business law
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What is enforceable rule
It means if you don’t comply with it then action can be taken against you legally
What is meant by backed by the state
The government stands behind it and can take action if broken
What is law
Enforceable rules backed by the state and it creates right and duties and is not always fair
Who does law apply to
Individual (natural person) and companies (legal person)
What is meant by predictability is vital for business
Businesses rely on the consistency and clarity of law to make informed decisions

Difference between civil and criminal law
Civil deals with disputes between 2 parties for example individual and business or 2 individuals and criminal deals with offences
Difference between civil and criminal law part 2
Criminal it is state vs individual that committed the crime and the victim role would be victim
Civil it is between 2 parties such as individual cus individual or government vs individual (if you didn’t pay taxes)
Difference between civil and criminal law part 3
Criminal it requires proof beyond reasonable doubt whereas civil it hears both stories and decides based on balance of probabilities( which side most likely to be true)
What is public law
The state and its interaction with the individuals and private organisations within that state for example if you committed a murder it would be state vs you
What is private law
Individual vs individual/ business and solving there disputes for example contracts,family law etc

Sources of uk law
Legislation(acts of parliament)-laws written by the parliament
Common law-courts make a rule when dealing with a individual case that becomes rule for future cases
Retained eu law/assimilated law- some of the eu laws was kept
What is primary legislation
Main law passed directly by parliament it is usually called an act of parliament
What is secondary/delegated legislation
Laws made by government or agencies using powers given by the act of parliament and it’s basically more detail under a act for example the act of parliament says driving must follow law and they can say the specific speeding limit drivers shouldn’t exceed under that act
What is constitution
A set of rules that explains how a country is governed/ran, what power the government has and protecting the rights of the people
What constitution does uk have
Uncodified constitution meaning that there’s no single written constitution instead it comes from multiple sources such as common law acts of parliament etc
What is doctrine of precedent
When judges follow past decision when making decision in similar cases

Ratio vs obiter
Ratio is the legal rule that leads to a judge making a certain decision in a case and is what future courts would willow for future similar cases
Obiter is things the judge says that not directly related to decision but are persuasive comments and they not binding (not used in future cases)
What are the Changing precedent
Distinguishing, overruling and reversing
Distinguishing
Courts can avoid following a precedent if they show the facts of the current case are different enough from the previous case
Overruling
When a higher court changes a precedent

What is reversing
When the higher court changes the decision made by a lower court in the same case

Court hierarchy
Supreme Court
Court of appeal
High court
Lower court
Supreme Court
Makes final decisions on law and can overrule decision made by other courts and it deals with important criminal cases constitutional and human rights

What’s meant by how a country is governed
Court of appeal
It hears appeals from lower courts and has 2 divisions criminal and civil. For example if someone loses case in high court can appeal to this one
High court
Civil court that deals with serious civil cases and also appeal form lower court can go here and there are 3 divisions queens bench division (civil disputes such as injury and defamation). Chancery division (cases such as business law and family division (deals with things like custody divorce etc. (image is regarding chancery division)
Lower courts
Courts interpret and apply the meaning of statues (law passed by parliament) as they are written in broad terms so can be unclear for the case they are working on

