Honors Biology Unit 6: Meiosis and Genetics
1/180
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
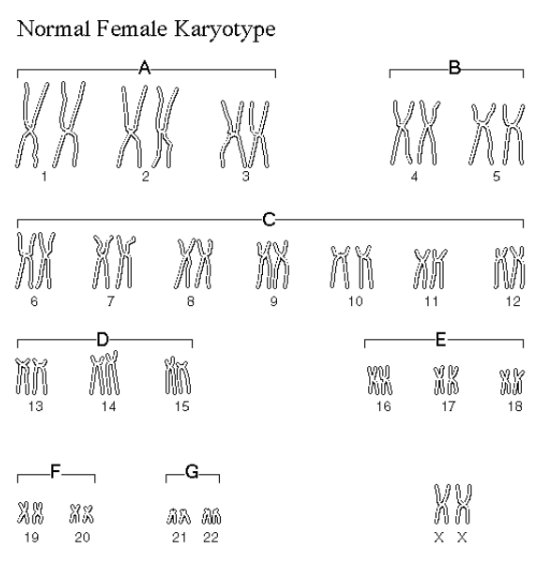
A chart of homologous chromosome pairs used to pinpoint unusual chromosome numbers in cells. (Humans = 23 Homologous Pairs / 46 total chromosomes)
Karyotype
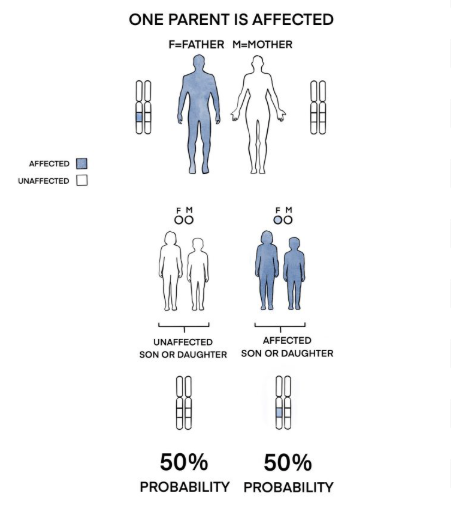
refers to how genetic traits are passed down through the 22 pairs of non-sex chromosomes (autosomes). It is a fundamental concept that explains the probability of a child inheriting a particular trait or disease from their parents, based on whether it is dominant or recessive.
Autosomal Inheritance
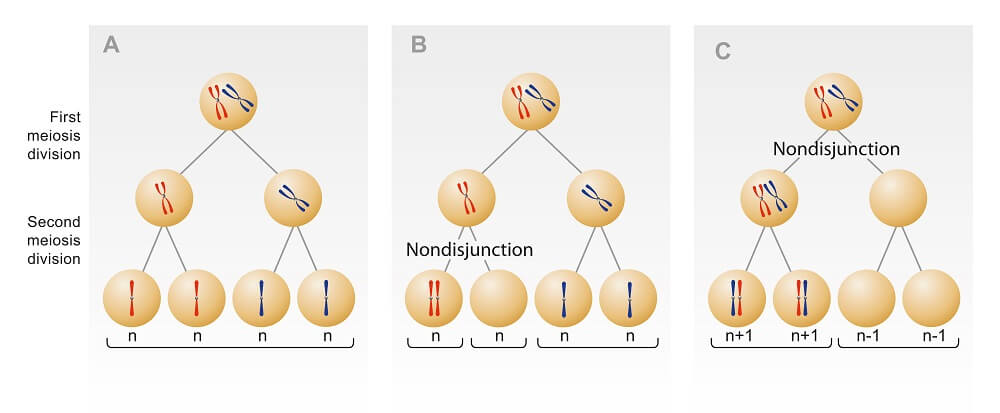
the failure of chromosomes or sister chromatids to separate correctly during cell division, either meiosis or mitosis. This error leads to daughter cells with an incorrect number of chromosomes, resulting in conditions like Down syndrome when an extra chromosome is inherited by a gamete.
