PCOL3022 Lecture 6: Monoamines
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:03 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
1
New cards
What are Monoamines?
- Subclass of neurotransmitters within the class of biogenic amines
- Contains 1 aromatic ring connected to an amino group by a 2-carbon chain
- Regulate cognitive processes like emotions, arousal, and certain types of memory
- Drugs that alter monoamine transmission are used to treat psychiatric and neurological disorders (depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, Parkinson's)
- Contains 1 aromatic ring connected to an amino group by a 2-carbon chain
- Regulate cognitive processes like emotions, arousal, and certain types of memory
- Drugs that alter monoamine transmission are used to treat psychiatric and neurological disorders (depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, Parkinson's)
2
New cards
What are the subclasses and neurotransmitters under Biogenic amines?
1. Catecholamines
- NAd
- Ad
- DA
2. Indoleamines
- 5-HT
3. Imidazoleamines
- Histamine
- NAd
- Ad
- DA
2. Indoleamines
- 5-HT
3. Imidazoleamines
- Histamine
3
New cards
What are the key features of Monoamine Neurotransmitters?
- Synthesised from decarboxylated amino acids
- Synthesis mainly by cytosolic enzymes
- Mainly activate GPCRs
- Characteristic anatomical distribution: synthesis is limited to a few subcortical or brainstem regions, which project to multiple cortical and limbic target regions
- Synthesis mainly by cytosolic enzymes
- Mainly activate GPCRs
- Characteristic anatomical distribution: synthesis is limited to a few subcortical or brainstem regions, which project to multiple cortical and limbic target regions
4
New cards
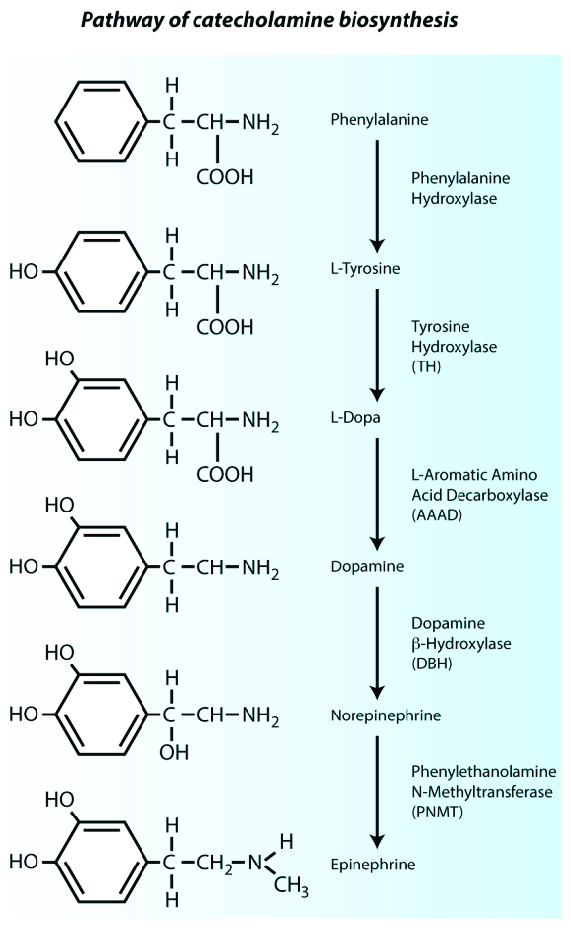
How are Catechcholamines synthesised?
- Precursors: L-tyrosine --> L-DOPA --> dopamine --> noradrenaline --> adrenaline
- Enzymes: Tyrosine dehydroxylase (rate-limiting step) --> aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase --> dopamine B-hydroxylase --> phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase
- Enzymes: Tyrosine dehydroxylase (rate-limiting step) --> aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase --> dopamine B-hydroxylase --> phenylethanolamine N-methyl transferase
5
New cards
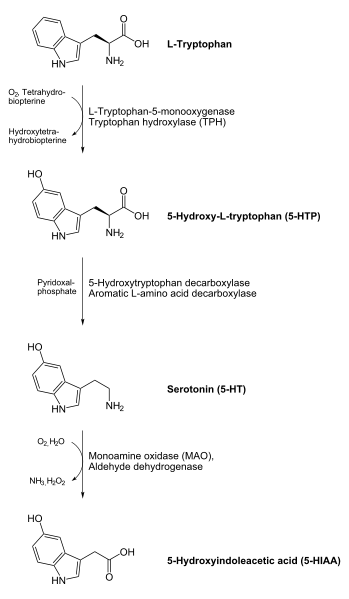
How are Indoleamines synthesised?
