Physics Midterm
1/149
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
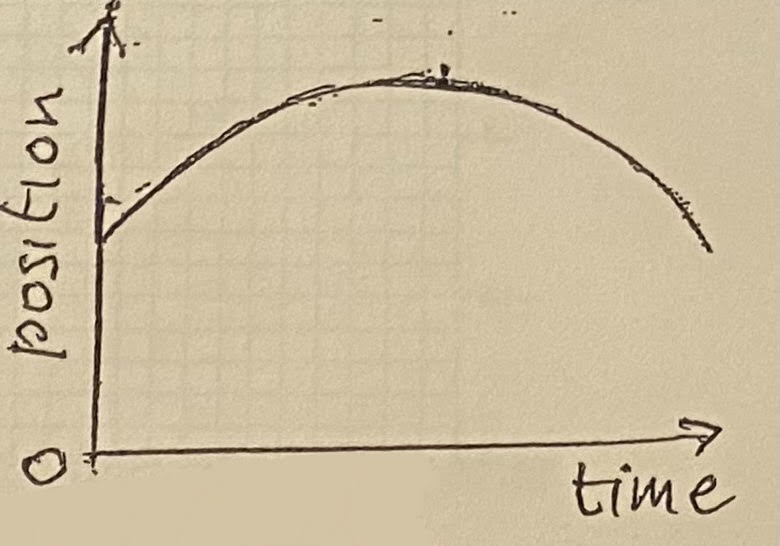
An object moves according to the graph shown. What two answers are correct from the options.
(a) The object moves toward the reference point, stops and then moves away from the reference point
(b) The object moves away from the reference point, stops and then moves towards the reference point
(c)The object speeds up, stops and then speeds up again
(d)The object slows down, stops and then speeds up
B and D
Which is faster, an object traveling at a velocity of -12 m/s or at -18 m/s?
-18
Does a speedometer in a car measure velocity or speed?
Speed
You and your dog go for a walk in the park. On the way, your dog takes many side trips to chase squirrels or examine fire hydrants. When you arrive at the park, do you and your dog have the same displacement?
Yes
When an object starts from rest, what is the original velocity?
(a) depends on the problem
(b) alway positive
(c) 0 m/s
(d) always negative
C
An object in free fall (or falling under gravity only)
(a) experiences no air resistance
(b) undergoes a downward acceleration
(c) has an acceleration with a magnitude or absolute value of 9.81 m/s2 near Earth’s surface
(d) all of the above
D
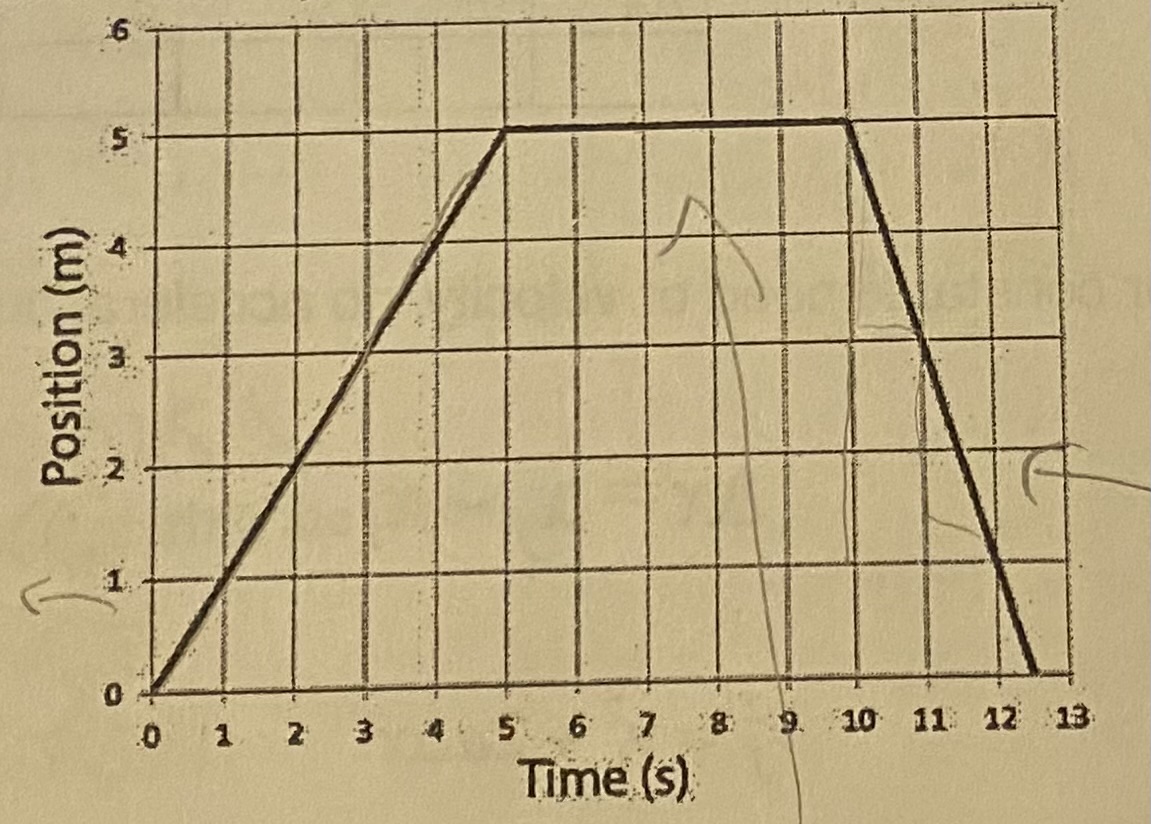
During which interval is the object moving the fastest?
(a) 0s to 5s
(b) 5s to 10s
(c) 10s to 12.5s
(d) the speed is the same during these three intervals
C
Which would hit the ground first if dropped from the same height in a vacuum chamber, a feather or metal bolt?
