Chapter 3 Princeton
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
abiotic
related to factors or things that are separate and independent from living things, nonliving.
acid
any compound that releases hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. Also, a water solution that contains a surplus of hydrogen ions.
air mass
mass-enormous bodies of air that move as a unit.
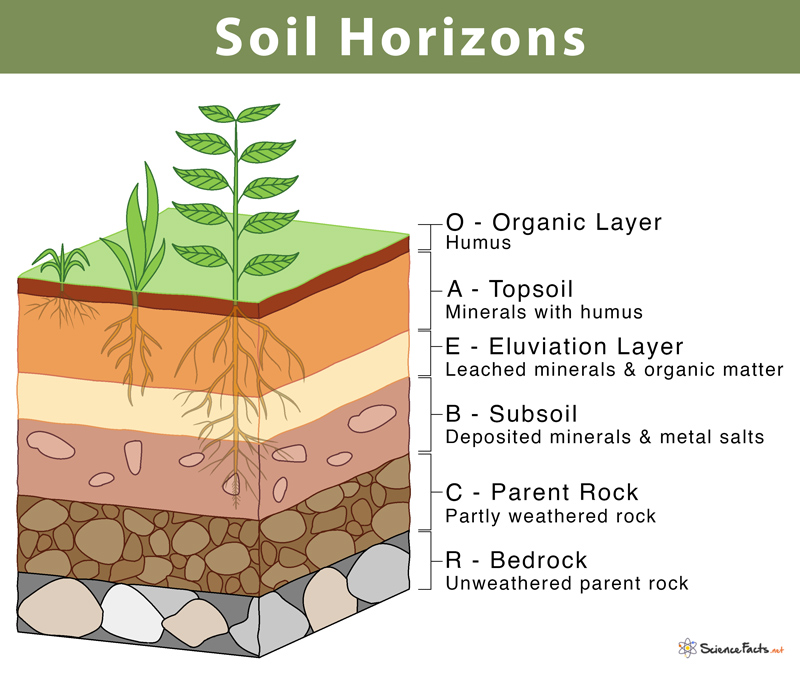
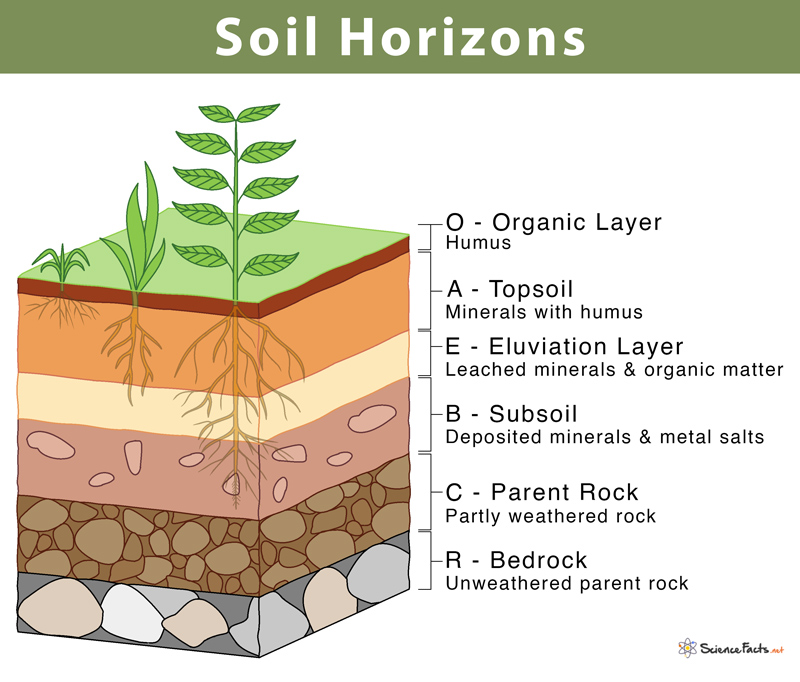
