Self assessment + dissection guide terms
1/732
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
733 Terms
Acromion Process
Flat, expanded projection at the outer end of the spine of the scapula (shoulder) and articulates with clavicle
Cervical vertebrae
Most superior series of vertebrae, Short bifid spinous processes, Anterior and posterior tubercles, Transverse formen holds vertebral artery
Deep (investing) fascia
Thin, whitish connective tissue that surrounds skeletal muscles, blood vessels, nerves, etc.
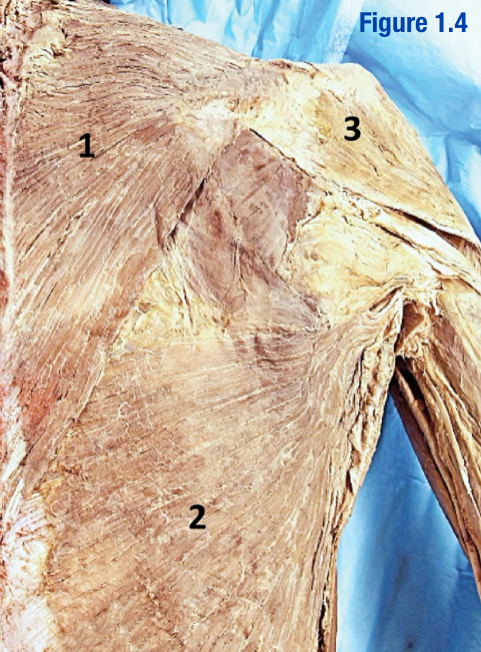
Deltoid; 3
Muscle lateral to trapezius
Origin: Lateral 1/3 of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus
What number in the diagram?
Dermis
Contain blood and lymph vessels, nerves, hair follicles, erector pili muscles, and sweat and sebaceous glands
Epidermis
Superficial layer of skin
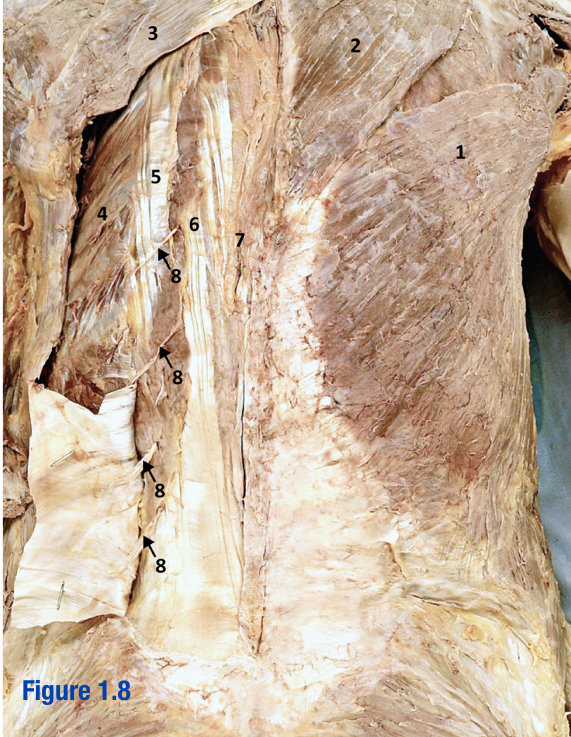
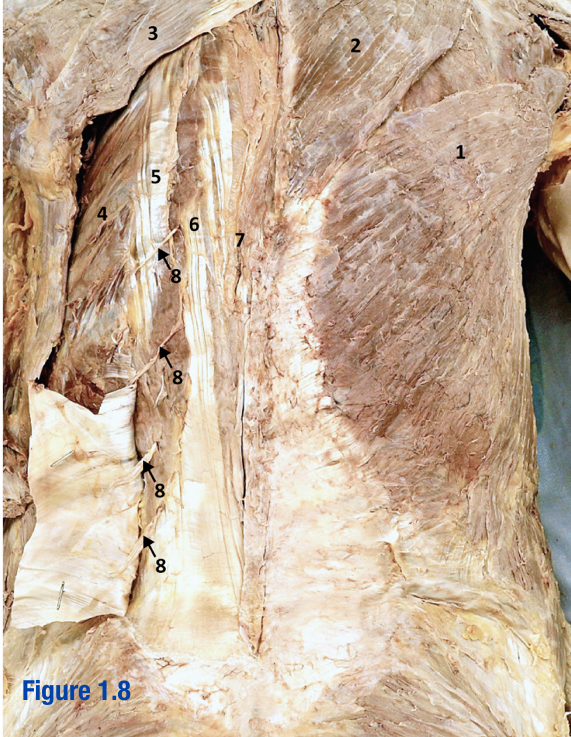
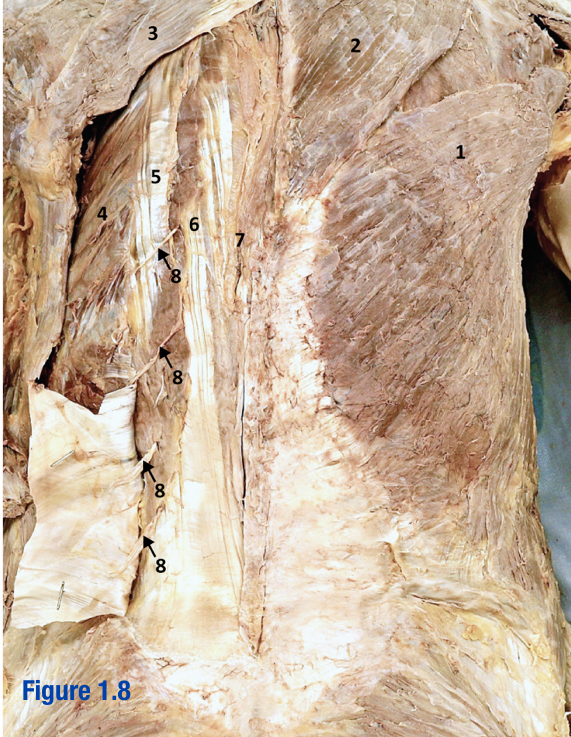
