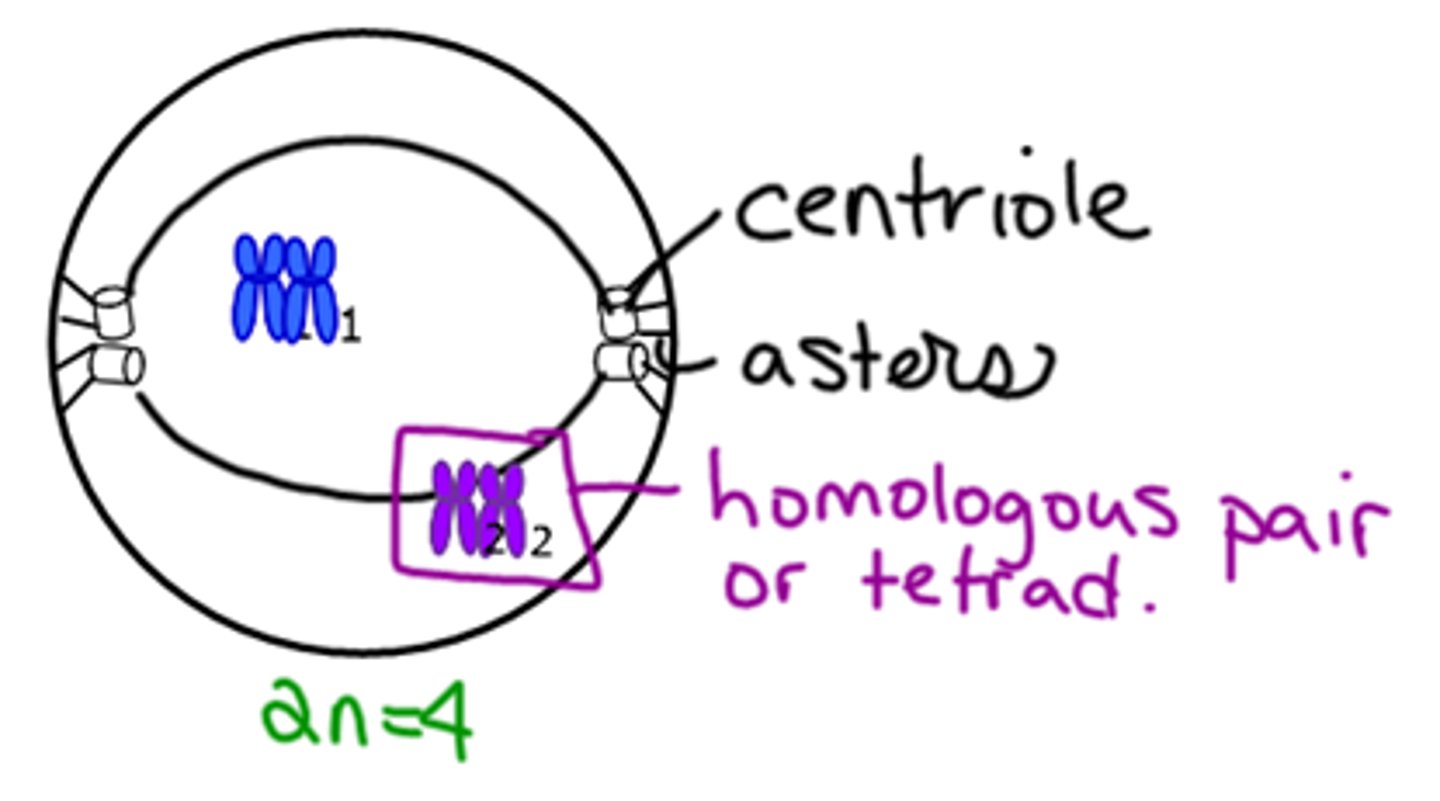
Prophase I
Synapsis - homologous chromosomes (tetrads) pair up.
Crossing over may occur - exchange of genetic material.
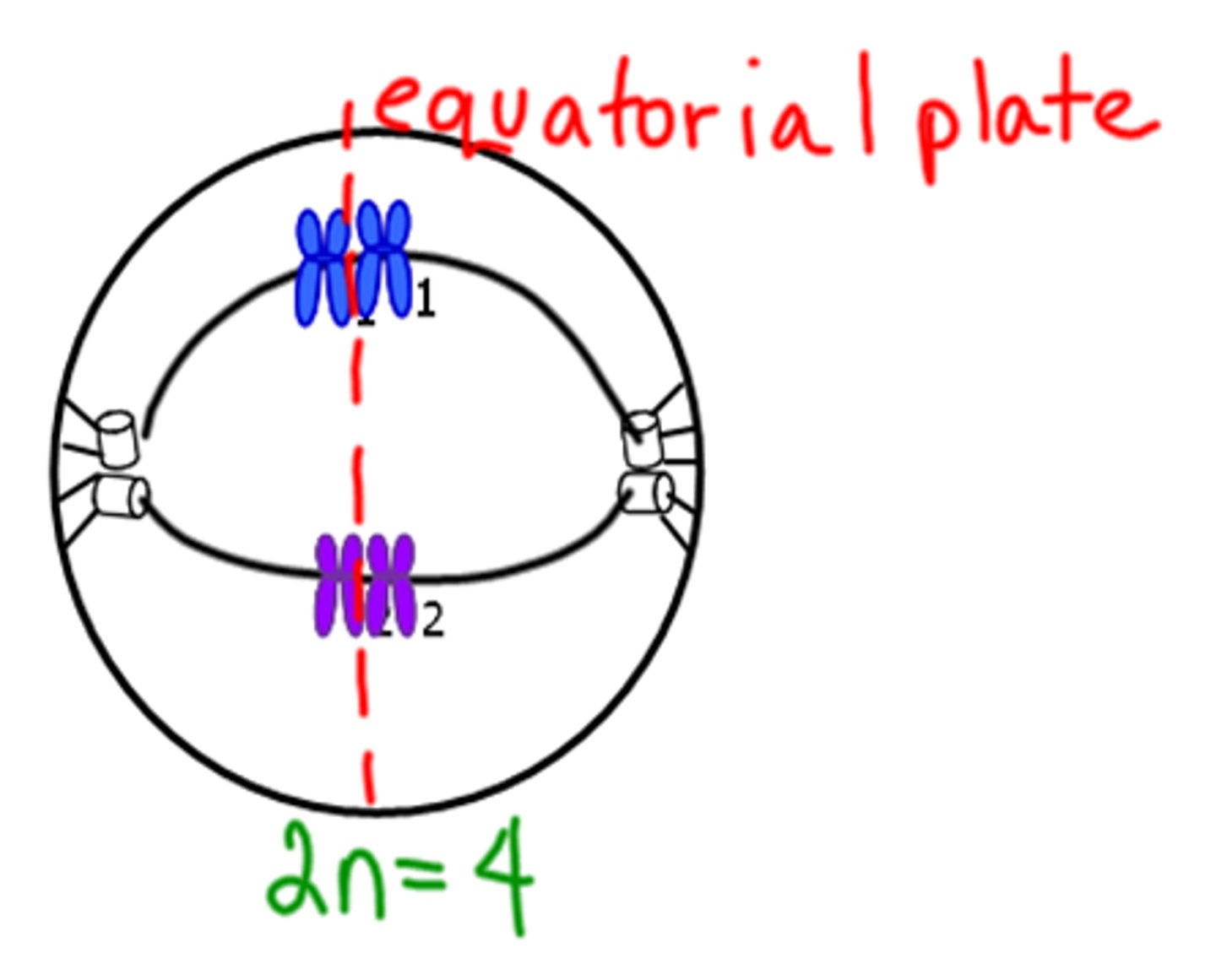
Metaphase I
Homologous pairs line up in the middle on the metaphase plate.
