CHAPTER 19: THE HEART
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:00 AM on 2/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
1
New cards
The cardio vascular system has how many divisions?
2 major divisions
2
New cards
What are the 2 major divisions?
Pulmonary Circuit and Systemic Circuit
3
New cards
What is a Pulmonary Circuit
Carries blood to the lungs for gas exchange and returns it to the Heart
4
New cards
What is a Systemic circuit?
supplies blood to every organ of the body including other parts of the lungs and to the Heart Wall
5
New cards
Which side of the heart supplies the Pulmonary Circuit
The Right Side.
6
New cards
Explain the process of The Pulmonary Circuit
oxygen poor blood is pumped into THE PULMONARY TRUNK which divides into RIGHT and LEFT PULMONARY ARTERIES.
\
The R and L PULMONARY ARTERIES transport blood to the air sacs ( alveoli ) of the lungs where carbon dioxide is unloaded and oxygen is picked up.
\
The oxygen rich blood flows using the PULMONARY VEINS to get to the LEFT side of the heart.
\
The R and L PULMONARY ARTERIES transport blood to the air sacs ( alveoli ) of the lungs where carbon dioxide is unloaded and oxygen is picked up.
\
The oxygen rich blood flows using the PULMONARY VEINS to get to the LEFT side of the heart.
7
New cards
Which side of the Heart supplies Systemic Circuit??
The Left Side
8
New cards
Explain the process of Systemic Circuit?
Blood leaves it by traveling through through AORTIC ARCH and passes down posterior to the heart.
\
The AORTIC ARCH supplies the head neck and upper limbs then it travels through the THORAIC and ABDOMINAL CAVITIES and issues smaller arteries to the other organs before branching into lower limbs .
\
After circulation to the entire body is done, the deoxygenated systemic blood returns to the right side of the heart by traveling through to big veins called the SUPERIOR vena cava
( drains the upper body) AND INFERIOR vena cava ( drains everything below the diaphragm.
\
The AORTIC ARCH supplies the head neck and upper limbs then it travels through the THORAIC and ABDOMINAL CAVITIES and issues smaller arteries to the other organs before branching into lower limbs .
\
After circulation to the entire body is done, the deoxygenated systemic blood returns to the right side of the heart by traveling through to big veins called the SUPERIOR vena cava
( drains the upper body) AND INFERIOR vena cava ( drains everything below the diaphragm.
9
New cards
The heart lies within a thick partition called the?
Mediastinum
10
New cards
Wha does the mediastinum contain?
The heart, great blood vessels ,esophagus, trachea and thymus
11
New cards
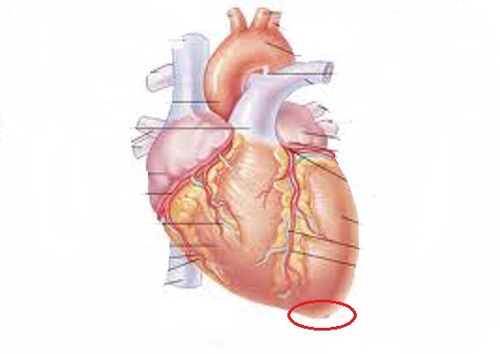
What is the red circle implying when looking at the heart?
The apex
12
New cards
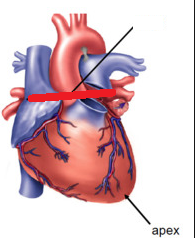
What is the red line implying when looking at the heart
The Base
13
New cards
What is the pericardial sac aka pericardium?
A double walled sac that encloses the heart
14
New cards
What is the Fibrous Pericardium?
a tough fibrous sac that is the outer wall of the pericardium
15
New cards
What is the serous pericardium?
Thin membrane that is second to last layer that surrounds the heart
16
New cards
what is pericardial fluid
secreted by the serous pericardium. The fluid lubricates the membranes and allows the heart to beat with minimal friction
17
New cards
How many layers does the serous pericardium have
2
18
New cards
What are the 2 layers of the serous pericardium ?
parietal layer and visceral layer
19
New cards
Where is the parietal layer?