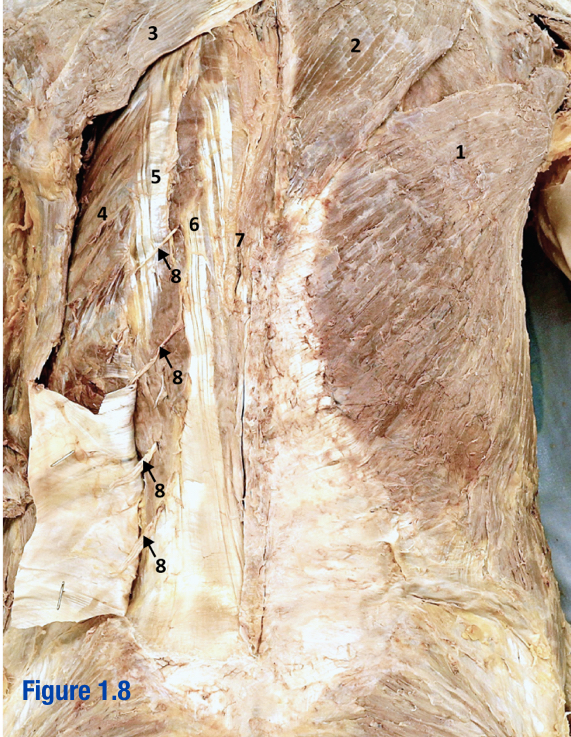
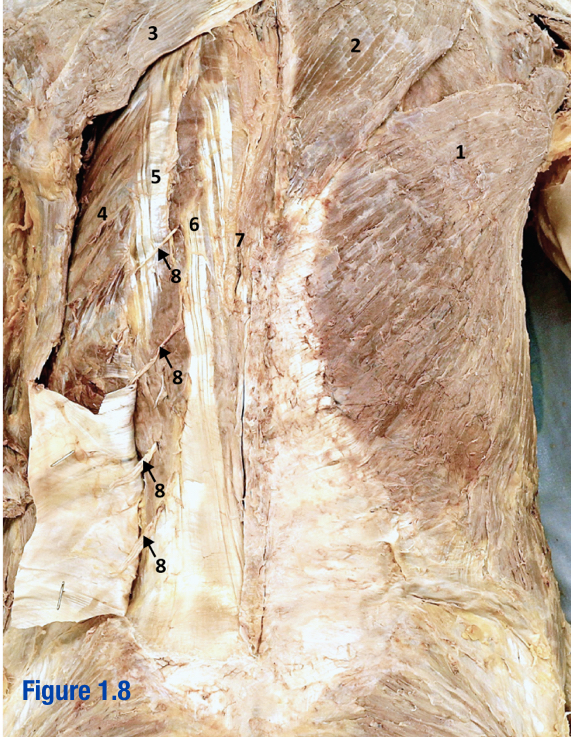
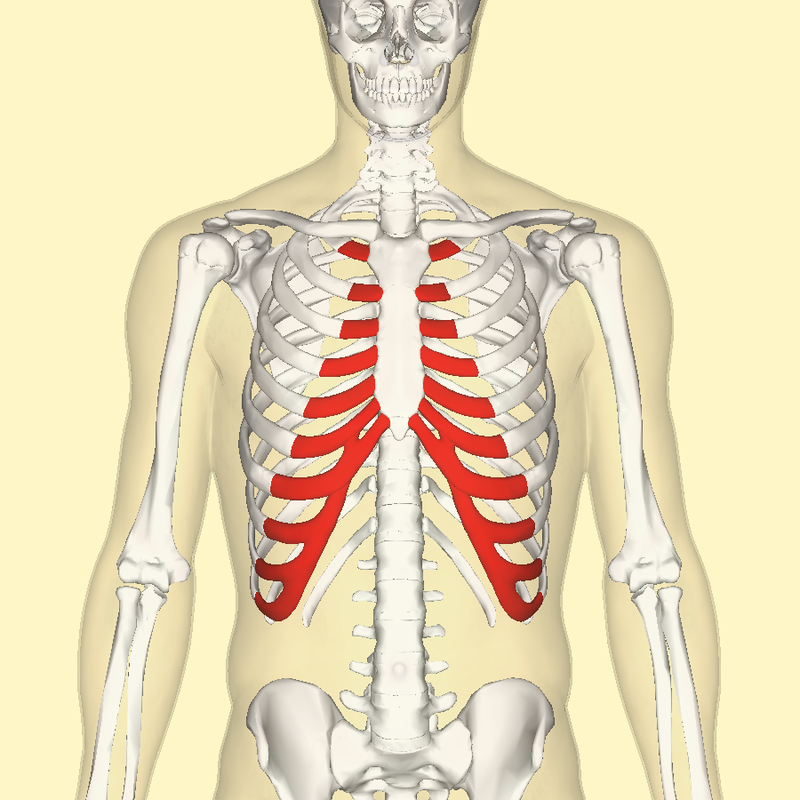
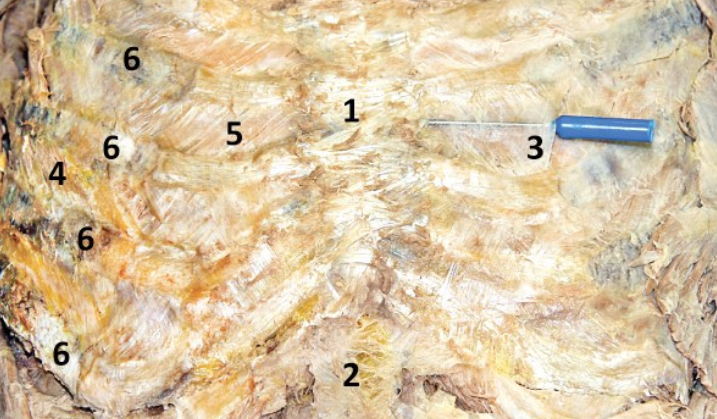
Erector spinae; 5-7
3 muscles that run longitudinally along the vertebrae (spinalis, longissimus, and iliocostalis) - Include number in diagram
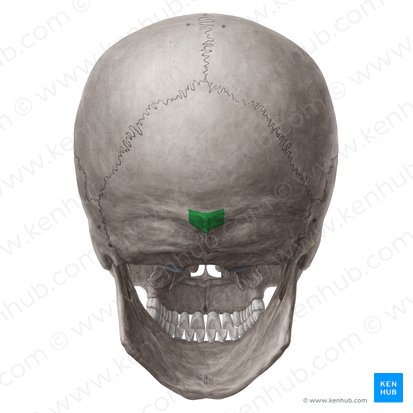
External occipital protuberance
Bump on occipital bone
Iliocostalis; 5
Most lateral of 3 erector spinae muscles - Include number in diagram
Langer’s Lines
Tension lines formed by the collagen and elastin composing dermis that are arranged in parallel configuration
Latissimus dorsi; 1
Inferior to trapezius
Origin: Spinous processes of lower thoracic vertebrae, thoracolumbar fascia, iliac crest, and inferior ¾ ribs
Insertion: Floor of intertubercular groove of humerus
Include number in diagram
Levator scapulae; 3
Origin: Transverse processes of C1/4
Insertion: Medial border of scapula (between superior angles and root of scapular spine)
