ID E3_ medchem questions
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
bottom: miconazole
bc of more chloro groups. makes it soluble in EG and castor oil
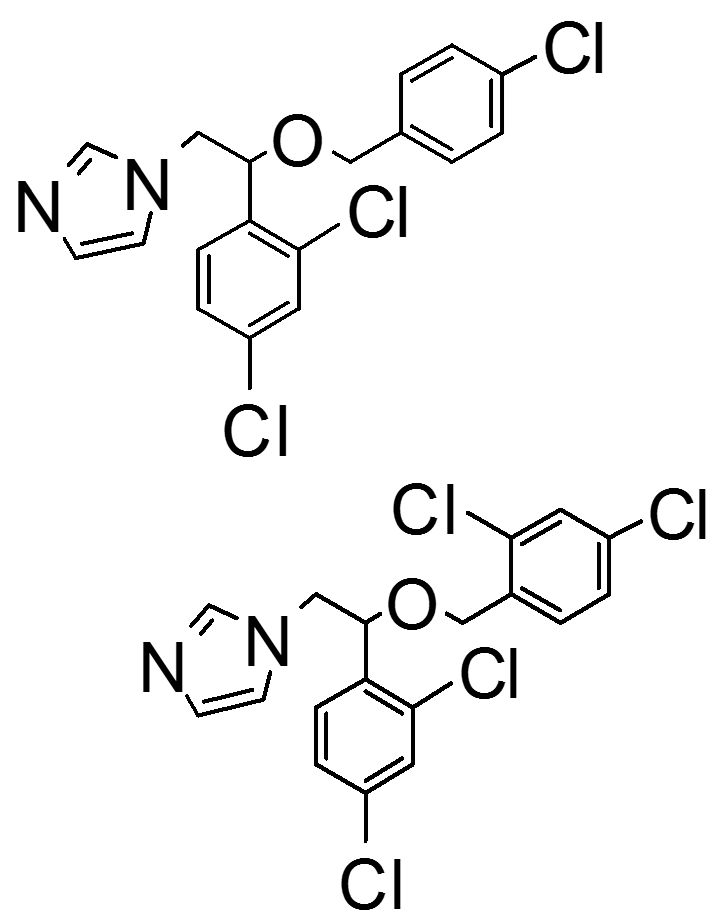
comparing structure of econazole, which is more lipophilic
top: econazole
bottom: miconazole
;
GI distrubance/toxicity
what are the adverse effects of these structures;
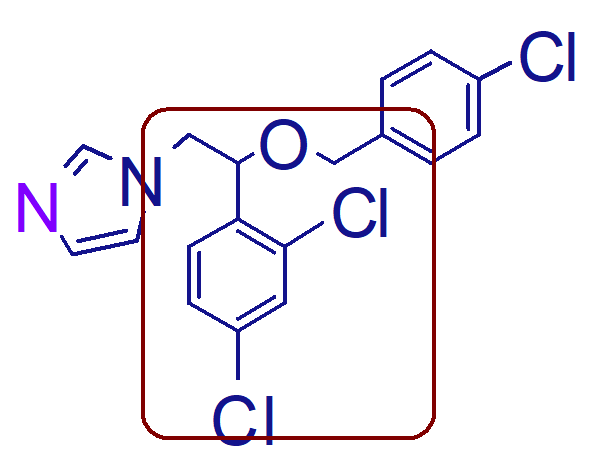
nitrogen not attached to a carbon
which nitrogen forms nitrate salts;
IM
has more chloro compared to econazole, making it more soluble in EG and castor oil
how is this molecule (miconazole) given;
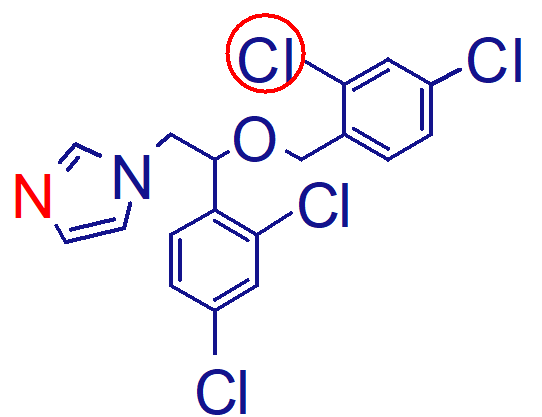
thrombophlebitis
puritis
GI upset
adverse effects of miconazole;
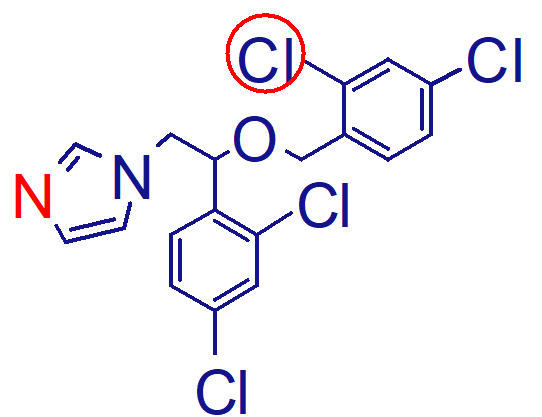
the butyl, 4Cs and S make it more lipophilic, therefore increasing its antifungal activity
used as a cream
what is the important point of this molecule (butoconazole nitrate);
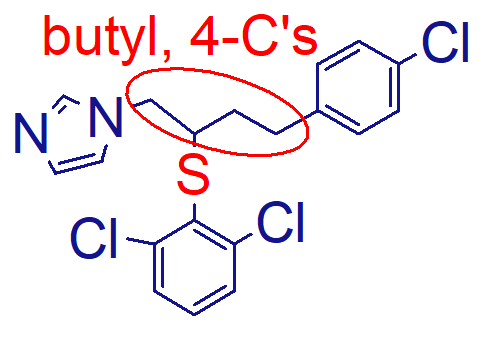
due to removal of 5 carbon linker and placement of S it is sparingly water soluble
important point of this molecule (sulconazole nitrate);
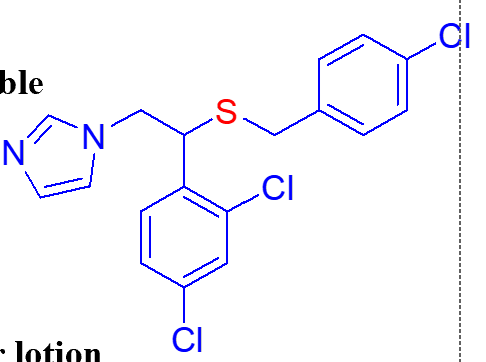
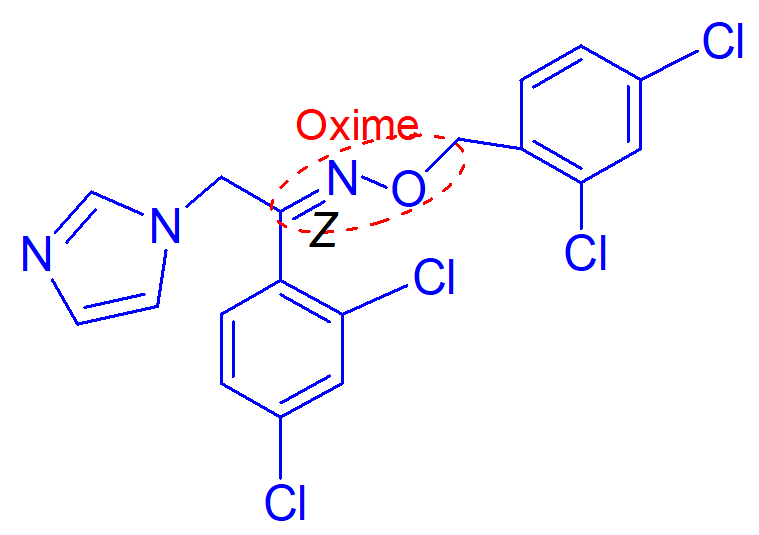
oxime must have Z geometry