Interpretation approaches
Literal rule, golden rule, mischief rule and purposive approach
Literal rule
Judges take the words of statue at face value for example if it says no vehicle allowed to park in a space it will count something like a bike as a vehicle
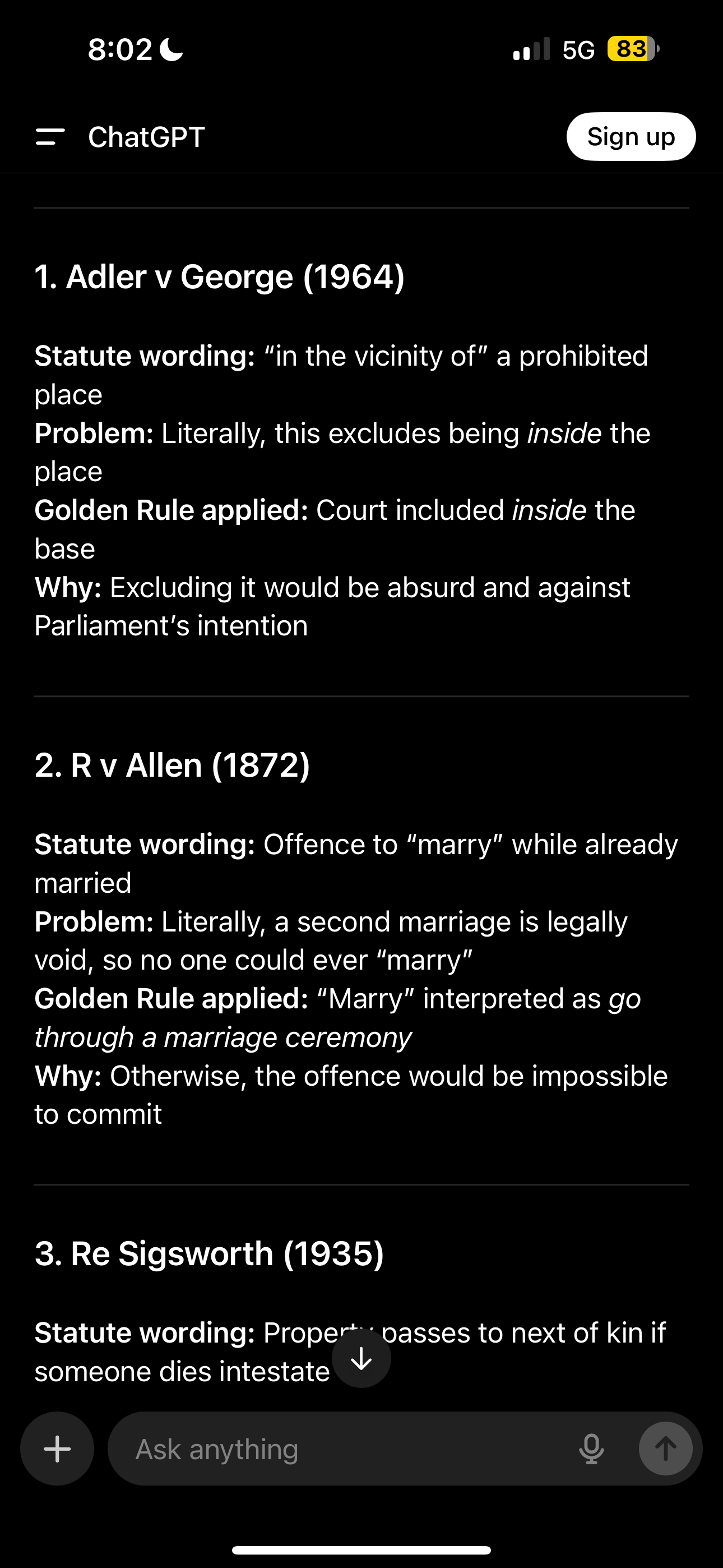
Golden rule