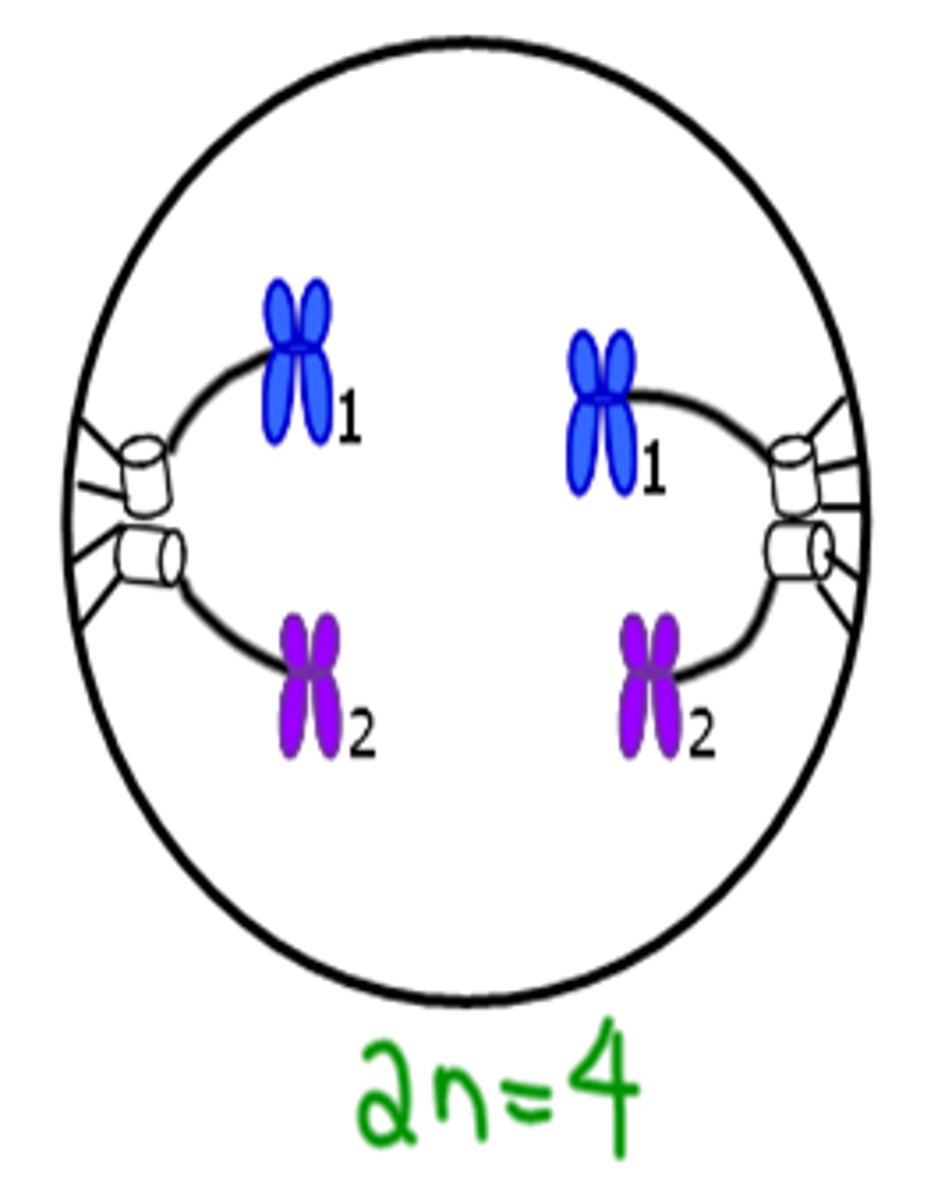
Anaphase I
Segregation - Homologous pairs separate to opposite poles.