Include number in diagram
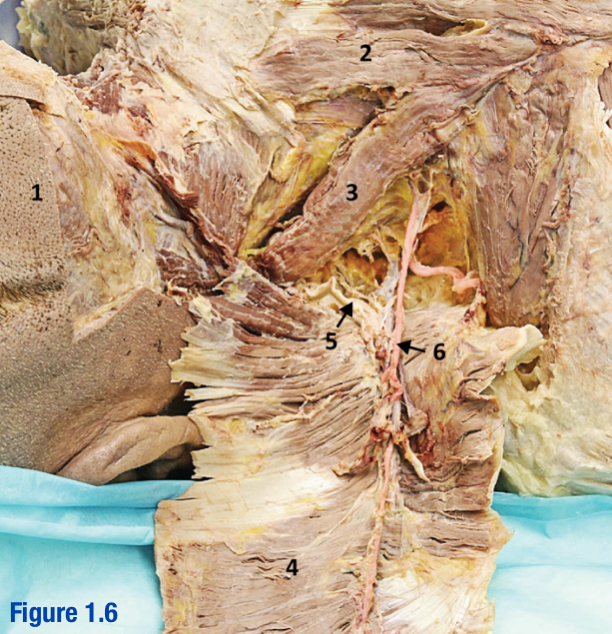
Longissimus; 6
Middle of the 3 erector spinae muscles - Include number in diagram
Mastoid process
Part of temporal bone just behind the ear
An attachment site for many muscles
Nuchal ligament
Ligament that extends from external occipital protuberance to spinous process of C7
Posterior cutaneous VAN; 8
Superficial branches of dorsal rami
Provides somatosensation and vasculature to skin on back
Include number in diagram
Rhomboid major and minor
Located deep to trapezius (2 muscles)
Scapula
Flat triangular bone that connects upper arm to collarbone
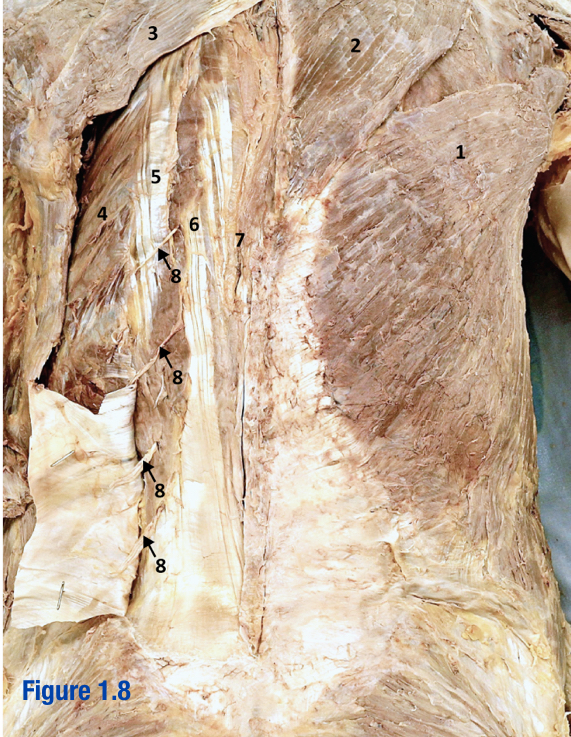
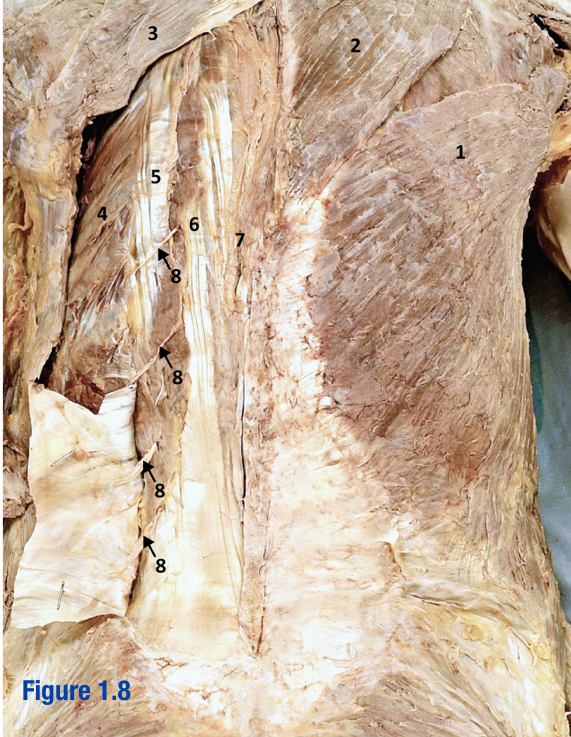
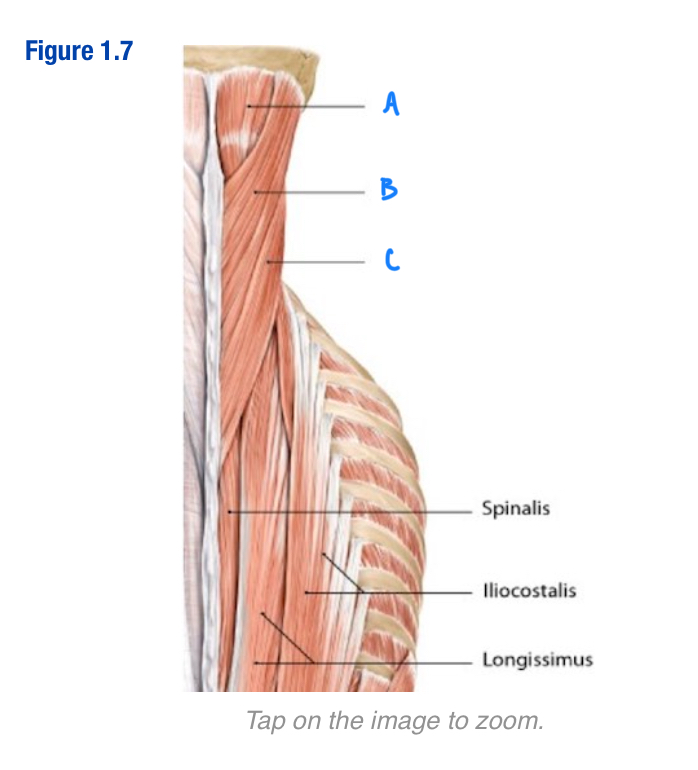
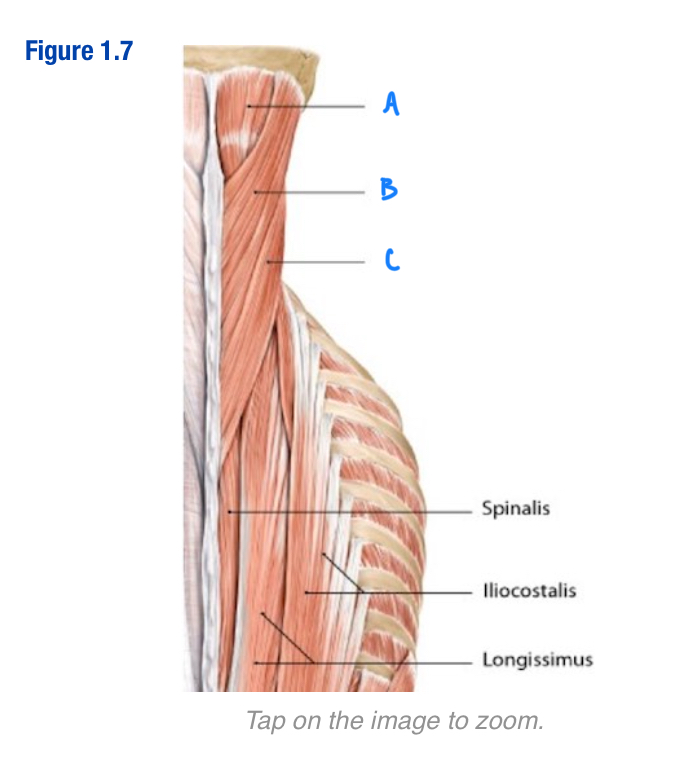
Semispinalis capitis; A
Vertically running muscle
Deep to splenius capitis and splenius cervicis
Located along spine
Which letter in the diagram
Superficial fascia