Lines the inside of the fibrous pericardium
20
New cards
Where is the visceral layer?
adheres to the heart surface and forms the outmost layer of the heart itself ( epicardium )
21
New cards
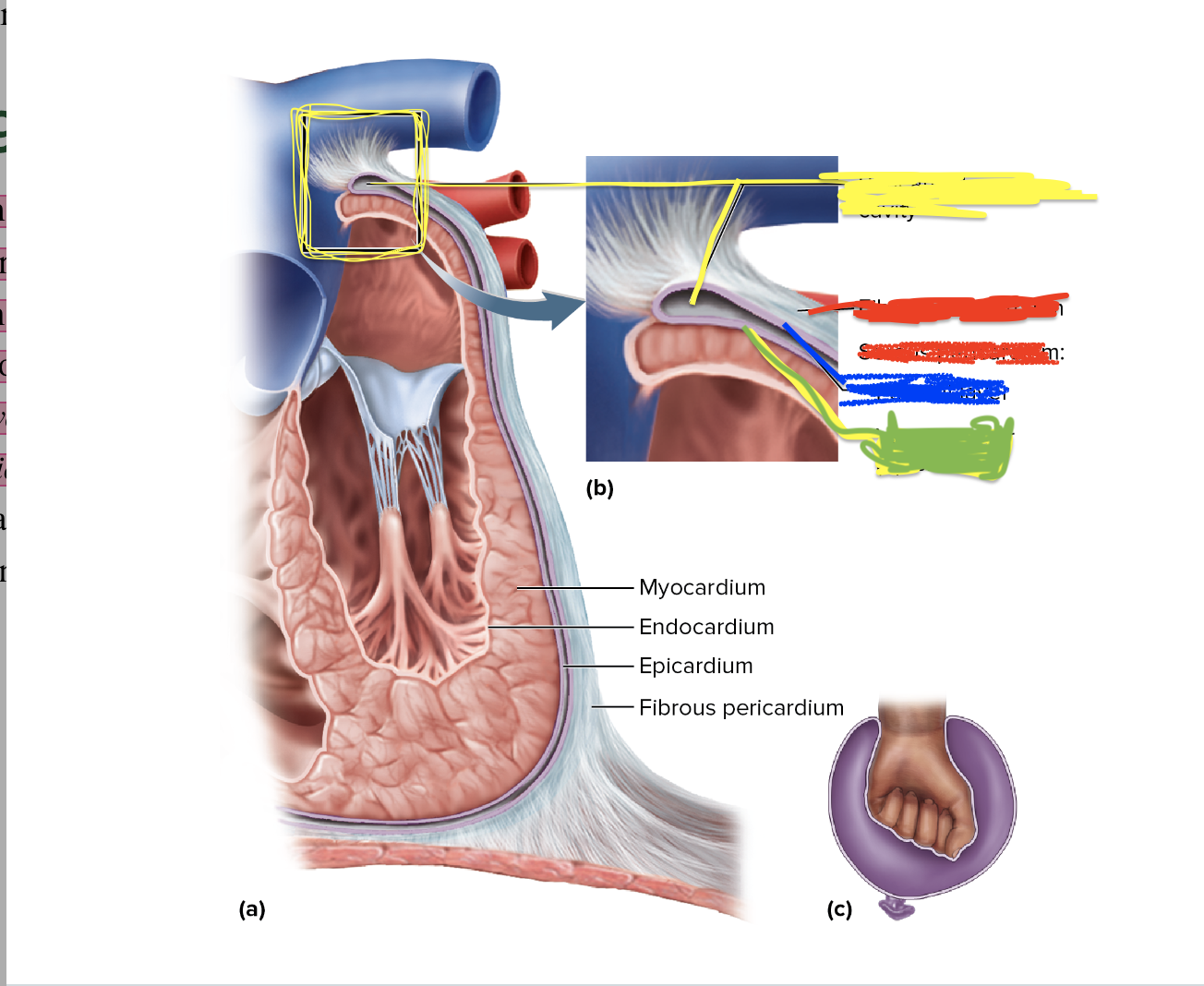
What is the yellow depicting?
Pericardial Cavity
22
New cards
What is the red depicting?