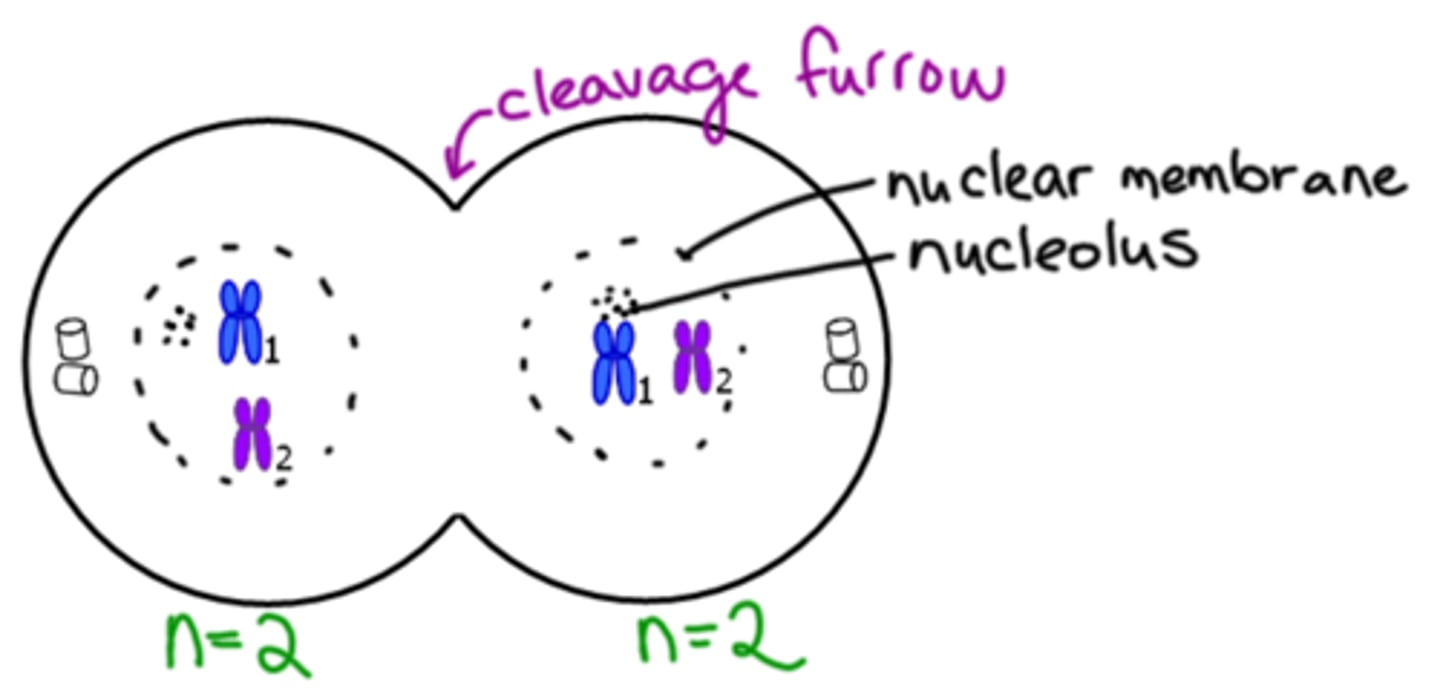
Telophase I
Cleavage furrow. Replicated chromosomes reach the poles.
Prophase II
Chromosomes can be seen.
Cells are haploid (n).
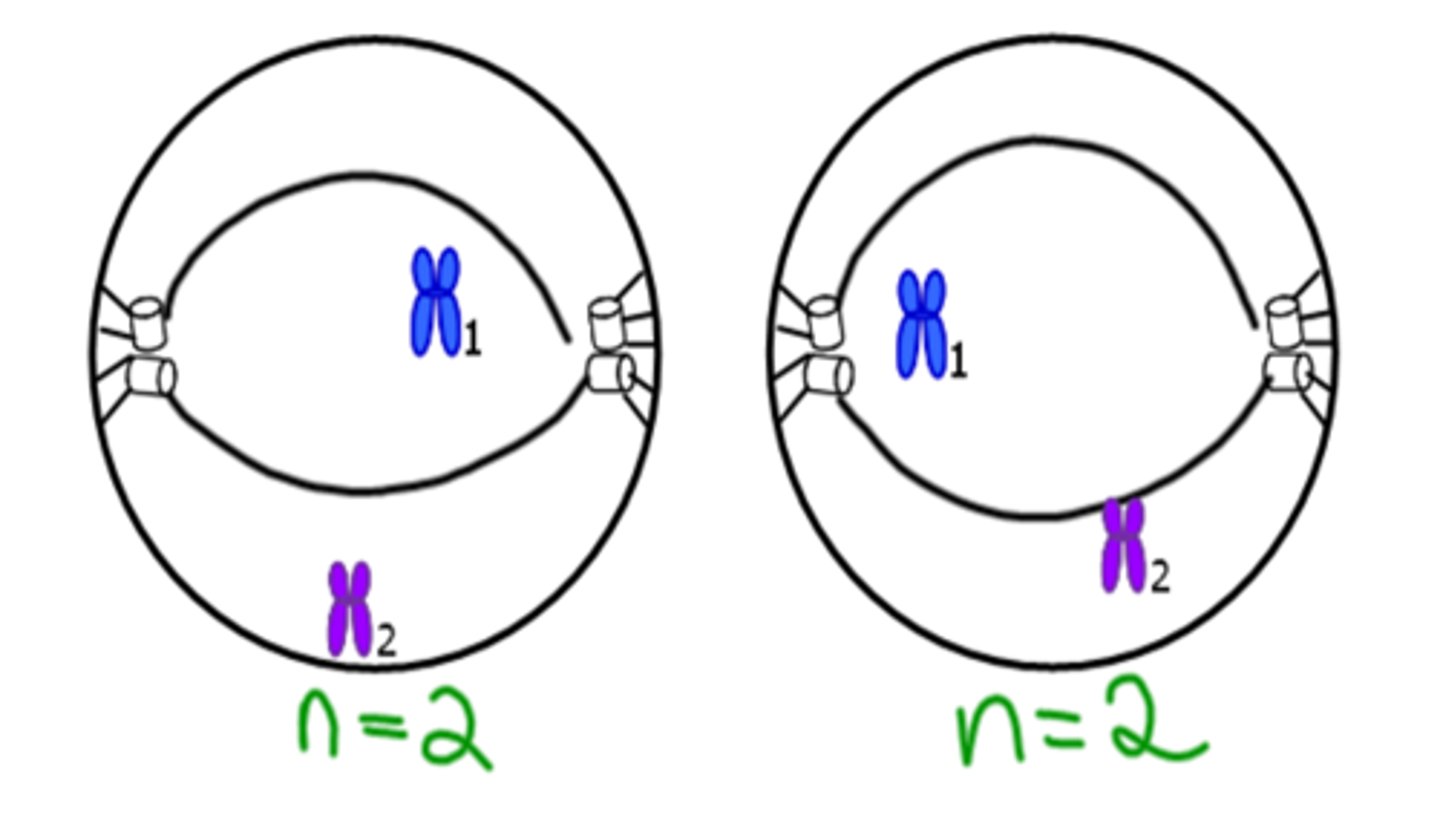
