6 - Intermolecular Forces and Lab Techniques
1/84
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts related to intermolecular forces and their properties in chemistry.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
85 Terms
Intramolecular Forces
Forces that bond different atoms within a molecule.
(Strongest to Weakest) Ionic, Covalent, Metalic
Polarimetry
Technique used to measure the optical activity or Chirality of a compound
Silver nitrate in Alcohol Test
A qualitative test used to identify the presence of alkyl halides (Cl, Br, or I) in organic compounds.
Reagents: AgNO3 in alcohol
Positive Result: An opaque precipitate of Ag compound formed (color varies by halide)
Eluent
Nonpolar solvent commonly used in column chromatography to flush the mixture through the column, aiding in separation of compounds.
Gas-Liquid Chromatography
Where a gas mobile phase carries vaporized samples through a tube coated with a liquid stationary phase.
Separation is based on BPs and a molecules polarity.
Lower BPs and Non-polar molecules usually elute first
What is the best way to separate a carboxylic acid from an amine?
Extract the Carboxylic acid into aqueous NaOH
Intermolecular Forces
Forces that bind separate, individual molecules together.
(Strongest to Weakest) Hydrogen bonding, Dipole-Dipole, Dispersion Forces
How does branching affect BP of molecules with same molecular weight and same IM forces?
As branching Increases, the boiling point decrease (Indirect)
How does branching affect MP of molecules with the same molecular weight and same IM forces?
Usually as branching increases, MP increase (DIrect)
Except: For straight chains (with no branching) which should be the highest MP
As intErmolecular forces increase, what happens to boiling point, melting point, and vapor pressure?
Hydrogen Bonding > Dipole-Dipole > Dispersion Forces
BP increases (Direct)
MP increases (Direct)
Vapor Pressure Decreases (Indirect)
Which force is stronger: Intramolecular or Intermolecular forces?
IntrAmolecular Forces
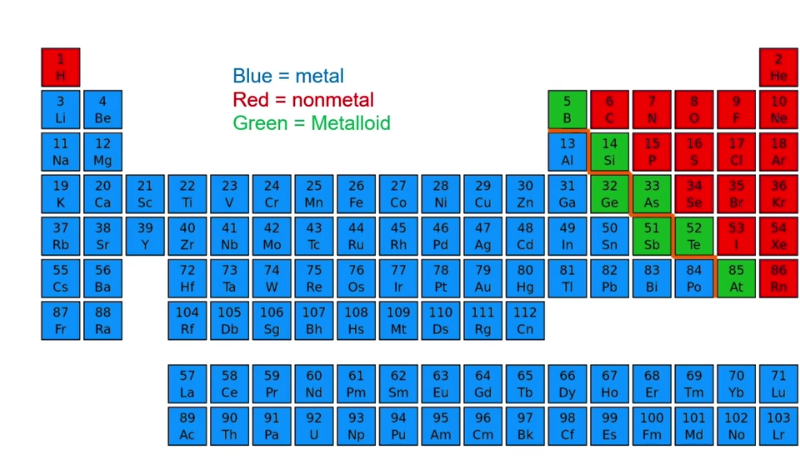
Identify the Metals, Non Metals, and Metalloids in the periodic table
Does Hydrogen bonding increase boiling point?
Yes
Covalent Bond
A bond formed when two or more non-metal atoms share electrons.
Ionic Bond
A bond formed when metals transfer electrons to non-metals, creating ions.
Formed Between Metal and Non-Metal Atoms
Metallic Bond
A bond formed when metal atoms allow their electrons to flow freely.
Covalent Network Solid
A non-metal solid made of a network of covalent bonds,
Diamond, Quartz
Ionic Solid
A solid made of ionic bonds
high melting point
brittle.
Hydrogen Bonding
A strong intermolecular force occurring between molecules that have hydrogen bonded to N, O, F.
Dipole-Dipole Forces
Attractive forces between polar molecules.
Cause a partial positive and partial negative charge
Only occur in polar, non-ionic molecules, that do not have H bonded to N,O,F
Dispersion Forces
Weak intermolecular forces arising from temporary shifts in electron density.
Ion-Dipole Forces
Forces that occur between ionic compounds and polar molecules.
Hydrogen Bonding Examples
Examples include H-O, H-N, and H-F bonds.
Molecular Compounds
Compounds that only have covalent bonds.
Cation
A positively charged ion formed when a metal loses an electron.
Anion
A negatively charged ion formed when a non-metal gains an electron.
Examples of Ionic Compounds
Sodium chloride (NaCl), Silver chloride (AgCl).
Bonding Forces
Forces that hold atoms together within a molecule.
Polar Molecule
A molecule with a net dipole moment due to unequal sharing of electrons.
Nonpolar Molecule
A molecule that does not have a net dipole moment.
Chemical Properties of Metals
Metals generally conduct electricity and heat, have high melting and boiling points.
Intrinsic Properties
Properties that do not depend on the amount of material present.
Extrinsic Properties
Properties that depend on the amount of material present.
Solubility Principle
Like dissolves like; polar substances dissolve in polar solvents.
Homogeneous Mixture
A mixture that has a uniform composition throughout.
Heterogeneous Mixture
A mixture that has a non-uniform composition.