fibrous pericardium/Serous pericardium
23
New cards
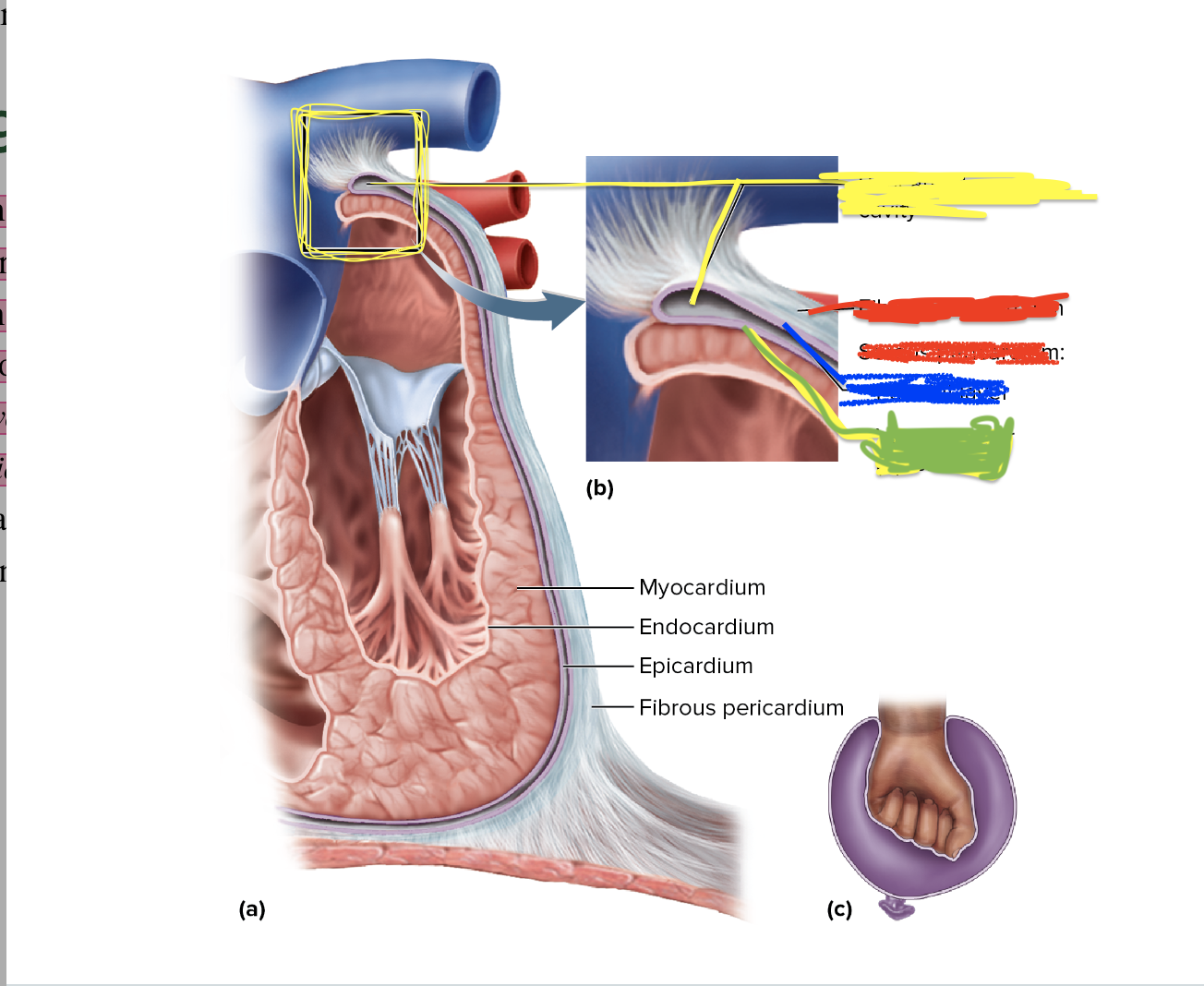
What is the blue depicting?