Metaphase II
Chromosomes line up in the middle
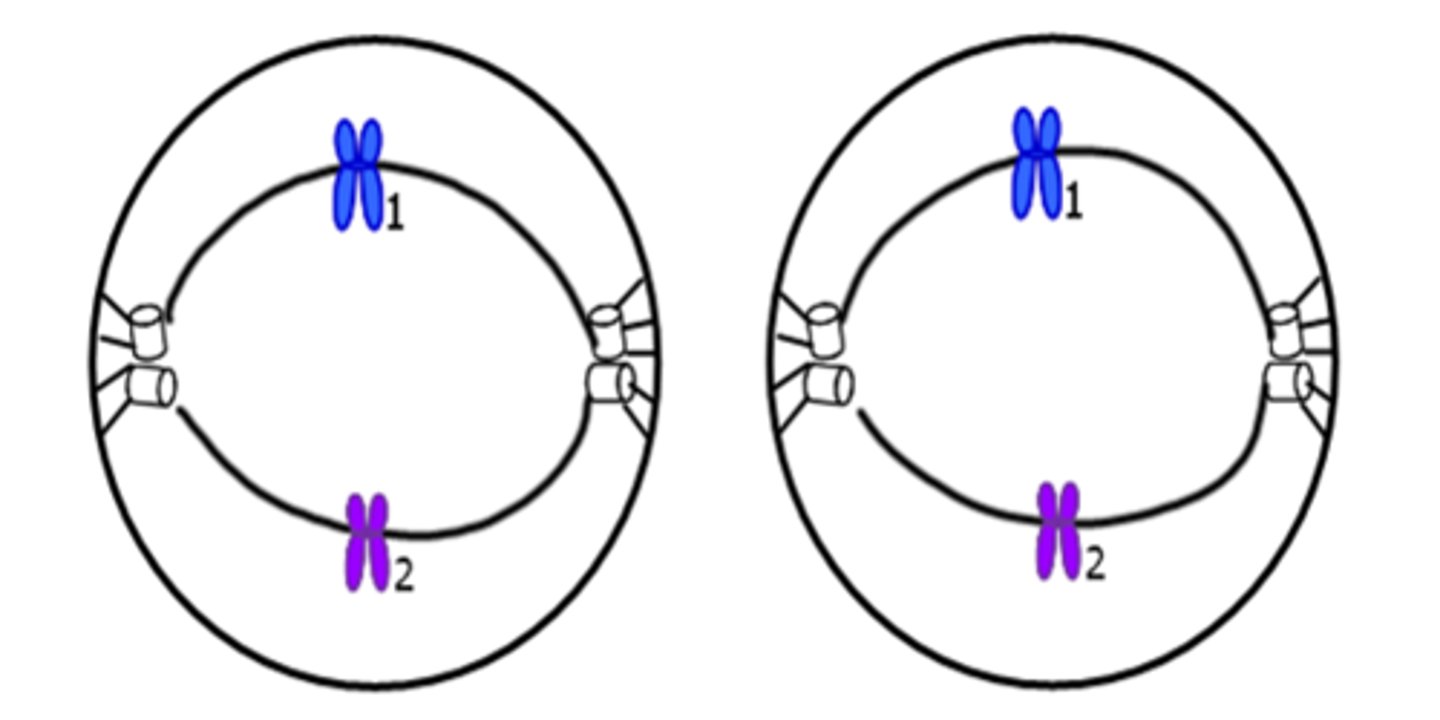
Anaphase II
Centromeres split. Single chromosomes move apart.
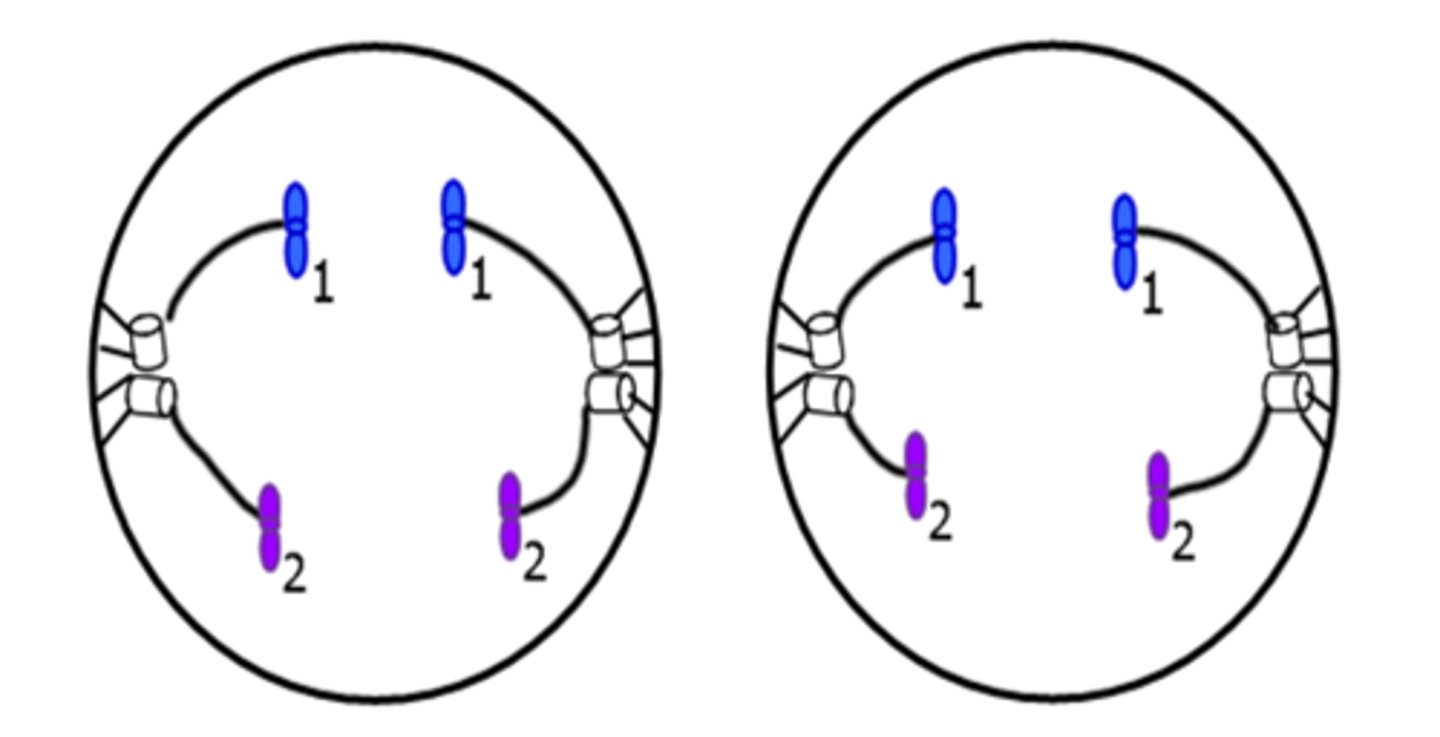
Telophase II
Cleavage furrow.