Nondisjunction
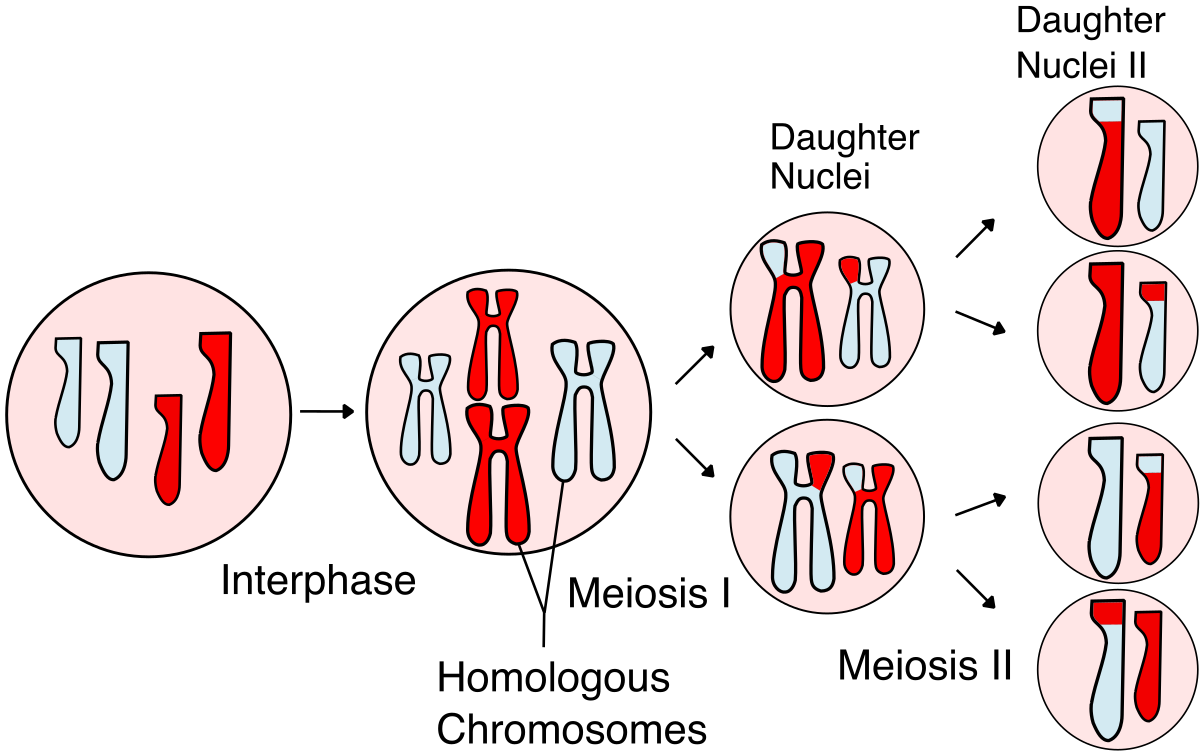
a specialized cell division process that reduces the chromosome number by half to create four genetically diverse gametes (sperm and egg cells). It's crucial for sexual reproduction because it ensures that when gametes fuse, the resulting offspring has the correct chromosome number and is genetically unique, unlike the identical cells produced through mitosis.
Meiosis
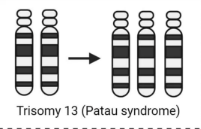
a condition where an organism has three copies of a specific chromosome instead of the usual two
Trisomy
a version of a gene/a gene option
Allele
an allele that shows its effect even if only one copy is present. represented with a capital letter.