Connective tissue that is deep to the skin and contains varying amounts of fat
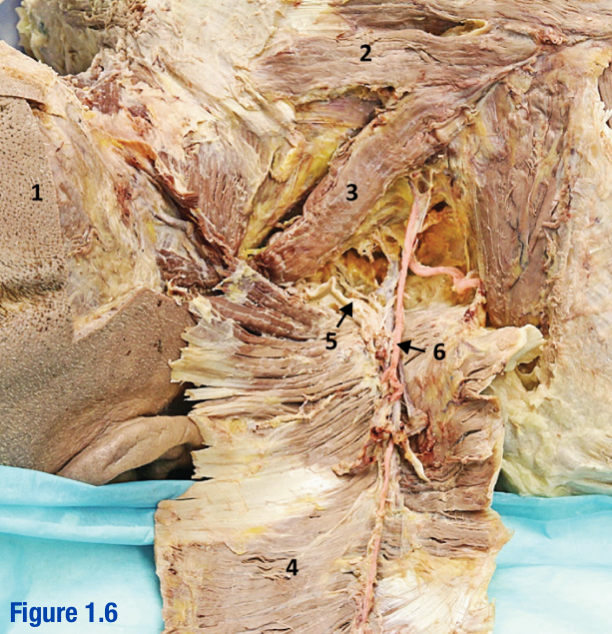
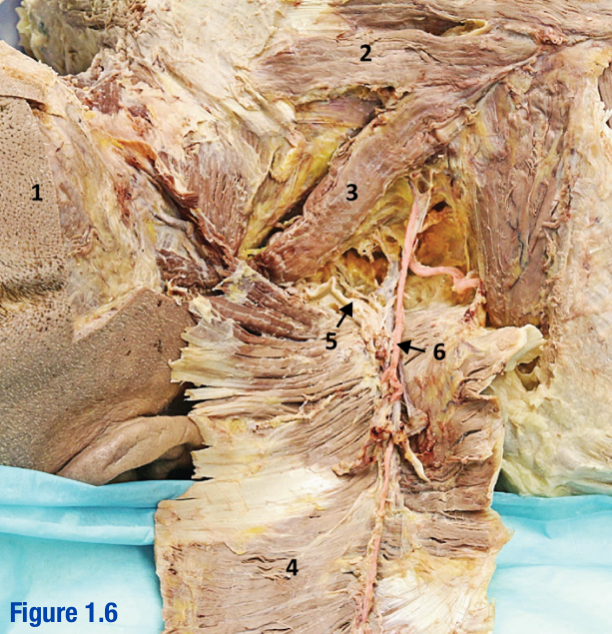
Spinal accessory nerve (CN XI); 5
Roots of this nerve exit cranium via foramen magnum; Deep to trapezius - Include number in diagram
Spinalis; 7
Most medial of 3 erector spinae muscles (next to vertebral column) - Include number in diagram
Spinous process
Posterior projection of vertebrae
Splenius capitis; B
Oblique running muscles
“Middle” of the 3 capitis/cervicis muscles
Sueprior to splenis cervicis
Include letter in diagram
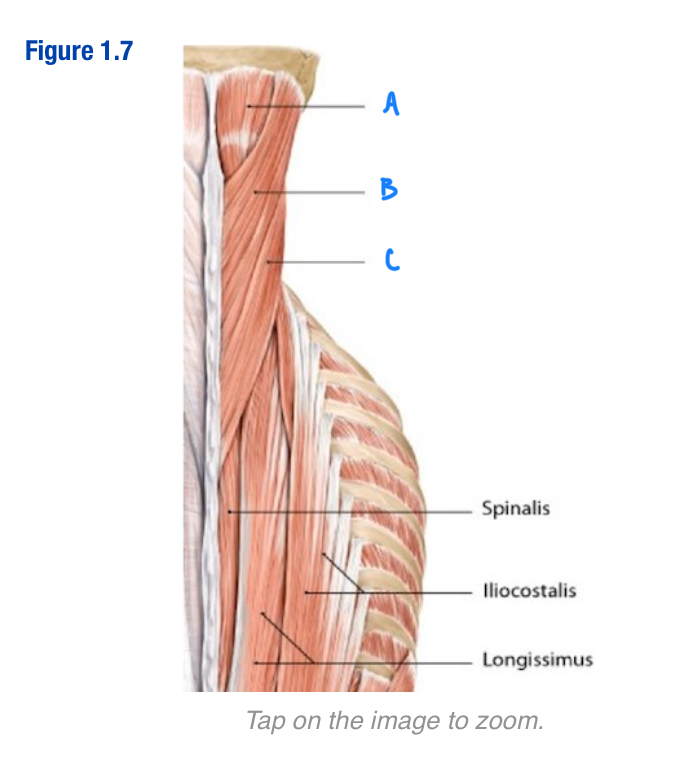
Splenius cervicis; C
Deep to trapezius and rhomboid muscles
Oblique running muscles
Most lateral of the 3 capitis/cervicis muscles
Include letter in diagram
Superior nuchal lines
Faint bony ridge that extends laterally from external occipital protuberance
Thoracic vertebrae
2nd series of vertebrae
Heart shaped body
Articular facets
Rib articulations (demifacets and facet on transverse process)
Transverse cervical a. and v.; 6
Arises from thyrocervical trunk (branch of subclavian) - Include number in diagram
Transverse process
Lateral process off of the vertebrae
Trapezius; 2
Large diamond-shaped muscle - Include number in diagram
Vertebral prominens
Another name for C7
Cephalic vein
Vein located between deltoid and pectoralis major
Cephalic v. → Axillary v. → Subclavian v. → Brachiocephalic v. → Superior vena cava → Right atrium
Path of cephalic v. to R atrium
Clavicle
Bone located superficial to structures of the neck and thorax but deep to muscles of the thorax
Sternocleidomastoid and Platysma
What muscles attach to the clavicle?
Costal cartilage
Hyaline cartilage that connects the ribs to the sternum
Costal groove
Groove located on the inferior border of ribs 2 to 12
By pulsations of the intercostal a.
How is the costal groove formed?
Intercostal VAN
What lays within the costal groove?