the lower the concentration the more potent this drug is
important point of this molecule (oiconazole nitrate);
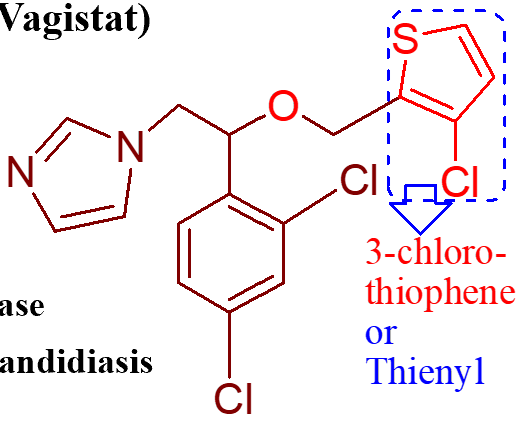
best azole choice for candida glabrata
important points of this molecule (ticonazole);
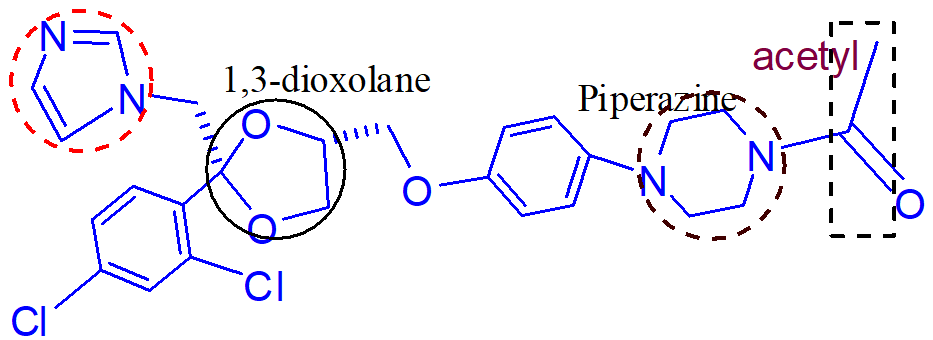
broad spectrum antifungal that has oral bioavailability
depends on acidic pH for dissolution and absorption
has high tendency for hepatotoxicity
piperazine side chain increases hepatotoxicity
important points of this drug (ketoconazole)1.;
antacids
anticholinergic/H2 histamine antagonists
meds that inhibit the gastric absorption of ketoconazole;
N-deacetylketoconazole
inactive metabolite of ketoconazole that is hepatically excreted
causes hepatotoxicity;
amphotericin B
antagonized the activity of ketoconazole;
inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis (results in lowering of testosterone and corticosterone levels in humans)
drug-drug interactions (cyclosporine, phenytoin, terfenadine metabolism will decrease and concentrations will increase
what does inhibition of lanosterol 14 alpha-demethylase in humans from the use of azoles result in;
B
predict the most active steroisomer of A-D;
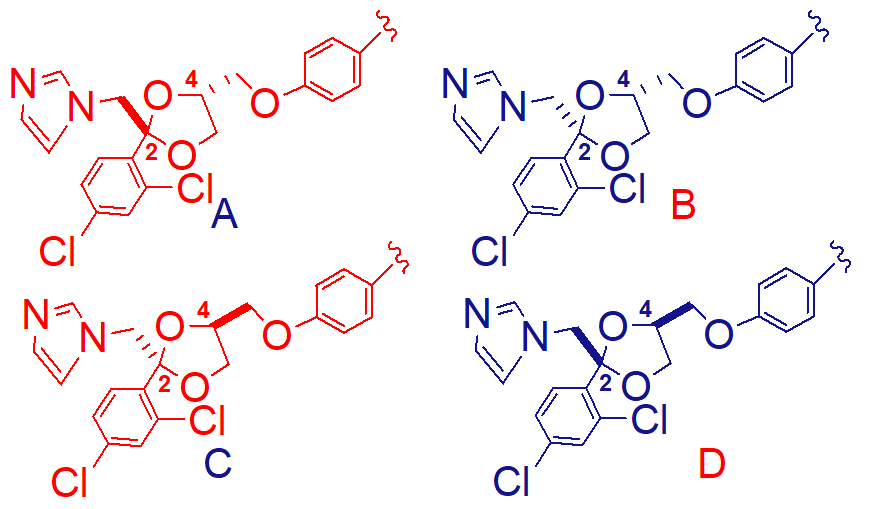
cis 2S 4R