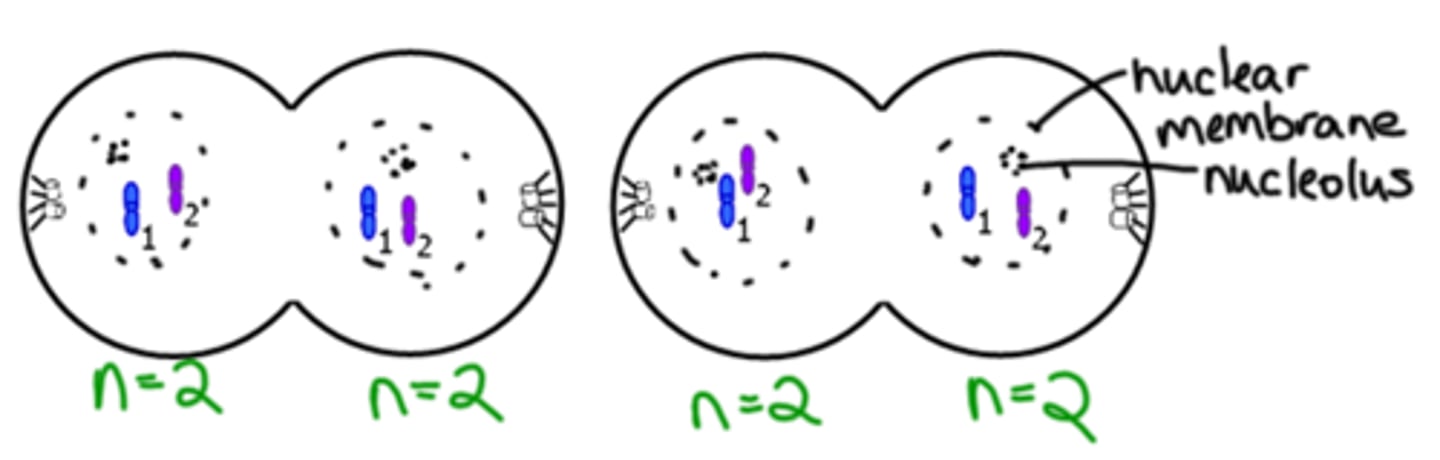
Fertilization
When a sperm enters an egg. It doubles the chromosome number.
Ex. In humans:
Sperm (23) + egg (23) = zygote (46 chromosomes) OR n + n = 2n
Zygote
sperm + egg or fertilized egg
2n
Sources of variation
1. Gamete success
2. Crossing over
3. Independent Assortment
Independent Assortment
The way the homologous pairs line up in Metaphase I is RANDOM!
tetrad
