Digestive System
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
Organs of the alimentary canal
S- stomach
A-anus
M-mouth
P-pharynx
L-large intestine
E-esophagus
S-small intestine
A-anus
M-mouth
P-pharynx
L-large intestine
E-esophagus
S-small intestine
2
New cards
Hard palate
forms the anterior roof
3
New cards
Soft palate
forms the posterior roof
4
New cards
Where is the tongue attached?
attached at the hyoid bone and styloid process of the skull by the ^^**lingual frenulum**^^ to the floor of the mouth
5
New cards
Where is the laryngopharynx?
below the oropharynx and connect the the ^^**esophagus**^^
6
New cards
What role does the esophagus have in the digestive system?
It has no digestive function
7
New cards
Mucosa
innermost membrane (it is moist consisting of surface epithelium, connective tissue, and small smooth muscle layer)
8
New cards
Submucosa
just beneath the mucosa, soft tissue with blood vessels, nerve endings, and lymphatics
9
New cards
Muscularis externa
smooth muscle layer, inner circular layer, outer longitudinal layer
10
New cards
Serosa
outermost layer of the wall contains fluid producing cells
11
New cards
What covers the peritoneal cavity?
Visceral peritoneum (the outermost layer)
12
New cards
What lines the abdominopelvic cavity?
parietal peritoneum (innermost layer)
13
New cards
Where does food enter?
The cardioesophageal sphincter
14
New cards
Where does food empty?
In the small intestine at the pyloric sphincter
15
New cards
Small intestine
The body’s *major digestive* organ, site of nutrient absorption into blood
16
New cards
Where does the small intestine extend?
From the pyloric sphincter to ileocecal valve
17
New cards
Subdivisions of the small intestine
Duodenum- attached to the stomach, curves around the head of the pancreas, enzymes are carries into the duodenum by the bile duct and pancreatic duct.
Jejunum- attaches anteriorly to the duodenum, middle section.
Ileum- extends from the jejunum to large intestine
Jejunum- attaches anteriorly to the duodenum, middle section.
Ileum- extends from the jejunum to large intestine
18
New cards
What are three small intestine structural modifications that increase surface area?
Microvilli- tiny projections of the plasma membrane (create a brush border appearance)
Villi- fingerlike structures formed by the mucosa, contains rich capillary bed and a modified lymphatic capillary called a *lacteal*
Circular folds- deep folds of mucosa and submucosa
Villi- fingerlike structures formed by the mucosa, contains rich capillary bed and a modified lymphatic capillary called a *lacteal*
Circular folds- deep folds of mucosa and submucosa
19
New cards
Describe the Large intestine
Large in diameter, but shorter in length the small intestine, frames the internal abdomen
20
New cards
Anus
opening of the large intestine
21
New cards
Saliva
mixture of mucus and serous fluids, helps to form a food bolus, contains salivary amylase to begin starch digestion, dissolves chemicals so they can be tasted.
22
New cards
Describe Bile (where its produced and stored)
produced by the cells in the liver and stored in the gall bladder
23
New cards
Where does bile enter?
From the duodenum
24
New cards
What does the buildup of bile result in?
Tissue turning yellow causing a condition called jaudice
25
New cards
How do nutrients detour through the liver?
Via the hepatic portal circulation
26
New cards
Peristalsis
alternating waves of contraction and relaxation the squeezes food along the GI tract
27
New cards
Food breakdown as chemical digestion
Carbs are broken down into simple sugars
Proteins are broken into amino acids
Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol
Proteins are broken into amino acids
Fats are broken down into fatty acids and glycerol
28
New cards
Absorption
\-End of products digestion are absorbed in the blood or lymph
\-Food must enter mucosal cells and then into blood or lymph capillaries
\-Food must enter mucosal cells and then into blood or lymph capillaries
29
New cards
Where does carb digestion begin?
In the mouth
30
New cards
How is starch broken down?
Into maltose by salivary amylase
31
New cards
List the actives of the pharynx and larynx
They have no digestive function
32
New cards
What does the rooting reflex do?
Help the infant find the nipple
33
New cards
What does the sucking reflex do?
Help an infant hold onto the nipple and swallow
34
New cards
Phenylketonuria
a genetic disorder, inability of tissue cells to metabolize phenylalanine which can result in brain damage and retardation
35
New cards
Anabolism
larger molecules are built from smaller ones
36
New cards
Acidosis
results from incomplete fat oxidation in which acetoacetic accumulates in the blood
37
New cards
What does acidosis breath smell like?
Has a fruity odor
38
New cards
When is acidosis common?
In “no carb” diets, diabetes mellitus, starvation
39
New cards
Role of the liver in metabolism
manufactures bile, detoxifies drugs and alcohol, degrades hormones, produces cholesterol, blood proteins, plays a central role in metabolism.
40
New cards
What is absorbed in the large intestine?
Water, ions, and vitamin K and B are absorbed
41
New cards
How is the release of pancreatic juice into the duodenum stimulated?
Vagus nerve & local hormone secretin and cholecystokinin
42
New cards
Pancreatic enzymes play the major digestive function, what is it?
Helps to complete digestion of starch
43
New cards
What does the presence of food and rising PH cause?
Release of the hormone gastrin; causes stomach to produce protein-digesting enzymes, mucus, hydrochloric acid (makes the stomach acidic)
44
New cards
What does acidic PH do?
Activates pepsinogen to pepsin for protein digestion (provides a hostile environment to microorganisms)
45
New cards
Need to know
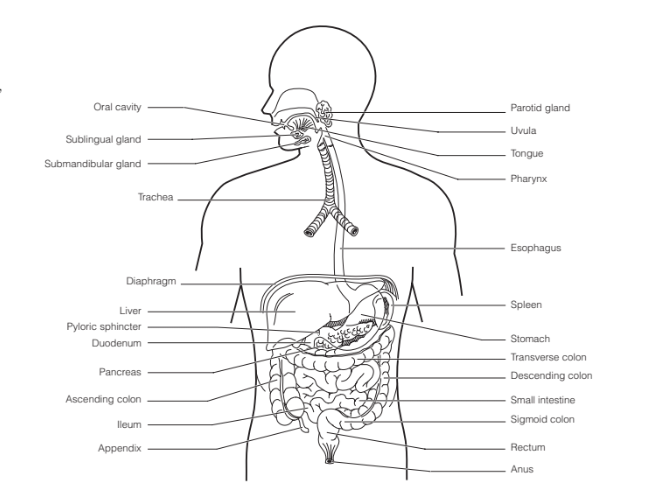
46
New cards
What is the function of the large intestine?
To dry out leftover food and produce feces.