note: cis configuration is required for activity of ketoconazole
isomer of ketoconazole that is the most active;
have extended conformation and mask the ability of the imidazole functionality
cis conformation expose the imidazole to the binding site allowing for better activity
why are the trans isomers of ketoconazole less active;
triazole pharmacophore makes it highly potent
bulky alkylation of the N makes dealkylation take a longer amount of time compared to ketoconazole
what are important points of this molecule (terconazole);
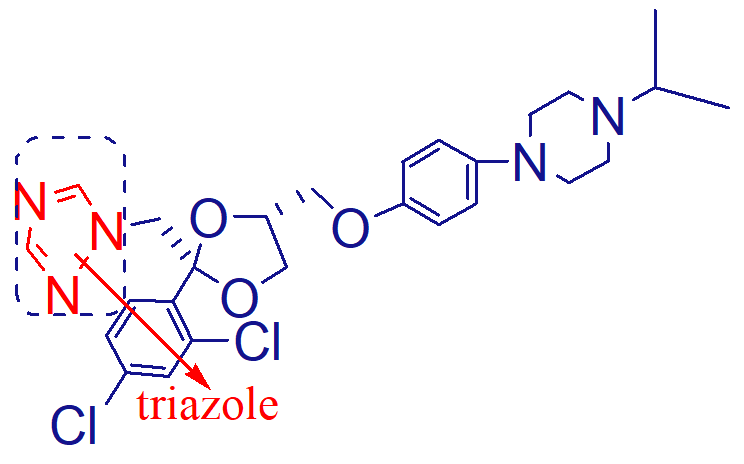
dealkylation
note: all azoles that have the substitution at the piperazine ring are dealkylated for inactivation
how is ketoconazole metabolized;
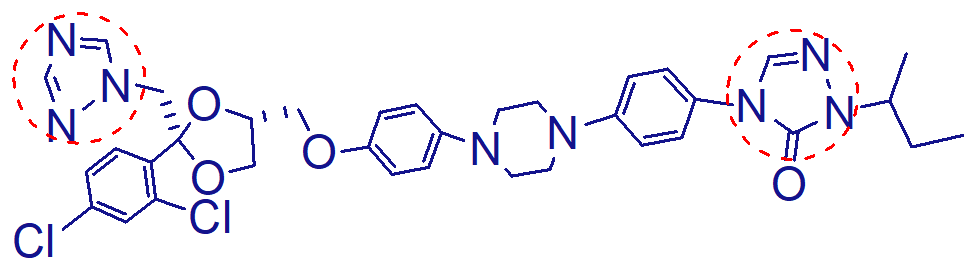
the 2 triazoles
the one with an oxygen is not basic and has no antifungal acivity but increases binding affinity
the one without the oxygen is basic
like ketoconazole, requires acidic environment for absorption but has less risk of hepatotoxicity
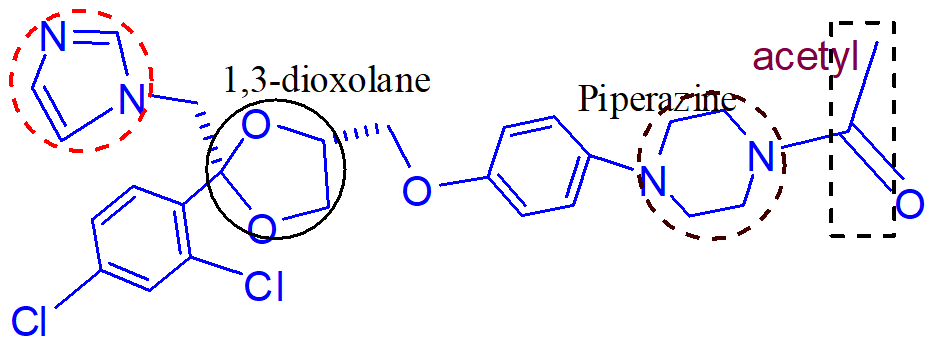
important points of this molecule (itraconazole);
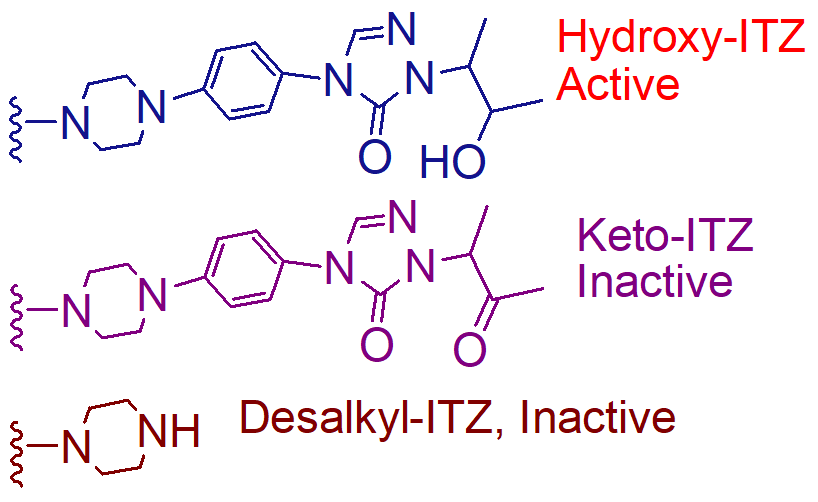
hydroxyitraconazole
note: the molecules are inactivated by N dealkylation but not on the triazole ring. dealkylation occurs on the piperazine ring