(a) feather
(b) metal bolt
(c) they would hit the ground at the same time
(d) they would be suspended in a vacuum
C
When there is no air resistance, objects of different masses
(a) Fall with different accelerations and with different displacements
(b) Fall with equal accelerations but with different displacements
(c) Fall with different accelerations and with similar displacements
(d) Fall with equal accelerations and with similar displacement
D
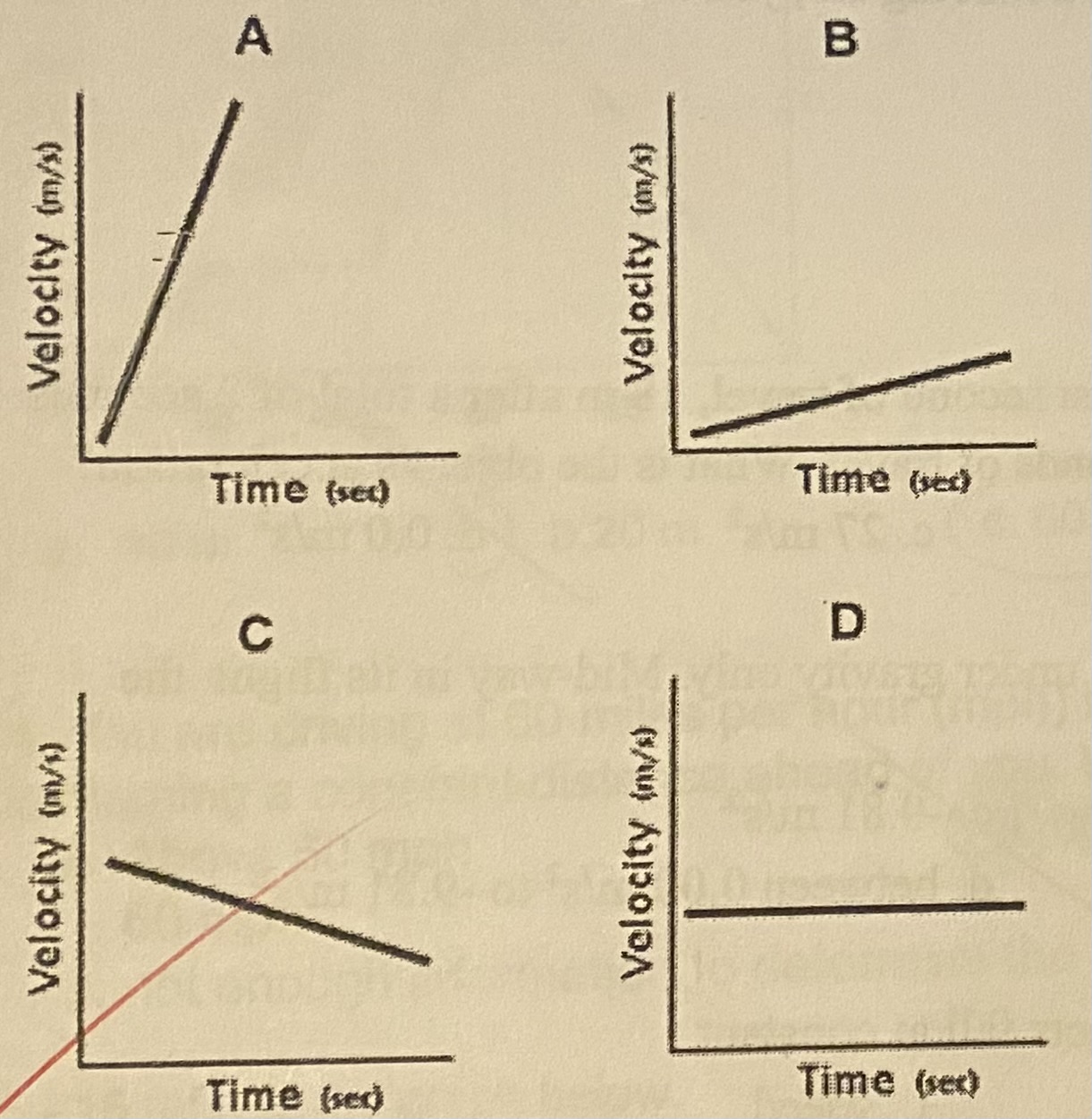
Which graph represents the greatest acceleration?
A
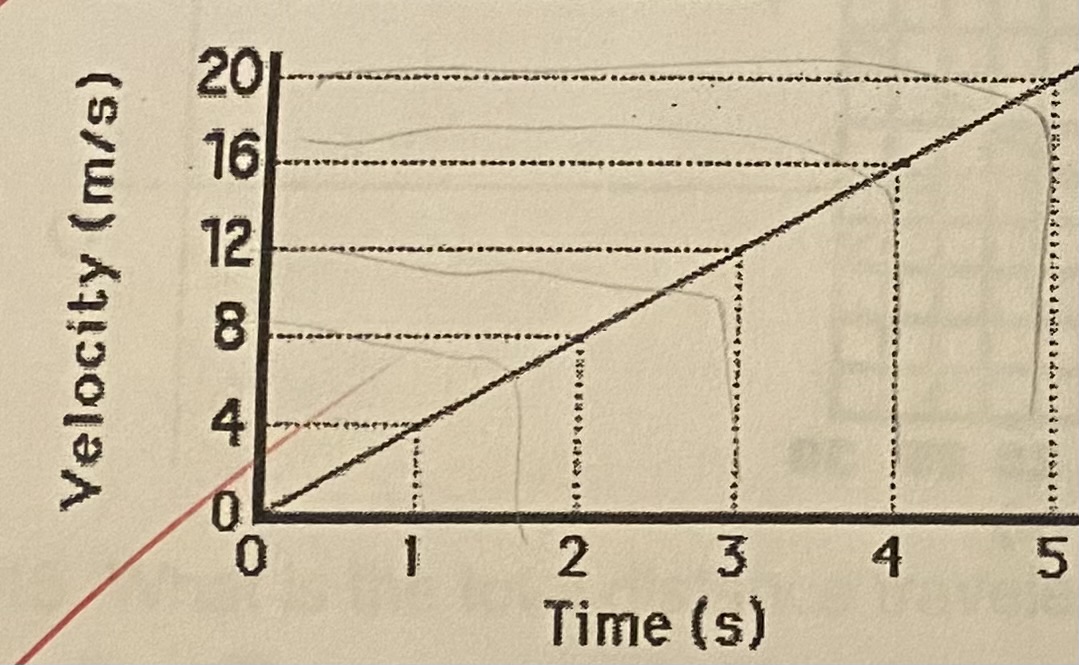
What does the graph below illustrate about acceleration?
(a) The acceleration increases
(b) The acceleration decreases
(c) The acceleration is constant
(d) The acceleration is zero
C
Suppose an object is in free fall. Each second the object falls,
(a) The same distance as in the second before
(b) With the same average speed
(c) A larger distance than in the second before
(d) With the same instantaneous speed
C
When you look at the speedometer in a moving car, you see
(a) instantaneous acceleration
(b) average speed
(c) instantaneous speed
(d) average distance traveled
C
An object travels 9.0m during the first second of travel, 18m after a total of 2 seconds of travel and 27m after a total of 3 seconds of travel. What is the object’s acceleration?