parietal layer
24
New cards
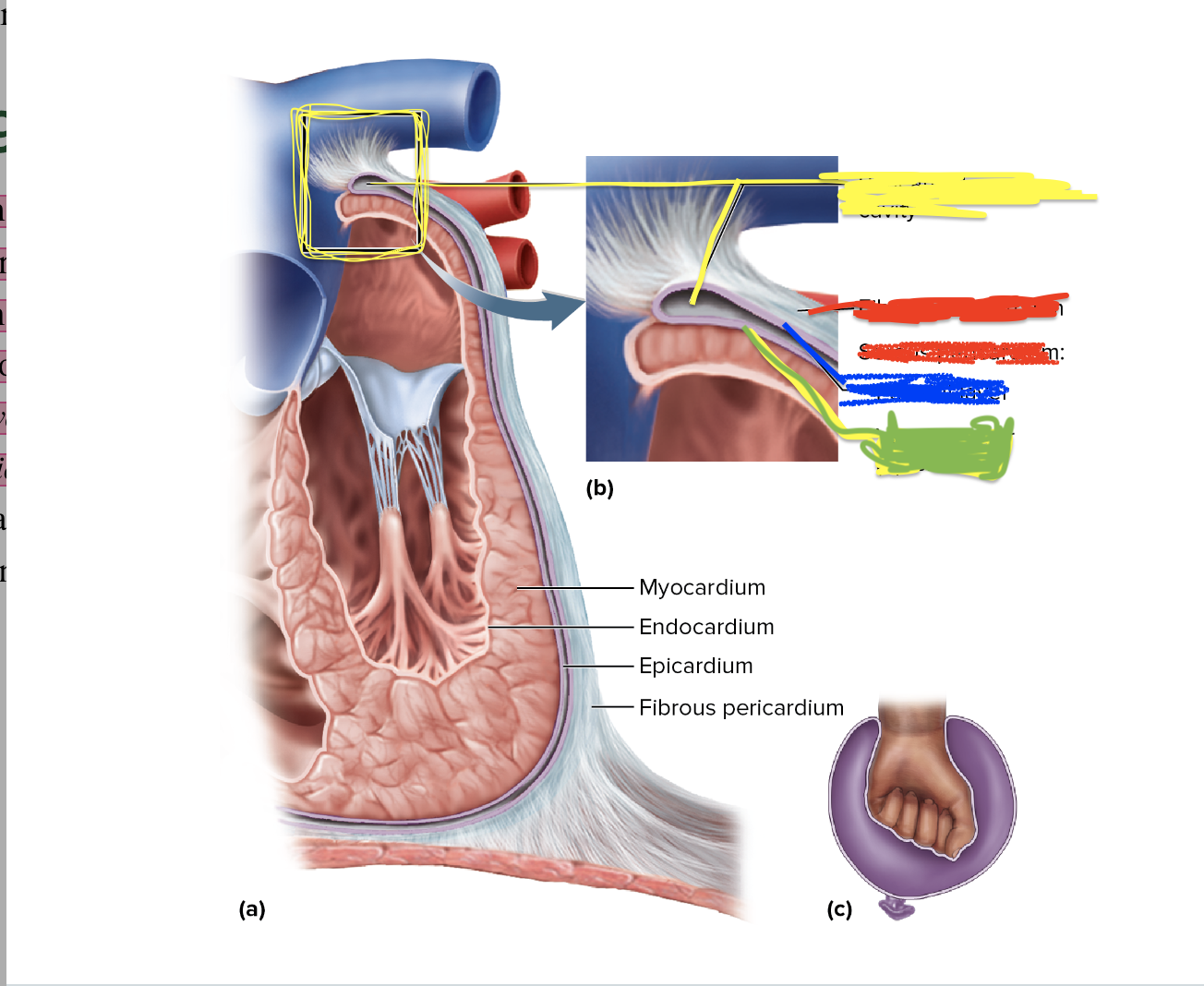
What is the green depicting?