- Precursors: L-tryptophan (essential amino acid - from diet) --> 5-HPT --> 5-HT
- Enzymes: Tryptophan hydroxylase (rate-limiting step) --> aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase
- While L-Try and 5-HTP can cross the BBB, 5-HT cannot. This helps to maintain appropriate concentrations in the PNS/CNS
- Enzymes: Tryptophan hydroxylase (rate-limiting step) --> aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase
- While L-Try and 5-HTP can cross the BBB, 5-HT cannot. This helps to maintain appropriate concentrations in the PNS/CNS
6
New cards
Examples of Drugs that Target Synthesis
- Dietary tryptophan (supplements) can increase 5-HT synthesis
- 5-HTP is used (as self-medication) to treat depression, anxiety, and insomnia -- Using the intermediate, instead of the precursor, means the rate-limiting step is avoided)
- L-DOPA used to increase DA synthesis in substantia nigra (Parkinson's)
- 5-HTP is used (as self-medication) to treat depression, anxiety, and insomnia -- Using the intermediate, instead of the precursor, means the rate-limiting step is avoided)
- L-DOPA used to increase DA synthesis in substantia nigra (Parkinson's)
7
New cards
How are monoamines stored?
- Transported into vesicles by VMAT (vesicular monoamine transporter)
- Stored as complex -- bound with ATP, protein, Ca2+, Mg2+
- Stored as complex -- bound with ATP, protein, Ca2+, Mg2+
8
New cards
How are monoamines released?
- Influx of Ca2+ causes release from vesicles
- Released when action potential occurs
- Released when action potential occurs
9
New cards
5-HT and NAd Storage and Release
- Released from varicosities and synapses
- Large amounts of NAd/5-HT released from varicosities into extracellular space
- Concentration gradients in projection areas of varicosities
- Large amounts of NAd/5-HT released from varicosities into extracellular space
- Concentration gradients in projection areas of varicosities
10
New cards
Examples of Drugs that Target Storage and Release
- Amphetamine (and its derivatives) are nonselective VMAT substrates
= Same for MDMA, dexamphetamine, methamphetamine
= Compete with endogenous monoamines for vesicular storage
= Increased concentration for cystosolic monoamine increases spontaneous leakage into synapse
= Used therapeutically: Adderall treats ADHD, narcolepsy
- Reserpine
= Disrupts storage of noradrenaline in the vesicular monoamine transporter by disruption the H gradient
= A range of areas where noradrenaline is stored and released to affect mood, blood pressure regulation, etc
= Same for MDMA, dexamphetamine, methamphetamine
= Compete with endogenous monoamines for vesicular storage
= Increased concentration for cystosolic monoamine increases spontaneous leakage into synapse
= Used therapeutically: Adderall treats ADHD, narcolepsy
- Reserpine
= Disrupts storage of noradrenaline in the vesicular monoamine transporter by disruption the H gradient
= A range of areas where noradrenaline is stored and released to affect mood, blood pressure regulation, etc
11
New cards
Receptor Activation: Dopamine
- All receptors are GPCRs
- D1-like (D1 and D5 receptors) - Gs protein-coupled - Excitatory
- D2-like (D2, D3, and D4 receptors) Gi protein-coupled - Inhibitory
- D1-like (D1 and D5 receptors) - Gs protein-coupled - Excitatory
- D2-like (D2, D3, and D4 receptors) Gi protein-coupled - Inhibitory
12
New cards
Receptor Activation: Adrenoreceptors
- a1-adrenoreceptors - Gq protein-coupled - Excitatory
- a2-adrenoreceptors - Gi protein-coupled - Inhibitory
- B-adrenoreceptors (1,2,3) - Gs protein-coupled - Excitatory
- Ad affinity: B2 > B1/B3 > a
- NAd affinity: a > B2 >> B2
- a2-adrenoreceptors - Gi protein-coupled - Inhibitory
- B-adrenoreceptors (1,2,3) - Gs protein-coupled - Excitatory
- Ad affinity: B2 > B1/B3 > a
- NAd affinity: a > B2 >> B2
13
New cards
Receptor Activation: Serotonin
- 5-HT1 (1A, 1B, 1D, 1E, 1F, 1-like) - Gi protein-coupled - Inhibitory
- 5-HT2 (2A, 2B, 2C) - Gq protein-coupled - Excitatory
- 5-HT3 - Ligand-gated ion channel (Na+) - Excitatory
- 5-HT4 - Gs protein-coupled - Excitatory
- Also 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 - Various g protein-coupled - Excitatory
- 5-HT2 (2A, 2B, 2C) - Gq protein-coupled - Excitatory
- 5-HT3 - Ligand-gated ion channel (Na+) - Excitatory