(a) 9.0 m/s2
(b) 17 m/s2
(c) 27 m/s2
(d) 0.0 m/s2
D
A rock is thrown vertically upwards under gravity only. Mid-way in its flight the acceleration is
(a) 0 m/s2
(b) 9.81 m/s2
(c) -9.81 m/s2
(d) between 0 and -9.81 m/s2
C
In the absence of air resistance, objects fall at constant
(a) velocity
(b) distance each second
(c) speed
(d) acceleration
D
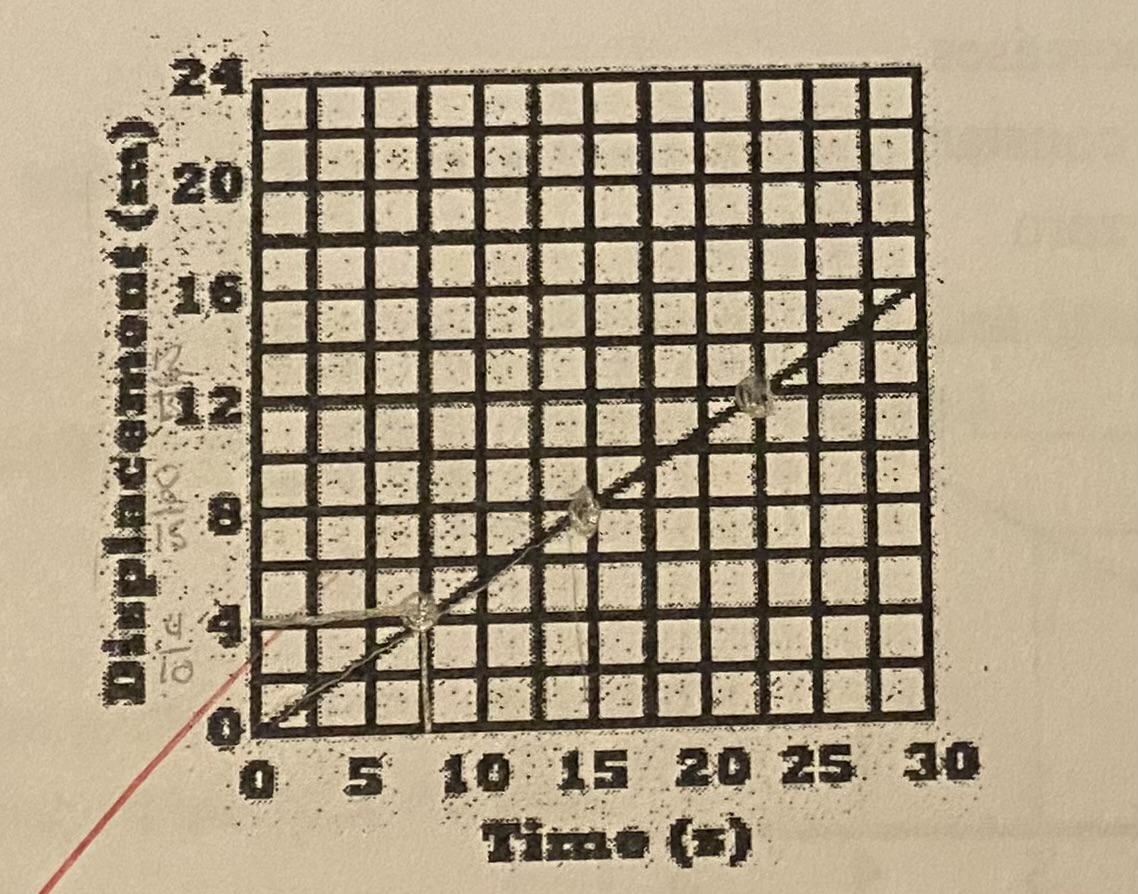
What type of motion is seen in this graph?
(a) Acceleration
(b) Constant velocity towards the reference point
(c) Rest
(d) Constant velocity away from the reference point
D
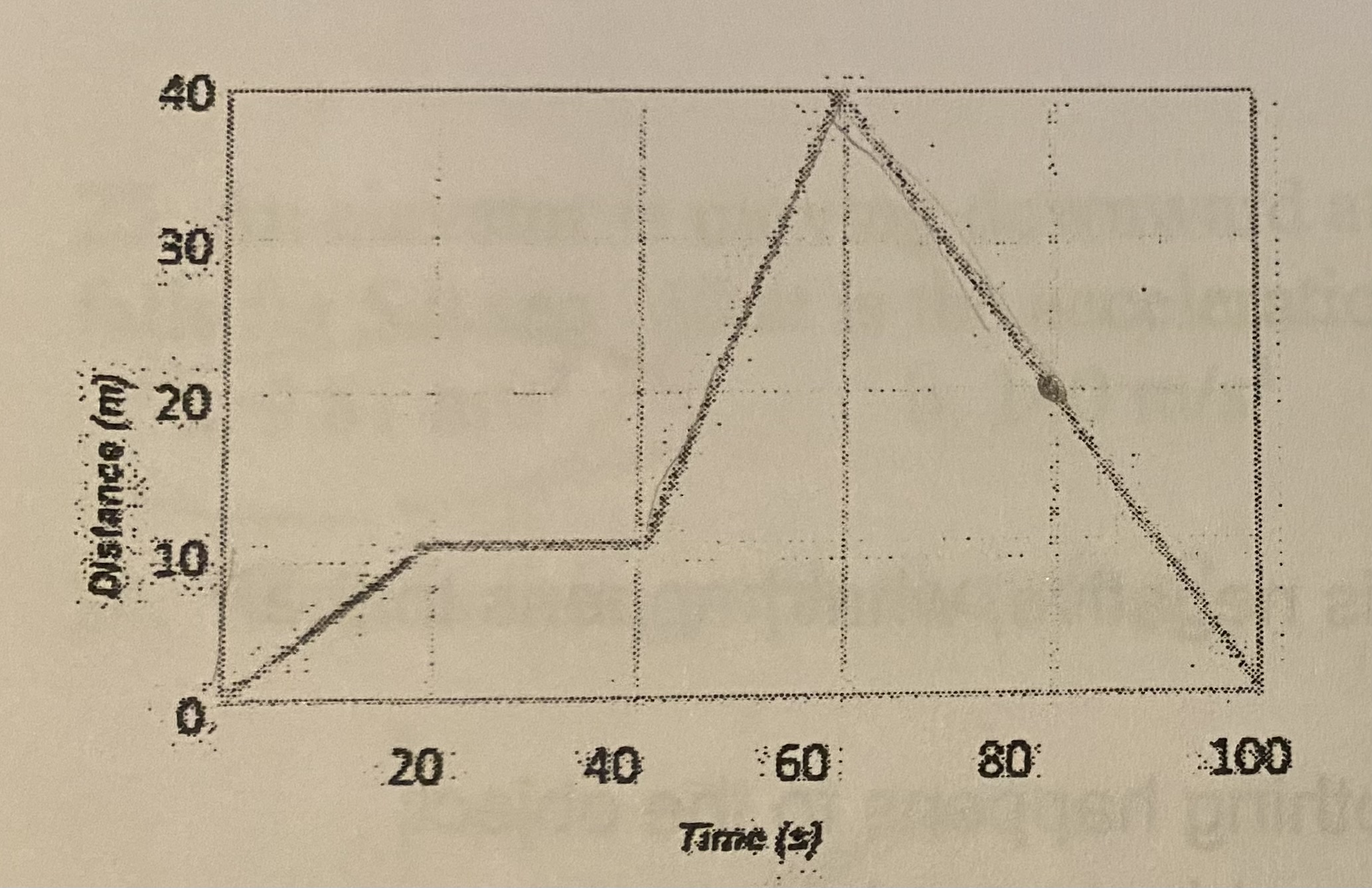
After the first 80 seconds, what distance had this object traveled?
(a) 10m
(b) 20m
(c) 60m
(d) 100m
C
You are driving at 60mph behind another car which is maintaining a constant distance ahead of you. What is the speed of that car?