Costal margin
Inferior border of the ribcage
Costochondral joint
Joint between costal cartilage and rib
Dermatome
Strip of skin innervated by dorsal and ventral cutaneous nerves from a single spinal nerve
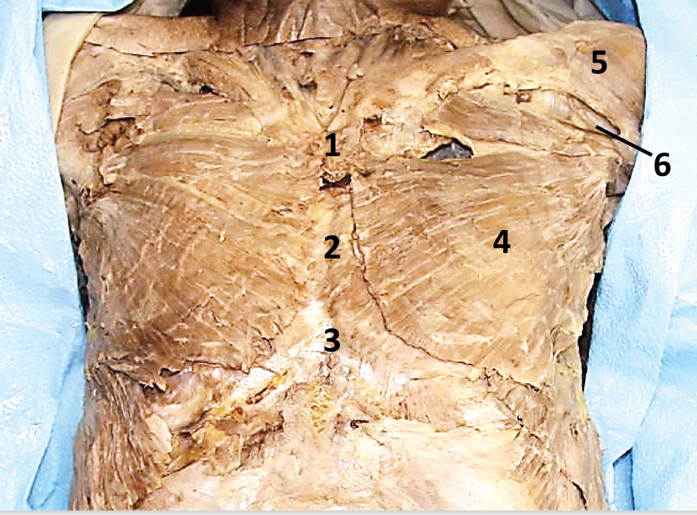
External intercostal membrane; 3
The most medial part of the external intercostal m. that is a semi-transparent membrane (directly superficial to the internal intercostal m.) - Include number in diagram
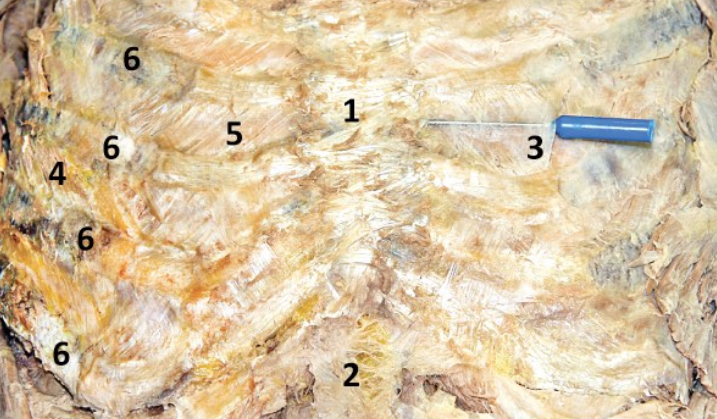
External intercostal muscle; 4
Muscles lateral to the costochondral joint - Include number in diagram
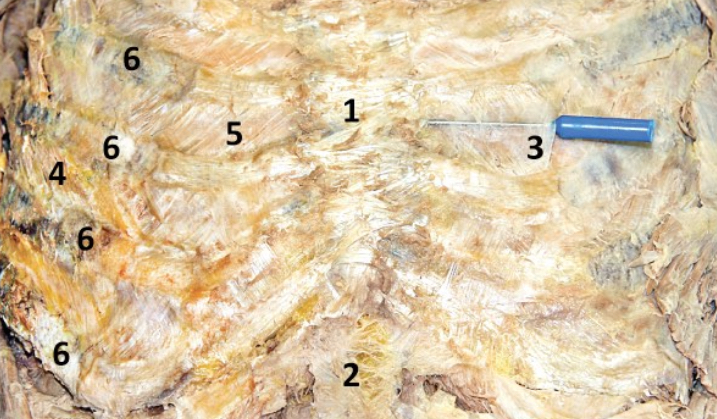
Elevate ribs and expand the chest cavity (inhilation)
Function of external intercostal m
Genu/symphysis of the mandible
Point of fusion where the 2 halves of the mandible join together during development (midline - near chin)
Gonial angle
Inferior angle of the mandible
Arch of aorta → L subclavian a. → Costocervical trunk → Intercostal a.
Path of intercostal a. from arch of aorta (L side)
Arch of aorta → R brachiocephalic a. → R subclavian a. → Costocervical trunk → Intercostal a.
Path of intercostal a. from arch of aorta (R side)
Ventral rami of 1st 11 thoracic n.
Where do intercostal nerves arise from?
Internal intercostal m.; 5
M. located deep to external intercostal membrane - Include number in diagram
Pull ribs down and in (reducing volume of thoracic cavity)
Function of internal intercostal muscle
Lateral pectoral n.; 3
Supplies innervation to pectoralis major (located superiorly in pectoralis major) - Include number in diagram
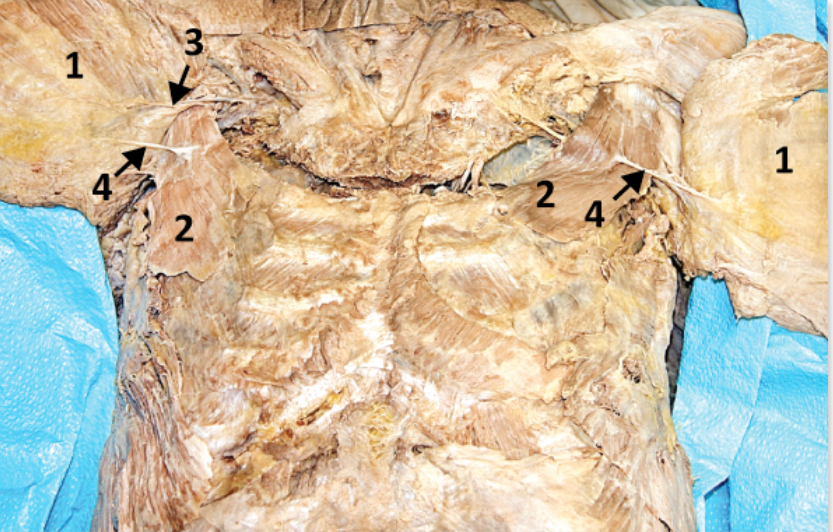
Lateral cord of brachial plexus
What is the lateral pectoral nerve a branch of?