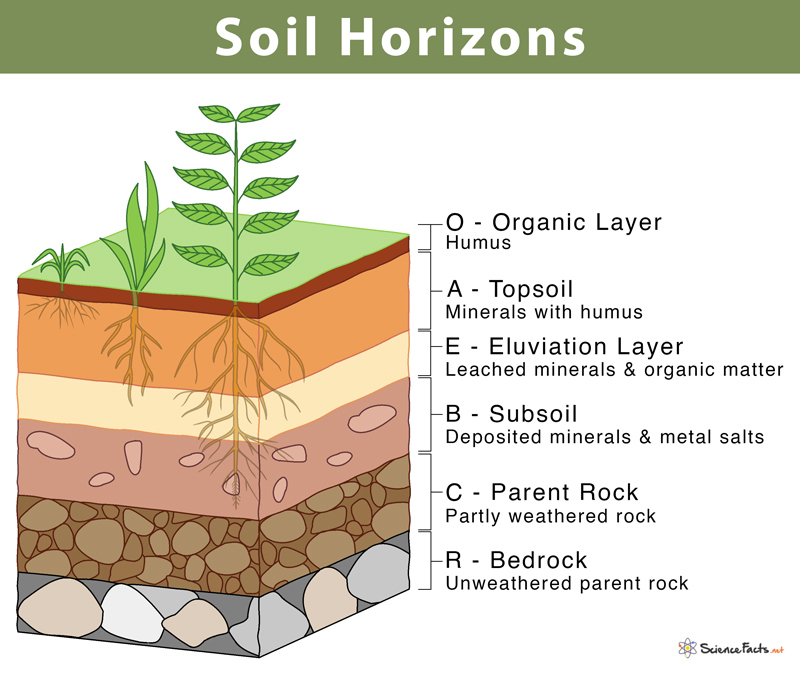
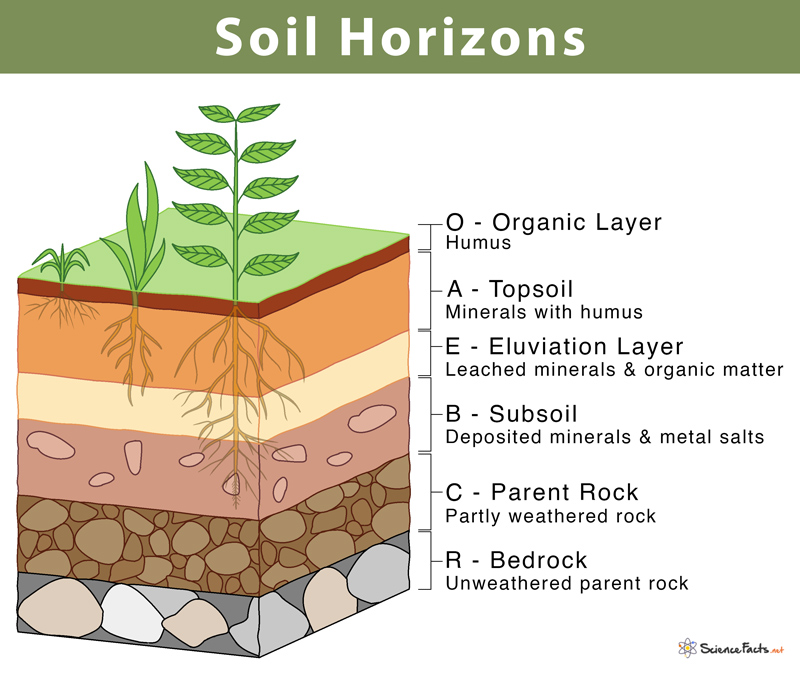
A layer
a soil horizon the layer below the O layer is called the A layer. The A layer is formed of weathered rock, with some organic material often referred to as
topsoil.
alkaline
a basic substance chemically, a substance that absorbs hydrogen ions releases hydroxyl ions, in reference to natural water, a measure of the base content of the water.
