Molecular Medicine Exam #1 - Pulmonary and Hematological Diseases
1/242
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
243 Terms
Categories of Gene Mutations
Point mutations within coding sequences
Mutations within noncoding sequences
Deletions and insertions
Structural alterations in protein-coding genes
Trinucleotide-repeat mutations
Hereditary disorders:
Transmitted in germline; familial
Congenital
“Born with”
T/F Congenital diseases are not all genetic
True
T/F Not all genetic diseases are congential
True
Transmission patterns for single-gene disorder
Autosomal dominant
Autosomal recessive
X-linked recessive
Cystic fibrosis inheritance pattern
Autosomal recessive
Cystic fibrosis
caused by mutation in cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene, which codes for an anion channel (Cl- and bicarb)
Results in viscous secretions in exocrine glands and in the epithelial lining of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and reproductive tracts
Cystic Fibrosis carrier frequency
1 in 20 in people of Northern European descent
most lethal genetic disease that affects people of this descent (1 in 2500 live births)
Chromosome that carries CFTR Gene
Chromosome 7
CFTR domains
2 transmembrane domains
2 nucleotide-binding domains (NBDs)
regulatory R domain
CFTR function and binding process
Binds to epithelial cells
Increases levels of cAMP
PKA activated and phosphorylates R domain of CFTR using ATP
Opens Cl- ion channel
CFTR Transport throughout the cell
Nucleus: Chromosome 7 CFTR gene —> CFTR mRNA
ER: Translation and folding
Golgi: Processing
Cell surface: Function
Cystic Fibrosis pathogenesis - Lumen of sweat duct (exocrine gland)
Mutated CFTR, INCREASES NaCl concentration in sweat
Cystic Fibrosis pathogenesis - Airway (Lining of organ)
decreased Cl- secretion
Increased Na+ and H2O reabsorption leading to thick and sticky mucus —> blocks pancreatic ducts, etc
NORMAL CFTR function in lumen of sweat duct
CFTR opens Cl- channel, allowing for Cl- to go into the lumen from the extracellular space
CFTR activates ENac, allowing Na+ to enter the cell (augments Na+ absorption)
NORMAL CFTR function in airway
CFTR opens Cl- channel allowing Cl- to enter the extracellular space from the cell
CFTR inhibits ENac, preventing Na+ entry into the cell and reduced H2O reabsorption = normal mucus
What does a mutated CFTR gene do in airways
Leads to dehydrated mucus —> defective mucociliary action (crushes cell’s cilia) and the mucus will plug the airways (leads to decreased lung function in some cases)
Describe Class I of CFTR mutation
Class: Protein Production
CFTR defect: No functional CFTR protein
Type of Mutation: Frameshift, nonsense, splice
Drug: kalydeco (ivacaftor)
Describe Class II of CFTR mutation
Class: Protein Processing
CFTR defect: CFTR trafficking/processing
Type of Mutation: Missense, deletion
Drug: Orkambi (Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor) + Trikafta (Elexacaftor + Tezacaftor + Ivacaftor)
Describe Class III of CFTR mutation
Class: Gating
CFTR defect: Defective channel regulation
Type of Mutation: Missense, amino acid change
Drug: Kalydeco (ivacaftor) + Trikafta (elexacaftor + tetracaftor + ivacaftor) + Symdeko (tetracaftor + ivacaftor)
Describe Class IV of CFTR mutation
Class: Conduction
CFTR defect: Decreased channel conductance
Type of Mutation: Missense, amino acid change
Drug: Kalydeco (ivacaftor) + Trikafta (elexacaftor + tetracaftor + ivacaftor) + Symdeko (tezacaftor + ivacaftor)
Describe Class V of CFTR mutation
Class: Insufficient protein
CFTR defect: Reduced synthesis of CFTR
Type of Mutation: Splicing defect, missense
Drug: Kalydeco (ivacaftor) + Trikafta (elexacaftor + tezacaftor + ivacaftor)
Describe Class VI of CFTR mutation
Class: n/a (not included in website)
CFTR defect: Decreased CFTR stability
Type of Mutation: Missense, amino acid change
Drug: Stabilizer
T/F the different types of CFTR mutation classes act as molecular targets dependent on genotypic variability
True
Each CFTR mutation class affects CFTR differently and provide basis for treatment and modulatory therapy
Describe the relationship between level of CFTR function and severity of symptoms