Visceral layer
25
New cards
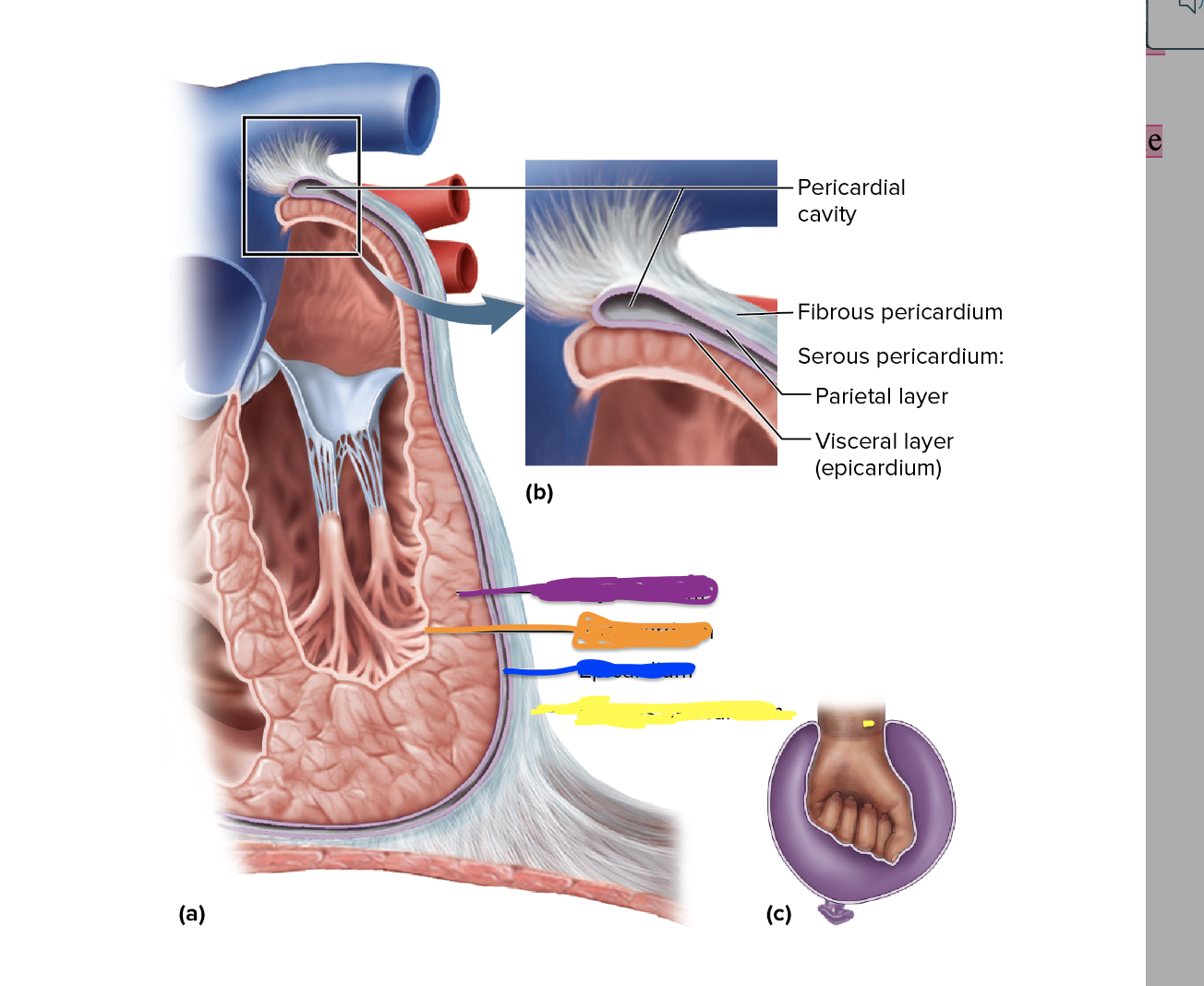
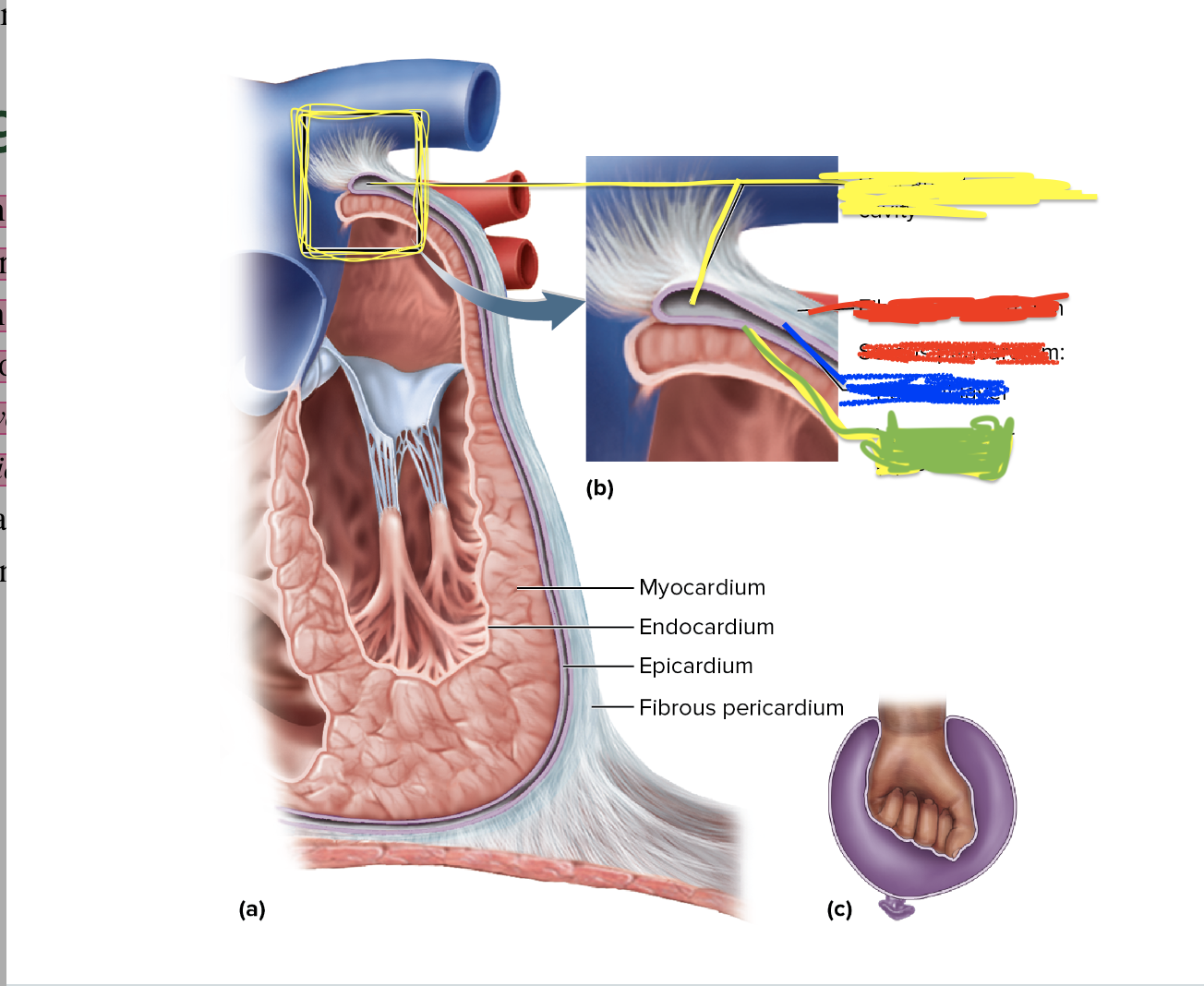