metabolite of itraconazole that is active
and it is much more active than itraconzole;
unlike ketoconazole, itraconazole is not hepatotoxic and does not induce adrenal/testicular suppression at therapeutic doses
they both inhibit CYP450, which metabolize xenobiotics and antihistamic drugs like terfenadine and astemizole
what is the difference between ketoconazole and itraconazole;
fluo-phenyl is much less toxic than chloro-fenyl
highly water soluble and can cross BBB
it does not interfere with corticosteroid or androgen biosynthesis in therapeutic doses
what is important about this molecule (fluconazole);
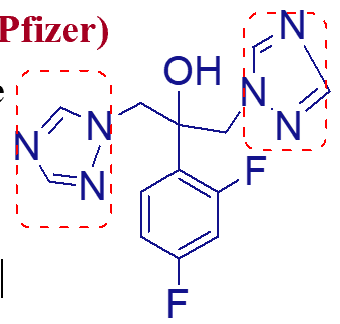
fluconazole
azole of choice for cryptococcal and coccidioidal meningitis;
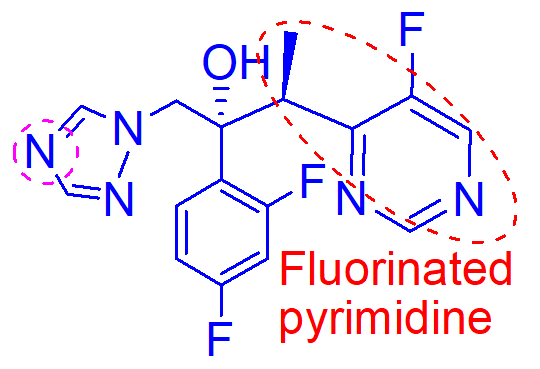
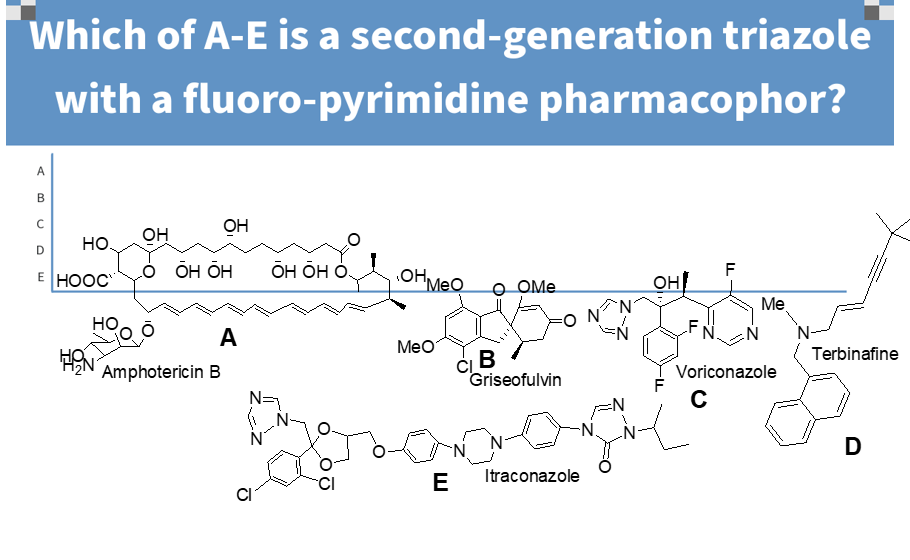
fluorinated pyrimidine give better potency and activity versus resistant strains of aspergillus species
imadine nitrogen oxygenation results in loss of activity
causes hepatotoxicity and photophobia
H2O insoluble
what is important about this molecule (voriconazole);
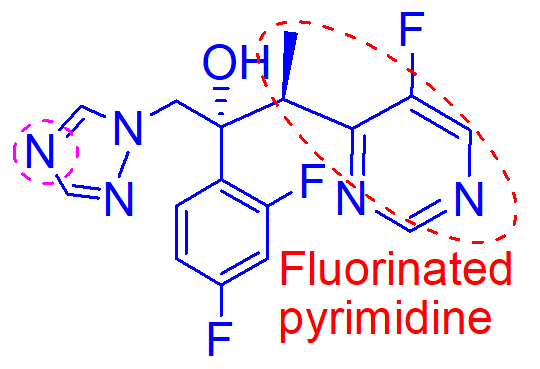
oxygenation of the N of the active pharmacophore
how is this molecule inactivated;
