AP Chem Test 3B
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topics 3.7 to 3.13
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Calculate the volume of 1.25 M lithium chloride solution that can be made with 13.3 g of lithium chloride?
0.251 L LiCl solution

What would be the concentration of chloride ion in a solution that is made by dissolving 10.0 g zinc chloride in a solution that has a final volume of 500. mL?
0.294 M Cl1-

How many grams of potassium hydroxide would be dissolved in 250 mL of a 0.10 M solution of potassium hydroxide?
1.4 g KOH

What is the nitrate ion concentration in 100. mL of magnesium nitrate solution that has 2.5 g dissolved magnesium nitrate?
0.34 M

What volume of 0.25 M lithium fluoride solution can be made by dissolving 5.0 g lithium fluoride?
0.77 L LiF

What mass of sodium hydroxide would be required to make 1.0 L of a 0.75 M solution of sodium hydroxide, NaOH?
30. g

What is the molar concentration of a solution made by dissolving 2.9 g sodium acetate in water to a total volume of 25 mL?
1.4 M

What is the calcium ion concentration in 1.5 M calcium chloride? What is the chloride ion concentration?
1.5 M
3.0 M
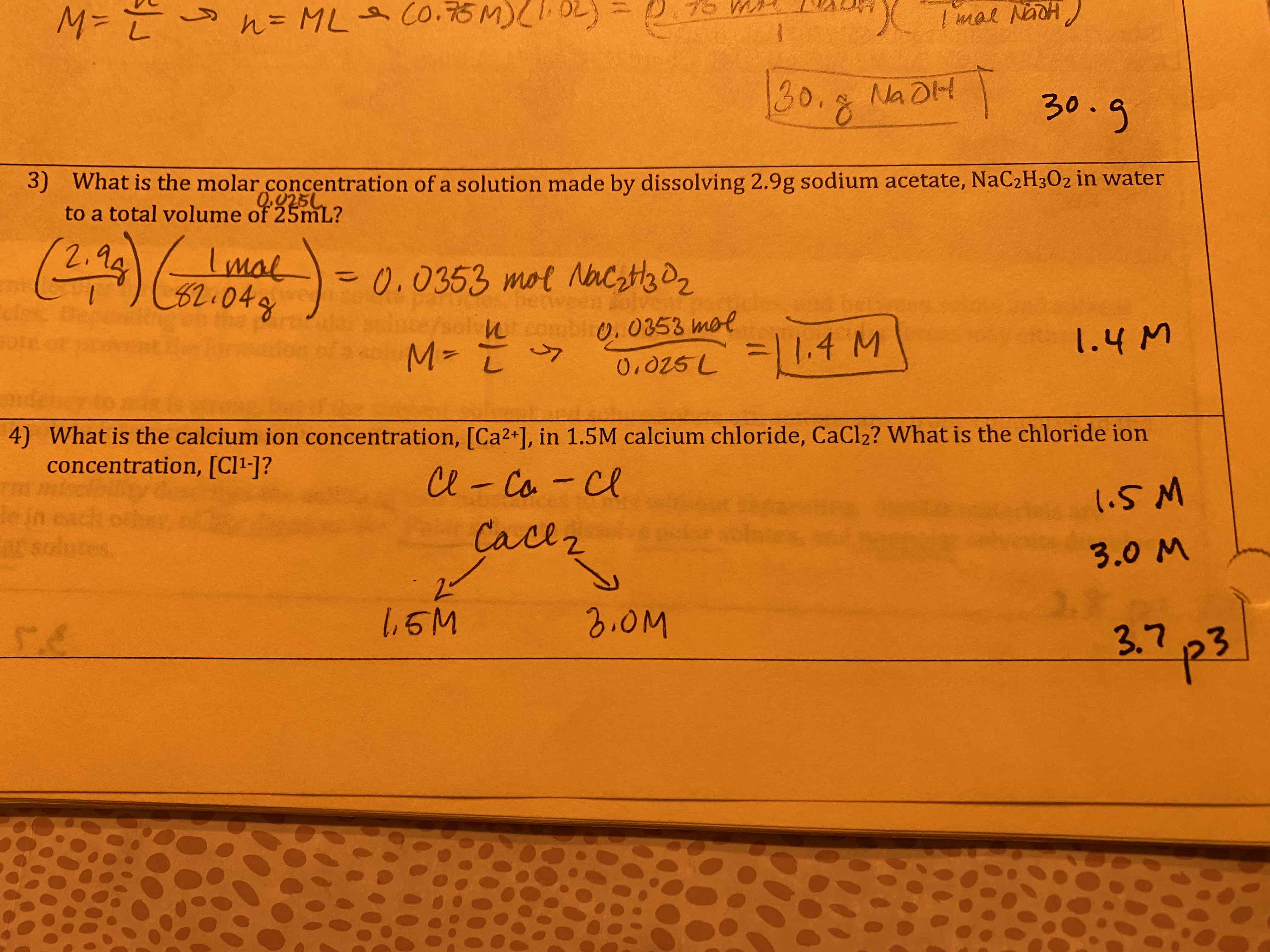
What is the acetate ion concentration of a 100 mL of calcium acetate solution with 25.0 g dissolved calcium acetate?
3.16 M
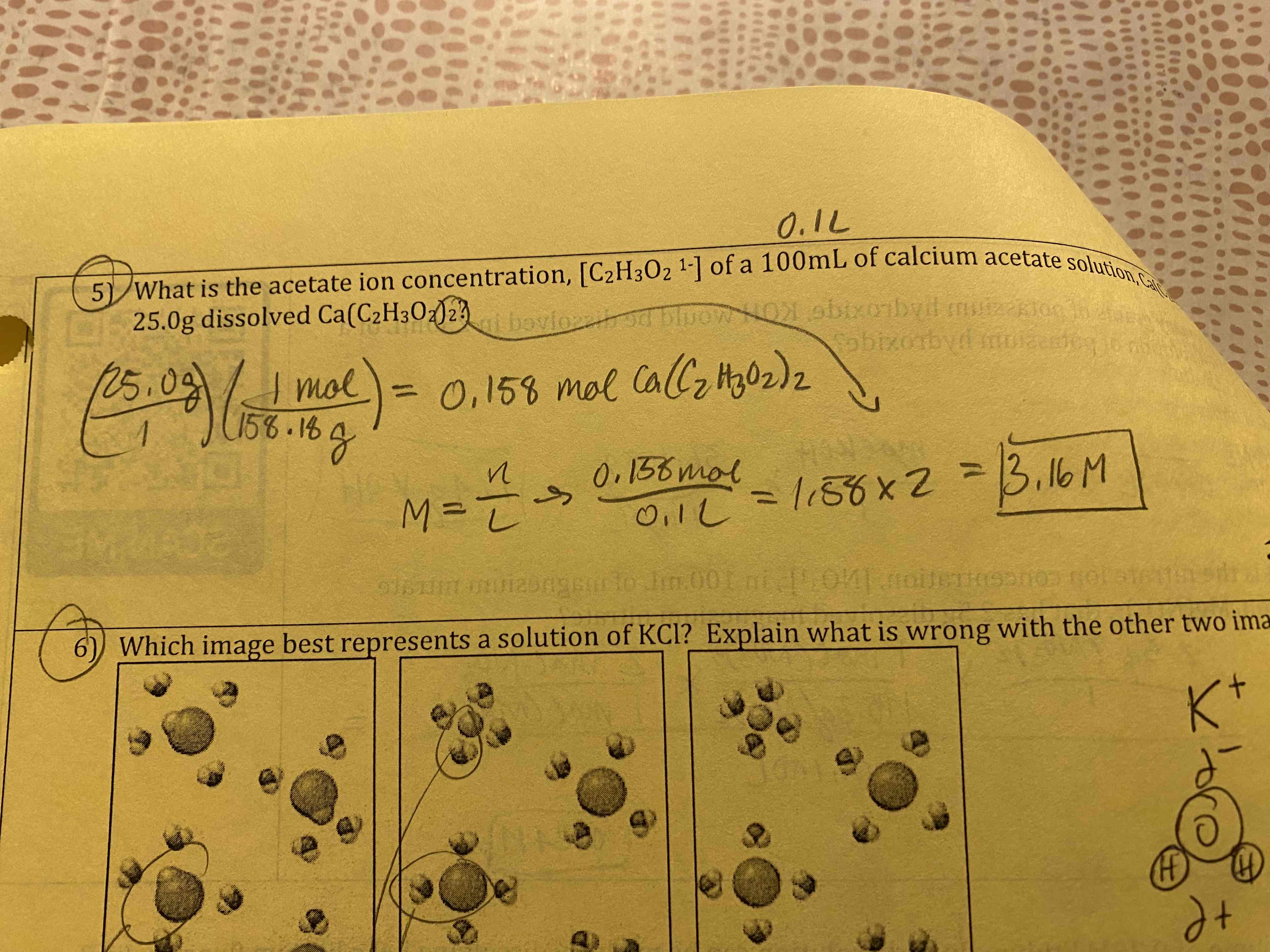
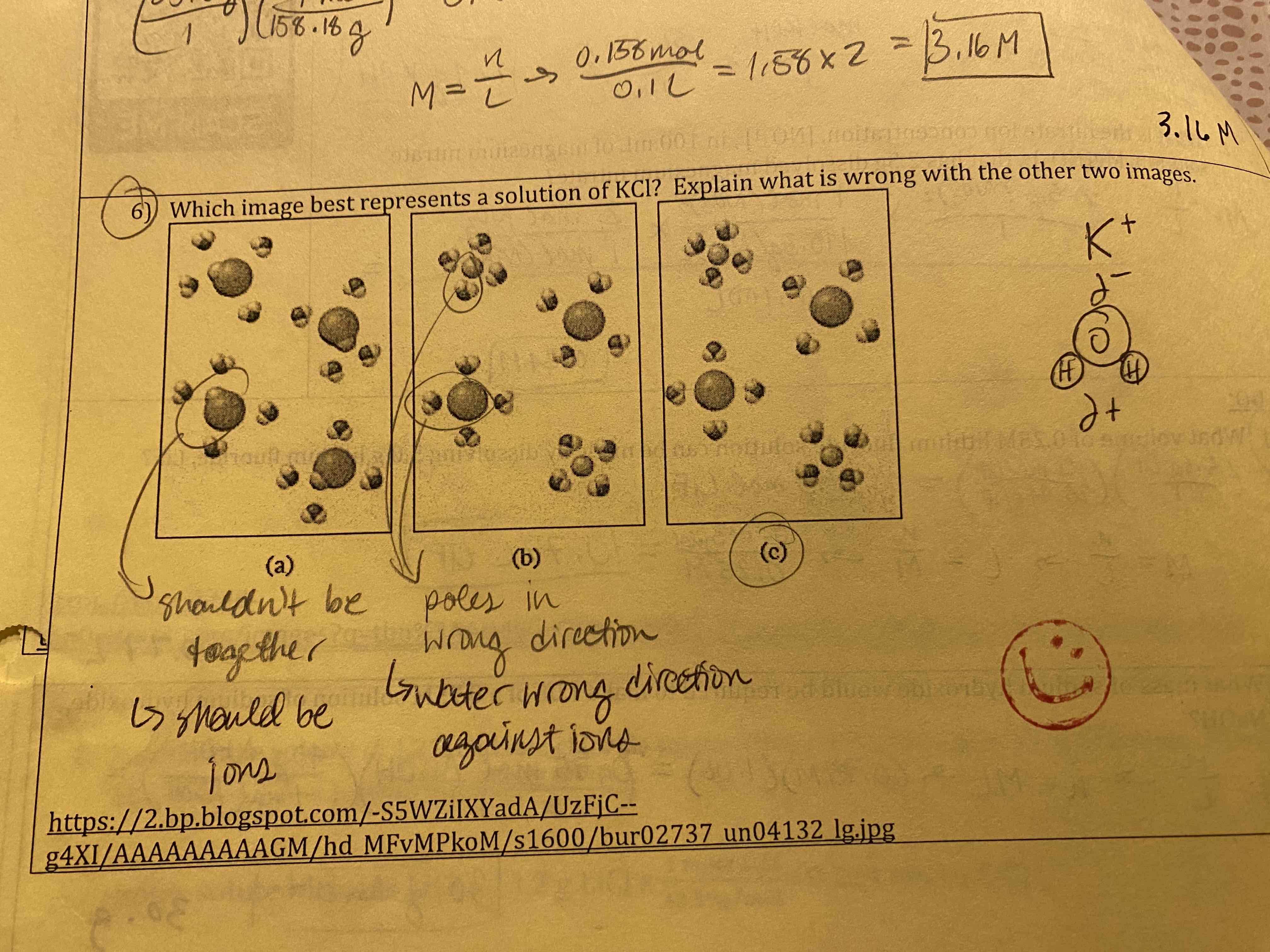
Which image best represents a solution of KCl? Explain what is wrong with the other two images.
