AWS Services Overview and Best Practices
1/546
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
547 Terms
What is CloudFront primarily used for?
CloudFront is great for static content that must be available everywhere.
What is the caching behavior of CloudFront?
Files are cached for a TTL (Time to Live), which may be up to a day.
What must be set up for S3 Cross Region Replication to function?
Replication must be set up for each region where you want the replication to happen.
How frequently are files updated in S3 Cross Region Replication?
Files are updated in near real-time.
What type of content is S3 Cross Region Replication best suited for?
It is great for dynamic content that needs to be available at low-latency in a few regions.
What is the primary function of S3 Transfer Acceleration?
It increases transfer speed by transferring files to an AWS edge location, which then forwards the data to the S3 bucket in the target region.
How does S3 Transfer Acceleration improve transfer speed?
By using an AWS edge location to forward data to the S3 bucket.
What is the purpose of AWS Global Accelerator?
To improve global application availability and performance using the AWS global network.
How does AWS Global Accelerator optimize routing?
It leverages the AWS internal network to optimize the route to your application, providing up to 60% improvement.
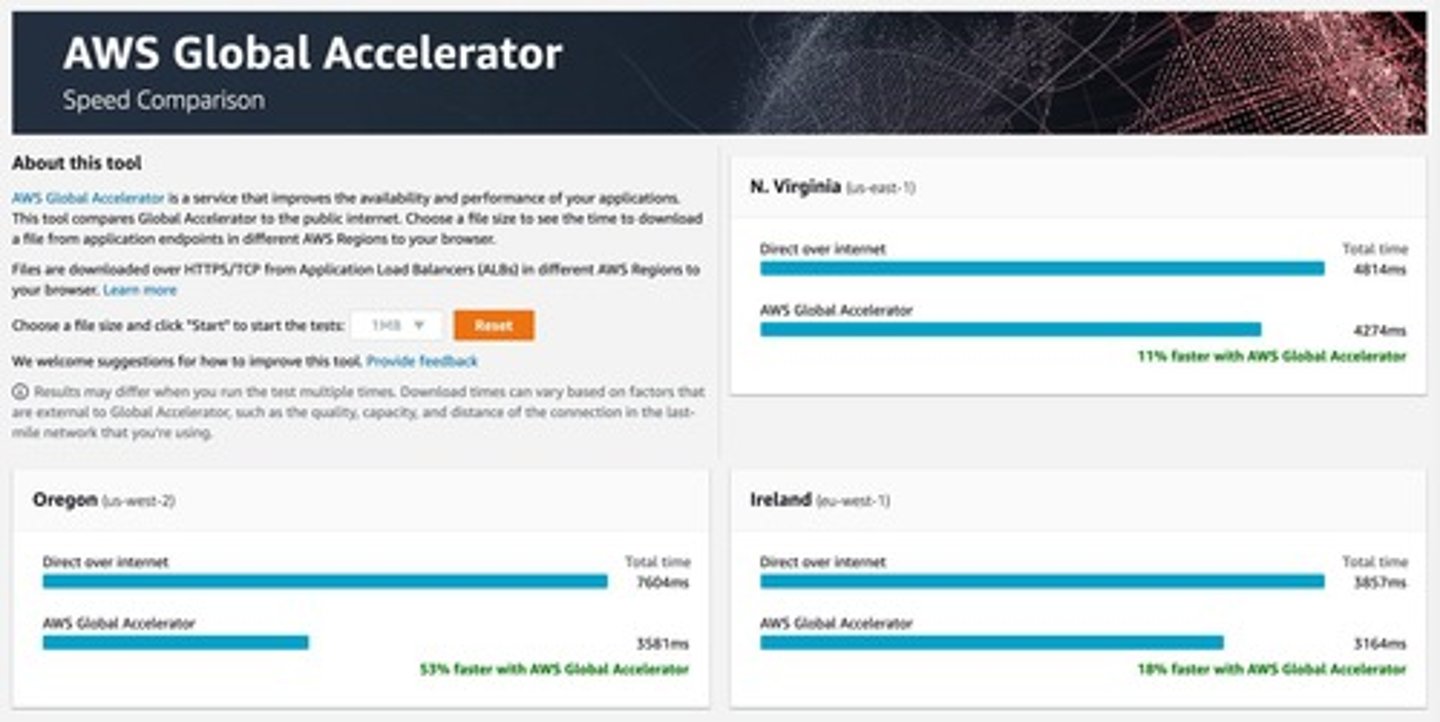
What is created for your application when using AWS Global Accelerator?