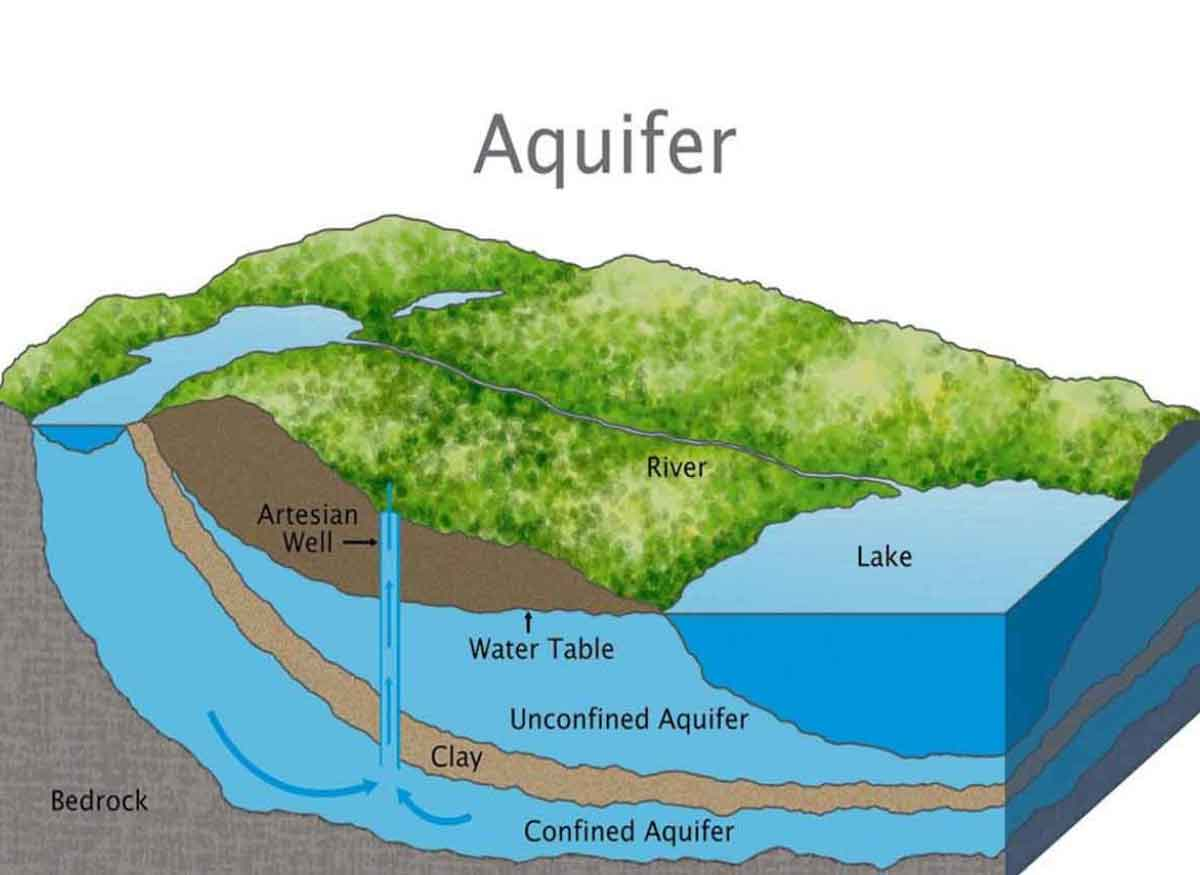
aquifer
an underground layer of porous rock, sand, or other material that allows the movement of water between layers of nonporous rock or clay. Aquifers are frequently tapped for wells.
arable
land that's fit to be cultivated.
asthenosphere -- the part of the mantle that lies just below the lithosphere.
atmosphere
the gaseous mass or envelope surrounding a celestial body especially the one surrounding the earth which is retained by the celestial body's gravitational field.