(a) should be ions
(b) water wrong direction against ions
(c) correct
Of the molecules above, which would form hydrogen bonds with water, which would form dipole-dipole attractions with water, and which would form London dispersion forces only with water?
Alcohol and amine has hydrogen bonds with water. Ether and ketone has dipole-dipole with water. Alkane has LDF with water.
Draw particulate models of two alkane molecules. Draw how the strongest intermolecular force present acts between the molecules. What is the name of this force?
LDF
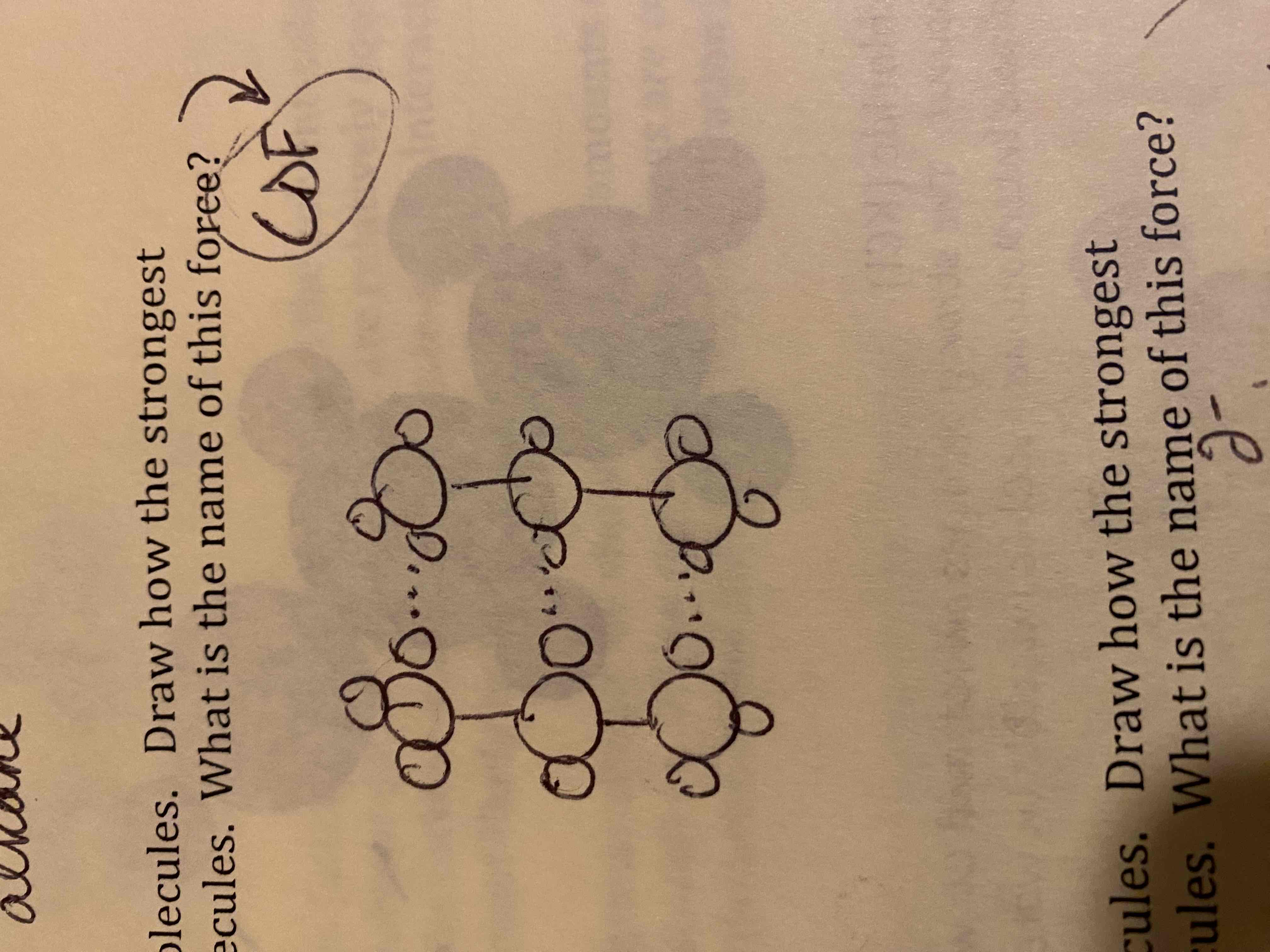
Draw particulate models of two of the ether molecules. Draw how the strongest intermolecular force present acts between the molecules. What is the name of this force?
Dipole-dipole
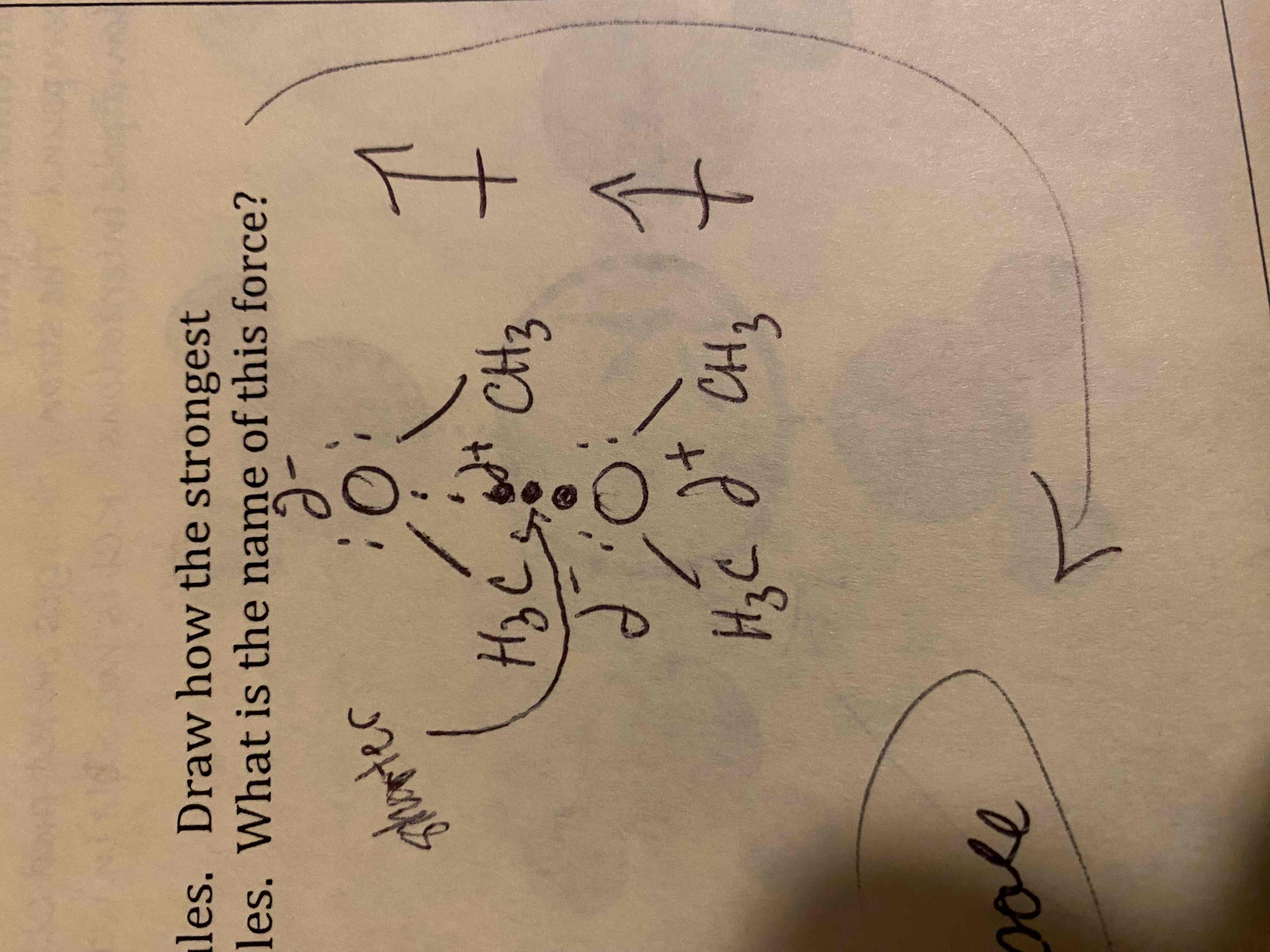
Draw particulate models of two of the amine molecules above. Draw how the strongest intermolecular force present acts between the molecules. What is the name of this force?