Two Anycast IP addresses are created for your application.
How does traffic flow when using AWS Global Accelerator?
Traffic is sent through Edge Locations to your application.
What is the main difference between AWS Global Accelerator and CloudFront?
CloudFront is a Content Delivery Network that caches content, while Global Accelerator does not cache and proxies packets to applications.
What type of content does CloudFront improve performance for?
CloudFront improves performance for cacheable content such as images and videos.
How do AWS Global Accelerator and CloudFront relate in terms of network usage?
Both use the AWS global network and its edge locations around the world.
What security feature do both AWS Global Accelerator and CloudFront integrate with?
Both services integrate with AWS Shield for DDoS protection.
What is the primary benefit of using Edge Locations in AWS services?
Edge Locations help in serving content closer to users, improving performance and reducing latency.
What type of content is S3 Cross Region Replication designed for?
S3 Cross Region Replication is designed for dynamic content that needs low-latency access.
What is the role of Edge Locations in S3 Transfer Acceleration?
Edge Locations serve as the initial point for transferring files to the S3 bucket.
What is the expected outcome of using AWS Global Accelerator for an application?
Improved availability and performance of the application globally.
What does the term 'Anycast IP' refer to in the context of AWS Global Accelerator?
Anycast IP refers to the two IP addresses created for routing traffic to the application through the nearest Edge Location.
What are the benefits of using AWS Outposts?
Benefits include low-latency access to on-premises systems, local data processing, data residency, easier migration from on-premises to the cloud, and it is a fully managed service.
What is the purpose of AWS Outposts?
AWS Outposts provide server racks that extend AWS infrastructure, services, APIs, and tools to on-premises environments, allowing businesses to build applications just like in the cloud.
What types of applications can benefit from AWS Outposts?
Applications that require low-latency access, local data processing, and data residency.
What is AWS WaveLength?
AWS WaveLength brings AWS services to the edge of 5G networks, embedding infrastructure within telecommunications providers' datacenters.
What are WaveLength Zones?
WaveLength Zones are infrastructure deployments at the edge of 5G networks that enable ultra-low latency applications.
What is a key feature of AWS WaveLength regarding traffic?
Traffic does not leave the Communication Service Provider's (CSP) network, ensuring high-bandwidth and secure connections.
What are some use cases for AWS WaveLength?
Use cases include smart cities, ML-assisted diagnostics, connected vehicles, interactive live video streams, AR/VR, and real-time gaming.
What do AWS Local Zones do?
AWS Local Zones place AWS compute, storage, database, and other selected services closer to end users to support latency-sensitive applications.
How do AWS Local Zones relate to AWS Regions?
They serve as an extension of an AWS Region, allowing for the extension of a VPC to more locations.
What AWS services are compatible with AWS Local Zones?
Compatible services include EC2, RDS, ECS, EBS, ElastiCache, and Direct Connect.
What is the role of AWS in managing Outposts Racks?
AWS sets up and manages Outposts Racks within the on-premises infrastructure.
What is required for the physical security of Outposts Racks?
The customer is responsible for the physical security of the Outposts Rack.
What type of cloud infrastructure do AWS Outposts support?
Hybrid Cloud infrastructure, which combines on-premises and cloud-based systems.
What is a key advantage of using AWS for HTTP use cases?
AWS improves performance for a wide range of applications over TCP or UDP, particularly for those requiring static IP addresses and fast regional failover.
What AWS services can be used on Outposts?
Services include Amazon EC2, Amazon EBS, Amazon S3, Amazon EKS, Amazon ECS, Amazon RDS, and Amazon EMR.
What are the two ways businesses can manage their IT systems with AWS?
One way is through the AWS cloud using the AWS console, CLI, and APIs, and the other is through their on-premises infrastructure.