(a) above 60mph
(b) 60mph
(c) less than 60mph
(d) not enough information to tell
B
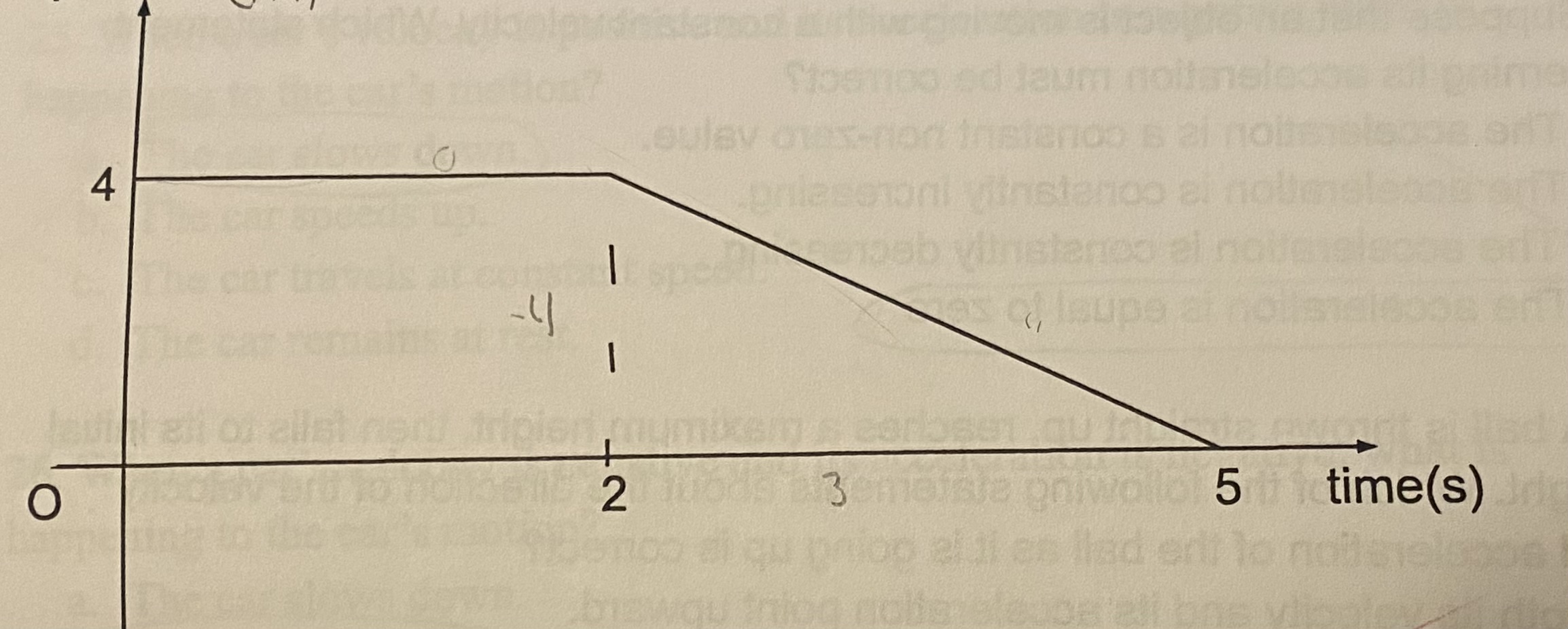
What is the total distance traveled at the end of 5s?
(a) 0m
(b) 14m
(c) 9m
(d) 4m
D
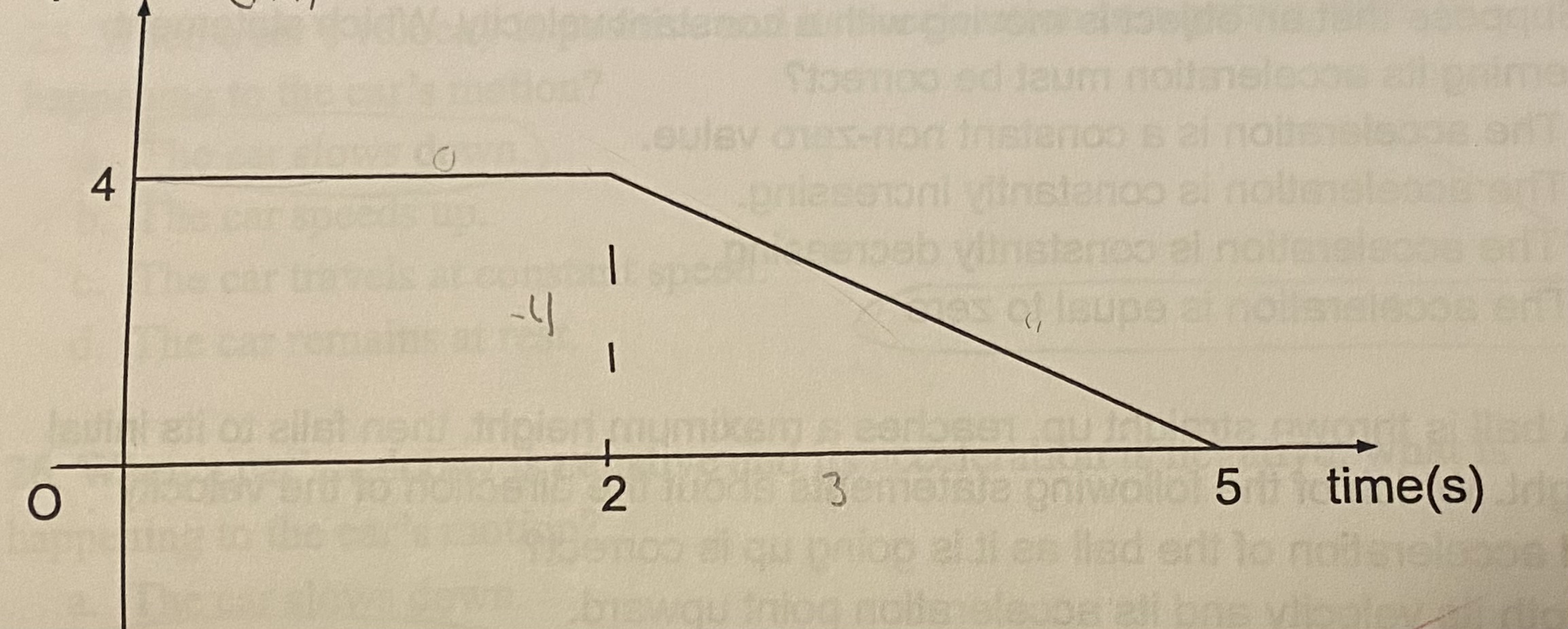
What is the acceleration of the object from 2s to 5s?
(a) 4/3 m/s2
(b) -4/3 m/s2
(c) 0 m/s2
(d) 6 m/s2
C
Which of the following would be considered a velocity?
(a) 12.3 m/s2 up
(b) 3.8m north
(c) 22 km/min forward
(d) all of these
C
When velocity is positive and acceleration is negative, what happens to the object’s motion?
(a) The object slows down
(b) The object speeds up
(c) Nothing happens to the object
(d) The object remains at rest
A
The baseball catcher throws a ball vertically upward and catches it in the same spot as it returns to the mitt. At what point in the ball’s path does it experience zero velocity and nonzero acceleration at the same time?
(a) midway on the way up
(b) at the top of it trajectory
(c) the instant it leaves the catcher’s hand
(d) the instant before it arrives in the catcher’s mitt
B
Suppose that an object is moving with a constant velocity. Which statement concerning its acceleration must be correct?
(a) The acceleration is a constant non-zero value
(b) The acceleration is constantly increasing
(c) The acceleration is constantly decreasing
(d) The acceleration is equal to zero
D
A ball is thrown straight up, reaches a maximum height, then falls to its initial height. Which of the following statements about the direction of the velocity and acceleration of the ball as it is going up is correct?
(a) Both its velocity and its acceleration points upward
(b) Both its velocity and its acceleration points downward
(c) Its velocity points upward and its acceleration points downward
(d) Its velocity points downward and its acceleration points upward
C
A 10kg rock and a 20kg rock are thrown upward with the same initial speed v and experience no significant air resistance. If the 10kg rock reaches a maximum height h, what maximum height with the 20kg ball reach?
(a) h/2
(b) h
(c) 2h
(d) 4h
(e) h/4
B
An elevator is moving downward at a rate of 3 m/s when its cable breaks. Its falls for 5 seconds. What is the acceleration of the elevator after the cable breaks?
