Newton's laws of motion
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Newton's First Law
An object remains in the same state of motion unless a resultant force acts on it
Resultant force
single force that has the same effect as the original forces on an object acting together
When the resultant force is zero
object is stationary or continues to move at the same speed/direction
Newton's Second Law
acceleration of an object is proportional to the resultant force acting on the object, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object
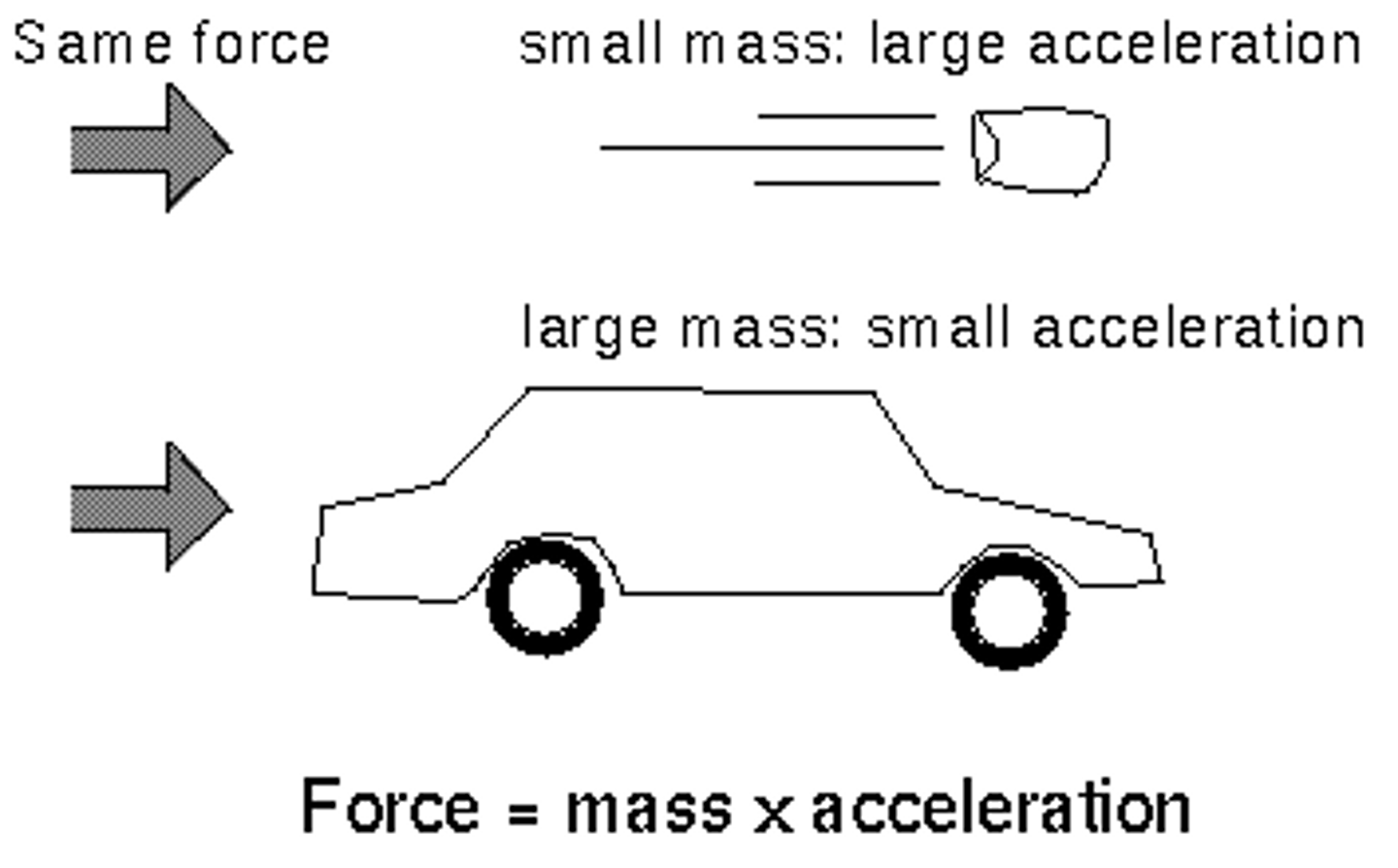
The equation linking resultant force, mass and acceleration
F = ma
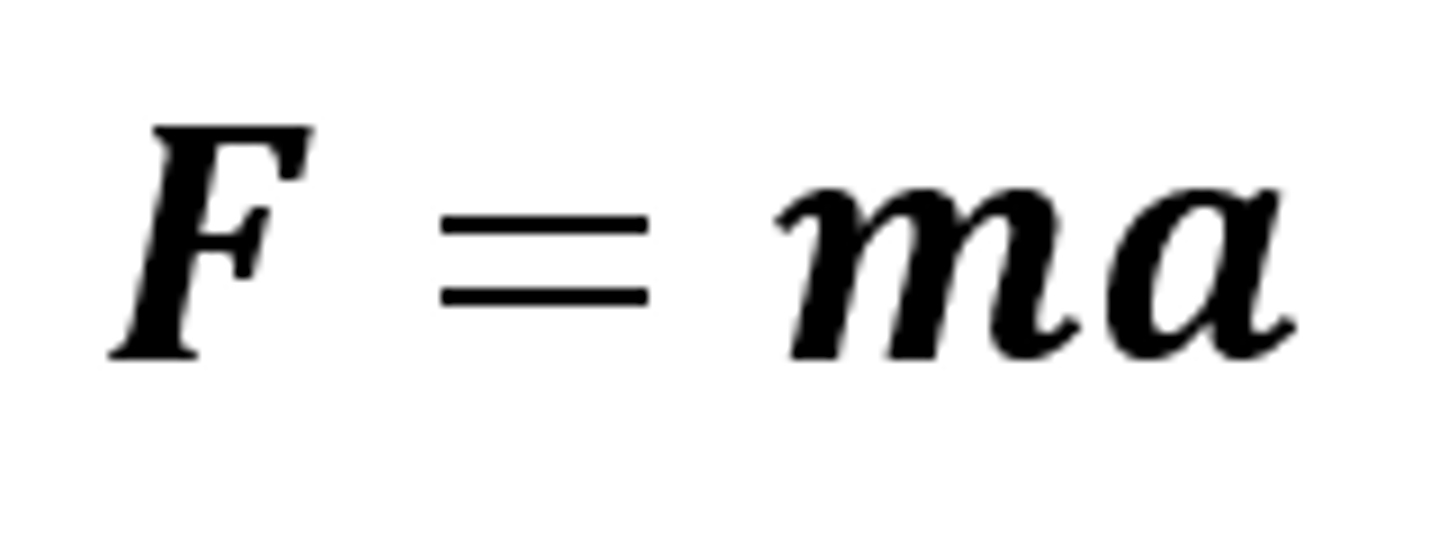
F
The symbol for force
m
The symbol for mass
a
The symbol for acceleration
Unit for mass
Kilograms (kg)
Unit for acceleration
Metres per second squared (m/s²)
Newton's Third Law
for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction
Inertia
an object continues in their state of rest or of in uniform motion
Inertial mass
how difficult it is to change the velocity of an object or the ratio of force ÷ acceleration