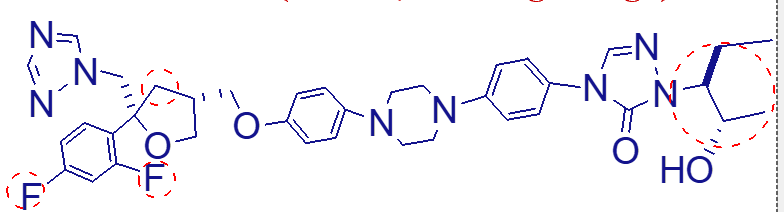
has very long half life
excreted in feces unchanged
can cause GI and liver enzyme change
what are the important points of this molecule (posaconazole);
allylamines have less effect on mammalian cells and have less inhibition of mammalian cholesterol synthesis
azoles vs allylamines;
allylamine has antifungal activity
what are the important points of this molecule (naftifine HCl);
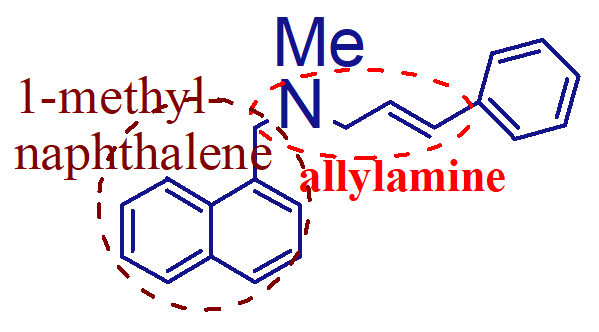
orally active vs onychomycoses (nail ringworm)
highly lipophilic
what are the important points of this molecule;
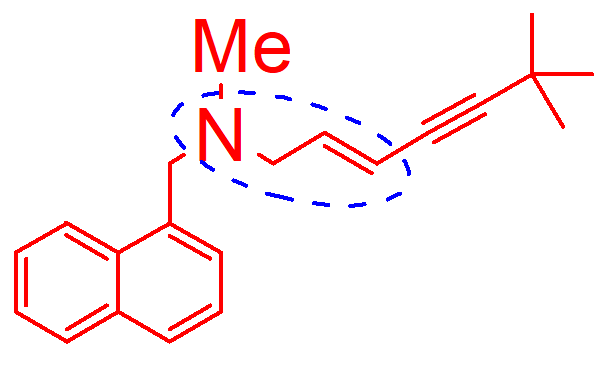
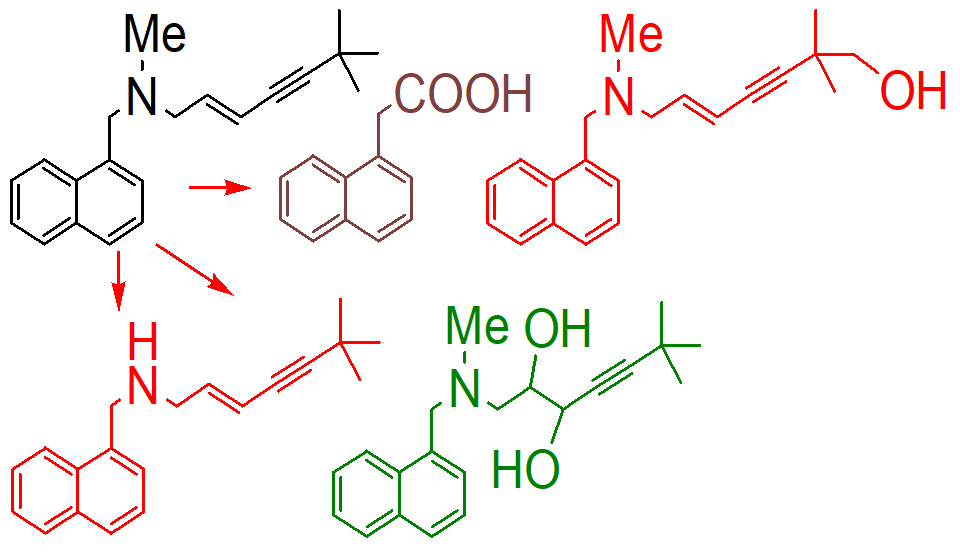
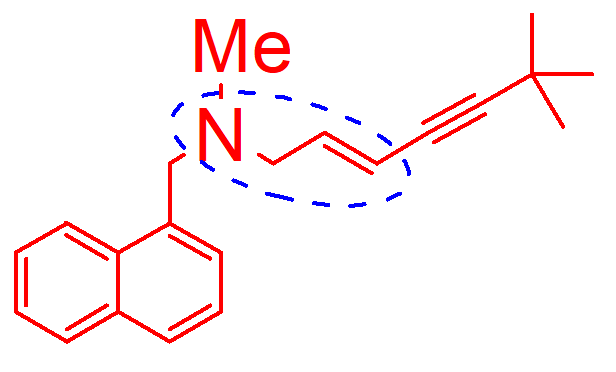
N dealkylation
oxidative d alination
hydroxination
how is this molecule inactivated;
not an allylamine but has same activity
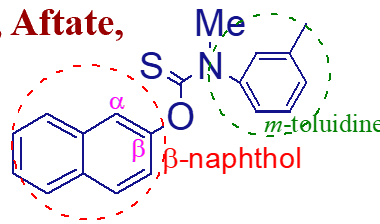
thiocarbamate ester of beta-naphthol-m-toluidine contributes activity
what is the importance of this molecule (tolnaftate);
propionic acid and zinc propionate
propionic acid: non volatile and odorless
zinc propionate: unstable to moisture
nonirritant, nontoxic fungicide acid in sweat;
undecylenic acid
irritant and not used to mucous membranes
obtained by destructive distillation of castor oil