Dominant
an allele whose effect is hidden unless two copies are present
Recessive
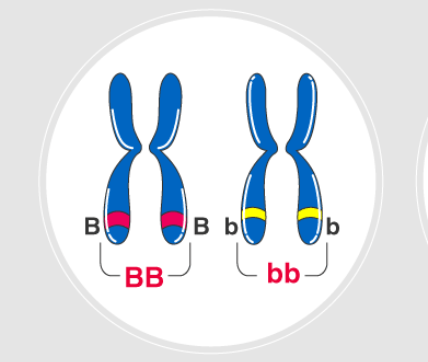
having two identical alleles for a gene
Homozygous
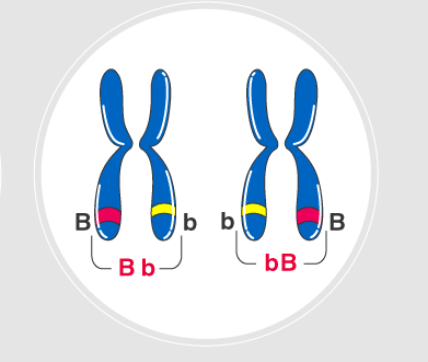
having two different alleles for a gene
Heterozygous

the genetic label of a trait
Genotype

the physical expression of a trait
Phenotype
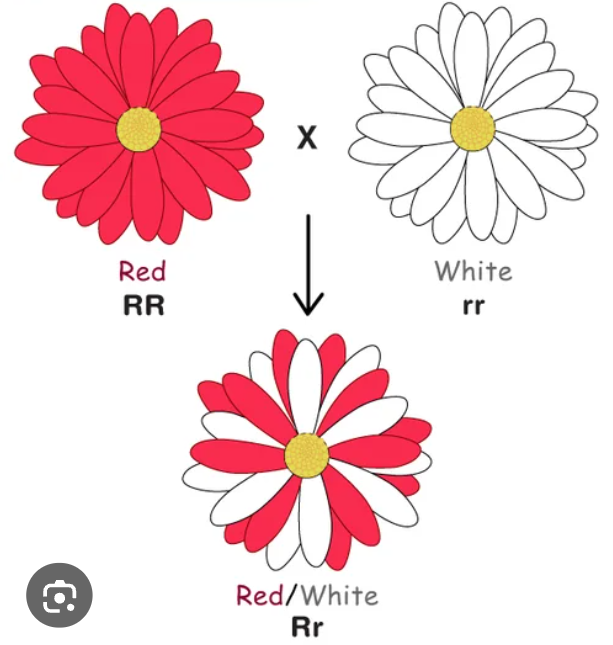
when both alleles are fully expressed but separately in the phenotype, sometimes seen as spotting
Codominance
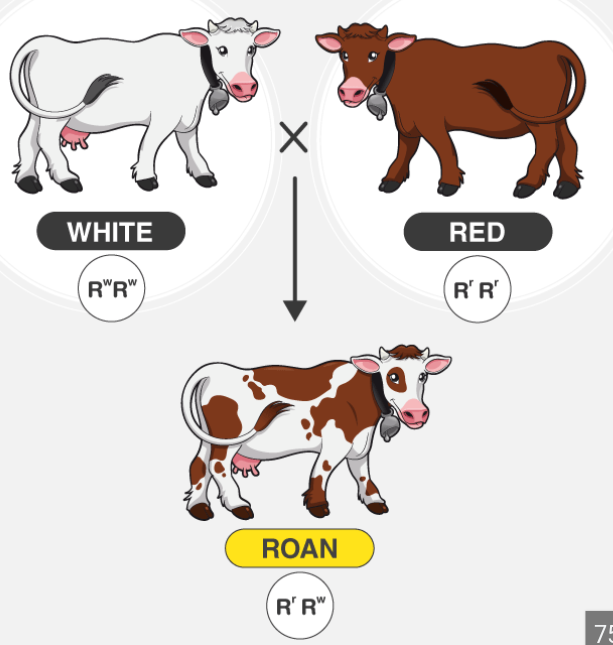
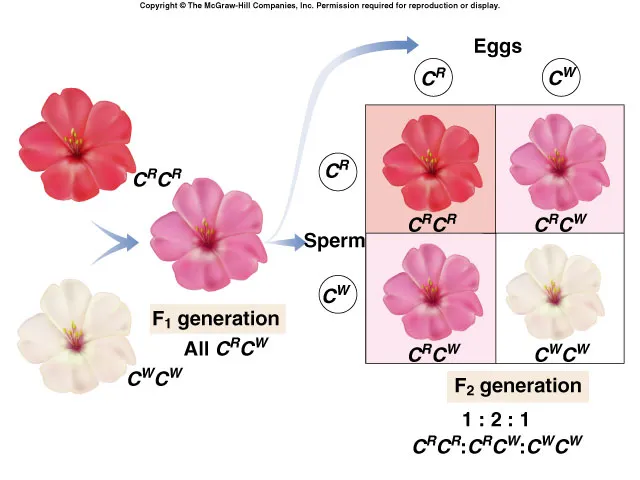
when the phenotype is a blend of two alleles
Incomplete Dominance
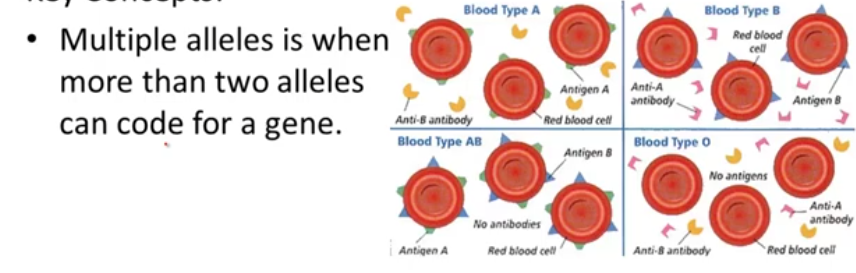
the presence of three or more alternative forms of a gene that can occupy the same locus on a chromosome. This happens to a whole population, not just one individual.