What is depicted in the purple?
Myocardium
26
New cards
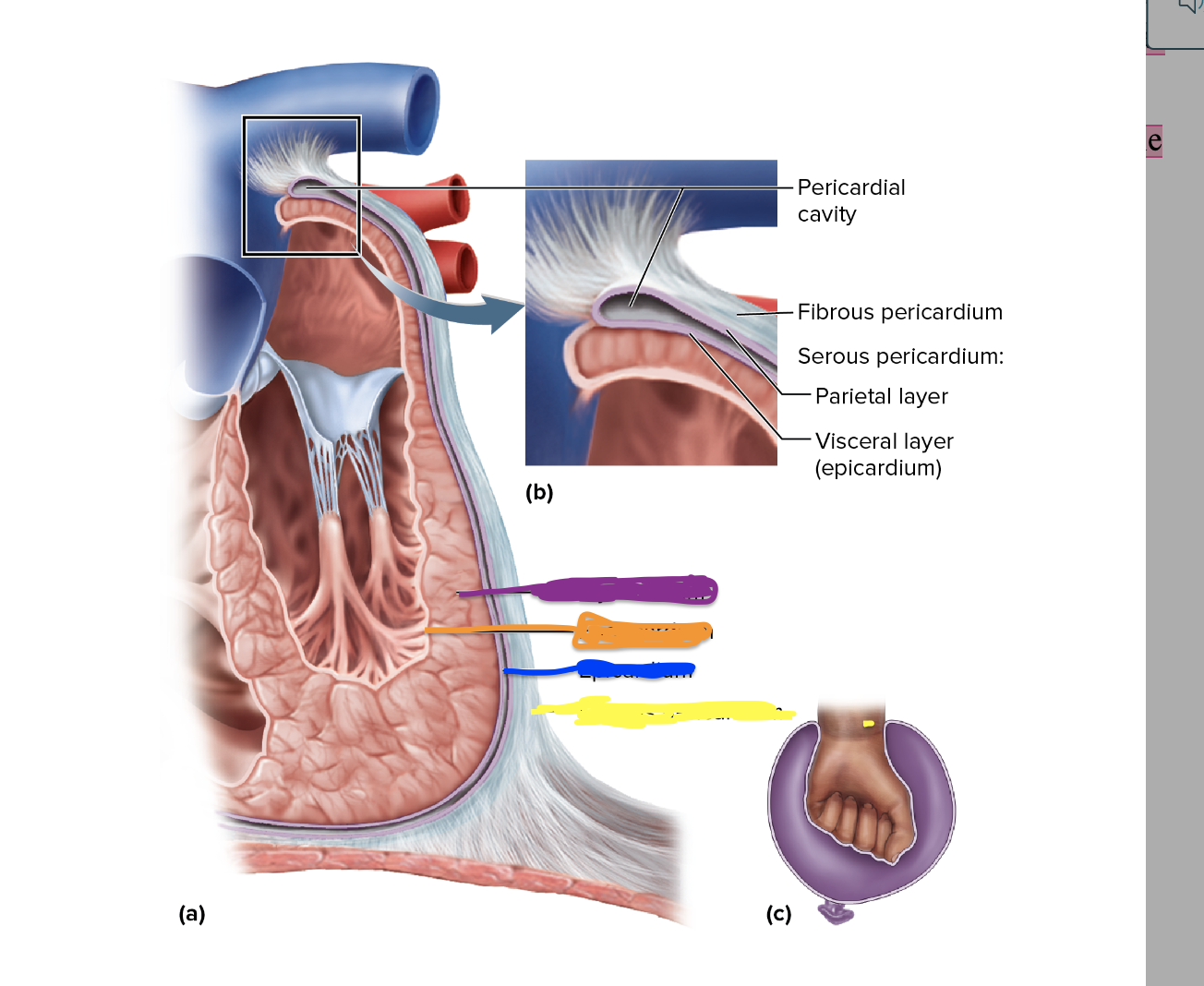