HIGHER CFTR function = LESS Severe
inverse relationship
<5% CFTR function symptoms
Severe chronic sinusitis
Severe lung disease
High sweat chloride
Pancreatic INsufficiency
Meconium ileus
Absent vas deferens
<10% - <20% CFTR function symptoms
Moderate chronic sinusitis
Variable lung disease
Intermediate sweat chloride
Pancreatic sufficiency
Distal intestinal obstruction syndrome
Absent vas deferens
50% CFTR function symptoms
increased rate of chronic sinusitis
increased rate of lung disease
increased risk of absent vas deferens
Specific CFTR Gene mutations we have to know:
F508 deletion (most common)
Arg117His (milder mutation)
Clinical features of CF
Chronic sinopulmonary disease manifested by:
persistent infection with CF pathogens
Constant cough; airway obstruction
Digital clubbing
Nasal Polyps
Gastrointestinal and nutritional abnormalities
intestinal: meconium ileus
pancreatic: insufficiency, pancreatitis
Hepatic: jaundice
Nutritional: failure to thrive
Salt-loss syndrome
Male urogential abnormalities —> obstructive azoospermia
CF pathogens
Staphylococcus aureus
Haemophilus influenzae (non-treatable)
Pseudomona aeruginosa
Burkholderia cepacia
Teenager with Anosmia
had chronic inability to smell and nasal congestion
treated with amoxicillin and corticosteroids that helped temporarily
nasopharyngoscopy showed complete opacification
polyps due to chronic inflammation
sweat chloride test had a diagnostic positive; genetic sequencing had a (TG)13-5T cystic fibrosis mutation
more mild variant
had sufficient pancreatic function and normal trypsinogen levels
had sinus surgery, clearance treatments, antibiotics
Describe CFTR Modulator Class: Potentiator and give drug and mutation examples
helps open the CFTR channel and increases Cl- and bicarb influx
targets gating, conduction, and insufficient protein mutations (Class III, IV, and V)
Drug Ex: Ivacaftor, Deutviacaftor, Elexacaftor
Mutation Ex: F508del
Describe CTFR Modulator Class: Corrector and give drug and mutation examples
Helps normalize the folding of defective CFTR protein and its movement
Targets processing mutations (Class II)
Drug Ex: Vanzacaftor, Elexacaftor, Tezacaftor, Lumacaftor
Mutation Ex: F508del
Describe CTFR Modulator Class: Amplifier and give drug and mutation examples
Increases expression of abnormal CFTR mRNA and production of protein
Targets processing, gating, conduction, insufficient classes (Classes II-V)
Drug Ex: N/A
Mutation Ex: F508del
Describe CTFR Modulator Class: Stabilizer and give drug and mutation examples
Limits removal and degradation of CFTR protein from cell surface
Targets processing, gating, conduction, insufficient classes (Classes II-V)
Drug Ex: N/A
Mutation Ex: F508del, N1303K, I507del, R117H, D115H, R347PE
Gating mutation
correctly produce and process CFTR protein BUT ion channels do not open properly
responds to potentiators
Ex: missense, small deletion mutations
F508del
Residual Function mutation
Retains CFTR function
Milder phenotype
usually respond to potentiators
Minimal function mutations
Negligible function at baseline
DO NOT respond to CFTR modulators
List the 8 structures in the respiratory pathway from where air enters to alveoli
Nares → nasal cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
Muscles involve in inhalation
diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
in labored breathing, muscles of the neck and back may also be involved
Muscles involve in exhalation
recoil of diaphragm and external intercostal muscles
internal intercostal muscles and abdominal muscles
Surfactant Purpose
surface tension at the air–liquid interface in the alveoli
this prevents their collapse
Why accumulation of elastase —> elastin breakdown = bad for alveoli
Mathematical relationship between VC, IRV, ERV and TV
VC = IRV + ERV + TV
If CO2 blood levels are too LOW, how does the brain maintain homeostasis
DECREASES Respiratory rate to RAISE CO2 levels
**LOWER RR = LOWER V = MORE CO2 in body
Respiratory. system mechanisms to prevent infection
vibrissae in the nares (hairs)
lysozyme in the mucous membranes
the mucociliary escalator
macrophages in the lungs
mucosal IgA antibodies
mast cells.