Dipole-dipole
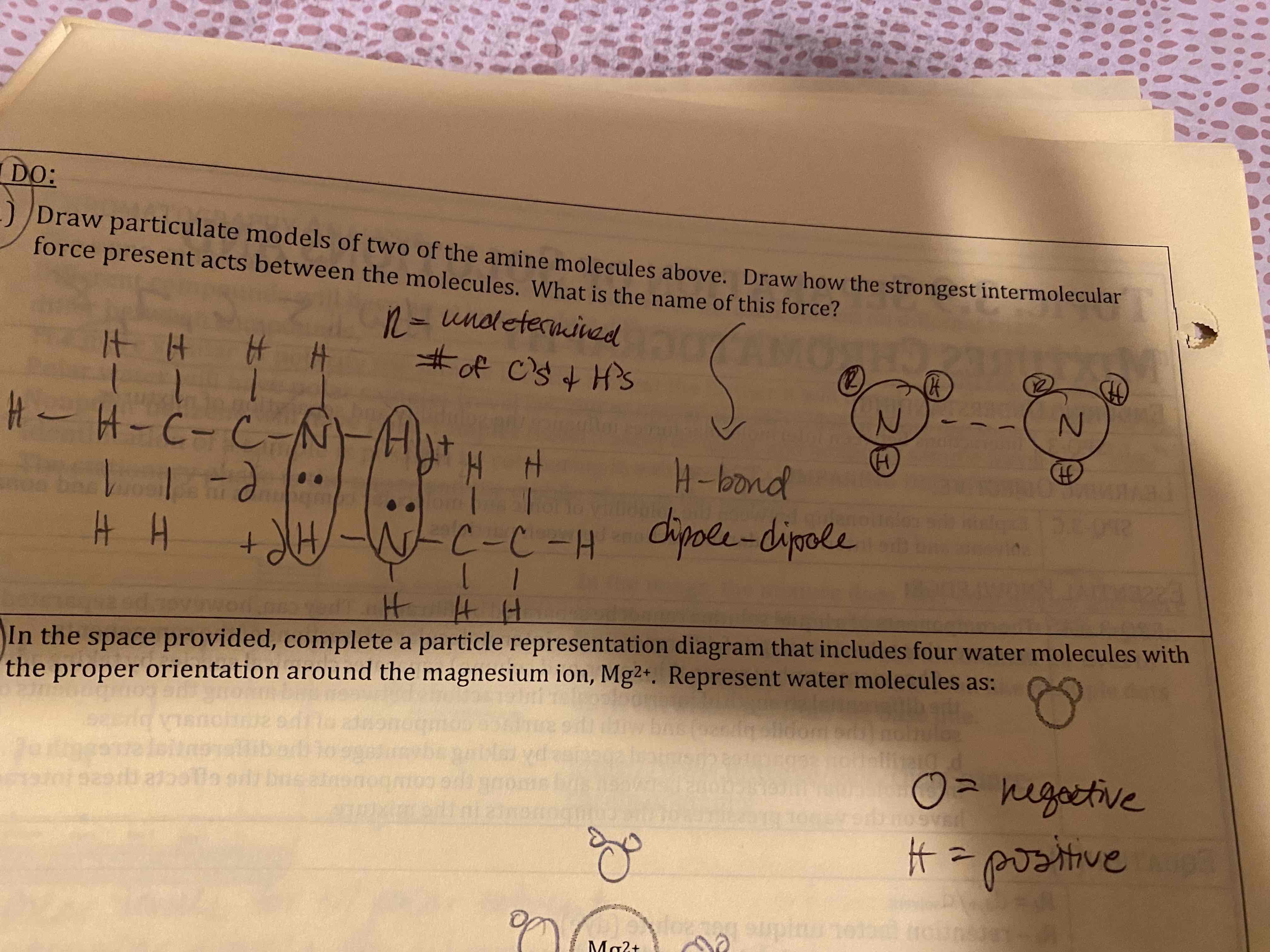
In the space provided, complete a particle representation diagram that includes four water molecules with the proper orientation around the magnesium ion.
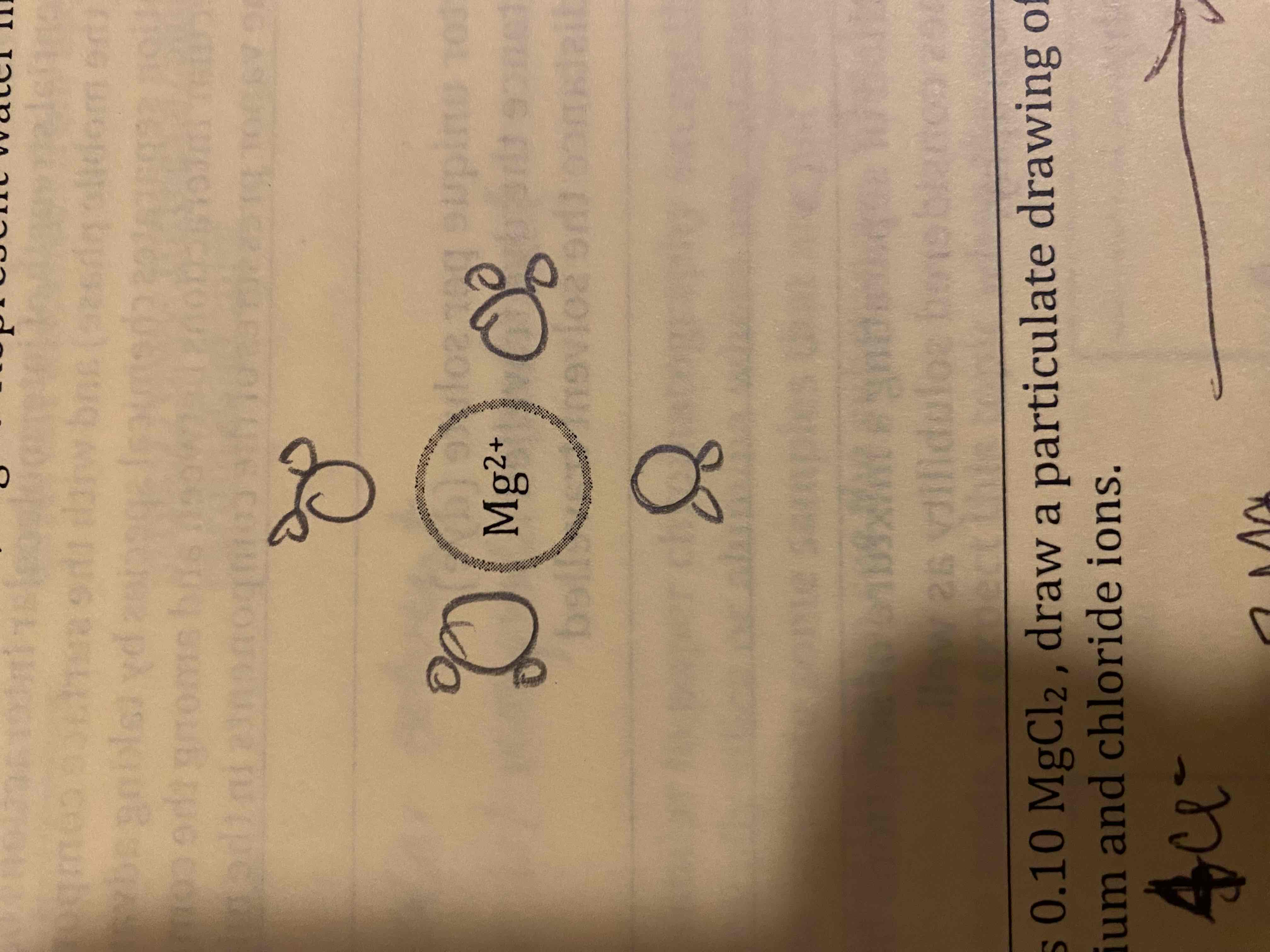
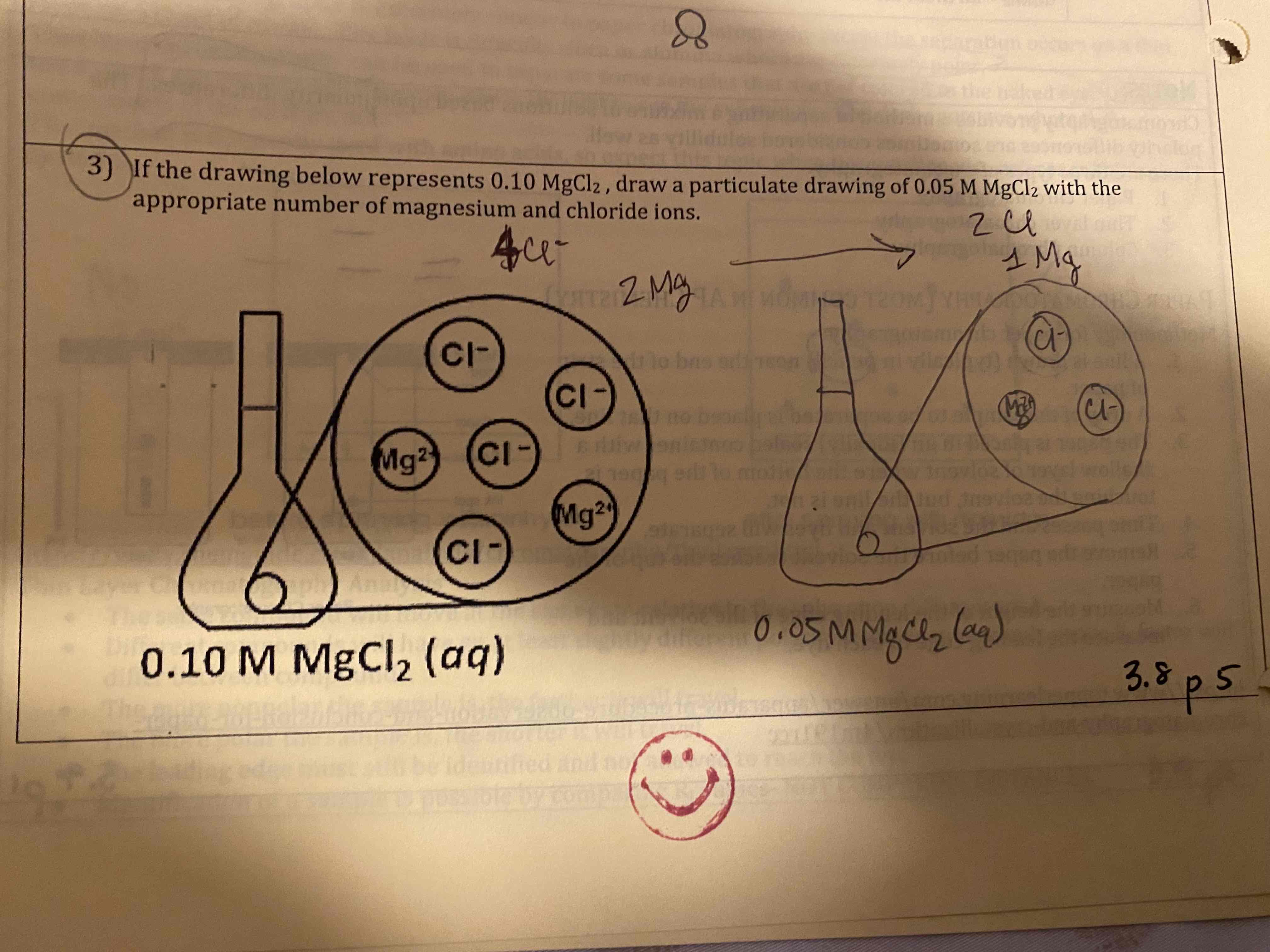
If the drawing below represents 0.10 MgCl2, draw a particulate drawing of 0.05 M MgCl2 with the appropriate number of magnesium and chloride ions.