Medial pectoral n.; 4
Supplies innervation to pectoralis major and minor (located laterally - pierces into to pectoralis minor) - Include number in diagram
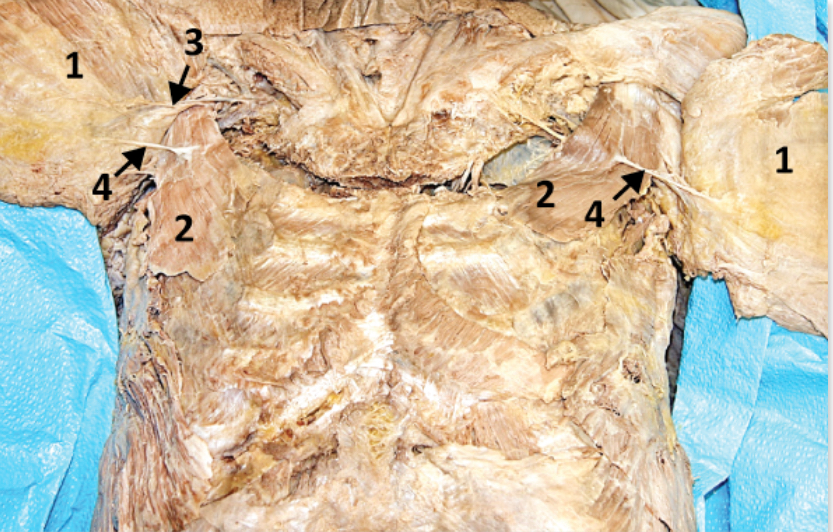
Branch of medial cord of brachial plexus
What is the medial pectoral n. a branch of?
Pectoralis major; 4
Superficial muscle in thorax (innervated by medial and lateral pectoral nerves) - Include number in diagram
Pectoralis minor; 2
Deep to pectoralis major (innervated by medial pectoral n.) - Include number in diagram
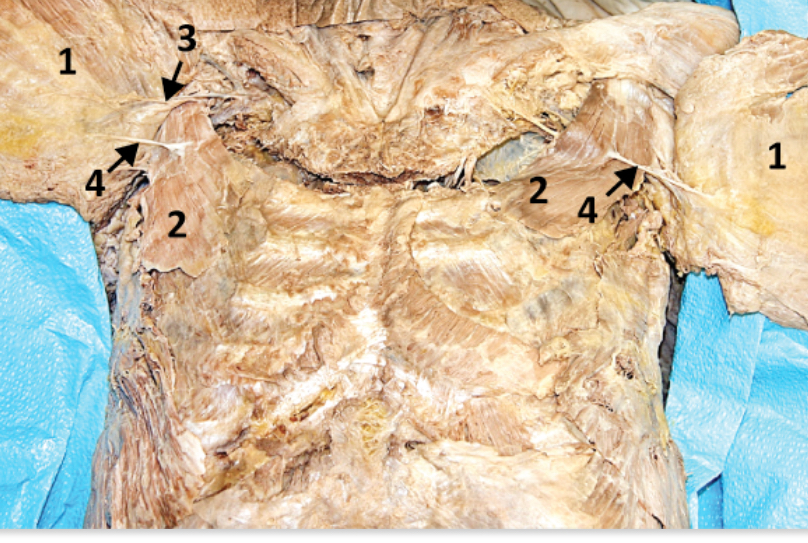
Sternocostal joint
Joint between manubrium and costal cartilage which joins the anterior ends of the 1st rib
Subcostal n.
Ventral ramus of T12 that lies below the 12th rib
Suprajugular notch
Notch at the superior margin of the manubrium
SS, SM, ANS
Fiber types in ventral rami
Internal (mammary) thoracic artery
Anterior intercostal artery originates from …
Intercostal space
Location of anterior intercostal artery
Anterior and posterior intercostal arteries
What arteries anastamose at the level of the costochondral junctions?
Brachiocephalic trunk, L CCA, L Subclavian A
What are the branches of the aortic arch (R → L)?
Apex of the heart
Tip of the ventricle pointing inferolaterally
Left ventricle (aortic valve between)
What chamber of the heart does the ascending aorta arise from?
Arches over the root of the lung to join with the SVC outside the pericardial sac
Azygous vein general path
R subclavian A and R common carotid A
What does the brachiocephalic trunk give rise to?
internal jugular (IJV) and subclavian v.
Convergence of what veins contribute to the brachiocephalic vein?
Superior vena cava (SVC)
R and L brachiocephalic veins join to form …
Immediately posterior
Location of esophagus relative to trachea
Transverse thoracis muscles (adjacent to the lower and end of the sternum)
What is the innermost intercostal muscle?
Brain, face, neck
What regions does the internal jugular vein drain?
Course vertically adjacent to the sternum between the internal intercostal muscles and transverse thoracis muscle
Path of internal mammary/thoracic artery
Superior epigastric a. and musculophrenic a.
What are the terminal branches of the internal mammary/thoracic artery?
Pulmonary veins
Where does the left atrium receive blood from?
Ascending branch or aorta
Where does the left ventricle pump blood to?