Bicarbonate buffer system chemical equation
CO₂ + H₂O ⇌ H₂CO₃ ⇌ HCO₃⁻ + H⁺
How does pH change in respiratory failure
lower pH of the blood
ventilation slows = less CO2 out = right shift = more H+ ions generated = more acidic
Total lung capacity (TLC)
maximum volume of air in lungs when one inhales completely (usually around 6-7 liters)
Residual Volume (RV)
volume of air remaining in lungs when one exhales completely
Vital capacity (VC)
difference between TLC and RV (max-min)
Tidal Volume (TV)
volume of air inhaled or exhaled in a normal breath
Expiratory reserve volume (ERV)
volume of additional air that can be forcibly exhaled after a normal exhalation
Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV)
volume of additional air that can be forcibly inhaled after a normal inhalation
TLC Lung volume equation
TLC = IRV + TV + ERV + RV
Capacity Lung volume equation
sum of more than 1 lung volume
Kalydeco generic name
(IVACAFTOR)
Kalydeco Class, Mechanism of action, Indication, Adverse effects
Class: potentiator
Mechanism of action:
binds to CFTR and opens anion channel
unlocks gate and holds it open
Indication: approved for people with CF aged 1 month and older who have one of 97 mutations
AE:
Serious: elevated liver enzymes, anaphylaxis, intracranial hypertension, cataracts (cataracts in children and adolescents)
Common: headache, URI, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, rash, dizziness
Symdeko Class, Mechanism of action, Indication, Adverse effects
Class:
tezacaftor = corrector
ivacaftor = potentiator
Mechanism of action:
tezacaftor: helps the CFTR form the right shape, move to the cell membrane, and stay in the membrane longer
ivacaftor: opens up the gate and holds it open
Indication:
Approved for people with CF ages 6 and older with 2 copies of the F508 del mutation AND
Approved for people with CF ages 6 and older with a single copy of one of 154 mutations
AE:
Serious: elevated liver enzymes, anaphylaxis, intracranial hypertension, cataracts (cataracts in children and adolescents)
Common: headache, nausea, sinus congestion, and dizziness
**Fewer side effects, like chest tightness, and fewer drug interactions than Orkambi (lumacaftor/ivacaftor)
Orkambi Class, Mechanism of action, Indication, Adverse effects
Class: modulator
Mechanism of action:
Lumacaftor: helps the CFTR form the right shape, move to the cell membrane, and stay in the membrane longer (only about 1/3 of the CFTR protein reaches the cell surface with lumacaftor)
Ivacaftor: opens gate and holds it
Indication: Approved for people with CF aged 1 year and older who have 2 copies of the F508del mutation (F508del/F508 del) in the CFTR gene
AE:
Serious: elevated liver enzymes, anaphylaxis, intracranial hypertension, cataracts (cataracts in children and adolescents), breathing problems, an increase in BP
Common: shortness of breath, chest tightness, nausea, diarrhea, fatigue, increase in creatine kinase (CK), rash, URI symptoms, flu or flu-like symptoms, and irregular periods/increase in the amount of menstrual bleeding
Symdeko generic name
tezacaftor/ivacaftor
orkambi generic name
lumacaftor/ivacaftor
Trikafta Class, Mechanism of action, Indication, Adverse effects
Class:
elexacaftor & tezacaftor = correctors
ivacaftor = potentiator
Mechanism of action:
elexacaftor & tezacaftor: help the CFTR form the right shape, move to the cell membrane, and stay in the membrane longer
ivacaftor: opens the gate and holds it open
Indication: Approved for people with CF ages 2 and older who have at least 1 copy of the F508del mutation or at least 1 copy of 271 mutations
AE:
Serious: liver damage and liver failure, serious allergic reactions, intracranial hypertension, cataracts (cataracts in children and adolescents)
Common: headache, URI symptoms, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, rash, increases liver enzymes and bilirubin, increase in CK, flu, inflamed sinuses
Alyftrek Kalydeco Class, Mechanism of action, Indication, Adverse effects
Class:
Vanzacaftor & tezacaftor = correctors
Deutivacaftor = potentiator
Mechanism of action:
Vanzacaftor & tezacaftor = correct the CFTR protein so it forms the right shape and moves to the cell membrane
Deutivacaftor = binds to defective CFTR and holds open chloride channel; deuterated form of ivacaftor (replace hydrogens with deuterium, a heavier, stable isotope of hydrogen) that has a longer half-life allowing once daily dosing
Indication: people with CF ages 6 & up who are also eligible based on mutations for Trikafta or 31 other rare mutations
AE:drug-induced liver injury and failure, intracranial hypertension, cataracts (in pediatric patients)
Outcomes:
Improvements in lung function comparable to Trikafta
Reduction in sweat chloride levels greater than that seen with Trikafta
Trikafta generic name
(ELEXACAFTOR/TEZACAFTOR/IVACAFTOR)