(a) -9.81m/s2
(b) 140m/s2
(c) 160m/s2
(d) 180m/s2
A
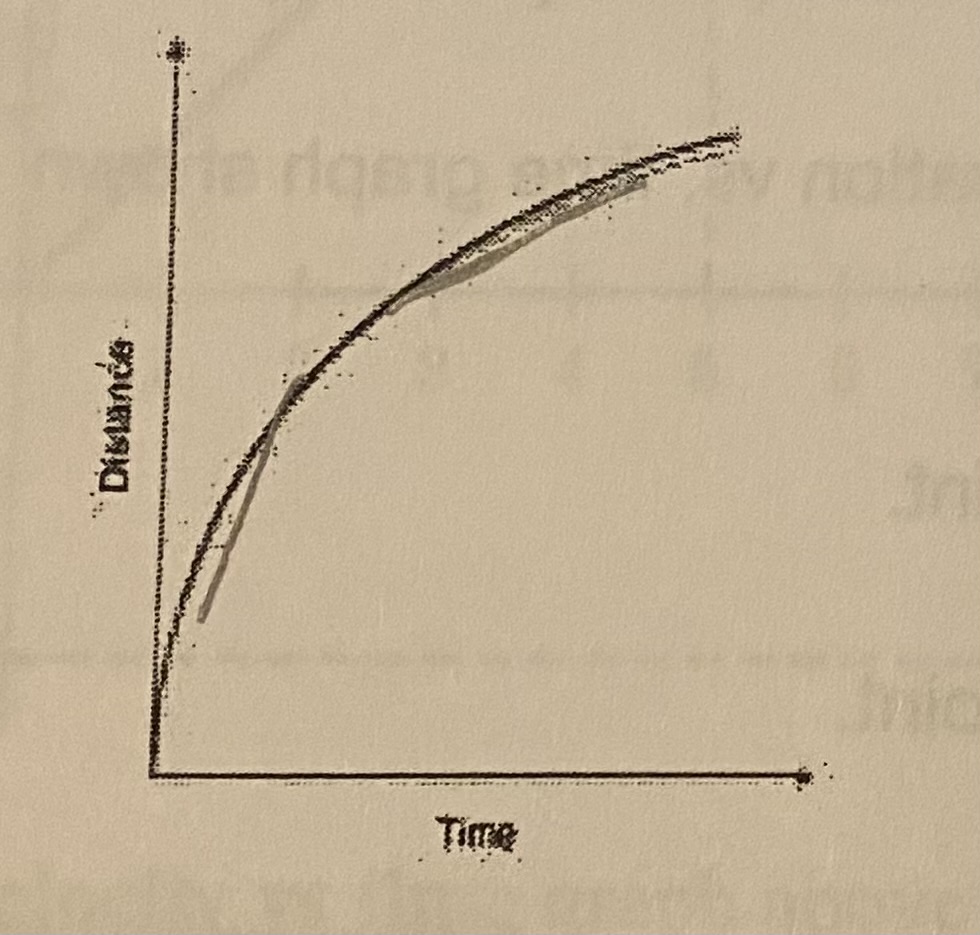
What is this graph showing?
(a) Constant Speed
(b) No motion
(c) Speeding up
(d) Slowing down
D
When a car’s velocity is negative and its acceleration is negative, what is happening to the car’s motion?
(a) The car slows down
(b) The car speeds up
(c) The car travels at a constant speed
(d) The car remains at rest
B
Which of the following values is a vector?
(a) Speed
(b) Time
(c) Distance traveled
(d) Velocity
D
The velocity versus time graph for an object moving in the negative direction and speeding up is
(a) a horizontal line in the negative quadrant (IV)
(b) a horizontal line in the positive quadrant (I)
(c) a line with a positive slope in the negative quadrant (IV)
(d) a line with a negative slope in the negative quadrant (IV)
D
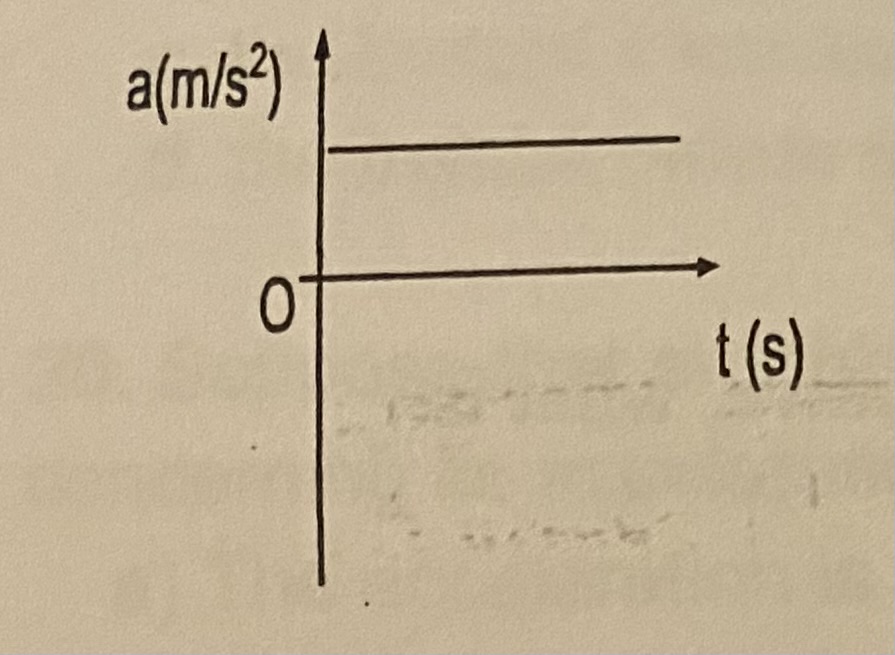
How would an object move to create the acceleration vs. time graph shown below?
(a) stand still
(b) speed up while moving away ref. point
(c) move at a constant speed
(d) slow down while moving away from ref. point
C
A vector is a quantity that has
(a) magnitude and direction
(b) direction only
(c) magnitude only
(d) no magnitude or direction
A

What is the maximum or greatest magnitude of vector A and B combined in any arrangement?
