Unit 4 Mental Health Study Guide
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
The 4 D’s of Mental Disorders:
Deviance
Distress
Dysfunction
Danger
Deviance (4D’s)
different, extreme, unusual
Distress (4D’s)
unpleasant & upsetting to the person diagnosed
Dysfunction (4D’s)
causes interference with daily life
Danger (4D’s)
poses risk to themselves or others
Theoretical Perspectives
in mental health refer to frameworks that help explain the causes and treatment of psychological disorders. These perspectives include Biological, Humanistic, Behavioral. Psychodynamic, Cognitive, & Sociocultural.
Biological Perspective
focuses on the physiological and genetic factors that influence mental health, including brain chemistry and structure.
Humanistic Perspective
a psychological approach that emphasizes individual potential and stresses the importance of growth and self-actualization.
Behavioral Perspective
A psychological approach that focuses on observable behaviors and the ways in which they are learned and reinforced through interactions with the environment.
Psychodynamic Perspective
A theory of psychology that emphasizes the influence of the unconscious mind and childhood experiences on behavior and mental states. It was developed by Sigmund Freud and includes concepts like defense mechanisms and psychosexual development.
Cognitive Perspective
A psychological approach that emphasizes mental processes, such as perception, memory, and problem-solving, in understanding behavior and emotions.
Sociocultural Perspective
A psychological approach that examines how cultural and social contexts influence behavior, attitudes, and mental processes, including factors such as race, gender, and socioeconomic status.
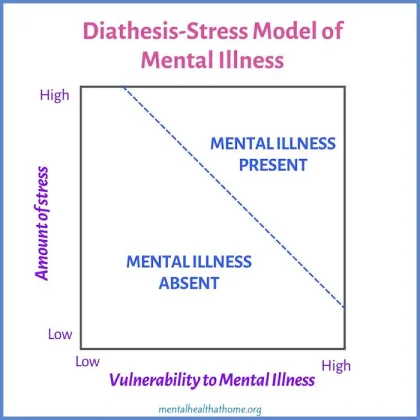
Diathesis- stress model
the diathesis-stress model predicts that an individual's reaction to an event will depend on their genetic makeup. An individual with a particular gene is more likely to develop depression if they are exposed to a stressful life event. Thus, the stronger the diathesis (genetics) the less stress is necessary for the disorder to develop.
DSM 5
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition, is a comprehensive classification system used by mental health professionals to diagnose and categorize mental disorders. It provides standardized criteria and descriptions to guide clinical practice.
Classification System
Used to categorize & understand mental disorders, aiding in diagnosis, research, & communication among therapists (THE DSM5 is a classification system)
How does the biological perspective see mental illnesses & treat them?
Mental illness results from problems in communication within the brain (neurotransmitters). To treat they emphasize pharmaceuticals and medicine to target presumed biological abnormalities
How does the behavioral perspective explain mental illness and how do they treat it?
See it as learned behaviors from the environment and conditioned responses. Treat by finding new ways of behavior by utilizing the same learning strategies that led to the development of the disorder.
How does the humanistic perspective explain mental illness and how do they treat it?
Mental illness is a product of having an unmet need that disturbs homeostasis. These are treated by self-actualization and positive regard in which the therapist is fully acceptive of all aspects of the patient.
How does the psycho-dynamic perspective explain mental illness and how do they treat it?
Mental illness is caused by unconsious conflicts in the the mind that are rooted in past experiences & trauma. Can be treated through bringing these unconscious conflicts to the consious; speaking on the unresolved issues and looking at the past and present links to become more aware of the process behind them.
How does the cognitive perspective explain mental illness and how do they treat it?
Mental illness is caused by negative thoughts which lead to negative emotions, anxieties & behaviors. Therapy focuses around communication to change the way one THINKS.
How does the socio-cultural perspective explain mental illness and how do they treat it?
Mental Illness is not just determined by personalities or a patient’s brain but by the social conditions they face. Different individuals in the same circumstance will have similar levels of mental health & illness. Treatment often incorporates cultural understanding & community support
Agoraphobia
An anxiety disorder that causes intense fear of becoming overwhelmed/not being able to escape. Thus patients will avoid new places (large spaces, crowds, unfamiliar areas).
Symptoms:
fear
rapid heart rate
hyperventilating
flushing
Cause: usually caused by a pre-existing panic disorder that develop agoraphobia.
Treatments:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Medication
Lifestyle Changes
Panic Disorder
Multiple unexpected panic attacks when sudden and strong fear is present in reaction to ordinary events. Usually occur without any warning without pre-existing conditions
Symptoms:
chest pain
difficulty breathing
hyperventilating
nausea
trembling
Cause: Can be caused by a traumatic life experience, having a close family member with panic disorder or an imbalance of neurotransmitters.
Treatments:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Exposure Therapy
Social Anxiety Disorder
Condition that causes fear & anxiety when around people in a social setting with fear of being perceived or judged.
Symptoms:
sweating
little to no eye contact
nervous behavior/trembling
low self-esteem, high self-conscious
avoiding social situations (finding them scary)
Causes: can sometimes run in families but environmental factors (such as stress and society), as well as brain hyperactivity in the areas of fear and anxiety (the amygdala) play a role
Treatments:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
antidepressants (medication)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Condition that causes constant worry over everyday things & a fear of being overwhelmed.
Symptoms:
restlessness
irritability
difficulty concentrating
headaches
difficulty sleeping
shortness of breath + heart palpitations
Causes: Can be passed on down the lineage (biological relative), but also can be incurred by experiencing a traumatic event, managing a chronic illness, and experiencing child abuse.