What is depicted in the orange
Endocardium
27
New cards
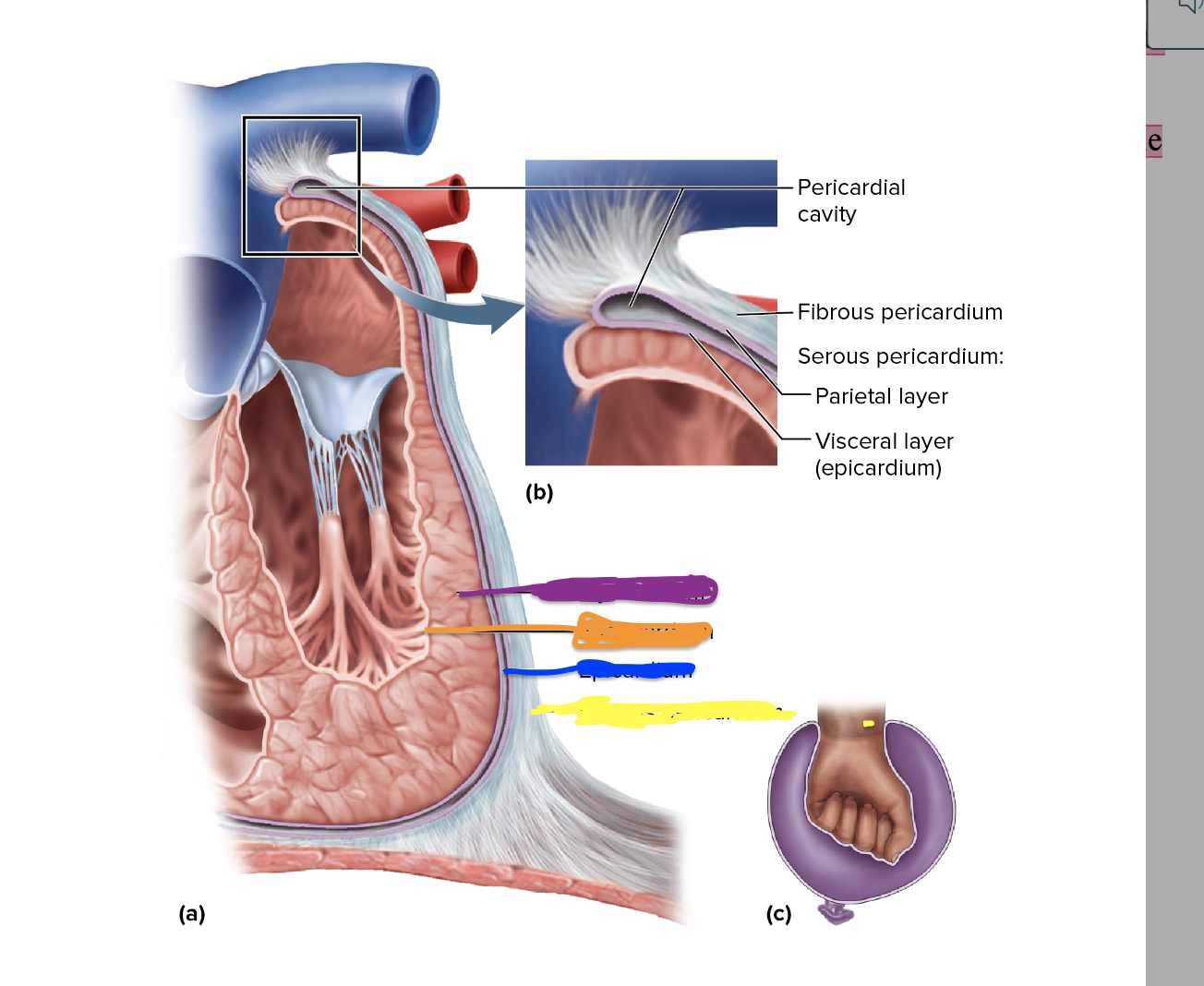