alyftrek generic name
(VANZACAFTOR/TEZACAFTOR/DEUTIVACAFTOR)
Obstructive Lung Disease
characterized by an increase in resistance to airflow due to diffuse airway disease, which may affect any level of the respiratory tract
Restrictive Lung Disease
marked by reduced expansion of lung parenchyma and decreased total lung capacity
chest wall disorders
chronic interstitial and infiltrative disease
Small Airway disease
Emphysema (Alveolar wall destruction or overinflammation)
Chronic Bronchitis (Productive cough, airway inflammation)
Bronchial hyperresponsiveness
Asthma (reversible obstruction)
Chronic Bronchitis Anatomic Site, Major Pathologic Changes, Etiology, Signs/Symptoms
Anatomic Site: Bronchus
Major Pathologic Changes: Mucous gland hyperplasia, hypersecretion
Etiology: Tobacco smoke, air pollutants
Signs/Symptoms: Cough, sputum production
Brochiectasis Anatomic Site, Major Pathologic Changes, Etiology, Signs/Symptoms
Anatomic Site: Bronchus
Major Pathologic Changes: Airway dilation and scarring
Etiology: Persistent or severe infections
Signs/Symptoms: Cough, purulent sputum, fever
Asthma Anatomic Site, Major Pathologic Changes, Etiology, Signs/Symptoms
Anatomic Site: Bronchus
Major Pathologic Changes: Smooth muscle hyperplasia, excess mucus, inflammation
Etiology: Immunologic or undefined causes
Signs/Symptoms: Episodic wheezing, cough, dyspnea
Emphysema Anatomic Site, Major Pathologic Changes, Etiology, Signs/Symptoms
Anatomic Site: Acinus
Major Pathologic Changes: Airspace enlargement; wall destruction
Etiology: Tobacco smoke
Signs/Symptoms: Dyspnea
Small Airways disease/broncholitis Anatomic Site, Major Pathologic Changes, Etiology, Signs/Symptoms
Anatomic Site: Bronchus
Major Pathologic Changes: Inflammatory scarring/obliteration
Etiology: Tobacco smoke, air pollutants, miscellaneous
Signs/Symptoms: Cough, dyspnea
a1 Antitrypsin deficiency
normally inhibits elastase —> mutation leads to the accumulation of elastase —> more elastin break down —> less structural integrity
a1 Antitrypsin deficiency and COPD
alveolus release neutrophils during inflammation
neutrophils produce neutrophil elastase to break down elastin (extracellular protein to provide strength)
a1 Antitrypsin made by hepatocytes gets sent to alveolus via blood
The mutated glycoprotein will be unable to break down elastase = UNCHECKED
Elastase will continue to break down elastin —> Alveoli turn into one big cavity because they lost structural integrity —> Pan-acinar EMPHYSEMA (whole acinus lower lobes mostly affected)
a1 Antitrypsin Gene mutation
located on chromosome 14 on SERPINA1 (serine protease inhibitor clade 1)
some cause complete absence
PiZ = misfolded —> stuck in ER —> cell dies
Normal PiM attributes 50% of function —> 2 normal copies = 100% normal amount of a1 Antitrypsin
Mutated PiZ attributes ~10% of function
PiM + PiZ = ~60% of normal levels a1 Antitrypsin (asymptomatic; safe for nonsmokers)
PiZ + PiZ = ~15-20% of normal a1 Antitrypsin levels —> a1 Antitrypsin deficiency!!
higher risk of lung and liver disease
minimal environmental risk factors can prevent individuals from experiencing symptoms
Types of COPD a patient with a1 Antitrypsin deficiency may develop
Pan-acinar emphysema
chronic bronchitis
bronchiectasis
**recall another common cause of COPD is smoking, therefore if a patient smokes and has the mutation, they experience an earlier onset of COPD
a1 Antitrypsin deficiency symptoms
SOB
wheezing
mucus production
chronic cough
cirrhosis
inability to make coagulation factors
build of toxins —> hepatic encephalopathy
Portal hypertension —> esophageal varices
Hepatocellular carcinoma
Jaundice (Juvenile)
minority of infants with PiZZ can develop liver failure
symptoms for SERPINA1 mutation with ABSENT a1 Antitrypsin
ONLY has LUNG-COPD related symptoms:
SOB
wheezing
mucus production
chronic cough
Diagnosis of a1 Antitrypsin deficiency
chest x-ray or CT —> look for hyper inflated lungs and damaged tissue
pulmonary function —> slow exhale
Blood test —> low a1 Antitrypsin levels
Cirrhosis via liver ultrasound or biopsy
liver cells stained with periodic acid schiff (PAS) —> stains glycoproteins pink (PAS +)
Diastase resist since a1 Antitrypsin is stuck in ER and cannot be destroyed
a1 Antitrypsin Therapies
Augmentation therapy: IV Infusion of normal a1 Antitrypsin
slows down progression
inhalers
supplemental oxygen
cirrhosis treatment (Ex: lactulose)
Why are trypsinogen levels high in patients with CF
mucus produces in patients with CF blocks pancreatic ducts
mucus traps digestive enzymes like trypsinogen —> leaks into blood
Processing, gating, conduction, or insufficient protein mutations
class II-V
A channel is created that retains at least some functional CFTR channel activity either at baseline or following exposure to other classes of CFTR modulators.