Serine and glycine are both amino acids where serine is polar and glycine is nonpolar. The two amino acids are not labeled and must be identified.
a. Explain why thin layer chromatography is more appropriate than paper chromatography in this case.
b. Describe how to set up a thin layer chromatography experiment that will help identify the two amino acids.
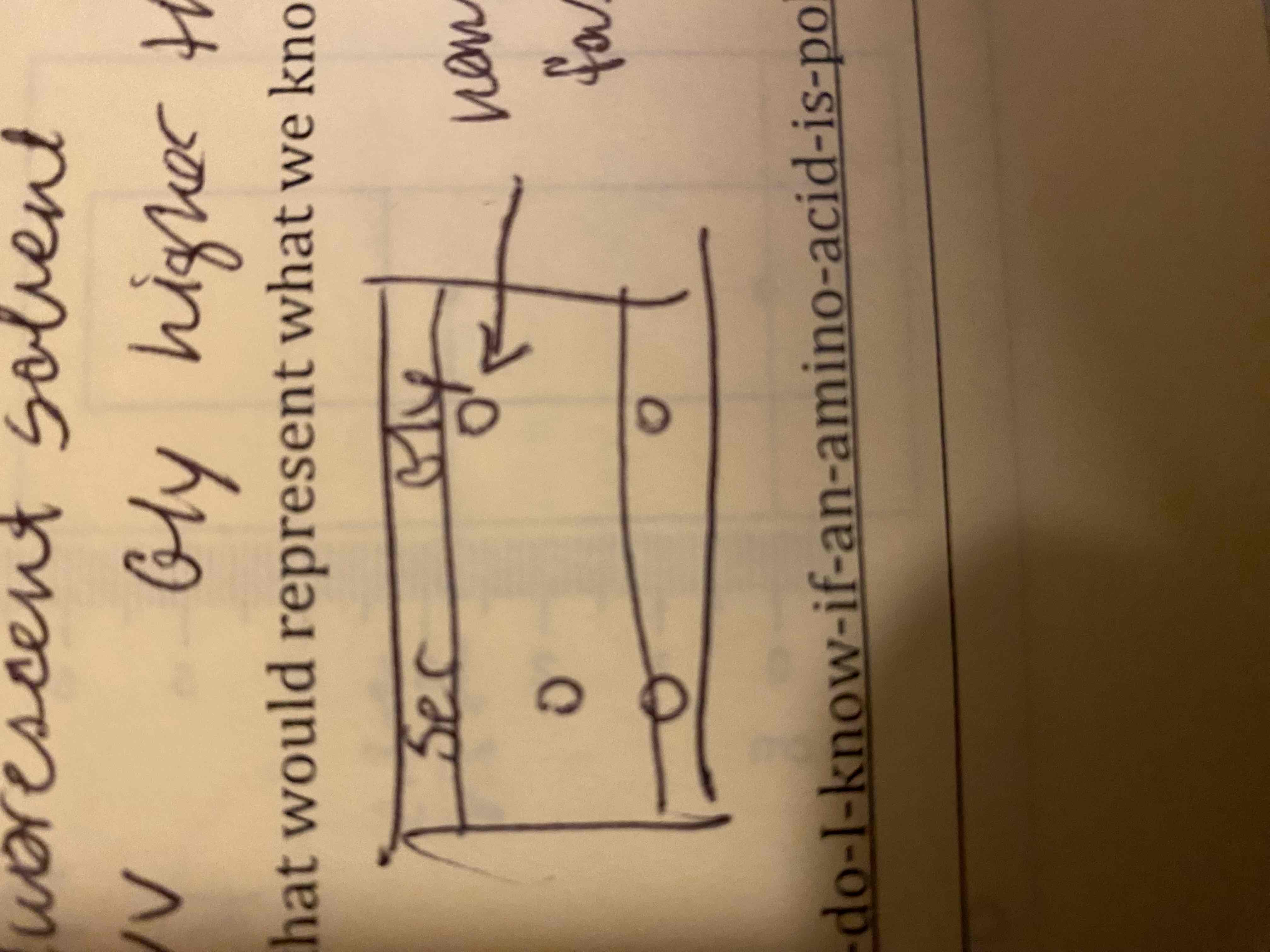
c. Draw a chromatogram that would represent what we know about the two amino acids.
a. No color to separate
b. Fluorescent solvent; UV; gly higher than ser
c. Non polar is faster
Which of the following is a most appropriate reason to perform a column chromatography over paper chromatography?
The goal is to separate and recover the parts of the mixture.
Explain how two students could perform chromatography on the same mixture, the colored samples all move different distances, yet they can correctly identify component parts.

A student was performing paper chromatography and let the separation continue overnight. The student wished to determine if the mixture contained a substance with an Rf factor of 0.343 where: Rf=(distance traveled by the component)/(distance traveled by the solvent)
a) What days would be affected by this error?
b) Explain the effect on the calculated Rf.
a) distance traveled by the solvent
b) the distance traveled by the solvent is unknown
The image below shows the completed chromatography separation of a mixture in the left, and an incomplete image of the same mixture’s separation on the right. The data on the left has a leading edge of solvent if 10.0 cm and the distance traveled by the dye was 8.0 cm. The data in the right shows the leading edge of solvent as 6.0 cm. What distance would you predict the same due to travel on the chromatography paper on the right?
4.8 cm
Calculate the Rf for the following where the lines on the chromatography paper represent the starting point of the due and the final distance traveled by the solvent.
0.54 & 0.85

Which of the following would travel the farthest in column chromatography?
C8H18
In paper chromatography, what physical property is most important to the separation?
Polarity
A distillation of several compounds was performed. Based on the physical property provided, place the substances in order of extraction.
1) diethyl ether
2) acetone
3) ethanol
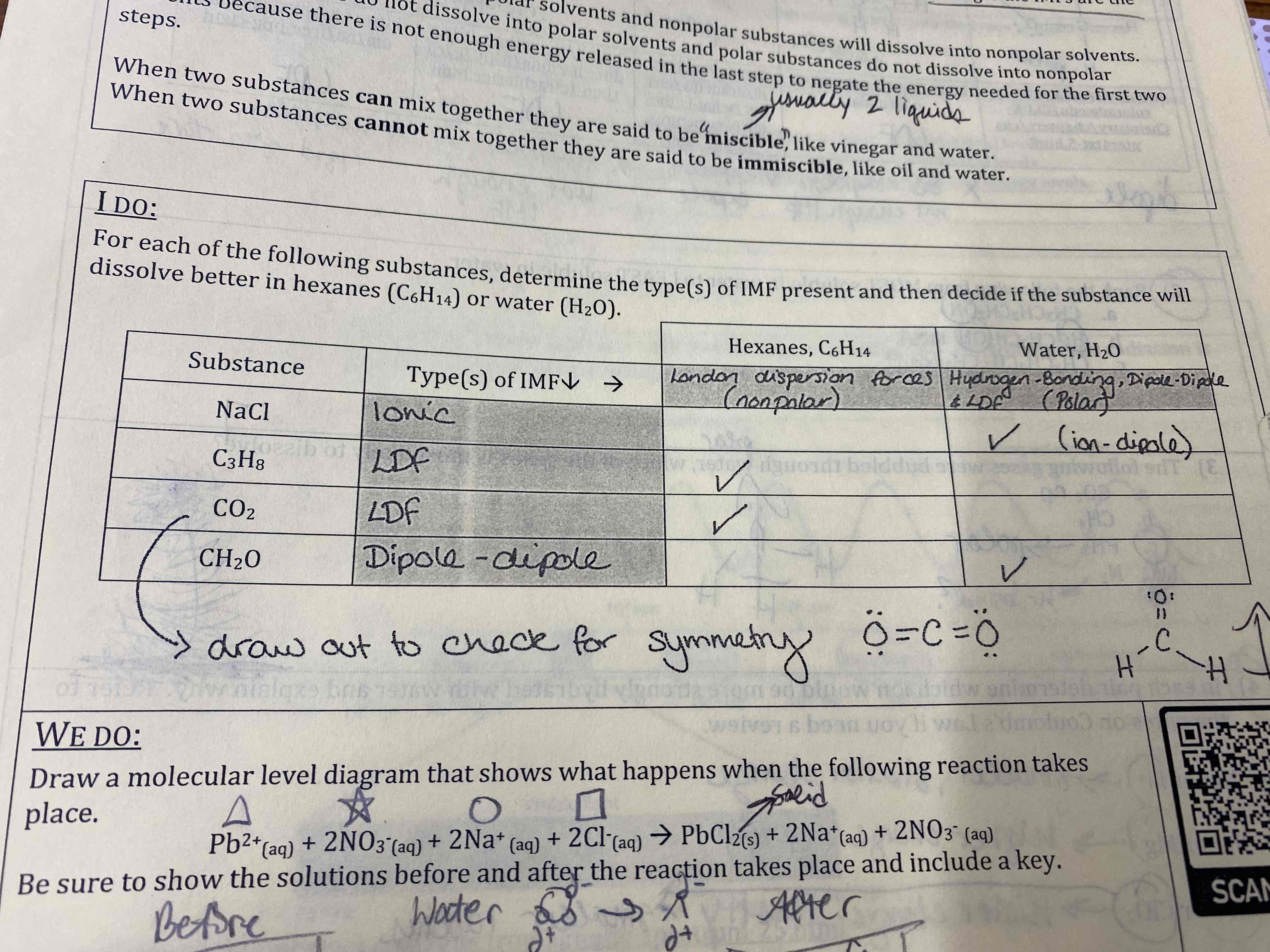
For each of the following substances, determine the type(s) of IMF present and then decide if the substance will dissolve better in because or water.