- 5-HT4 - Gs protein-coupled - Excitatory
- Also 5-HT5, 5-HT6, 5-HT7 - Various g protein-coupled - Excitatory
14
New cards
Inactivation
- Main mechanism for terminating action:
Reuptake via high-affinity Na+ dependent membrane transporter proteins (DAT, NET, SERT)
Reuptake via high-affinity Na+ dependent membrane transporter proteins (DAT, NET, SERT)
15
New cards
Examples of Drugs that Target Transport: Cocaine
Cocaine blocks DAT, NET, SERT to prevent dopamine re-uptake so it prolongs dopamine action in the synapse
Area: Dopamine mesolimbic pathway
Area: Dopamine mesolimbic pathway
16
New cards
Examples of Drugs that Target Transport: Amitriptyline
Amitriptyline blocks noradrenaline and serotonin transporters to prevent dopamine re-uptake so prolongs dopamine action in the synapse
Area: Wherever noradrenaline and serotonin are stored and released
Area: Wherever noradrenaline and serotonin are stored and released
17
New cards
Examples of Drugs that Target Transport: Bupropion
- Antidepressant
- Anti-nicotinic
Bupropion blocks the dopamine transporter to prevent dopamine re-uptake so prolongs dopamine action in the synapse
Area: Dopamine mesolimbic pathway
- Anti-nicotinic
Bupropion blocks the dopamine transporter to prevent dopamine re-uptake so prolongs dopamine action in the synapse
Area: Dopamine mesolimbic pathway
18
New cards
Drugs Targeting Reuptake: Antidepressants
- TCAs block NAT and/or SERT > DAT
- NRIs block NAT
- SNRIs block NAT, SERT
- SSRIs block SERT
- NRIs block NAT
- SNRIs block NAT, SERT
- SSRIs block SERT
19
New cards
Degradation
- Breakdown of the transmitter
- By MAO (monoamine oxidase)
= Bound to neuronal and non-neuronal mitochondria
= Has two isoforms: (a) MAO-A: non-selective, degrades all monoamines; (b) MAO-B: degrades DA only
= Used clinically for depression (both selective and non-selective)
= Used for Parkinson's (MAO-B selective inhibitors only)
- By COMT
= Specific for catecholamines
= In extraneuronal locations (outside)
- By MAO (monoamine oxidase)
= Bound to neuronal and non-neuronal mitochondria
= Has two isoforms: (a) MAO-A: non-selective, degrades all monoamines; (b) MAO-B: degrades DA only
= Used clinically for depression (both selective and non-selective)
= Used for Parkinson's (MAO-B selective inhibitors only)
- By COMT
= Specific for catecholamines
= In extraneuronal locations (outside)
20
New cards
CNS Dysfunctions and Diseases: Dopamine
- Mood
- Schizophrenia and psychosis
- Regulation of hormone release
- Reward and drug abuse
- Movement disorders
- DAT not considered a good target because often associated with addiction
- Schizophrenia and psychosis
- Regulation of hormone release
- Reward and drug abuse
- Movement disorders
- DAT not considered a good target because often associated with addiction
21
New cards
CNS Dysfunctions and Diseases: Noradrenaline
- Mood
- Anxiety
- Regulation of autonomic function
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Regulation of autonomic function
- Pain
22
New cards
CNS Dysfunctions and Diseases: Serotonin
- Mood
- Anxiety
- Regulation of autonomic function
- Regulation of hormone release
- Pain
- Anxiety
- Regulation of autonomic function
- Regulation of hormone release
- Pain
23
New cards
Dopamine pathways: Synthesis
- VTA
- Substantia nigra
- Hypothalamus
- Substantia nigra
- Hypothalamus
24
New cards
Dopamine pathways: Projects to...
- Mesolimbic pathwat
- Amygdala
- Hippocampus
- Mesocortical pathway
- Nucleus accumbens
- Cortex
- Straitum
- Nigro-striatal pathway
- Tubero-infundibular pathway
- Amygdala
- Hippocampus
- Mesocortical pathway
- Nucleus accumbens
- Cortex
- Straitum
- Nigro-striatal pathway
- Tubero-infundibular pathway
25
New cards
Noradrenaline pathways: Synthesis
- Locus coeruleus
- Reticular formation
- Reticular formation
26
New cards
Noradrenaline pathways: Projects to...
- Spinal cord
- Cerebellum
- Amygdala
- Hypothalamus
- Cortex
- Thalamus
- Septum
- Cerebellum
- Amygdala
- Hypothalamus
- Cortex
- Thalamus
- Septum
27
New cards
Serotonin pathways: Synthesis
- Raphe nuclei
28
New cards
Serotonin pathways: Projects to...
- Spinal cord
- Cerebellum
- Amygdala
- Hippocampus
- Septum
- Striatum
- Cortex
- Thalamus
- Cerebellum
- Amygdala
- Hippocampus
- Septum
- Striatum
- Cortex
- Thalamus