(a) 6m
(b) 10m
(c) 4m
(d) 14m
D
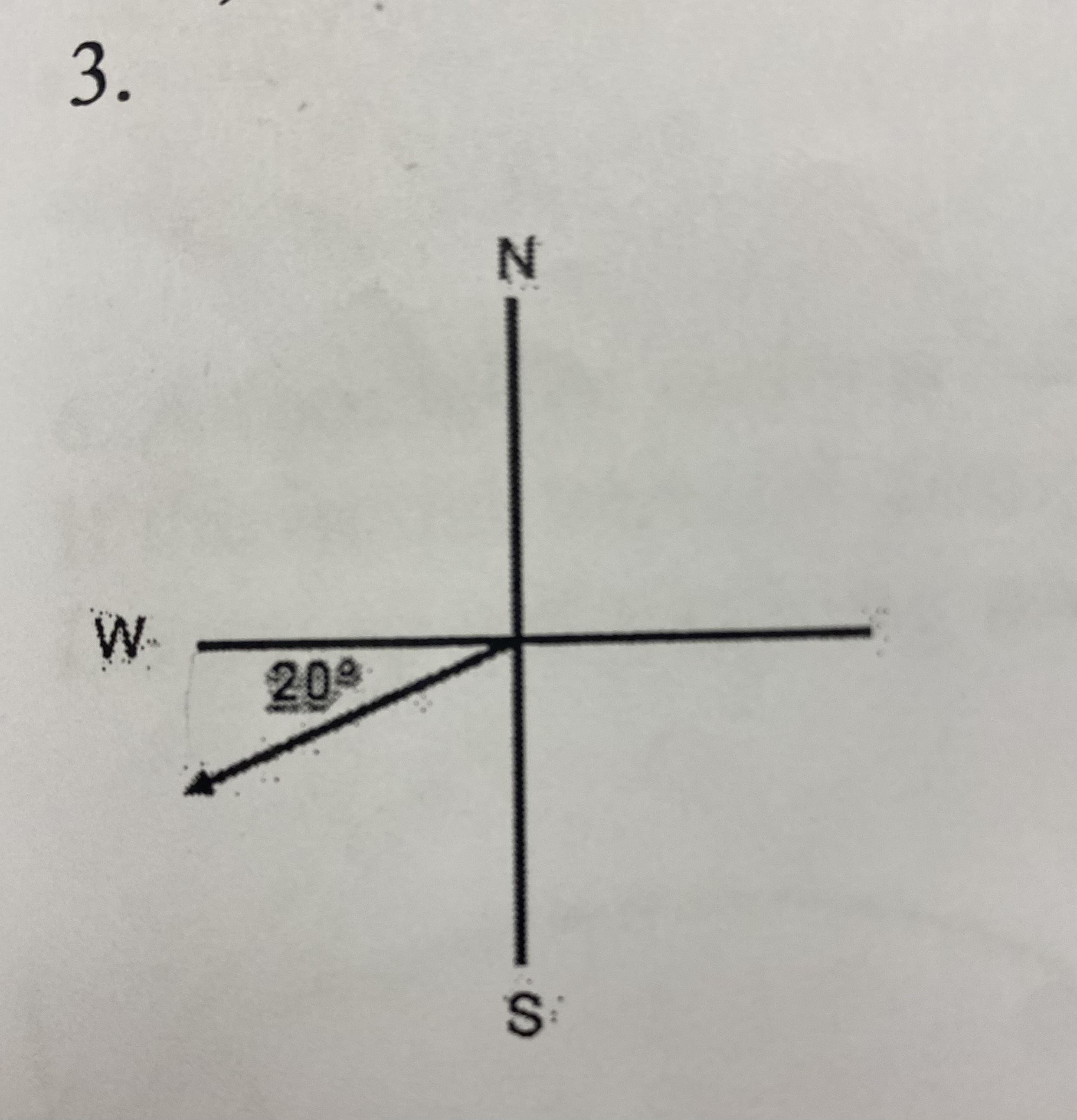
How would you describe the direction above?
(a) 20 degrees north of west
(b) 20 degrees west of south
(c) 20 degrees south of north
(d) 20 degrees south of west
D
What is the vertical component of velocity of an object moving at 5m/s at an angle of 30 degrees to the ground?
(a) 5 sin 30m/s
(b) 5 cos 30m/s
(c) 30 cos 5m/s
(d) 30 sin 5m/s
A
For the winter a duck is flying at velocity 10m/s due south. Suddenly a gust of wind is traveling at 2.5m/s blows against it. What is the resultant velocity of the duck?
(a) 7.5m/s south
(b) 12.5m/s south
(c) 12.5m/s north
(d) 12.5m/s north
A
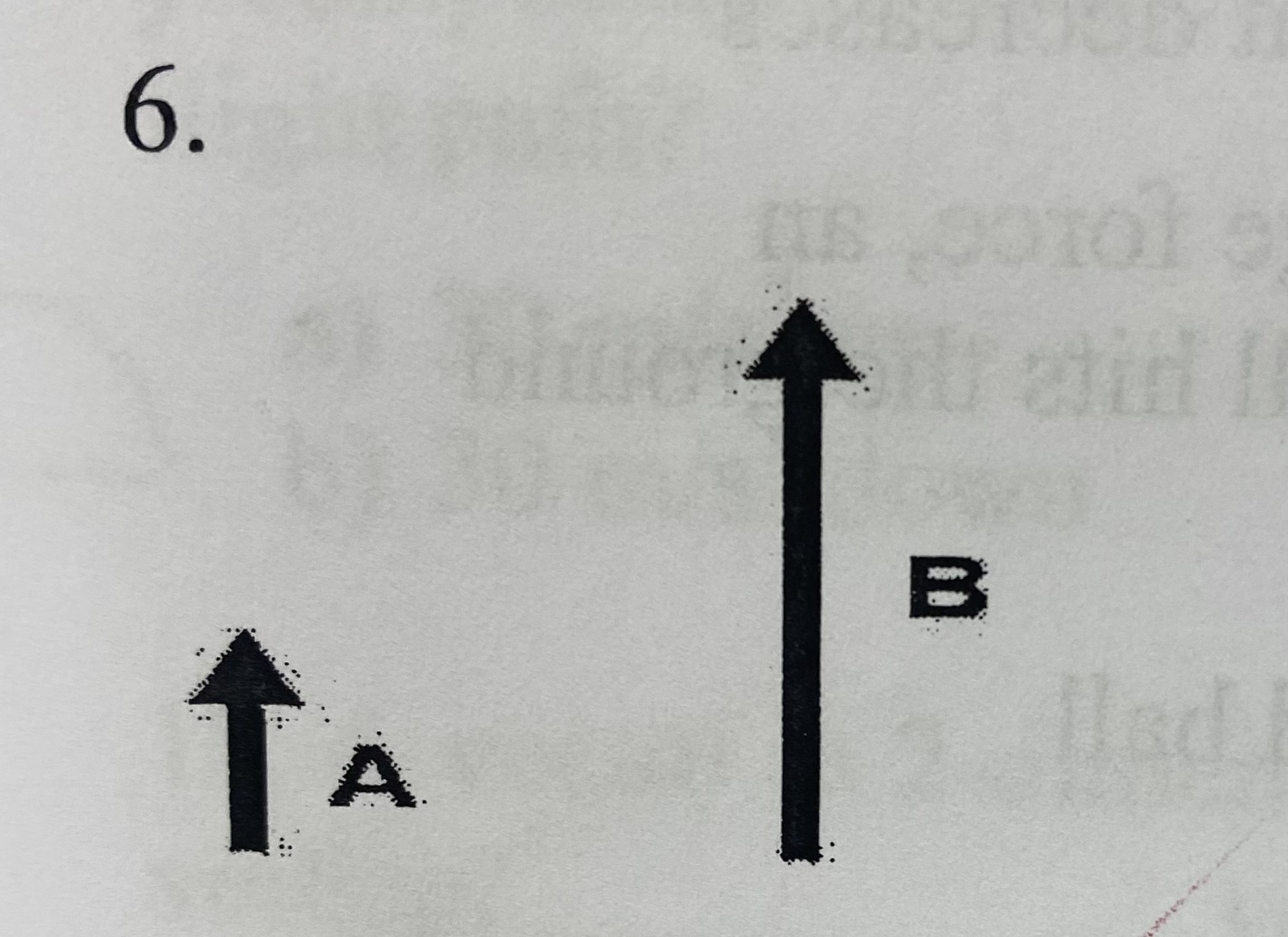
What is true about vector A and B as you see them above?
(a) they have a different direction and the same magnitude
(b) both direction and magnitude are the same
(c) they have the same direction and a different magnitude
(d) they have no direction and no magnitude
C
Which of the following is not an example of a projectile motion?
(a) a long jumper in action
(b) a baseball hit by a bat
(c) a volleyball served over a net
(d) a hot air balloon drifting towards earth
D
What is the path of a projectile?