NaCl: water
C3H8: hexanes
CO2: hexanes
CH2O: water
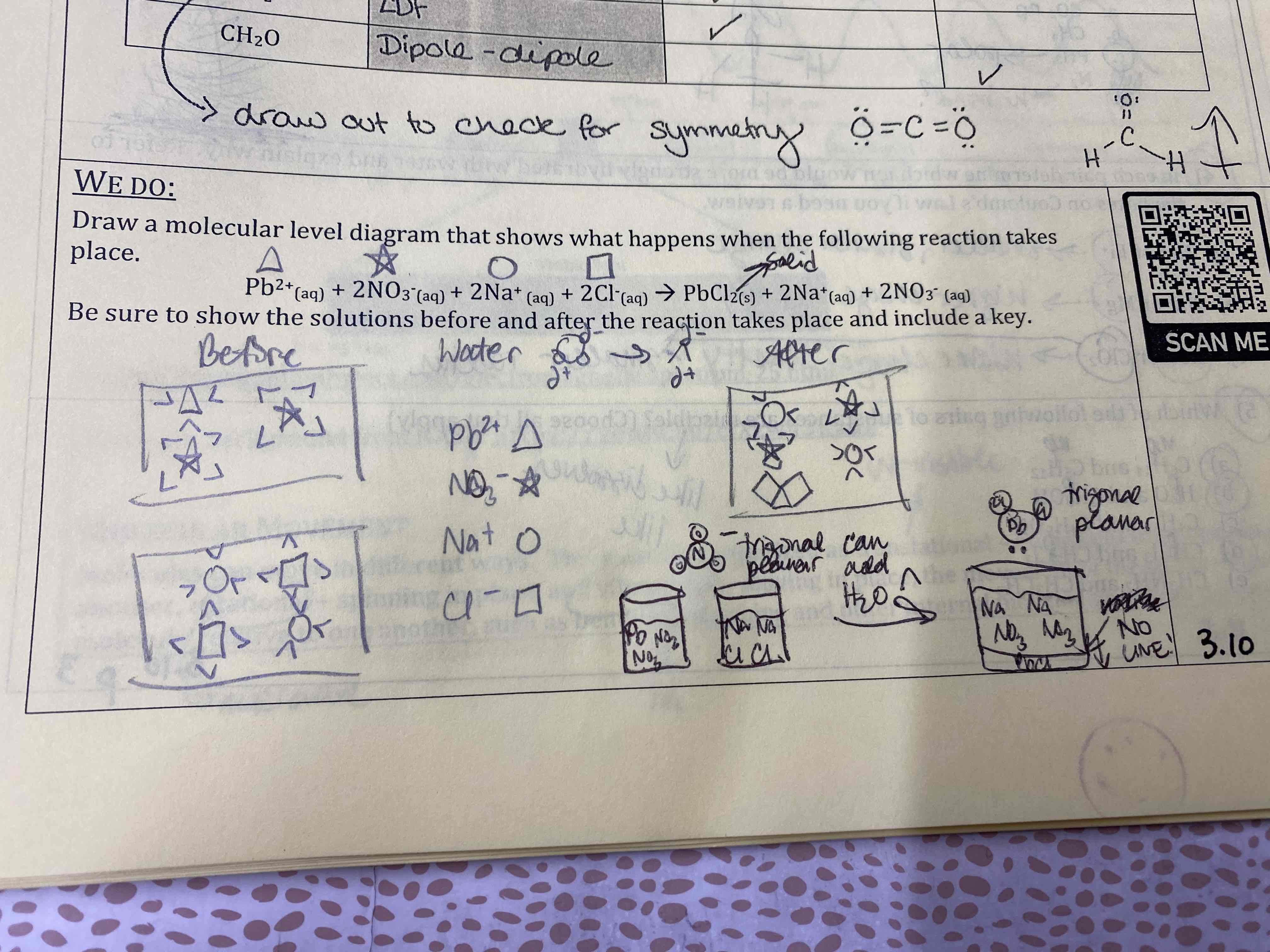
Draw a molecular level diagram that shows what happens when the following reaction takes place.
Be sure to show the solutions before and after the reaction takes place and include a key.
Look at the different structural formulas provided and determine which would be most likely to dissolve in methanol. Explain your selection based on the intermolecular forces.
Ammonia
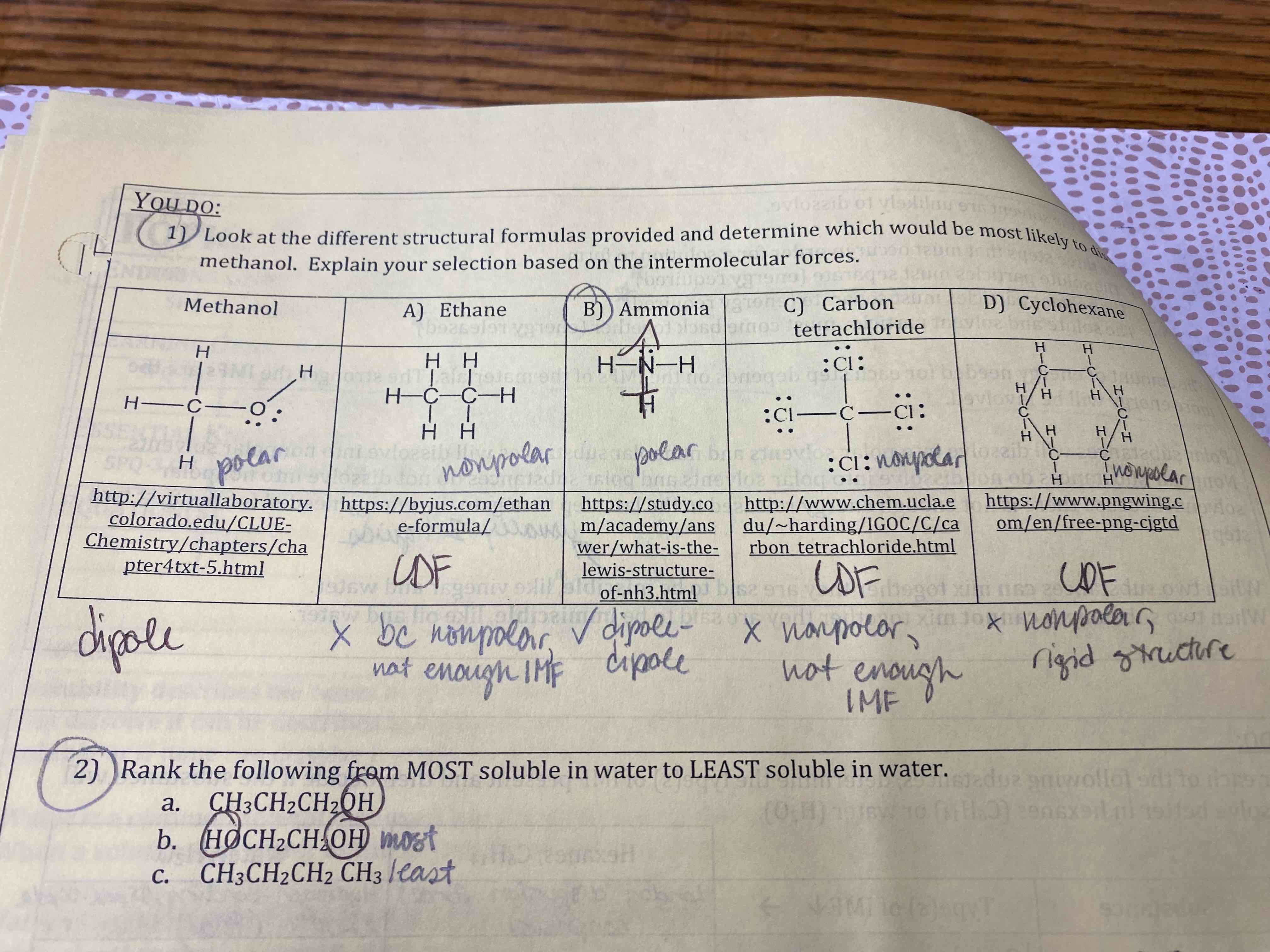
Rank the following from MOST soluble in water to LEAST soluble in water.
a. CH3CH2CH2OH
b. HOCH2CH2OH
c. CH3CH2CH2CH3
b, a, c
The following gases were bubbles through water, which of the gases is most likely to dissolve?
PH3
In each pair determine which ion would be more strongly hydrated with water and explain why. Refer to the notes on Coulomb’s Law if you need a review.
a) Li+; smaller, similar charge
b) Mg2+; higher charge density
c) ClO2- smaller radius
Which of the following pairs of substances are miscible? (Choose all that apply)
a) C6H14 and C5H12
b) H2O and CH3OH
d) CHCl3 and CH2Cl2
Two samples of copper (II) sulfate were analyzed using visible light spectroscopy. Sample One absorbed twice as much light as Sample Two.
a) What can you deduce about the concentrations of the two solutions?
b) What must be true of the solutions in order to get results from this type of spectroscopy?
c) Describe the type of changes that occur within the molecule during the process of UV-Vis spectroscopy.
a) The concentration of sample 1 is double that of sample 2.
b) They need to be colored.
c) The atoms within the molecule absorb energy. The energy causes electrons to jump from their ground state to an excited state.