viscous yellow oil, with characteristic odor;
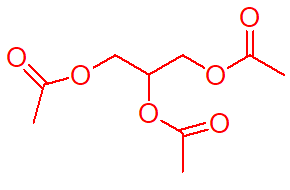
triacetin
glyceryl triacetate colorless oil with bitter taste
has fungicidal effect due to enzymatic hydrolysis by skin eserase to acetic acid;
interfere with cell membrane integrity/function in susceptible fungi
mechanism of action of phenols and related compounds;
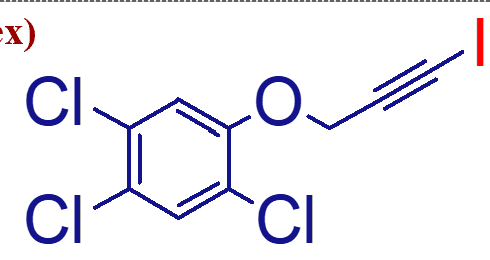
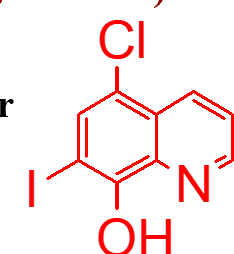
photosensitive, must be protected from light due to I
important points of this molecule (haloprogin);
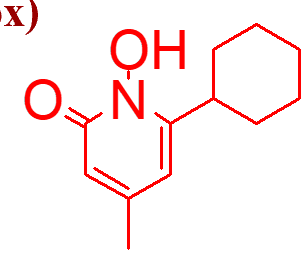
1st choice for tinea corporis, cruris, and pedis
2nd choice for onychomycoses after griseofulvin
blocks amino acid transport at low doses
important points of this moleule (ciclopirox olamine);
iodine is released in tissues
what important;
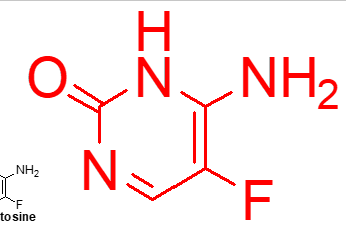
acts as a prodrug activated by fungal cytosine deaminase to 5-fluorouracil which is cytotoxic and anticancer
what important (flucytosine);
5-fluorodeoxyuridine
note: only effects fungal cells bc human cells do not have cytosine deaminase
active form of flucytosine;
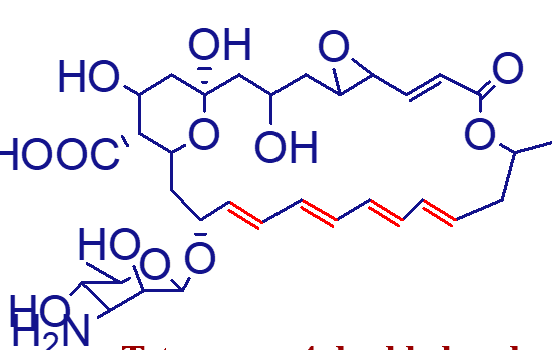