structure containing four chromatids that forms during meiosis to allow for crossing over to occur
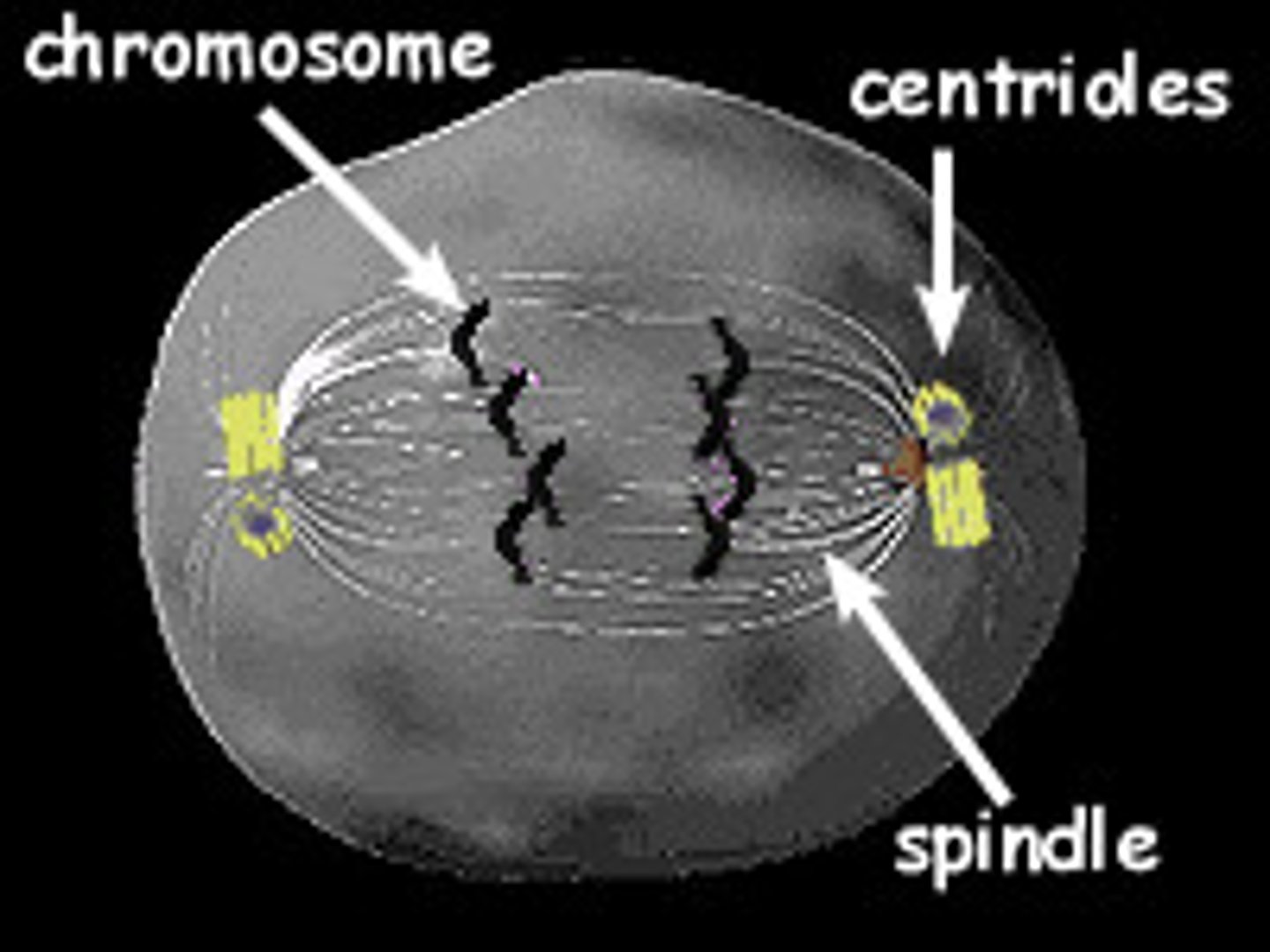
Centrioles
Cell organelle that aids in cell division in animal cells only
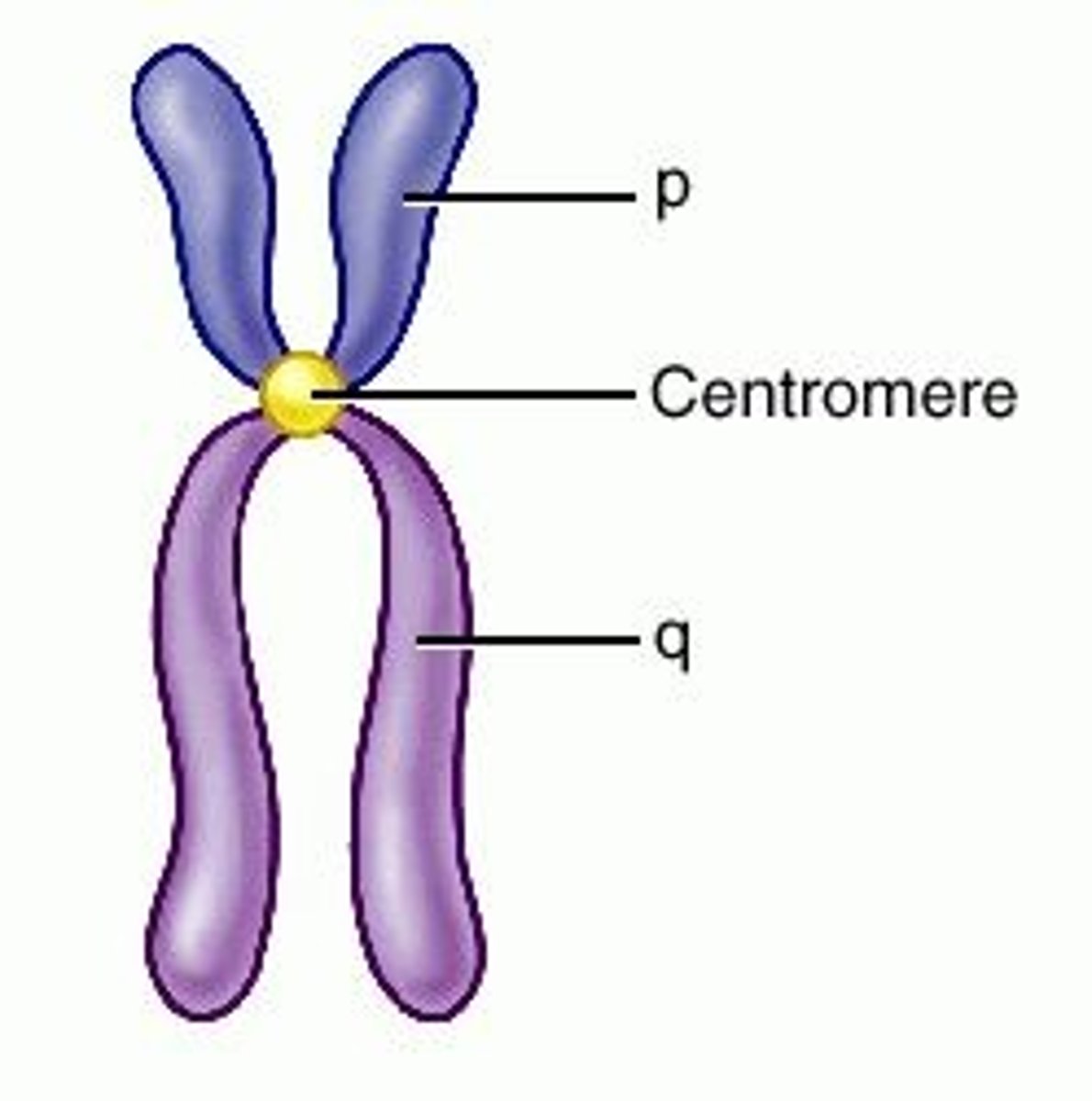
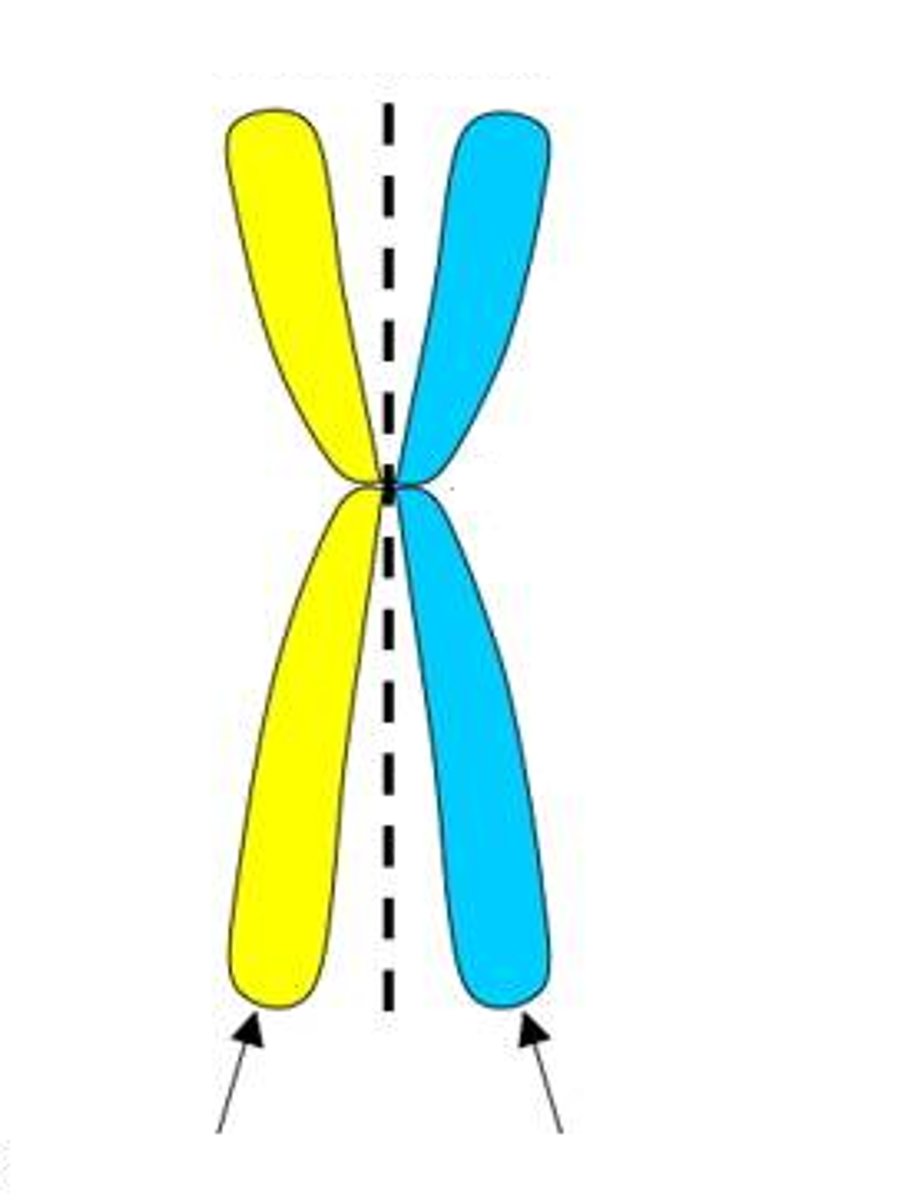
Centromere
Region of a chromosome where the two sister chromatids attach
spindle fibers
Protein structures which move the chromosomes during cell division.