What type of spectroscopy would be responsible for the change from *insert electron configuration*?
What type of spectroscopy would be responsible for the bending of the O-H bonds in water?
UV-Visible
IR
Match the type of electromagnetic radiation with the type of molecular motions or transitions that it causes.
A) Infrared
B) Ultraviolet-Visible Light
C) Microwaves
A) Vibrational Motion
B) Electronic Transitions
C) Rotational Motion
NO2 is a reddish brown color while N2O4 is a colorless. Based on this information only, which type of spectroscopy would be a good choice to determine the identity of an unknown sample that contained either NO2 or N2O4?
UV-V
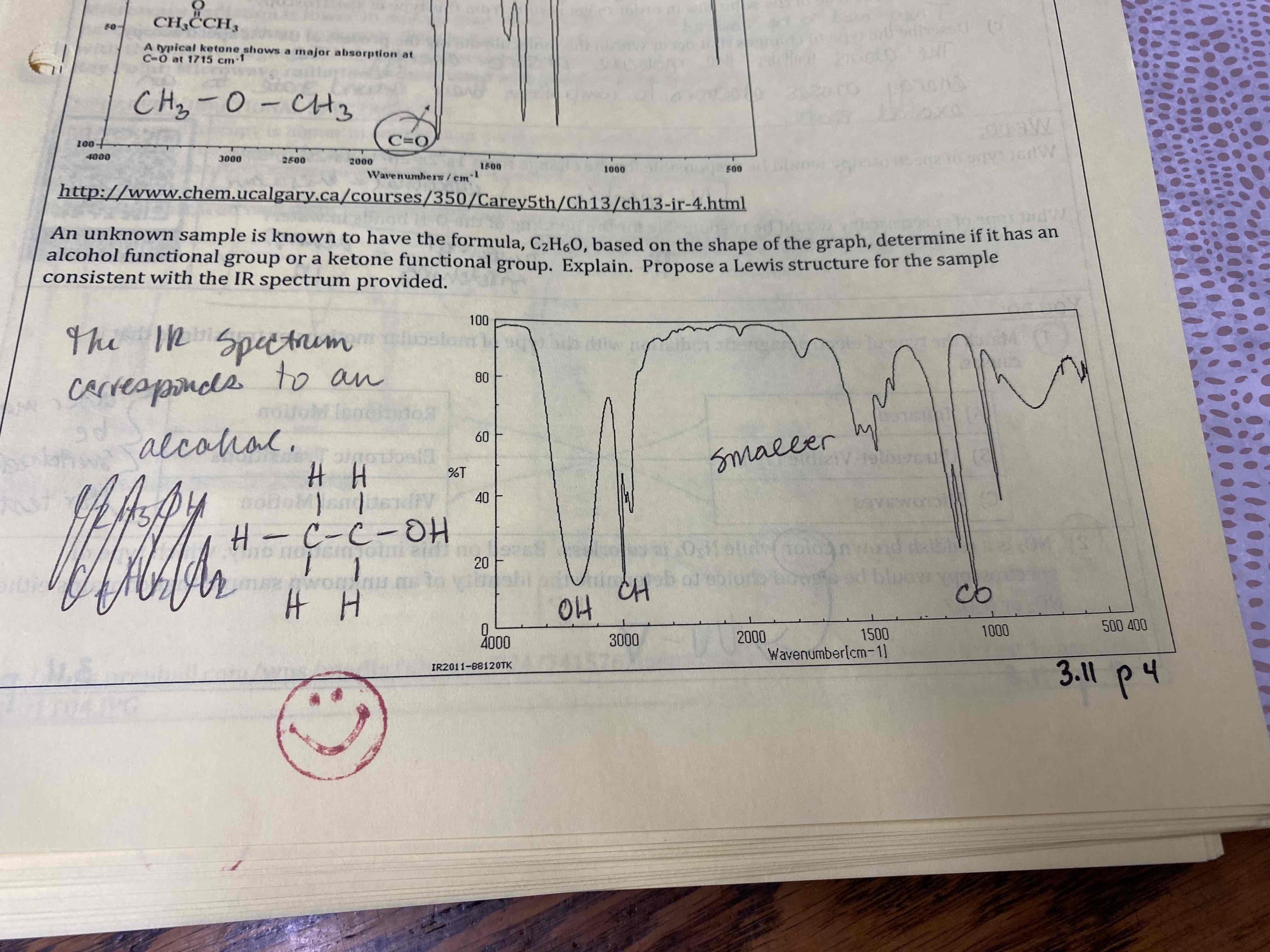
The IR spectra…
Corresponds to an alcohol
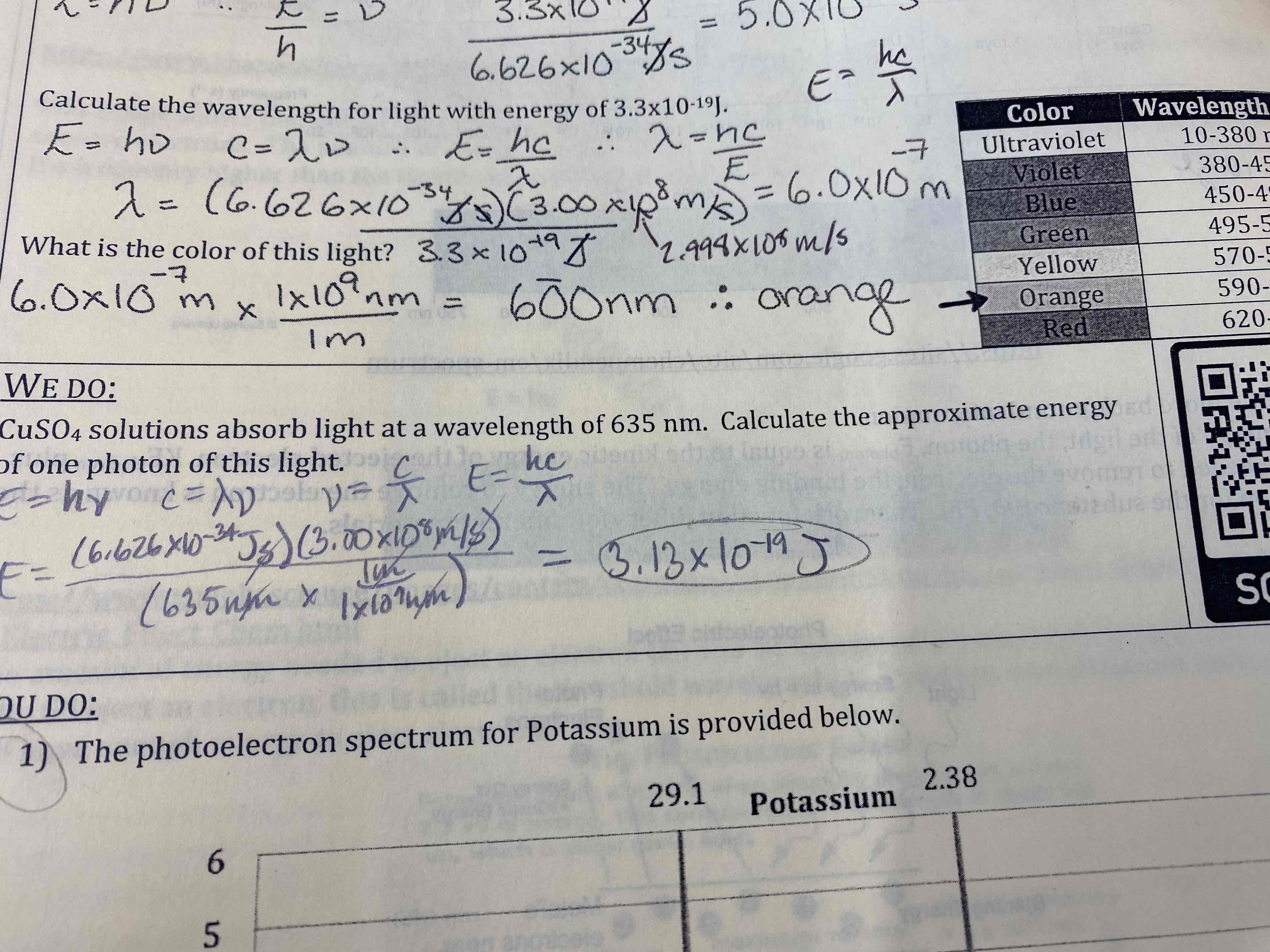
When a metal surface is exposed to light with increasing frequency and energy of photons, electrons first begin to be ejected from the meta when the energy of the photons is 3.3×10^-19 J.
What do the frequency of light with photon energy 3.3×10^-19 J?
Calculate the wavelength for light with energy 3.3×10^-19 J.
What is the color of this light?
5.0×10^14 s^-1
6.0×10^-7 m
600 nm: orange

CuSO4 solutions absorb light at a wavelength of 635 nm. Calculate the approximate energy of one photon of this light.