Multiple Alleles
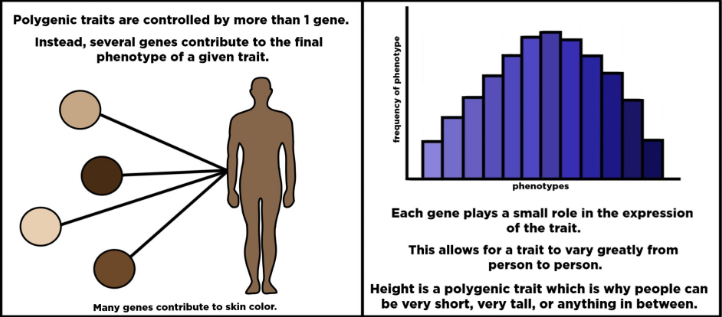
a trait controlled by two or more genes
Polygenic Trait
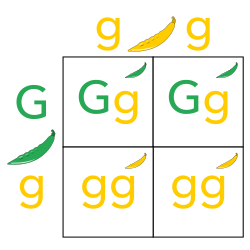
a diagram used to predict genetic crosses
Punnet Square
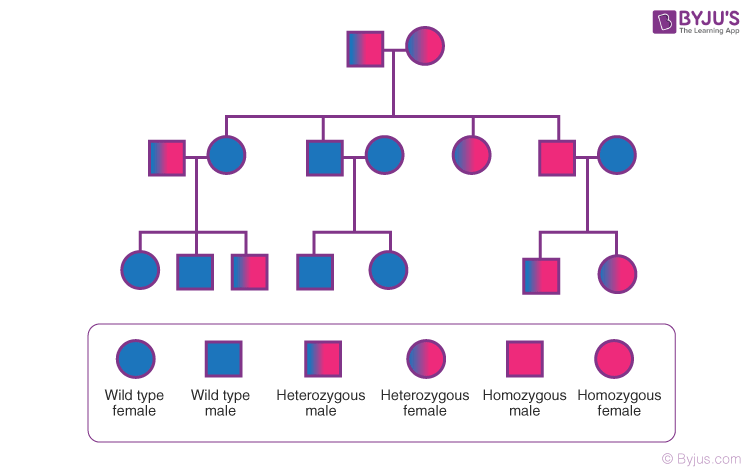
a diagram showing how traits are passed through generations
Pedigree Chart
reproduction that requires two parents to create offspring
Sexual reproduction
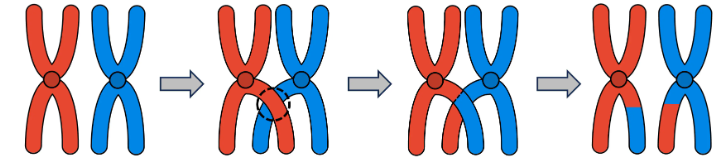
when DNA overlaps between the homologous chromosomes in meiosis and shares/mixes the DNA
Crossing over
the random segregation of alleles for different genes, resulting in various combinations of traits.
Independent assortment

difference in DNA even between the same organisms
Genetic variation
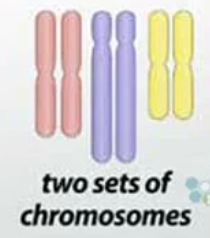
a cell or organism that contains two complete sets of chromosomes, one inherited from each parent.