Chromatid
one half of a duplicated chromosome
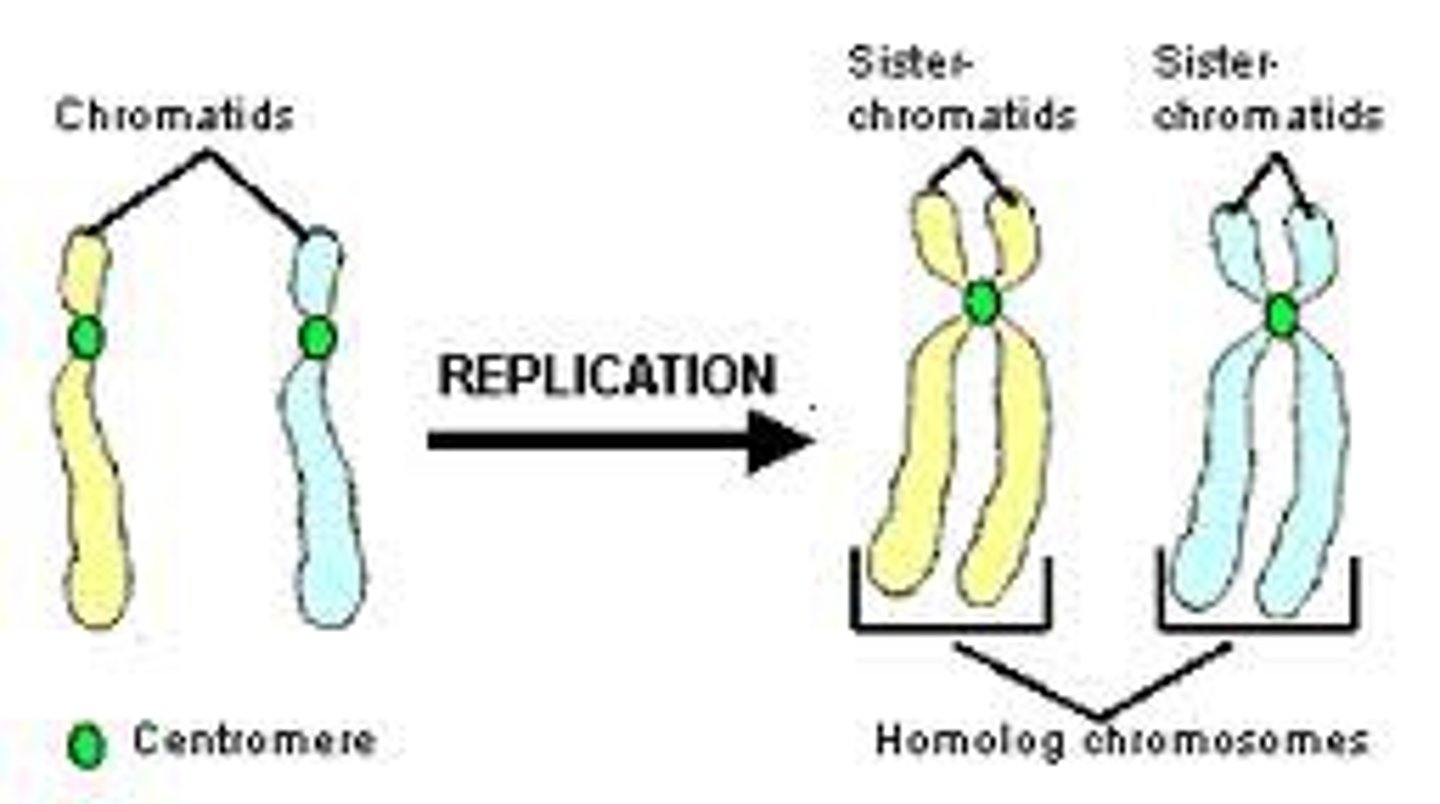
sister chromatids
Identical copies of a chromosome; full sets of these are created during the S subphase of interphase.