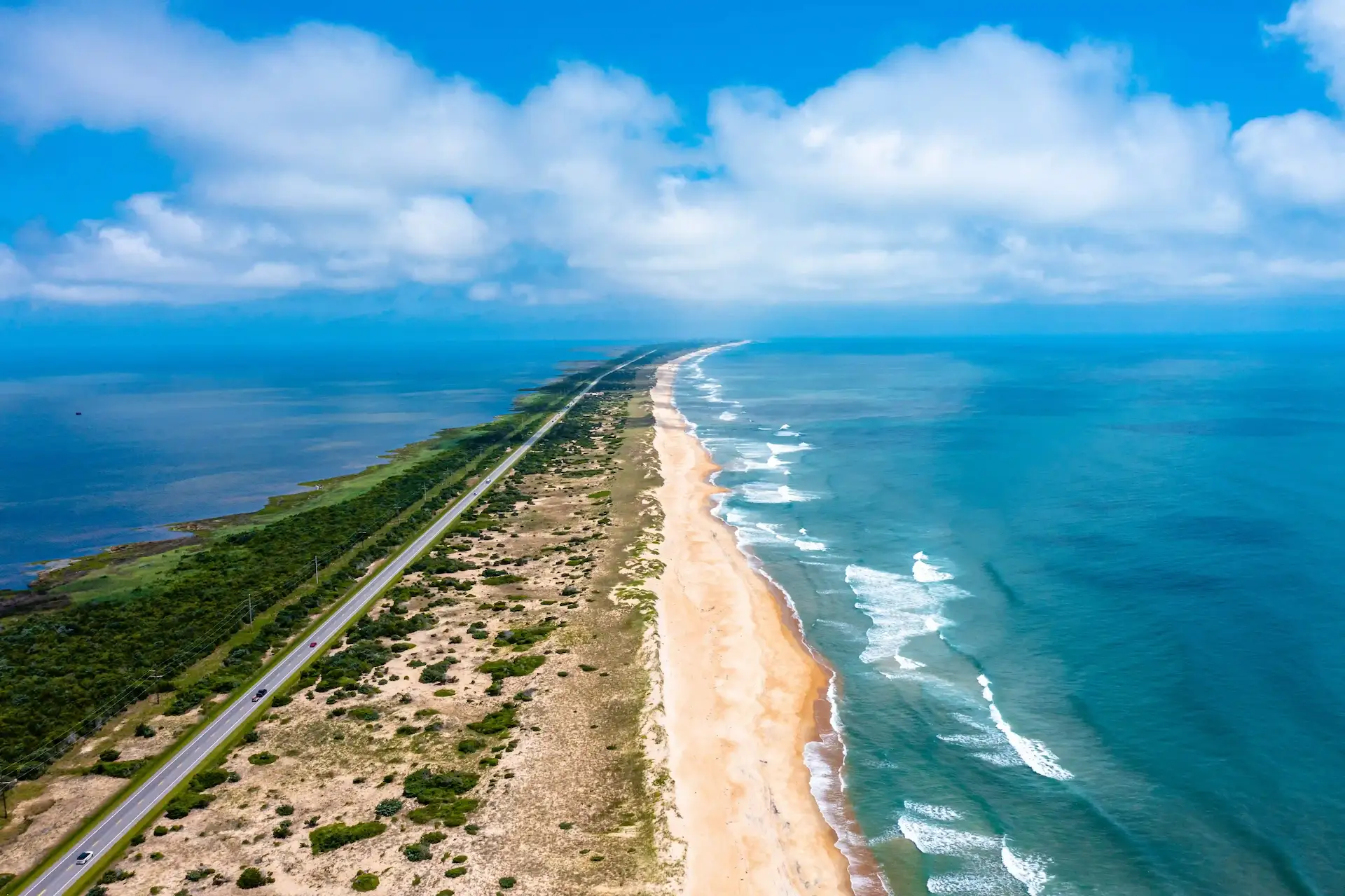
barrier island
a long, relatively narrow island running parallel to the mainland,built up by the action of waves and currents and serving to protect the coast from erosion by surf and tidal surges.

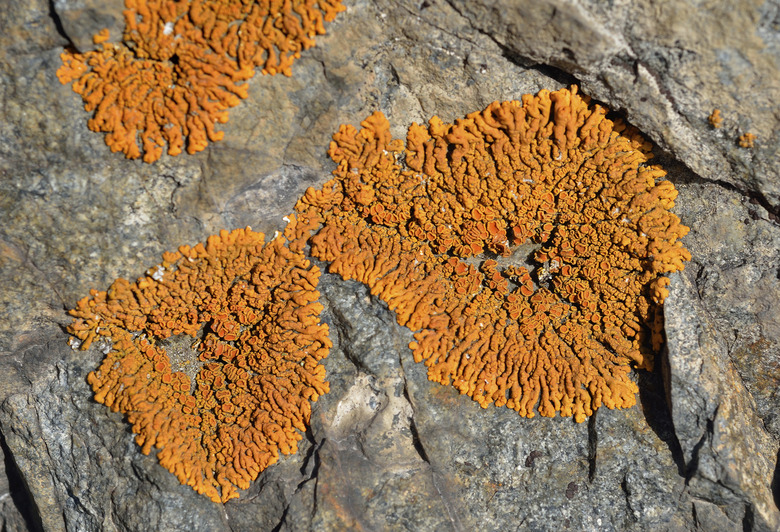
biological weathering
any weathering that's caused by the activities of living
organisms.