3.13×10^-19 J
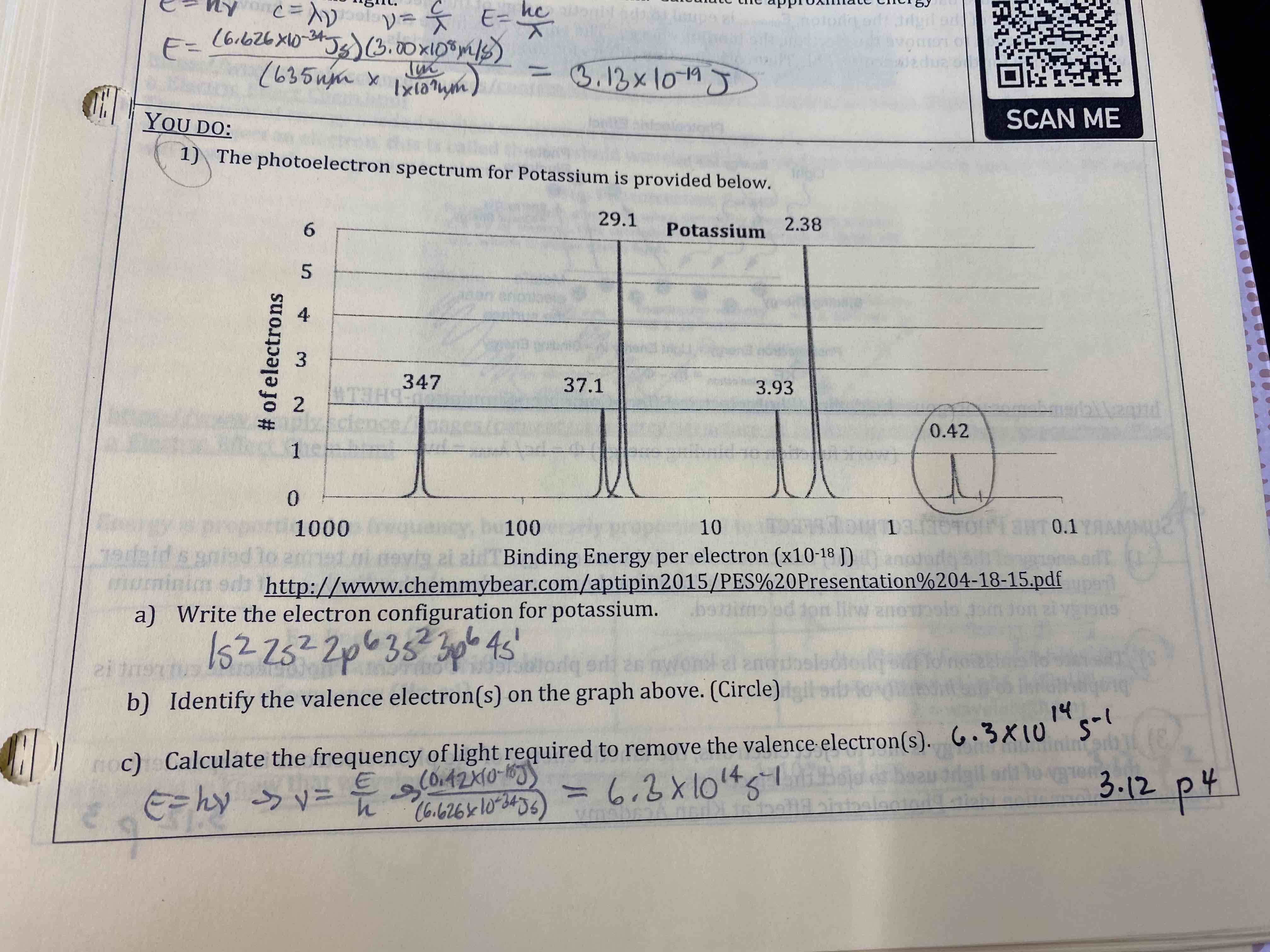
The photoelectric spectrum for potassium is provided below.
a) Write the electron configuration for potassium
b) Identify the valence electron(s) on the graph above (Circle)
c) Calculate the frequency of light required to remove the valence electron(s)
a) …
b) circle last peak
c) 6.3×10^14 s^-1
The energy required to eject an electron from sodium metal using the photoelectric effect is 275 kJ/mol. What is the maximum wavelength in nm needed for this to occur?
435 nm

Calculate the frequency of red light with a wavelength of 715 nm.
4.20×10^14 s^-1

The ionization energy of silver is 731 kJ/mol. Is light with a wavelength of 415 nm sufficient to remove an electron from a silver atom in the gaseous phase?
Not sufficient

Based on the provided calibration graph, if the absorbance of an unknown concentration of the solution was 0.34, what was the molarity of the solution?
3.0 μM
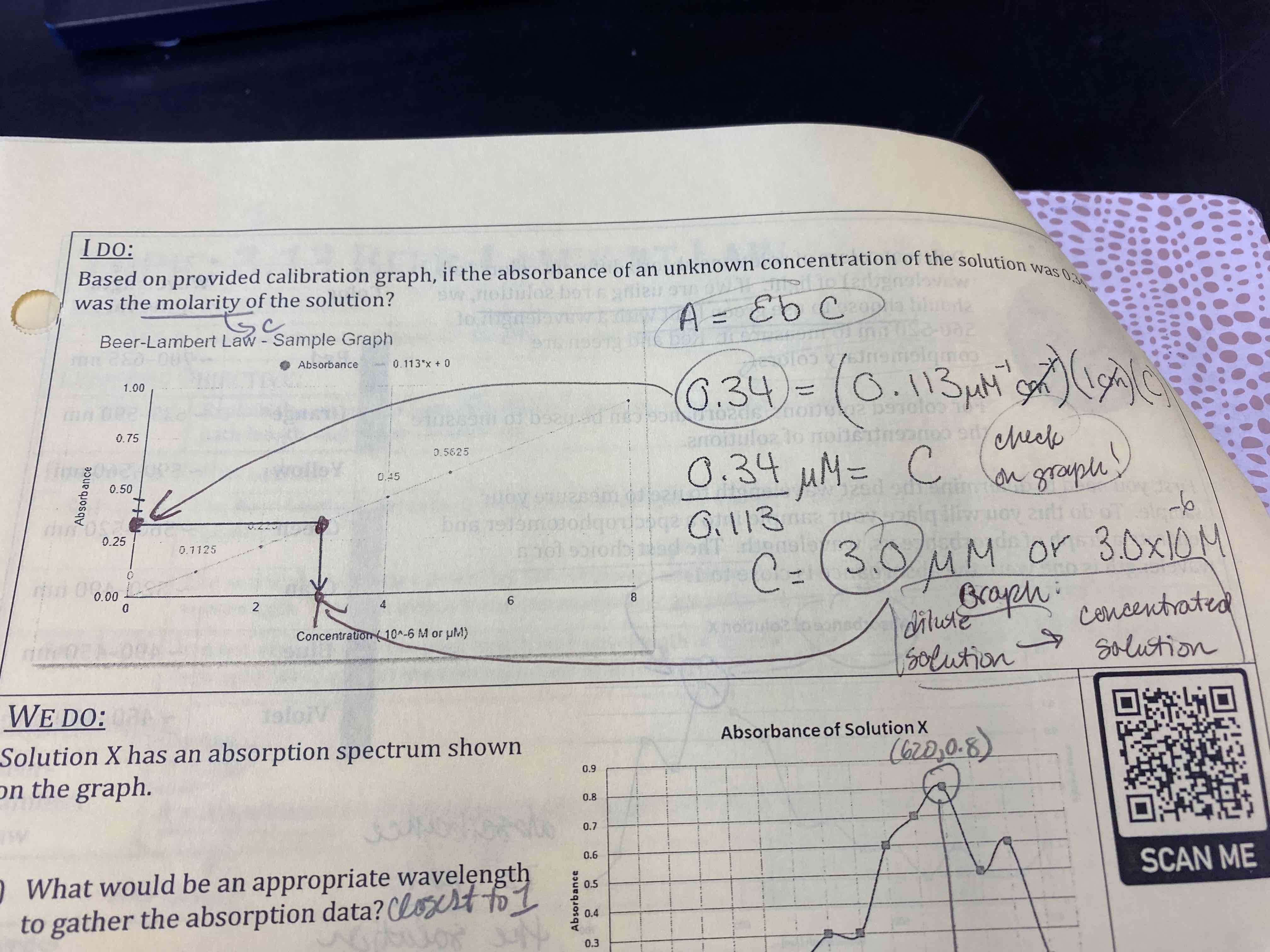
Solution X has an absorption spectrum shown on the graph.
A) What would be an appropriate wavelength to gather the absorption data?
B) what is the color of the light that is absorbed?
C) Predict the color of this solution.
D) A solution with an unknown amount of the same solute, X, was prepared and graphed as shown. How is the new solution (unknown concentration) different from the first one? How is it the same?
A) 620 nm
B) Orange
C) Blue
D) Unknown: 0.5 M
Known: 1.0 M
Same color, same peak absorbable
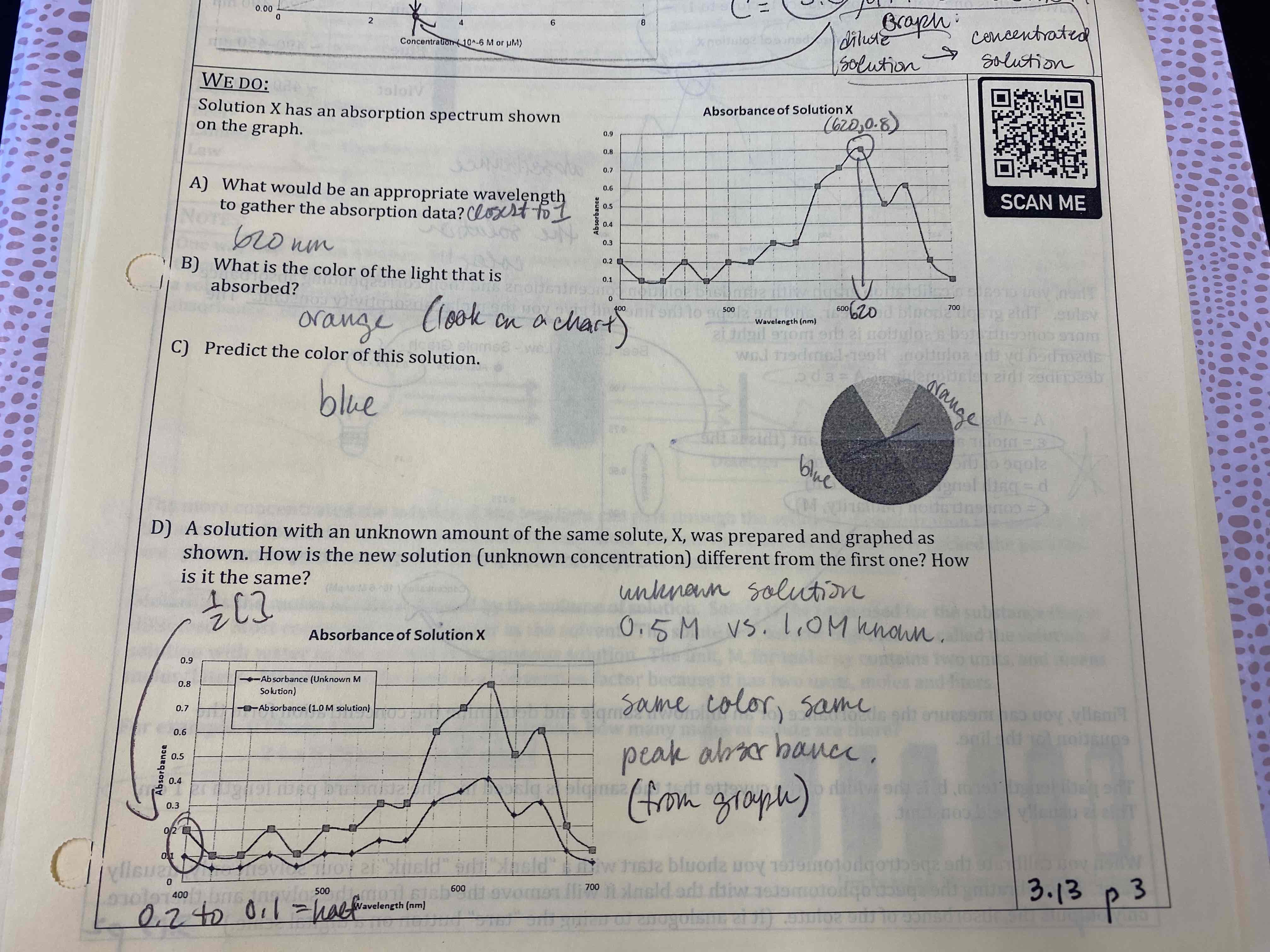
Water is added to dilute an 8 M solution of a red dye.