Allows judges to depart from legal meaning if it leads to a absurd result
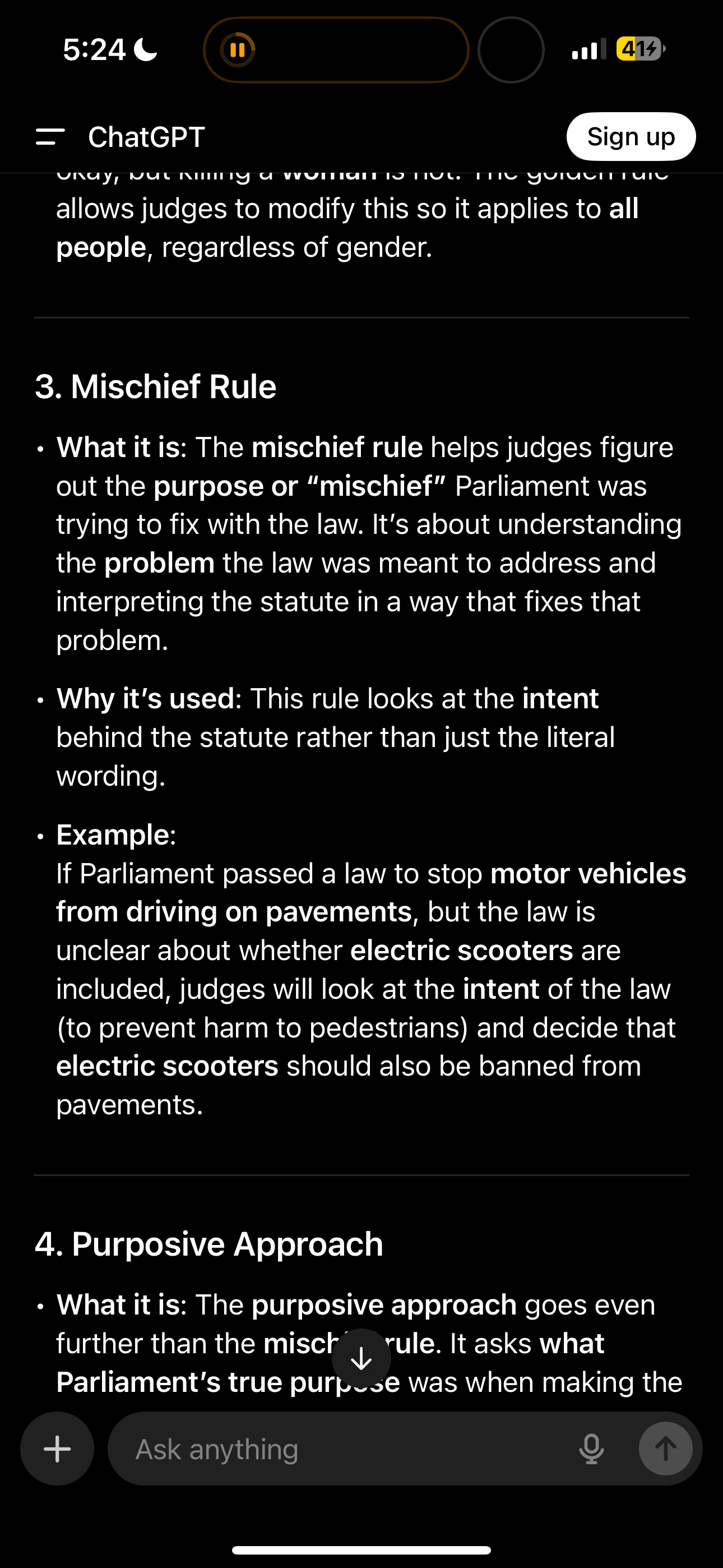
Mischief rule
When judges use the problem or mischief the government was tryna fix with a certain law and interpret it based on that
Purposive approach
Thinks about the true purpose of parliament when making a law and interpret based on that