Ligamentum arteriosum; 5
Adult remnant of the ductus arteriosus (shunt during fetal circulation) - Include number in diagram
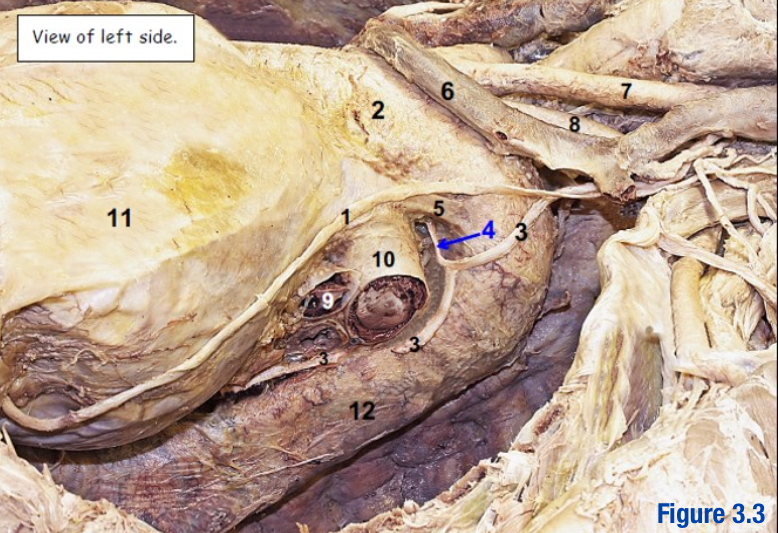
Potential space between the parietal and visceral pleura
What is the pleural cavity?
C3, 4, 5 ventral rami
What nerves give rise to the phrenic nerve?
Descend vertically through mediastinum between mediastinal parietal pleura and pericardium and course just anterior to root of the lung
Path of phrenic nerve
Sensory and motor
What fiber components does the phrenic n. have?
Vagus n. (CN X)
What nerve gives rise to the recurrent laryngeal n.?
Lower border of right subclavian a. and turns superiorly to ascend in the neck between the trachea and esophagus
Path of R recurrent layngeal n.
Coronary sinus, superior vena cava, and inferior vena cava
What does the right atrium receive blood from?
Tricuspid valve
What valve is present between the right atrium and ventricle?
Inferior epigastric artery
What does the superior epigastric artery anastamose with?
Brachiocephalic trunk and L CCA
The trachea is located immediately posteriorly to which branches of the aortic arch?
Crosses R subclavian between the brachiocephalic trunk and R brachiocepalic v.
Path of R vagus nerve (CN X)
Ligamentum arteriosum/Aortic arch
What does the left recurrent laryngeal n. turn under?
Arachnoid membrane
Located internal to the dura mater
Cauda equina
Bundle of dorsal roots and filum terminale, extends below conus medullaris to dural cul-de-sac (S2)
Atlas (C1)
Vetebrae that has no body; Superior articular processes large and form joint with occipital condyles; Primary movement = flexion and extension
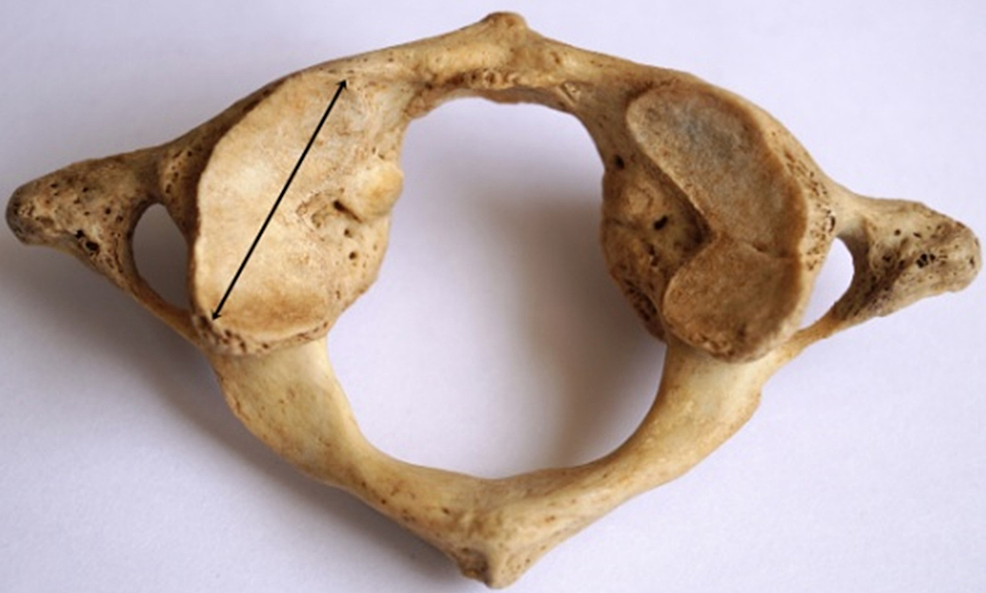

Axis (C2)
Vertebrae with small body with dens Dens articulates with C1 (atlantoaxial joint); Primary movement = lateral rotation
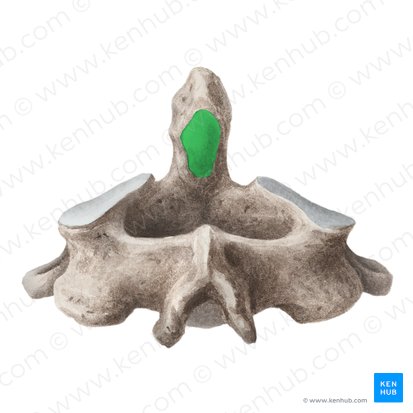
Coccyx
Terminal portion of vertebral column (fused)
Conus medullaris
Tapered distal end of spinal cord; Tip at L1 or L2; Comprised of S1-5 and coccygeal spinal cord segments
Denticulate ligament
Extension of pia mater; Coronal plane attaches laterally to dura; Separates ventral and dorsal roots
Dorsal ramus
Located within erector spinae; Smaller than ventral ramus