a) What happens to the concentration of a solution as water is added?
b) Complete the images below:
c) Explain why the absorbance of light decreases when the concentration of the solution decreases.
a) Decreases
b) Look at picture
c) Less concentration = less particles to absorb light
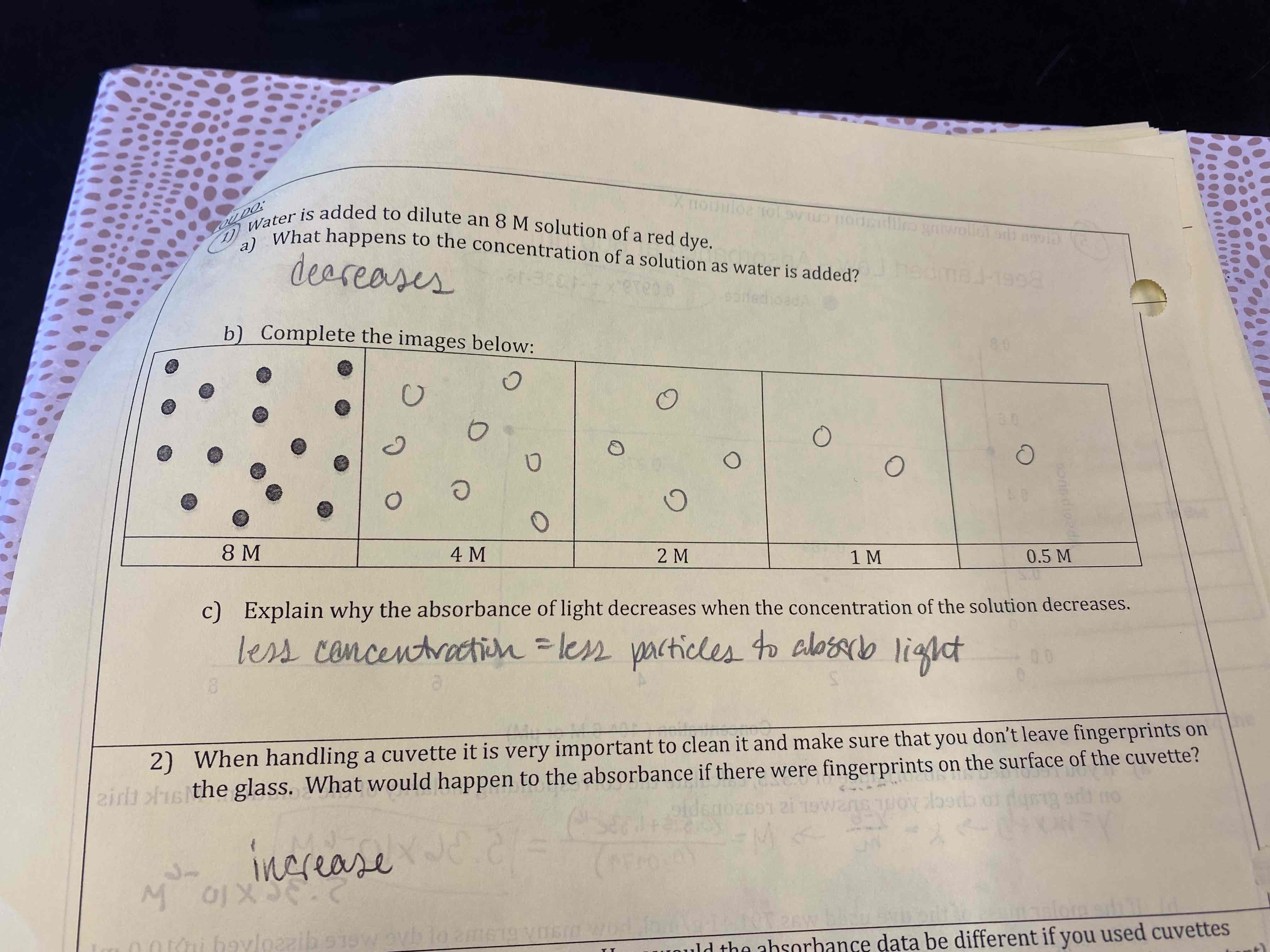
When handing a cuvette…
Increase
The standard size…
It would double; 4 dots to 8 dots
Determine the effect of the following errors in the measured absorbable for a pink colored 0.50 M solution of cobalt (II) chloride.
a) You rinsed the cuvette with water before adding the sample.
b) You used a cuvette that had previously contained 0.80 M CoCl2.
c) The solution was incorrectly made and the concentration was 0.05 M.
d) The spectrophotometer was calibrated with 0.05 M CoCl2 solution instead of water.
e) You used a cuvette that was scratched on the sides.
a) decrease
b) increase
c) decrease
d) decrease
e) increase
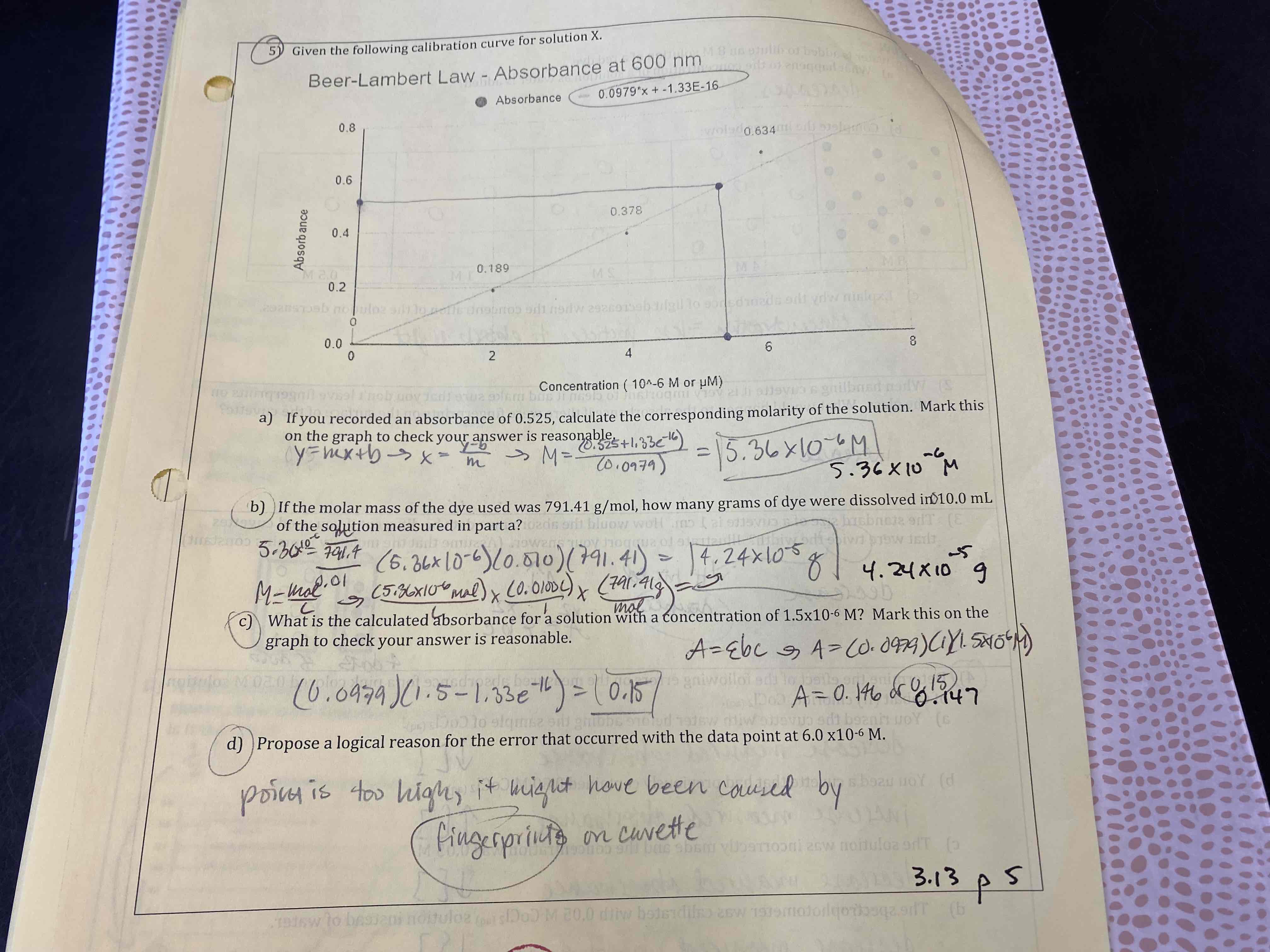
Given the following calibration curve for solution X.
a) If you recorded an absorbance of 0.525, calculate the corresponding molarity if the solution. Mark this on the graph to check your answer is reasonable.
b) If the molar mass of the dye was 791.41 g/mol, how many grams of dye were dissolved in 10.0 mL of the solution measured in part a?
c) What is the calculated absorbance for a solution with a concentration of 1.5×10^-6 M? Mark this on the graph to check your answer is reasonable.
d) Propose a logical reason for the error that occurred with the data point at 6.0×10^-6 M.
a) 5.36×10^-6 M
b) 4.24×10^-5 g
c) 0.15
d) fingerprints