Uk law after leaving eu
Some eu law was kept others was changed
Human rights activists 1998
Basic human rights protected such as freedom of speech, right to a fair trial, right to life etc and if you feel there violated then can go to uk court
Echr via Strasbourg
International treaty designed to protect human rights of someone believed there human right was violated by government or state they can take the case to echr via Strasbourg after using all options in national court and it is for countries that are in the council of Europe even uk post brexit
What are acts of parliament also called
Statue of legislation
5 things required for a contract
Offer, acceptance, consideration l, certainty of terms and intention to create legal relationship
What is consideration
The contract has to be a bargain (both exchanging this of value) and shouldn’t be a bare promise (someone promises to give you something for free) as the law will not enforce a bare promise)
Does it matter whether what your exchanging it’s fair for example 100 for iPhone 17
No as long as both exchanging things of value
Intention to create legal relations
The parties must intend that their agreement is to create legal responsibilities in both sides resulting in possible legal consequences if one part fails or defaults from obligations.
Certainty of terms
The terms of contract have to be sufficiently clear and certain to enable the courts to enforce the contract
What is an offer
Statement from the offeror to offeree identifying the terms which they are willing to be bound
What is invitation to treat
It is an invitation from one party to make an offer which they can accept or decline (invitation to negotiate) and it doesn’t show intention to immediately bound an example are shops display even if they have a price tag
are advertisements an offer or invitation to treat
Generally they are Invitations to treat the exceptions are if it’s made very clear that it’s an advertisement and it shows intention to be bound to offer
What is acceptance
The final and unconditional agreement to the offer and the terms in the offer it must correspond exactly to the offer (must accept the offer as it is)
What would counter offer do
Destroys the previous offer
What can also destroy offer
A time limit so for example if they state you have until tomorrow at 3.00 to accept this offer after that time the offer no longer valid
what happens if you make a offer and the offeror dies
The offer is broken
What happens if offerror dies but the offeree has already accepted
When possible the contract must still be performed
What would someone saying “I accept but only if your reduce price
A counter offer and it is not acceptance
Communication of acceptance general rule
(Need to finish this when PowerPoint released)
Postal rule
If you make a offer by post then the offer is recognised when the offeree received the item and when offeree replies to the offer and accepts it that is recognised when offeree posts it so not when you have received.
Will handing post to postman instead of post box count as a acceptance or offer
No
What happens if post lost when offeree sends acceptance
Then the acceptance is still recognised and if offeror doesn’t fulfill contract the offeree can take him to court
What does the postal rule have to be
Reasonable( for example if offeror sends offer through post then reasonable for offeree to send acceptance through post) to be continued……..
What is bilateral contract
Both parties make promises and one party offers to do something in return for a action bu the other party (for example, one person agrees to wash the other’s car in return for having their lawn mowed)
What is a unilateral contract
When one part promises to perform some action in return for a specific act but the second party is not promising to take any action ( for example dog poster says 1000 reward if you find the dog and second party has the choice to choose whether they find the dog and if they do first party has to pay)
What is a void contract
This is a contract that the law will not recognise and has no legal effect.
What is a voidable contract
One where the injured party(part which has been wronged or effected by the contract) has the option to continue with the contract or avoid the contract which will terminate it. And it has to be done within reasonable time to be fair to both parties
What would be reasonable times
This is used when there isn’t specific instructions in legislation or case law and it’s interpreted based on specific facts in the case
How would you revoke a unilateral contract
For example if the offer was advertised on a news paper posting another advertisement showing the offer has been revoked but if the acceptance includes performance of an act and the act has been started then it can’t be revoked
What is the general rule for acceptance
If the offer doesn’t require a particular way of acceptance you can accept it by any way such as email phone call etc but if it states a way have to follow that way or a way that’s quicker then the suggested way ( for example if asked to send by mail but send by email which is quicker)
When can silence be acceptance
In business to business transactions acceptance can be inferred from silence only if the offeree agreed in advance
What happens if someone sends you unsolicited goods( goods you did not ask for)
Sender cannot demand payment and asking for payment is a criminal offence (unsolicited goods and services act 1971) and also consumers protected from being forced to pay for goods they didn’t order (consumer protection distance selling regulation 2000)
What is deed
A written document that is witnessed signed and delivered showing a clear intention to be legally bound
Does deed require consideration
No for example executes a gift deed transferring something to someone for free even thought the receiver gives nothing in return it is still enforceable
What is considered a valuable consider
Either a interest, profit or benefit accruing to one party or some forbeance (patient,self control, tolerance),detriment,loss or resbonsibility given suffered or undertaken by the other party
What is the promisor and promised
Promisor is the person who makes the promise and the promises is the person who receives the promise and can enforce it
(A promise to pay b 600 if he paints A house in this case A is the promisor and b is the promisee)
2 types of consideration
Executed and executory
Executed consideration
Often seen in unilateral contracts and is when one party makes a promise in return for an act by the other party
Executory consideration
Often seen In bilateral contracts and is when both parties make promises
What does consideration have to be
Sufficient not adequate meaning that there has to be a exchange of things of value even if the things being exchanged isn’t fair
What is past consideration and does it count as a good/ valid consideration
Past consideration is when you perform an act and after the act performed the other part promises to give you something (for example made dinner for someone and they promised to give you 10 pound for it)
Would performing a existing duty good consideration
No it is not unless you exceed duty
Are existing duties good consideration
No because you are performing an act that you already are expected to do so will not provide a benefit for the promisor and a contract based on this will be unenforceable. Unless the existing duties is exceeded
What is the general contract law rule about part payment
Part payment of a debt will not prevent the party owed money to later claim balance even if agreed to take lower amount
What is the doctrine of promissory estoppel
Counter for part payment and it prevents someone from going back on a promise that was made to the other party and they relied on it and it can only be used as a defence not to use
What is the doctrine of privity off contract
Established that only parties to a contract may sue or be sued even if there’s a third party who benefits from the contract if they don’t make it can’t sue
Exceptions to doctrine of privity
Agency
Collateral contracts
Trusts
Restrictive covenants
Contracts for interested groups
Insurance contracts
What is a principle
Person or entity who authorises someone else to act for them and they are the real party
Agency
Agent is someone who authorised to act on behalf of another person known as principal. This means if agent makes contract with third party and third party is aware person acting as an agent the principal can sue and be sued on the the contract as if it were they who had agreed to the contract we
Collateral contact meaning
A contract established between 2 parties may indirectly create another contract with third party

Trust
The settlor transfers property to another person the trustee and the trustee holds and manages the property for the beneficiary and the settlor sets out rules and terms on how property’s should be managed and if not complied with beneficiary can enforce ir
What is life insurance

Insurance companies
Some insurance contracts created to benefit someone who is not the policy holder even though the third party did not buy the insurance or pay premium they may still claim the benefits

What is restrictive covenants
Legal promise in relation to land and it restricts what the owners can do on land to protect neighbours properties. And in the image c can sue

Contracts for interested parties
Contract may be created by one party but for the interest of themselves an turned whilst the other parties can’t claim breach of contract the party can ask the court to take the losses of other parties into account when determining damages
Scrutton ltd v midland silicones ltd (1962)
Scrutton was a company providing dock workers to a shipping company who was helping ship midland products the contract between midland and shipping company included a limitation clause that damage to goods restricted to 500 per unit the dock workers damaged one and Scrutton attempted to rely on limitation clause despite midland being unaware of contract between shipping company and Scrutton