biotic
living or derived from living things.
B layer
a soil horizon,receives the minerals and organic materials that are leached out of the A horizon.
chemical weathering
the result of chemical interaction with the bedrock that is typical of the action of both water and atmospheric gases.
C layer
a soil horizon, is made up of larger pieces of rock that have not undergone much weathering.
clay
the finest soil, made up of particles that are less than 0.002 mm in diameter.
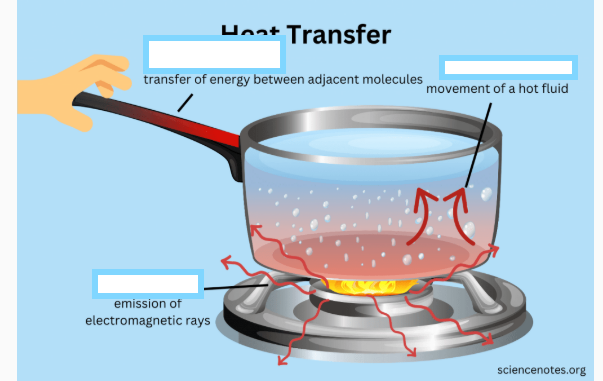
convection
the vertical movement of a mass of matter because of heating and cooling, this can happen in both the atmosphere and Earth's mantle.
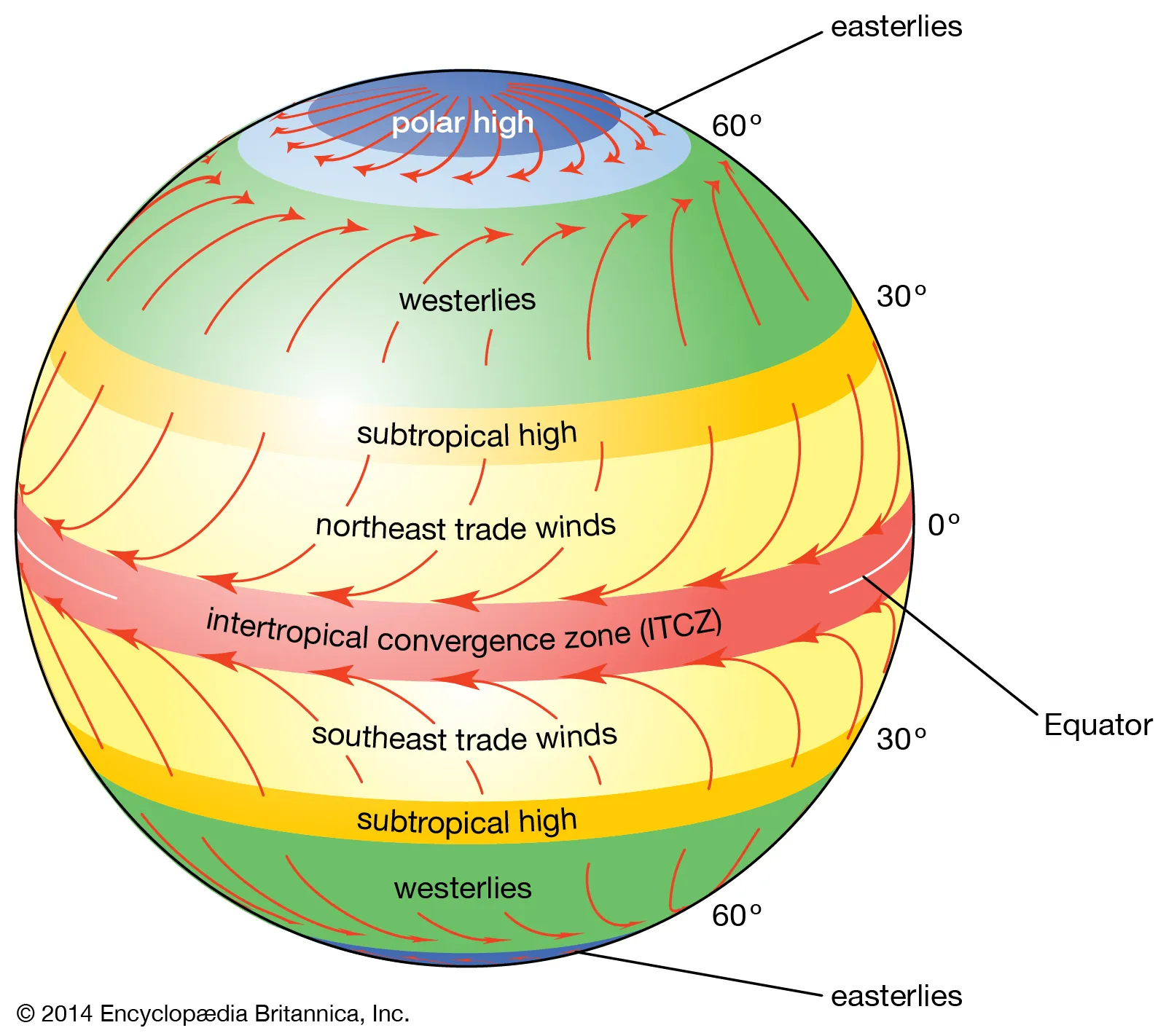
Southern Hemisphere.


Pacific Ocean surface waters in the central/eastern equatorial region become unusually warm
El Niño is a natural climate pattern where _____________, weakening east-to-west trade winds, which disrupts global weather, causing altered rainfall (droughts/floods) and temperature shifts, typically every 3-7 years, as the "warm phase" of theEl Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle, opposite to La Niña.
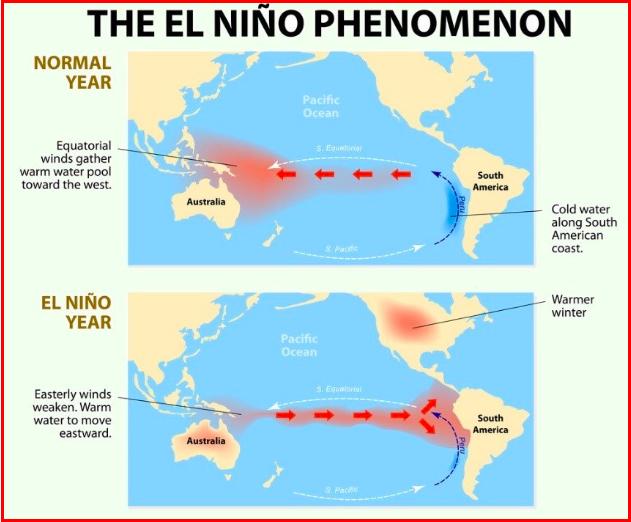
‘the child’
El Nino basically means
little girl
La Nina literally means
El Nino Southern Oscillations or the ENSO.