(a) a parabola
(b) a wavy line path
(c) a hyperbola
(d) projectile doesn’t follow a predictable
A
When representing velocity as a vector
(a) the direction of the arrow shows the direction of motion
(b) the length of the arrow represents the speed
(c) the length of the arrow is drawn to a suitable scale
(d) all of the other answers
D
The horizontal component of a projectile’s velocity is independent of the vertical component of its velocity
True or False
True
How do the magnitudes of the x-component and the y-component of the velocity of a normal projectile change as the projectile raises to its maximum height?
(a) the x and y component both remain constant
(b) the x component remains constant and the y component decrease
(c) the x and y components both decrease
(d) the y component remains constant and the x component decreases
B
At the instant a ball is thrown horizontally with a large force, an identical ball is dropped from the same height. Which ball hits the ground first?
(a) the horizontally thrown ball
(b) the dropped ball
(c) neither, they both hit the ground at the same time
(d) not enough information to make a conclusion
C
For a normal projectile, which statement is true concerning a projectile at its highest point?
(a) the horizontal and vertical components of velocity are equal
(b) the projectile’s velocity is zero and its acceleration is not
(c) the projectiles velocity and acceleration are both zero
(d) the projectiles velocity is horizontal and its acceleration is vertically downward
D
An ant on a picnic table travels 65cm west, then 28cm north, and finally 86cm east. What is the magnitude of the ant’s displacement relative to its original position?
(a) 35cm
(b) 21cm
(c) 179cm
(d) 151cm
A
A ball is launched horizontally at 20m/s and takes 1.3 seconds to hit the ground. What happens to the time the object takes to fall if launched from the same height horizontally but much faster at 40m/s?
(a) it would take twice the time (2.6 seconds) to hit the ground
(b) it would take more that 1.3 seconds but less than 2.6 to hit the ground
(c) it would take less than 1.3 seconds to hit the ground
(d) it would take 1.3 seconds to hit the ground
D
What angle would you throw a ball to get the greatest horizontal x-axis distance?
(a) 90 degrees to the horizontal
(b) 45 degrees to the horizontal
(c) 65 degrees to the horizontal
(d) 25 degrees to the horizontal
B
If a projectile is launched at an angle to the horizontal with a y-component of velocity of 30m/s what is its acceleration at the top of its flight path?
(a) 30 m/s2 up
(b) 30 m/s2 down
(c) 0 m/s2 down
(d) -9.81 m/s2 down
D
A vector in 2-dimensions can be broken down into horizontal and vertical _______________ vectors.
(a) component
(b) scalar
(c) uneven
(d) equivalent
A
If a projectile is launched at an angle to the horizontal with a x-component of velocity of 40m/s what is the acceleration of the object at the top of the flight path?
(a) 40m/s2 horizontally
(b) 40m/s2 down
(c) 0m/s2
(d) -9.81 m/s2 down
D
In the pilots perspective looking down, how does a package dropped from a horizontally moving place look like as it falls?
(a) Straight down
(b) Forward faster than the place
(c) Behind slower than the plane
(d) Stationary
A
What is the value of viy for any horizontal launch?
(a) 0m/s
(b) -10m/s
(c) 10m/s
(d) depends on the vx
A
If we ignore air resistance, we usually say that the horizontal component of acceleration of a projectile is
(a) Variable
(b) Equal to the vertical component of acceleration
(c) Constant
(d) 0m/s2
D
If a pilot wishes to drop off a large package at a target area on the ground while flying horizontally on a windless day, then he must release the package
(a) before reaching the target area
(b) when the plane is directly over the target area
(c)after passing the target area
(d) all the other answers
A
A car is ahead of you always keeping a steady distance of 100m away on a straight road. If you are driving 40mph, what is the speed of the car in front?
(a) more than 40mph
(b) less than 40mph
(c) 40mph
(d) not enough information to tell
C
What is the push or pull on an object that can cause it to accelerate called?
(a) mass
(b) force
(c) density
(d) speed
B
What is the sum of all forces acting on an object called?
(a) gravity
(b) reaction force
(c) acceleration
(d) net force
D
Newtons first law of motion is also called
(a) law of friction
(b) law of reaction
(c) law of action
(d) law of inertia
D
Newton’s first law of motion states that if there is no net force action on an object it will
(a) remain at rest
(b) have no acceleration
(c) move with a constant acceleration
(d) all of the others
D
ΣF=ma is a mathematical representation of Newton’s Second Law of motion.
True or False
True
How much net force is required to accelerate a car of mass 2000kg at 3m/s?
(a) 2000N
(b) 4000N
(c) 6000N
(d) 8000N
C
What will be different for an object of the moon compared with the earth?
(a) weight
(b) mass
(c) both a and b
(d) neither a or b
A
What do you multiply mass by to get the weight?
(a) gravity
(b) gravitational acceleration
(c) energy
(d) force
B
The normal force acts on any object that
(a) is in a gravity well
(b) is in the air
(c) is in a vacuum
(d) touches another surface
D
How big is the net force acting on an object with constant velocity?
(a) 0N
(b) larger than 0N
(c) smaller than 0N
(d) not enough information to tell
A
How does friction help is move from place to place?
(a) friction does not help us
(b) friction keeps us from slipping and sliding
(c) friction only helps cats
(d) friction makes us slip and fall
B
Why does a rolling ball stop? Because of
(a) Gravity
(b) Friction
(c) Waterfalls
(d) Sand
B
To reduce friction, one could
(a) remove wheels to reduce the downward pressure in trolleys
(b) use a lubricant such as grease
(c) place extra weight on the object that is moving
B
Which of the following forces is an example of a constant force?
(a) magnetic force
(b) frictional force
(c) gravitational force
(d) electric force
B
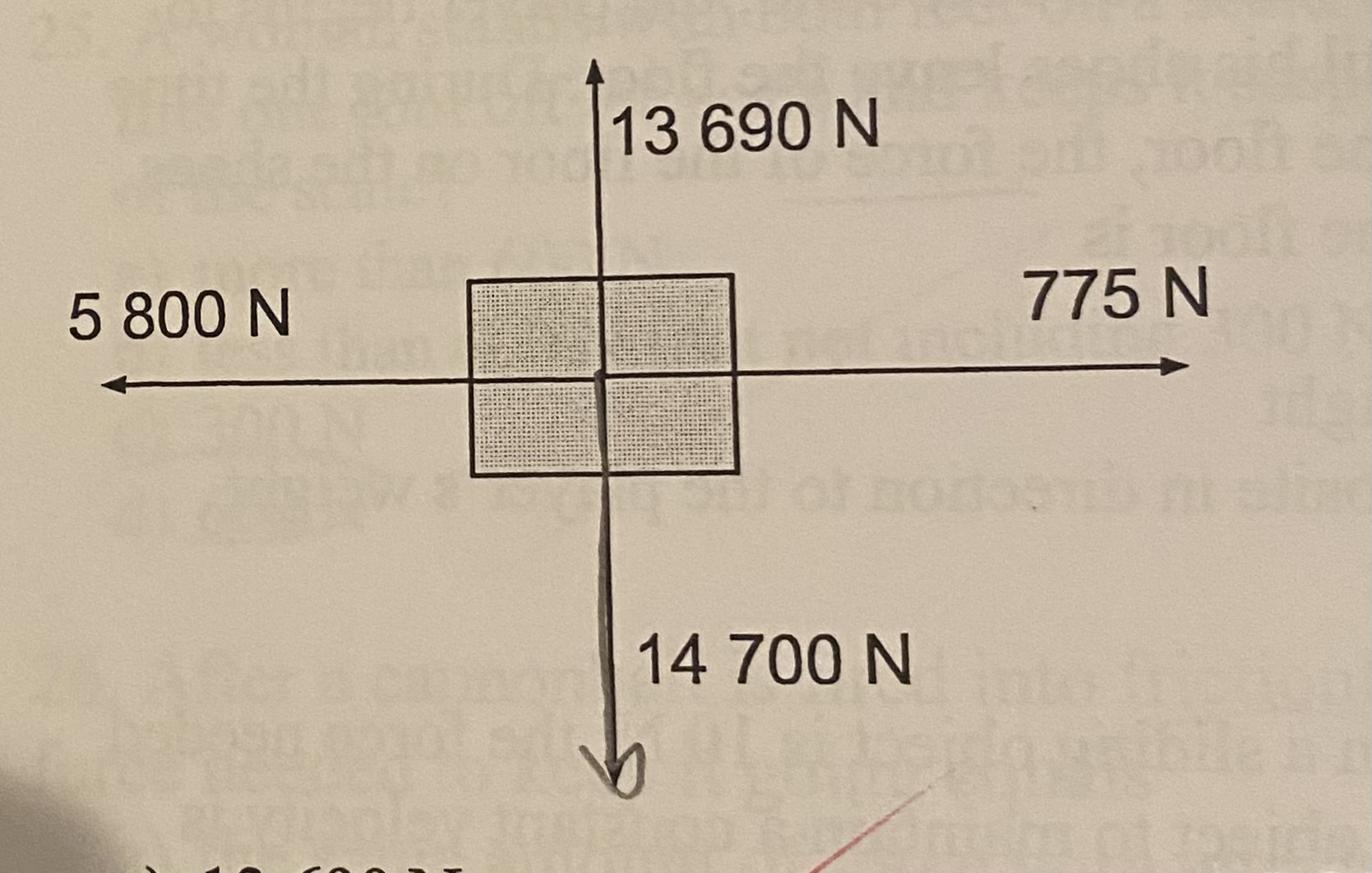
In the free-body diagram shown below, which of the following is the gravitational force action on the object?