Extraction Method
A technique used to separate compounds based on solubility.
Aqueous Layer
The layer of water in a separatory funnel after extraction.
Organic Layer
The layer containing organic solvents in a separatory funnel.
Distillation
A technique used to separate mixtures based on boiling points.
Based on boiling points
Best used when the difference in boiling points is greater than 25C
Fractional Distillation
Distillation used for separating liquids with close boiling points.
Like doing multiple simple distillations
Best used when the difference in boiling points are at about 25C
Sublimation
The process of a solid turning directly into gas.
can be used for purification
Recrystallization
A technique for purifying solid compounds.
Best used when desired solid is less soluble in the solvent than the impurities
Best used with non volatile solids
Thin-Layer Chromatography (TLC)
A technique used to separate and analyze compounds based on polarity.
Plate and spotting method
Used to separate non-volatile substances
Separates molecules based on polarity
The higher the spot the less polar the substance is and the lower the spot the more polar it is
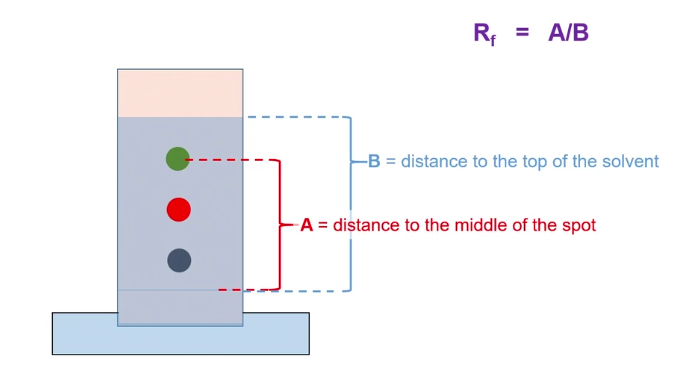
Retention Factor (Rf)
The ratio of the distance traveled by the compound to the distance traveled by the solvent.
= Distance of spot traveled / Distance of solvent traveled
Values are solvent specific; may change is solvent is changed
Column Chromatography
A method for separating compounds based on their polarity.
Most non-polar compound travels the fastest with the slowest being the most polar compound
Tollens’ Test
A qualitative test for determining if aldehydes are present
Reagents: Ag2O / NH3 or Ag(NH3)2
Positive Result: Sides of flask are coated in silver mirror
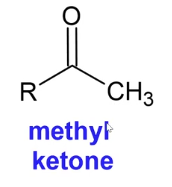
Iodoform Test
A qualitative test for determining if methyl ketones (Ketone with one CH3 group attached) are present
Reagents: I2/OH
Positive Result: Forms a yellow precipitate
Bromine Test
A test to determine the presence of alkenes and alkynes.
Reagents: Br2/CCl4
Positive Result: Brown color of bromine disappears and solution should be clear
Jones Test
A test for determining the presences of primary and secondary alcohols.
Reagents: CrO3 / H2SO4
Positive test: Orange reagent turns blue-green
Electrolyte
A substance that produces an electrically conducting solution when dissolved.
Melting Point
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid.
Boiling Point
The temperature at which a liquid turns into vapor.
Vapor Pressure
The pressure exerted by a vapor in equilibrium with its liquid at a given temperature.
Electronegativity
A measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons.
Carboxylic Acid
An organic compound containing a carboxyl group (-COOH).
Phenol
An aromatic compound with a hydroxyl (-OH) group.
Amine
A compound that contains a basic nitrogen atom.
Polar Solvent
A solvent that has a net dipole moment, such as water.
Nonpolar Solvent
A solvent that does not have a net dipole moment.
Brittle
A material that breaks easily under stress.
Conductive
A characteristic of materials that can conduct electricity.
Soluble
Capable of being dissolved in a solvent.
Insoluble
Incapable of being dissolved.
Charaterization
The process of identifying and verifying the properties of a compound.
Solubility
The ability of a substance to dissolve in a solvent.
Chemical Purity
The absence of impurities in a substance.
Silica Gel
Tiny polar beads commonly used in column chromatography.
Glassware
Equipment made of glass used in chemical laboratories.
Organic Chemistry
The study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and synthesis of organic compounds.
Functional Group
A specific group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for a characteristic of that compound.
Chemical Reaction
A process that leads to the transformation of one set of chemical substances into another.
Thermal Decomposition
The breakdown of a compound due to heat.
Solution
A homogeneous mixture composed of two or more substances.
Precipitation
The process of settling of solids from a solution.
Catalyst
A substance that increases the rate of a reaction without being consumed.
Stoichiometry
The calculation of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
Oxidation
A chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons, resulting in an increase in oxidation state.
Reduction
A chemical reaction that involves the gain of electrons, resulting in a decrease in oxidation state.
Acid-Base Reaction
A reaction that occurs between an acid and a base.
Deprotonation
The removal of a proton (H+) from a molecule.
Protonation
The addition of a proton (H+) to a molecule.
Electrophile
A reagent attracted to electrons that seeks to react with nucleophiles.
Nucleophile
A chemical species that donates an electron pair to form a chemical bond.
Chemical Bonds
The attractive forces that hold atoms together to form molecules.