Diploid
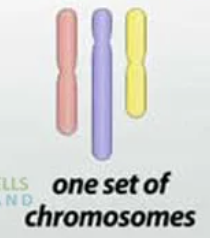
a cell or organism that has a single set of chromosomes, which is half the number of chromosomes found in diploid cells.
Haploid
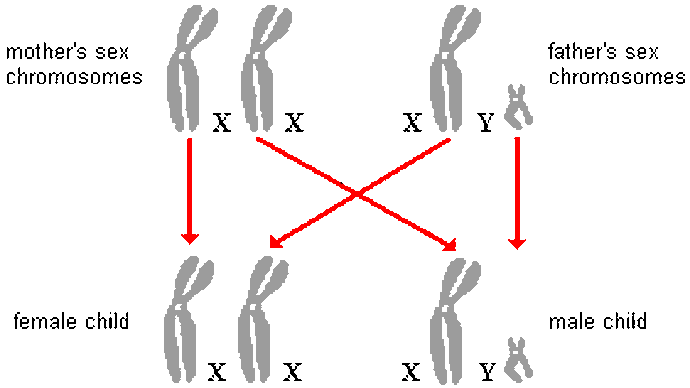
inheritance of traits on sex chromosomes
Sex-linked
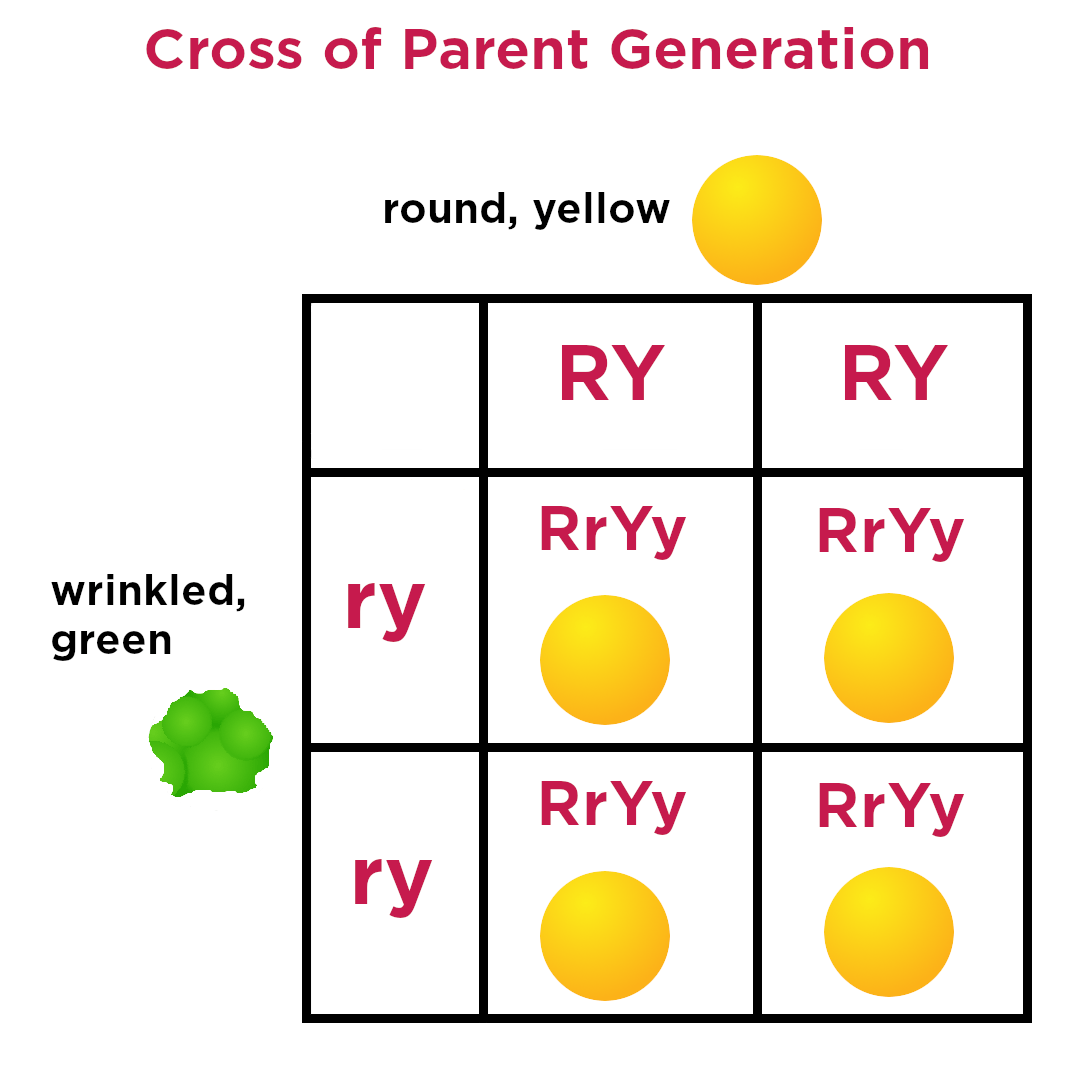
a genetic cross between two individuals that are each heterozygous for two traits, used to analyze the inheritance patterns of both traits simultaneously
Dihybrid cross
What is a karyotype?