What is the significance of AWS Outposts in a hybrid cloud setup?
They allow businesses to leverage AWS services on-premises, providing a seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments.
How does AWS WaveLength enhance application performance?
By providing ultra-low latency through 5G networks, enabling applications to operate more efficiently.
What is the relationship between AWS Local Zones and latency-sensitive applications?
Local Zones are designed to run latency-sensitive applications by placing AWS services closer to end users.
What is the main goal of AWS Outposts?
To provide a consistent AWS experience across on-premises and cloud environments.
What type of applications are ideal for AWS WaveLength?
Applications that require high bandwidth and low latency, such as real-time gaming and AR/VR.
What are AWS Local Zones?
AWS Local Zones are locations that bring AWS resources closer to users, improving latency-sensitive applications.
What is the purpose of AWS Route 53?
AWS Route 53 is a global DNS service that routes users to the closest deployment with the least latency and supports disaster recovery strategies.
How does AWS CloudFront improve user experience?
AWS CloudFront is a Global Content Delivery Network (CDN) that replicates parts of applications to AWS Edge Locations, decreases latency, and caches common requests.
What is S3 Transfer Acceleration?
S3 Transfer Acceleration is a feature that accelerates global uploads and downloads into Amazon S3.
What does AWS Global Accelerator do?
AWS Global Accelerator improves global application availability and performance using the AWS global network.
What are AWS Outposts?
AWS Outposts are racks deployed in your own data centers to extend AWS services.
What is AWS WaveLength?
AWS WaveLength brings AWS services to the edge of 5G networks, enabling ultra-low latency applications.
What are the two patterns of application communication?
The two patterns are synchronous communications (application to application) and asynchronous/event-based communications (application to queue to application).
What are the potential issues with synchronous communications?
Synchronous communications can be problematic during sudden spikes of traffic, such as needing to encode a large number of videos at once.
What services can be used to decouple applications?
Services include Amazon SQS (queue model), Amazon SNS (pub/sub model), and Amazon Kinesis (real-time data streaming model).
What is Amazon SQS?
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a service that enables decoupling of applications using a queue model.
What is the difference between Active-Passive and Active-Active configurations in multi-region setups?
Active-Passive configurations have one region actively serving traffic while another is on standby, whereas Active-Active configurations have multiple regions actively serving traffic simultaneously.
What is the significance of Availability Zones in AWS?
Availability Zones are isolated locations within a region that provide high availability and fault tolerance.
What is the benefit of using a Global CDN like CloudFront?
It decreases latency by caching content closer to users and improves user experience.
How does AWS Local Zones benefit latency-sensitive applications?
By bringing AWS resources closer to users, AWS Local Zones reduce latency for applications that require quick response times.
What is the role of Amazon Kinesis?
Amazon Kinesis is a service for real-time data streaming, allowing applications to process and analyze data in real-time.
What does the term 'Global Reads' Latency' refer to?
Global Reads' Latency refers to the time it takes for read requests to be processed across different regions.
What does the term 'Global Writes' Latency' refer to?
Global Writes' Latency refers to the time it takes for write requests to be processed across different regions.
Why is decoupling applications important?
Decoupling allows applications to scale independently and handle varying loads without being directly dependent on each other.
What is the purpose of caching in CloudFront?
Caching in CloudFront improves user experience by reducing the time it takes to retrieve frequently accessed content.
What is the advantage of using AWS Global Accelerator for applications?
AWS Global Accelerator enhances application performance and availability by routing traffic through the optimal AWS network paths.
What is Amazon SQS and its primary purpose?
Amazon SQS (Simple Queue Service) is a fully managed service used to decouple applications by allowing them to communicate through message queues.
What are the key features of Amazon SQS Standard Queue?
Standard Queue allows scaling from 1 message per second to tens of thousands, has a default message retention of 4 days (maximum 14 days), and supports unlimited messages in the queue.
How does Amazon SQS handle message deletion?
Messages are deleted after they are read by consumers.
What is the latency for publishing and receiving messages in Amazon SQS?
The latency is less than 10 milliseconds.
What is the difference between Amazon SQS Standard Queue and FIFO Queue?
FIFO Queue processes messages in the order they are received, ensuring that the first message sent is the first message processed.