In normal times, when the tropical South Pacific Ocean experiences high pressure, alternatively the tropical Indian Ocean experiences low pressure conditions. However, these pressure conditions are sometimes reversed, and result in low pressure in the Pacific and alternatively high pressure in the Indian Ocean. This is the periodic change in pressure conditions which is referred to as the Southern Oscillation. These changes in the pressure conditions being developed in the Pacific and Indian oceans are connected with the phenomenon of El Nino. This connected phenomenon is referred to as the ______________________.
warming , cooling
"Enso" most commonly refers to the El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), a major climate pattern of ______(El Niño) and _____(La Niña) in the tropical Pacific affecting global weather.
the part of the wide lower course of a river where its current is met by the tides. (brackish water)

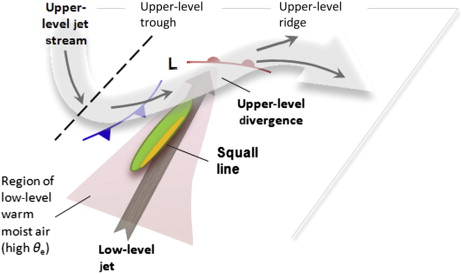
squall
A _________is a sudden, sharp increase in wind speed lasting minutes, as opposed to a wind gust, which lasts for only seconds
the phenomenon whereby the earth's atmosphere traps solar radiation, caused by the presence in the atmosphere of gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane that allow incoming sunlight to pass through but absorb heat radiated back from the earth's surface.
