54 - Energy metabolism in the body. Energy values of nutrients. The energy equivalent of Oxygen. Measurement of metabolic rate- direct/ indirect caliometry. Basal metabolic rate and daily energy requirements und der different physiological conditions.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
sections
energy metabolism in body
energy value of nutrients
energy equivalent of oxygen
measurement of metabolic rate - direct/indirect caliometry
basal metabolic rate
daily energy requirements
energy metabolism in body
Our body needs energy for anabolic and catabolic pathways.
energy from the breakdown of nutrients- carb, fat and protein consumed
Their energy contents is measurable in that they are fully “burned” to CO2 and water under an oxygen environment.
Energy = ability of a system to do work.
energy value of nutrients
Energy is storable in different forms such as kinetic energy, thermic energy, and electrical energy and so forth.
Unit of energy is J (Joule)
kcal- 4.18Kj
Energy values of nutrients
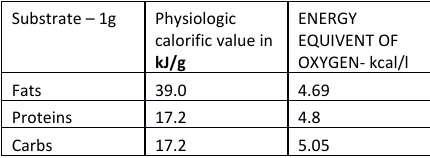
energy equivalent of oxygen
Energy equivalent of oxygen on a mixed diet : the amount of energy released during oxidation of a given substance for which one litre of O2 is used. At a predetermined RQ- respiratory quotient
measurement of metabolic rate - direct/indirect caliometry
The methods of measuring gas exchange are used to determine the amounts of utilized 02 and released C02 in litres per unit of time
Metabolic Rate – the rate at which metabolic reactions use energy. Some of the energy is used to produce ATP, and some is released as heat.
Calorimetry : method of measuring changes in state variables of the body to determine the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due to, for instance, chemical reactions, physical changes, or phase transitions under specified constraints. Calorimetry is performed with a calorimeter.
direct calorimetry measurement of the amount of heat produced by a subject enclosed within a small chamber.
Indirect calorimetry calculates heat that living organisms produce by measuring either their production of carbon dioxide and nitrogen waste (frequently or from their consumption of oxygen.
measurement of metabolic rate - direct/indirect caliometry (simplified
Gas Exchange Measurement
Measures how much O₂ is used and CO₂ is released (in liters per time).
Helps assess energy use in the body.
Metabolic Rate
Speed at which the body uses energy for metabolism.
Energy is used for ATP production and released as heat.
Calorimetry
Measures heat transfer in the body due to chemical or physical changes.
Done using a calorimeter.
Direct Calorimetry:
Measures actual heat produced in a closed chamber.
Indirect Calorimetry:
Estimates heat by measuring O₂ consumption or CO₂ and nitrogen waste output.
basal metabolic rate
amount of energy expended at rest. It is measured in supine position, at least 12 hrs after last meal, room temp 20-22 degrees celcius, subject lies down 30mins before test.
BMR is the minimal amount of energy needed to maintain basic physiological functions such as blood flow, breathing, excretion, innervation, secretion and body temperature.
Lower BMR values are regesitered only during sleep.
Factors affecting BMR are: sex, age, body mass, height, body surface area and certain physiological states such as physical activity, sleep, pregnancy, lactation.
Hormones increasing BMR are T3, T4 catecholamines etc.
Actual BMR: men – 6600 to 7000 kJ/24h woman- 6000-6400Kj/24hr
daily energy requirements
Energy intake depends on many factor and physical activity
Proteins- 0.8-1.3g/kg
Fat- 0.8g/kg
Carbs-sugars- 4-8g/kg