contain enes in the macrocycle which differentiate them from the antibacterial macrolide erythromycins
describe polyene antifungal antibioitcs;
26 membered
size of polyene antifungals;
mycoasamine
amphoteric
hydrophilic: OHs, COOH, and sugar parts
lipophilic: 4-7 double bonds (correlates with antifungal potency and inversely correlates with degree of toxicity)
contained in all polyene antifungals;
bind sterol containing membranes, inserting into and disrupting membrane functions, leaking of essential constituents
mechanism of action of polyene antifungals;
ergosterol containing
do polyenes have a higher affinity for ergosterol containin gmembranes or cholesterol containg membranes;
false
never give IM
T/F amphotericin can be given IM;
amphotericin
antigungal that forms salts with acids and alkali but cannot be used for oral systemic uses;
dextrose
what is amphotericin infused in;
saline
destroys amphotericin;
liposomal encapsulation and lipid complexes
formulations of amphotericin that decrease its toxicity;
nephrotoxicity
limits the use of amphotericin;
natamycin
has four double bonds and one non conjugated double bond;
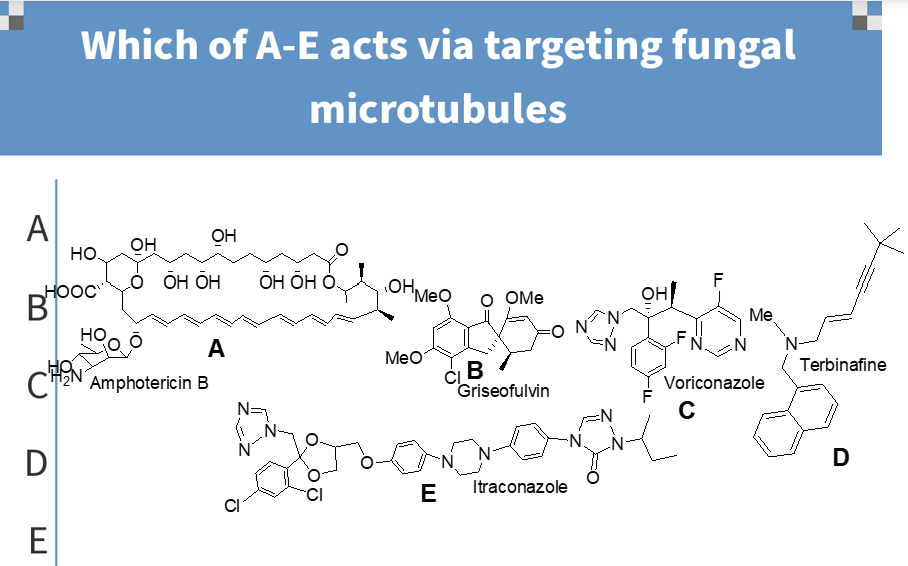
keratin/microtubules
what is griseofulvin attracted to;
fngistatic
action of griseofulvin;