Treatments:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Medication
Specific Phobia
Major Depressive Disorder
Causes a persistently low/depressive mood & a loss of interest in activities
Symptoms:
extremely low mood
loss of interest in activities that brought joy
increase or decrease in appetite
slowed speech
insomnia or hypersomnia
decreased concentration
suicidal ideation (thoughts)
fatigue
Cause: things such an imbalance of neurotransmitters (serotonin, noreperephine, & dopamine), childhood abuse/trauma, stressful live events, as well as genetic predisposition,
Treatment:
psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Antidepressants (medication)
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
Mania
Condition in which a patient displays over the top energy levels that is drastic from their usual self and persists
Symptoms:
invincibility
insomnia
racing thoughts & ideas
rapid talking
false beliefs & perceptions (delusions)
hallucinations
Impulsive behavior
Cause: Things like chemical imbalances in the brain, family history, lack of sleep, difficult life situations and even a side-effect of other seasonal effective disorders or physical/neurological damage/trauma.
Treatments:
antipsychotics (medication)
psychotherapy (talk therapy)
cognitive behavioral therapy
PTSD
Common health condition that can develop after a traumatic event.
Symptoms:
flashbacks
anxiety
negative thoughts & beliefs
hyper vigilance
irritability
nightmares
Cause: Abnormal levels of certain neurotransmitters (low levels of cortisol and high norephrine trigger causing a higher fight or flight response) & hormones + with brain changes.
Treatments:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Cognitive Processing Therapy
Group Therapy
Exposure Therapy
Antidepressants (medication)
Dissociative Amnesia
Inability to remember important information on yourself regarding distressing or upsetting events.
Symptoms:
flashbacks
lack of awareness
disorientation
wandering
Causes: common to occur with severe or long-term trauma through abuse, neglect, or violence of any kind.
Treatment:
remove any causes to the anemia/ things that amplify it
Mental health therapy
Anorexia Nervosa
an eating disorder that involves severe calorie restriction and a extremely underweight body frame with a fear of weight gain.
Sympotms:
intense fear of gaining weight
obsessive interest in dieting, calorie counting, etc.
purging through intentional vomiting or misuse of laxatives
misuse of dieting pills
compulsive or excessive over-eating
withdrawal
significant weight loss
being very self-critical
strong need for self control
Cause: genetics can predispose many to this condition but it mainly has to do with changes in brain chemistry (serotonin and dopamine depletion which control appetite, mood & impulses). additionally things like, trauma such as psychical abuse & sexual assault, environment and culture (diet/ unhealthy model culture), peer pressure, & emotional health (perfectionism), can lead to this disorder.
Treatments:
individual & group psychotherapy (talk therapy)
medication
hospitlization
developing long-term behavioral change
eliminating binge-eating/ purge behavior
nutritional rehabilitation to stabalize weight
Bulimia
an eating disorder that causes a patient to consume large amounts of food at one time (binge) and then get rid of it (purge).
Symptoms:
excessive excercise
preoccupation with body image
depression/anxiety
intense fear of gaining weight
withdrawal
shame/guilt around eating
fainting
muscle weakness
dehydration
Cause: Caused by both genetic factors & learned behavior. Popular culture & media Put bodily pressure on people which affects body image and self-esteem.
Treatments:
psychotherapy (talk therapy)
nutritional counseling
Antidepressants (Medication)
Schizophrenia
involves a disconnection from reality including hallucinations & delusions, also affecting a patients ability to recognize symptoms.
Symptoms:
unusual movement
disorganized speech
auditory hallucinations
isolation
delusions: false beliefs and perceptions
paranoia
self-medication
Cause: Things like imbalances in chemical signals, improper brain-development during embryonic phase, and a loss of connection between different areas in the brain can result in this disorder. Additionally, one’s environment, brain trauma, and substance abuse can contribute to the potential aggravation of the disease (it runs in families/is genetic)
Treatment:
1st and 2nd gen anti psychotics (medication)
psychotherapy
Electroconculsive Therapy (ECT)
Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
Condition in which a patient has frequent unwanted thoughts that cause one to perform repetitive behaviors.
Symptoms:
germaphobia
fear of making a mistake
fear of causing harm to others or yourself
need for order/symmetry
perfectionism
numbered rituals
arranging things specifically
repeatedly checking things
Causes: Simpler things like childhood trauma/abuse and Genetics can predispose patients to this disorder. However, things like Brain frontoral changes, and PANDAS syndrome, can all affect the patients subseptibility to this condition.
Treatments:
Psychotherapy (talk therapy)
Serotonin reuptake inhibitors/ SRI’s (medication)
Psychotropic medications
Drugs that affect the brain & nervous system to treat mental illness by influencing neurotransmitters. This includes antidepressants, anti-psychotics, anxiolytics, mood stabilizers, & stimulants.
Cognitive triad
Also known as the Negative Triad which speaks on the 3 negative beliefs about self, the world, and the future that are characteristic of major depressive episodes, as proposed by Aaron Beck.

All types of Exposure Therapy
Systematic Desensitization: Gradual exposure combined with relaxation techniques.
Flooding: Immediate exposure to the most fear-inducing situation.
Virtual Reality Exposure Therapy: Uses virtual reality technology to simulate feared environments.
In Vivo Exposure: Directly confronting fears in real life.
Token economy
a system in which target behaviors are reinforced with a token (secondary reinforcers) which can be later exchanged for rewards ( primary reinforcers).
Person-centered therapy
developed by Carl Rogers it is a non-directive approach in which the client takes the rains of the talk therapy, while the therapist simply guides from the side in order to explore the clients feelings & find their own solution.