What is Amazon Kinesis Data Streams used for?
Amazon Kinesis Data Streams is a managed service for real-time big data streaming, allowing the collection, processing, and analysis of streaming data at scale.
What is the role of Amazon Data Firehose in relation to Kinesis?
Amazon Data Firehose loads data from Kinesis Data Streams into destinations like Amazon S3, Redshift, and OpenSearch.
What is the purpose of Amazon SNS?
Amazon SNS (Simple Notification Service) is used to send a single message to multiple receivers through a publish/subscribe model.
How does Amazon SNS handle message subscriptions?
SNS allows multiple subscribers to receive messages from a single topic, with up to 12,500,000 subscriptions per topic.
What types of subscribers can receive messages from Amazon SNS?
Subscribers can include SQS, Lambda, HTTP(S) endpoints, SMS, and email notifications.
What is Amazon MQ and its primary use case?
Amazon MQ is a managed message broker service that supports traditional messaging protocols like MQTT, AMQP, and STOMP, allowing easier migration of on-premises applications to the cloud.
How does Amazon MQ compare to SQS and SNS in terms of scalability?
Amazon MQ does not scale as much as SQS and SNS, as it runs on servers and is designed for traditional applications.
What are the features of Amazon MQ?
Amazon MQ has both queue features similar to SQS and topic features similar to SNS, and it can run in Multi-AZ with failover.
What is the primary function of SQS in AWS architecture?
SQS serves as a queue service that allows multiple producers to send messages that can be read and deleted by multiple consumers.
What is the retention policy for messages in SQS?
Messages can be retained for up to 14 days.
What is the main function of SNS in AWS architecture?
SNS acts as a notification service that sends messages to multiple subscribers without retaining the messages.
What is the significance of low latency in Amazon Kinesis Data Streams?
Low latency allows for quick ingestion of data from numerous sources, making it suitable for real-time applications.
What types of data sources can feed into Amazon Kinesis?
Data sources can include click streams, IoT devices, metrics, and logs.
How do consumers interact with messages in SQS?
Consumers share the workload to read messages from the queue and can scale horizontally.
What is the maximum number of topics allowed in Amazon SNS?
The maximum number of topics allowed in Amazon SNS is 100,000.
What is the primary benefit of using SQS and SNS together?
Using SQS and SNS together allows for effective decoupling of application components, enabling scalable and reliable communication.
What is the main advantage of using Amazon MQ for migrating applications?
Amazon MQ allows traditional applications to use familiar messaging protocols without needing to re-engineer them for AWS services.
What does Amazon CloudWatch provide metrics for?
Every service in AWS.
What is a metric in the context of CloudWatch?
A variable to monitor, such as CPUUtilization or NetworkIn.
How frequently are default metrics collected in CloudWatch?
Every 5 minutes.
What is the purpose of CloudWatch dashboards?
To visualize and monitor metrics.
What additional cost option does CloudWatch offer for metrics?
Detailed Monitoring, which provides metrics every 1 minute.
What are some important metrics for EC2 instances?
CPU Utilization, Status Checks, and Network.
What metrics are associated with EBS volumes?
Disk Read/Writes.
What metrics can be monitored for S3 buckets?
BucketSizeBytes, NumberOfObjects, and AllRequests.
What is the CloudWatch Billing metric?
Total Estimated Charge, available only in us-east-1.
What can CloudWatch Alarms trigger?
Notifications for any metric, Auto Scaling actions, EC2 actions, and SNS notifications.
What are the possible states of a CloudWatch Alarm?
OK, INSUFFICIENT_DATA, and ALARM.
What types of logs can CloudWatch Logs collect?
Logs from Elastic Beanstalk, ECS, AWS Lambda, CloudTrail, and Route53.
What is required to send logs from an EC2 instance to CloudWatch Logs?
A CloudWatch agent must be run on the EC2 instance.
What is Amazon EventBridge used for?
To schedule tasks and react to events from AWS services.
What types of events can trigger actions in EventBridge?
Scheduled events (Cron jobs) and event patterns from AWS services.
What is the purpose of the Schema Registry in EventBridge?
To model event schemas.