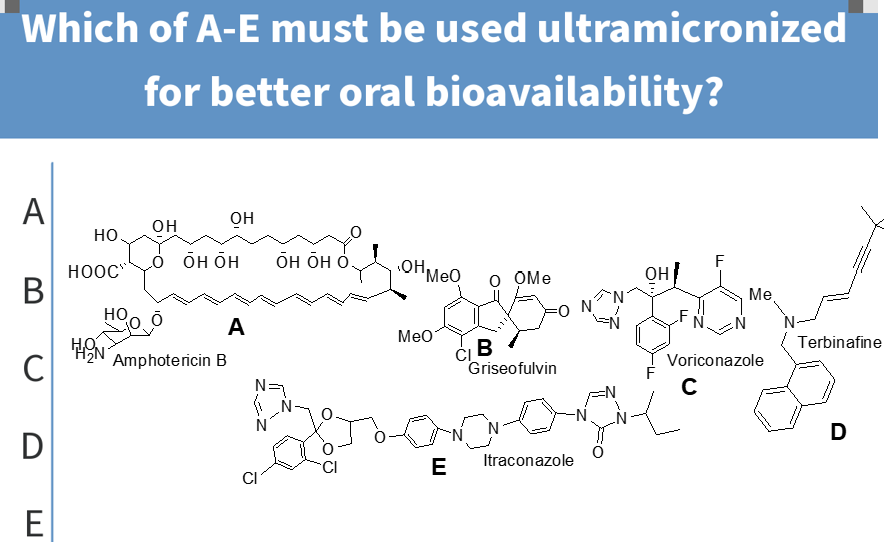
particle size reduction and administration with fatty meals
increases the oral bioavailability of griseofulvin;
echinocandins
penicillin of antifungals;
noncompetitive inhibitor of (1,3)-beta-d-glucans synthase
results in inhibition of cell wall synthesis
mechanism of action of echinocandins;
caspofungin
semisynthesit canalog of echinocandin from culture of the fungus glarea lozoyensis;
c. saline will destroy amphotricin soluble colloidal solution
why amphotericin B solution will not be compatible with saline IV
a. saline will degrade amphotricin liposomal conjugates
b. saline will form amphotricin toxic monosodium salt
c. saline will destroy amphotricin soluble colloidal solution
d. saline will form insoluble amphotericin B sodium salt;
d
;
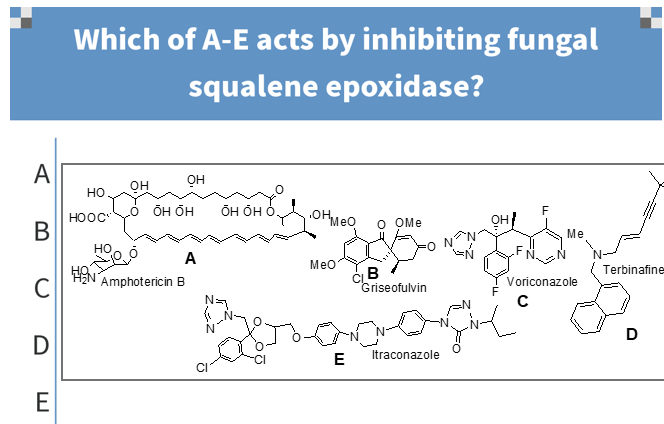
a
;
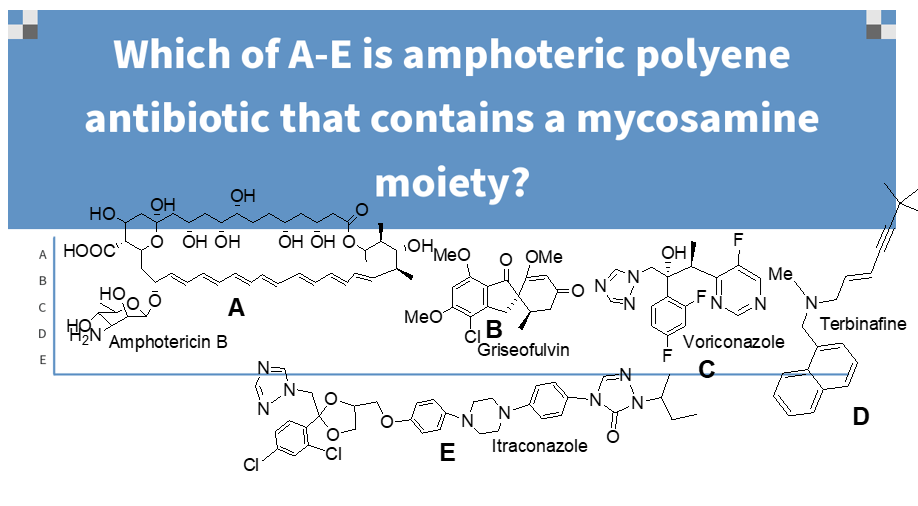
b
;
c
;
b
;
a
which should be conjugated with Na deoxycholate or liposome encapsulations before its systemic use;
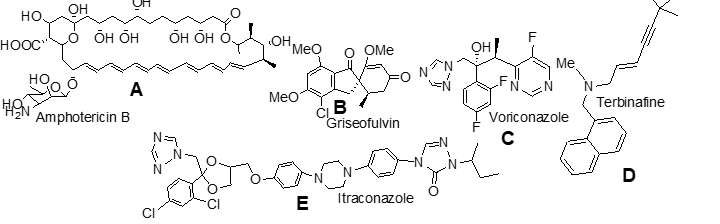
d
which is not opitcally active;
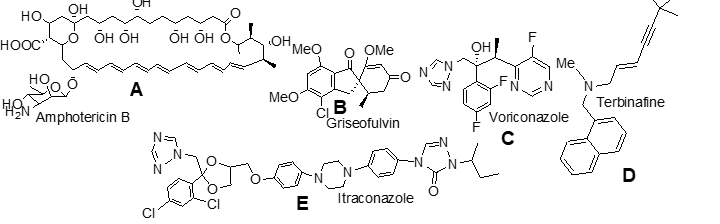
e
which possesses a bis-triazole pharmacophore;
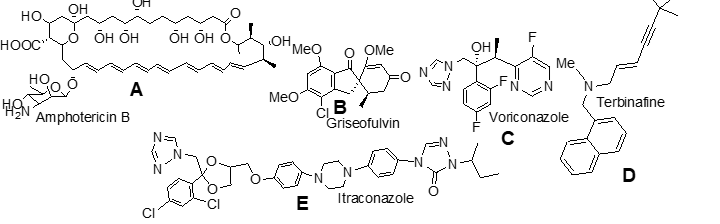
b
which will be the first pass metabolite of voriconazole;