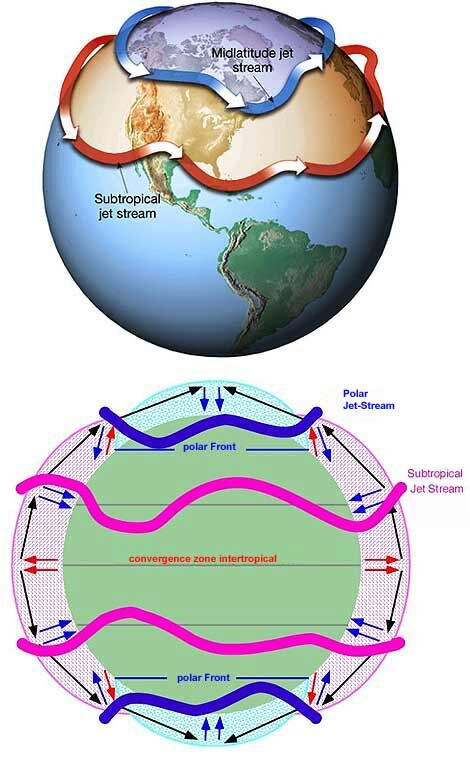
a system of vertical and horizontal air circulation predominating in tropical and subtropical regions and creating major weather patterns. keywords: circulation, subtropical.
the water from which a river rises a source.
horizon
a layer of soil.

a severe tropical cyclone originating in the equatorial regions of the Atlantic Ocean or Caribbean Sea or eastern regions of the Pacific Ocean, traveling north, northwest, or northeast from its point of origin, and usually involving heavy rains.
Iron & Nickel:
__________ The main metallic components, making up the bulk of the core.
Light Elements: Sulfur, oxygen, and silicon are present, influencing its density and properties.
a high-speed, meandering wind current, generally moving from a westerly direction at speeds often exceeding 400 km (250 miles) per hour at altitudes of 15 to 25 km (10 to 15 miles).
key: fast river of air that flows high up in the sky ✈☁.
Hot air and cold air meet
The air moves fast where they meet
soil composed of a mixture of sand, clay, silt, and organic matter. mantle-the layer of the earth between the crust and the core.

humus, loam
Ang_____ay nabubulok na organikong materyal, samantalang ang____ ay uri ng lupang may halong buhangin, banlik, luwad, at humus.
organisms. physical (mechanical) weathering-any process that breaks rock down into smaller pieces without changing the chemistry of the rock, typically wind and water.
PACIFIC, ATLANTIC
PACIFIC
OCEAN, AUSTRALIA
western
Philippines is located in the ____ part of the Pacific Ocean,
PACIFIC, 3-7 YEARS
AMERICA, 4-12 YEARS
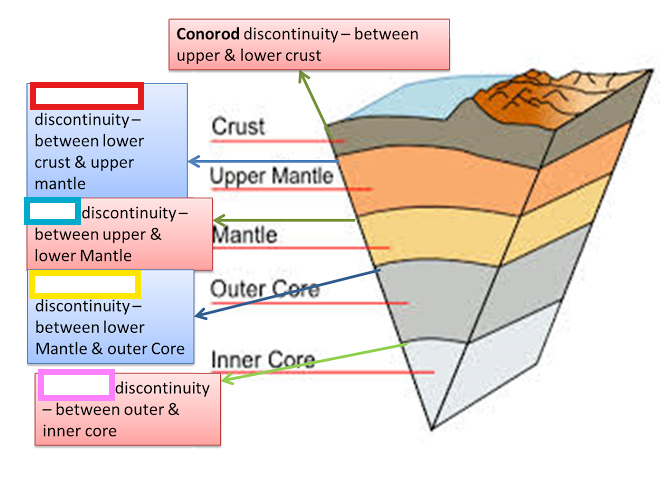
discontinuity, does not
exist at a uniform depth, because not
all regions of Earth are equally balanced in isostatic equilibrium
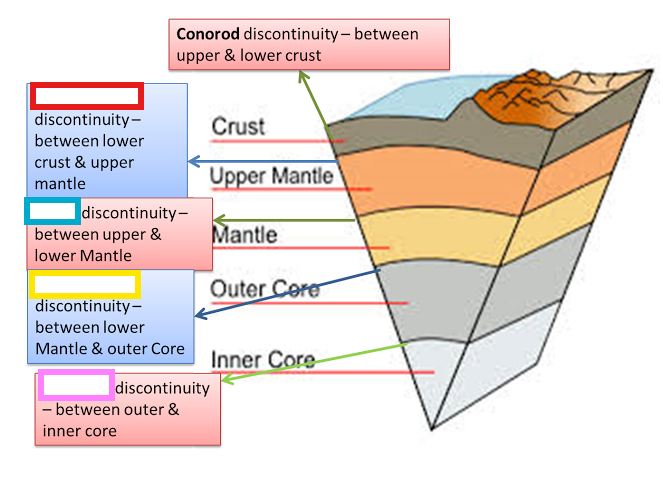
Conrad Discontinuity:
Transition zone between SIAL and SIMA.