Processing mutations
class II
CFTR protein is created but misfolds, preventing it from reaching the apical cell surface.
Insufficient protein mutations
class V
CFTR protein is created that has normal processing, channel, and gating properties, but the amount of protein present at the cell surface is deficient.
This can be caused by too little CFTR protein being produced or an increased rate of channel deactivation or removal from the cell surface.
Conduction mutations
class IV
CFTR protein is created and moves to the cell surface but with a malformed channel that limits the rate of chloride and bicarbonate movement.
What drug would work best for Class I - CFTR Production Mutations?
Kalydeco (Ivacaftor)
What drug would work best for Class II - CFTR Processing Mutations?
Corrector + Potentiator
Orkambi (Lumcaftor/Ivacaftor)
Trikafta (ELEXACAFTOR/TEZACAFTOR/IVACAFTOR)
What drug would work best for Class III - CFTR Gating and Class IV - Conduction Mutations?
Potentiators + Correctors
Kalydeco (Ivacaftor)
Trikafta (ELEXACAFTOR/TEZACAFTOR/IVACAFTOR)
Symdeko (TEZACAFTOR/IVACAFTOR)
What drug would work best for Class V - Insufficient CFTR Mutations
Splicing modulators
Antisense oligonucleotides
Kalydeco (Ivacaftor)
Trikafta (ELEXACAFTOR/TEZACAFTOR/IVACAFTOR)
What drug would work best for Class VI - CFTR Mutations
Stabilizers
Components of Blood
Plasma and Serum
Leukocytes (WBC
Platelets
erthrocytes (RBC)
Plasma
liquid portion of blood minus the cells
consists of:
water
blood proteins
salts
respiratory gases
hormones
serum
plasma minus clotting factors
(-) Anti coagulant vial
Serum + blood clot
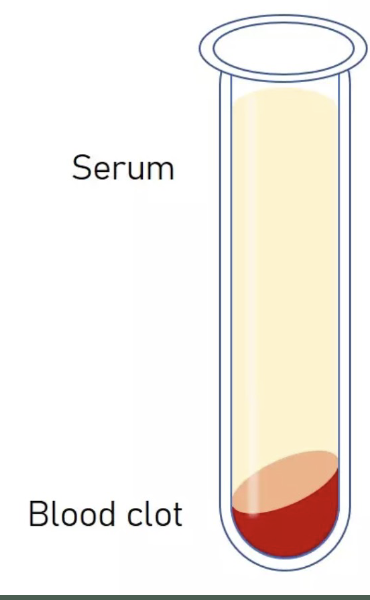
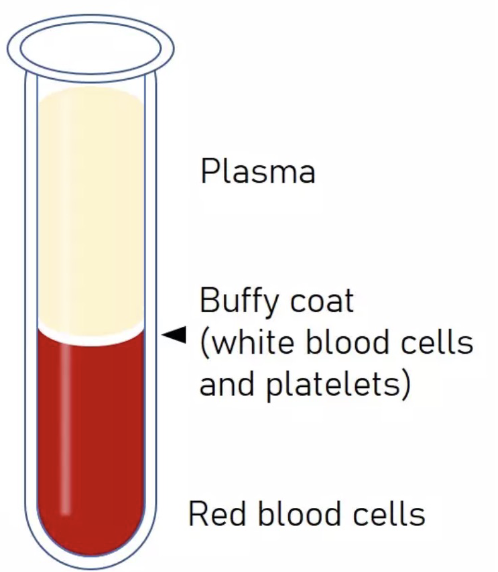
(+) Anti coagulant vial
Plasma
Buffy coat (white blood cells and platelets)
Red blood cells
Types of WBC
neutrophil
lymphocyte
basophil
eosinophil
manocyte