A chart of homologous chromosome pairs
How many homologous pairs do humans have?
23 homologous pairs
What is the purpose of a karyotype?
To pinpoint unusual chromosome numbers in cells
What are homologous chromosome pairs based on?
Length, centromere position, and banding patterns
What are autosomes in humans?
Chromosomes not involved in sex determination
Which homologous pairs are autosomes in humans?
Pairs 1-22
What do sex chromosomes control in humans?
Inheritance of sex characteristics
What is the composition of the 23rd homologous pair in humans?
XY or XX
What does XX represent in terms of sex chromosomes?
Female (♀)
What does XY represent in terms of sex chromosomes?
Male (♂)
What typically causes abnormal karyotypes?
Errors during meiosis
What is nondisjunction?
failure of homologous pairs to separate
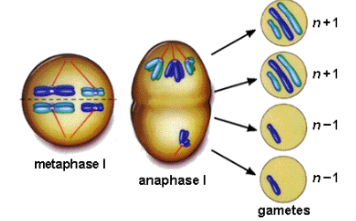
What can result from nondisjunction?
Extra or missing chromosomes in gametes
What is trisomy?
having an extra chromosome
What is down syndrome classified as?
Trisomy 21
What causes down syndrome?
Nondisjunction during anaphase 1
What is the incidence of Down Syndrome?
1 in 700 live births
What is unique about Down Syndrome among autosomal trisomies?
Affected individuals can live to see adulthood
What is Turner Syndrome characterized by?
Missing sex chromosomes
What is a consequence of Turner Syndrome
Sterile females
What is a consequence of Turner Syndrome
XXY sex chromosomes
What are the characteristics of Klinefelter Syndrome?
Sterile males with female characteristics
What is Jacobs Syndrome characterized by?
XYY sex chromosomes
What is a common trait of individuals with Jacobs Syndrome?
Typically taller males
How is the XXX condition distinguished?
By karyotype analysis
What is Cru de chat Syndrome caused by?
Deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5
What are the symptoms of Cru de Chat Syndrome?
Severe mental retardation and a small head
What is a characteristic sound of babies with Cru de Chat Syndrome?
Cries that sound like a distressed cat
What are the causes of abnormal karyotypes?
Mistakes during meiosis
Nondisjunction
Translocations
What are the results of nondisjunction?
Extra chromosomes in some gametes
Too few chromosomes in others
Large-scale genetic changes
What are chromosomal mutations?
Mutations at the chromosome level
Occur when parts of chromosomes break off
Rejoin incorrectly during crossing over
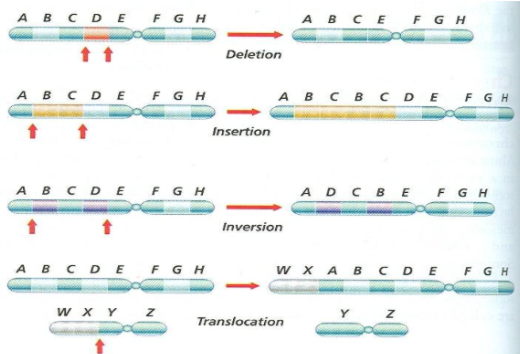
What are the four types of chromosomal mutations?
Deletions
Insertions
Inversions
Translocations
What are the consequences of chromosomal mutations?
Abnormal gene distribution to gametes
Extra copies of genes
Lack of essential genes