Repiti Discontinuity
Transition zone between Outer mantle and Inner mantle.
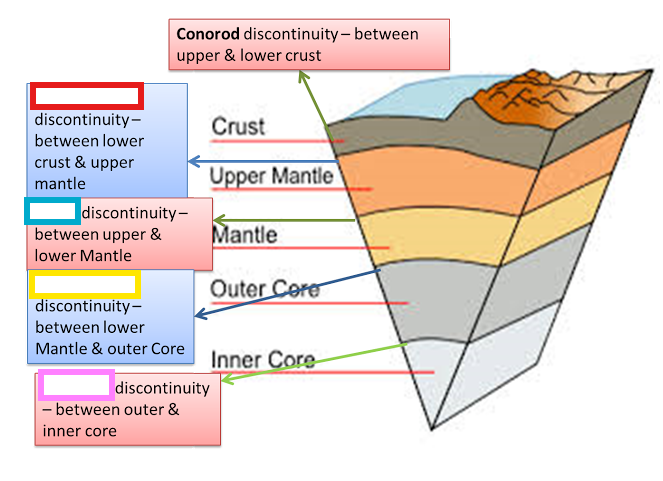
Gutenberg Discontinuity
Transition zone between Mantle and Core.
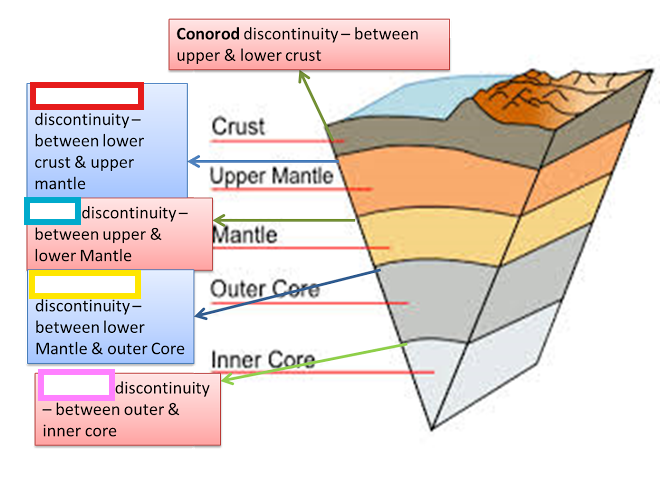
Lehman Discontinuity:
Transition zone between Outer core and Inner core.
Fission splits a large atom into smaller ones, while fusion joins small atoms together.
Which statement BEST describes the difference between nuclear fission and nuclear fusion?
used in nuclear power plants
If Fusion → happens in the Sun ☀
Fission → ______________
The Sun produces energy using nuclear fusion, which joins small atoms together.
Which statement about the Sun’s energy is CORRECT?
a bloom of dinoflagellates that causes reddish discoloration of coastal ocean waters. Certain dinoflagellates of the genus Gonyamlax produce toxins that kill fish and contaminate shellfish.

abrupt.
water-scarce-countries that have a renewable annual water supply of less than 1,000 m3 per person.