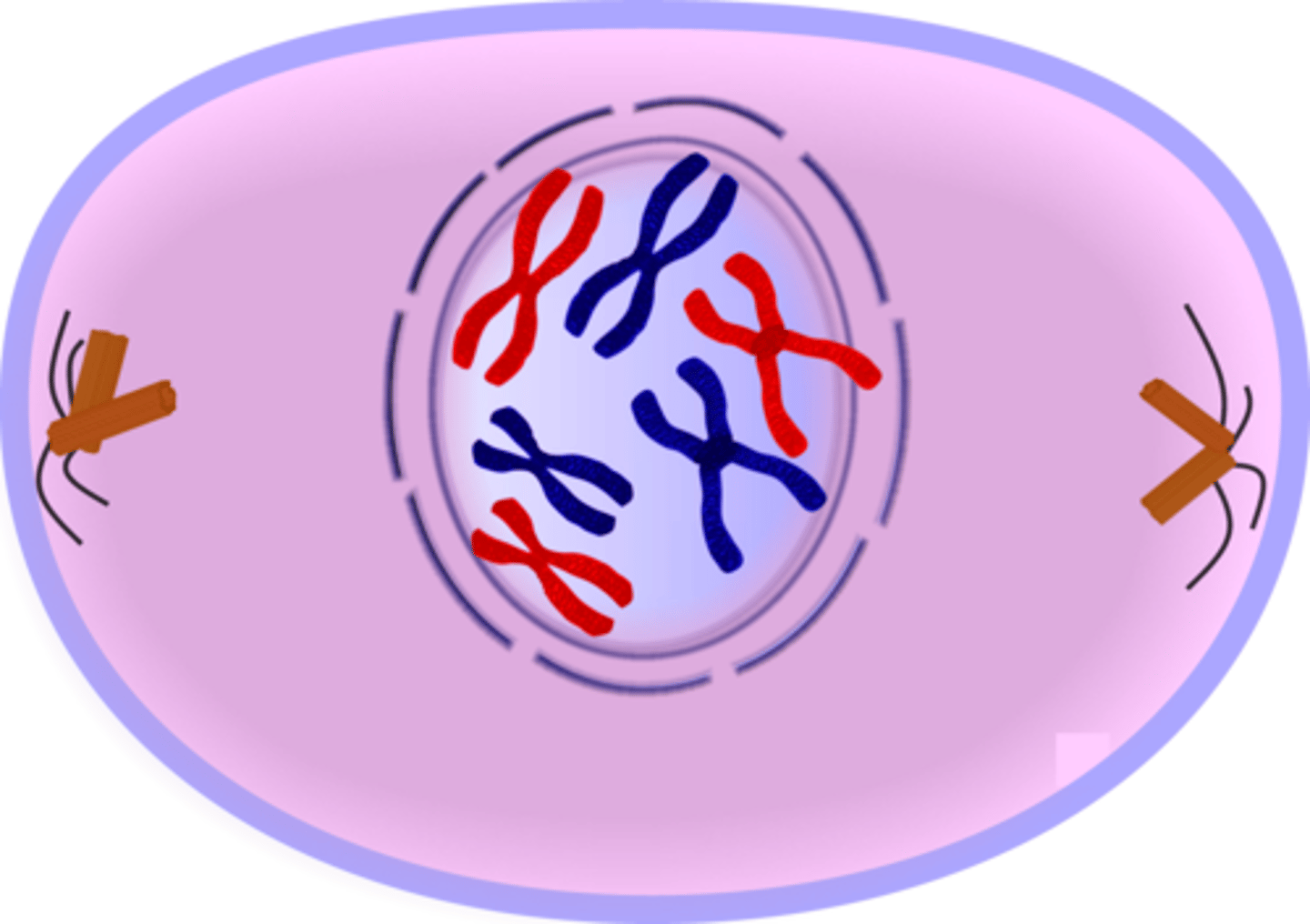
Purpose of interphase
Growth, DNA replication, and organelle duplication
S phase of Interphase
chromosome replicate and DNA synthesizes
G1 Phase of Interphase
Longest phase, cell grows, organelles duplicate, RNA synthesizes and enzymes
G2 phase of Interphase
More RNA and protein synthesis, ATP storage in prepartion fo rmitosis
Prophase of Mitosis
Metaphase of Mitosis
Anaphase of Mitosis
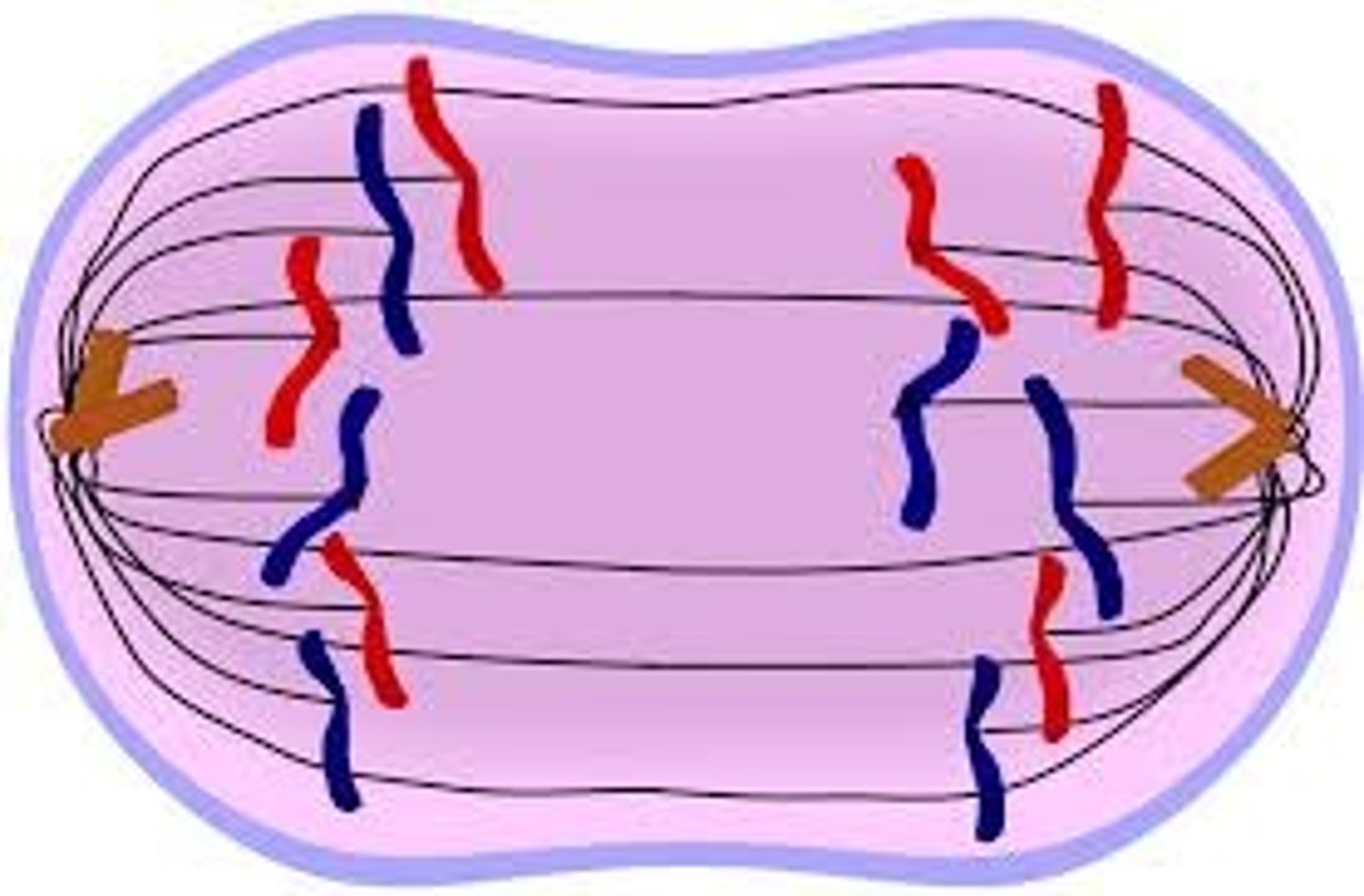
Telophase of Mitosis