(a) 13690 N
(b) 14700 N
(c) 5800 N
(d) 775 N
B
What is the mass of an object that has a weight of 489N?
(a) 69.9 kg
(b) 20.0 kg
(c) 10.0 kg
(d) 49.8 kg
D
A wagon with a weight of 300N is accelerated across a level horizontal surface 0.50 m/s2. What net horizontal force acts on the wagon? g= 9.81 m/s2
(a) 150N
(b) 9N
(c) 15N
(d) 610N
C
A hockey stick hits a puck on the ice. Identity an action-reaction pair, and compare the forces exerted by each object.
(a) The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the stick
(b) The puck exerts a force on the stick; the stick exerts a force on the ice
(c) The stick exerts a force on the ice; the ice exerts a force on the puck
(d) The stick exerts a force on the puck; the puck exerts a force on the ice
A
The simple statement by Newton that for every action there is an equal but opposite reaction is which of his laws of motion?
(a) third
(b) first
(c) second
(d) fourth
A
As a basketball player starts to jump for a rebound, the player begins to move upward faster and faster until his shoes leave the floor. During the time that the player is in contact with the floor, the force of the floor on the shoes to enable the player to move off the floor is
(a) zero
(b) greater than the players weight
(c) equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the player’s weight
(d) less than the player’s weight
B
Suppose the force of friction on a sliding object is 10N; the force needed in the opposite direction on the object to maintain a constant velocity is
(a) 0N
(b) less than 10 N
(c) more than 10 N
(d) 10 N
D
Friction
(a) acts in a direction that opposes the motion of an object
(b) comes from microscopic bumps that acts as obstruction to the object’s motion
(c) acts between the surfaces sliding or attempting to slide past one another
(d) all of the others
D
An unfortunate bug splatters against the windshield of a moving car. Compared to the force of the car on the bug, the force of the bug on the car is
(a) larger
(b) the same
(c) smaller
(d) needed more information to say
B
A rock is thrown vertically into the air. At the top of the flight the net force on it is
(a) its weight
(b) 0N
(c) more than its weight
(d) less than its weight but not 0N
A
A woman stands with both feet on a scale which then reads 600N. If she lifts one foot off the scale and keeps it suspended, what will be the reading of the scale?
(a) more than 600 N
(b) less than 600 N
(c) 300 N
(d) 600 N
D
After a cannonball is fired into friction-less space, the amount of force needed to keep it going equals
(a) the same amount of force with which it was fired
(b) one half force with which it was fired
(c) twice the force with which it was fired
(d) 0N
D
Which of the following is the tendency of an object to maintain its state of motion (or the object’s reluctance to change its state of motion)?
(a) velocity
(b) acceleration
(c) force
(d) inertia
D
If gravity pulls you towards the center on the earth, why don’t you fall through the pavement when you stand or sit or run on it?
(a) because gravity runs out
(b) because gravity does not act through pavement
(c) gravity is not a force
(d) the pavement exerts an equal force in the opposite direction on you
D
If a bicycle and a parked car have a head-on collision, the force of impact is greater on the bicycle than on the car
True or False
False
As the mass of an object increases, the inertia of the object decreases
True or False
False
If the net force acting on an object is 0 N, then the object is either at rest or moving at a constant speed in a straight line
True or False
True
A measure of the force of gravity acting on an object is
(a) frictional force
(b) weight
(c) inertia
(d) mass
B
Suppose a cart is being moved by a fixed force. If suddenly a load is dumped into the cart so that the cart’s mass doubles, what happens to the cart’s acceleration?
(a) it quadruples
(b) it halves
(c) it stays the same
(d) it doubles
B
A box is dragged without acceleration in a straight line path across a level surface by force of 13 N. What is the frictional force between the box and the surface?
(a) 13 N
(b) less than 13 N
(c) more than 13 N
A
When the angle of an incline with a block resting on it increases, the normal force
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) stays the same
(d) there is no normal force
B
A person is attracted towards the center of Earth by a 400N gravitational force. The force with which Earth is attracted towards the person is
(a) 440 N
(b) smaller than 440 N
(c) larger than 440 N
(d) 0 N
A
A hammer drives a nail into a piece of wood. Identify the action reaction pair in this situation.
(a) The nail exerts a force on the hammer, the hammer exerts a force on the wood
(b) The hammer exerts a force in the nail, the wood exerts a force on the nail
(c) The hammer exerts a force in the nail, the hail exerts a force on the hammer
(d) The hammer exerts a force in the nail, the hammer exerts a force on the wood
C
An object is pushed and released horizontally so that it moves with a constant velocity in an environment where there is no restive or force. What force is required to keep the object moving at this velocity?
(a) a constant force
(b) an increasing force
(c) a decreasing force
(d) no force
D
The force between two masses m1 and m2 separated by a distance r is given as Fg=Gm1m2/r2. Fg is always attracticve and never repulsive
True or False
True
If the net force acting on a cart doubles, what happens to the cart’s acceleration?
(a) it is cut in half
(b) it is doubled
(c) it is quadrupled
(d) it stays the same
B
Which has greater mass, an object of weight 30N on the moon or an object of weight 30N on earth?
(a) both have the same mass
(b) the object on the earth
(c) the object on the moon
(d) can’t be determined
C
Your car is travelling at a constant velocity of 60mph; your driving force from your car engine is 5000N. What is the combined resistive force acting against the car?
(a) 0N
(b) greater than 5000N
(c) 5000N
(d) less than 5000N
C
If an object is falling freely, the force action on it is
(a) no force
(b) an increasing force
(c) a constant force
(d) a decreasing force
C