What is depicted in blue
Epicardium
28
New cards
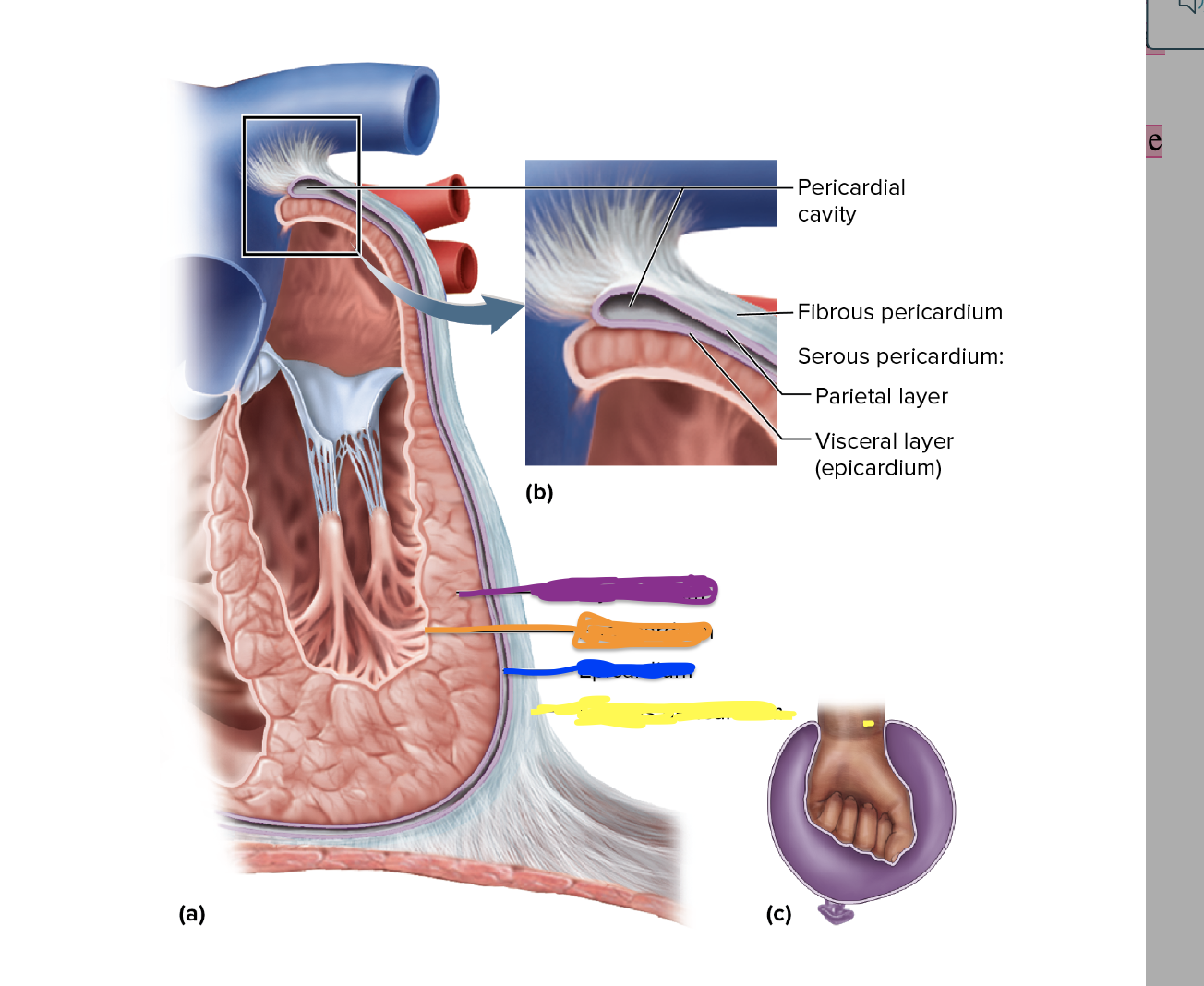
What is depicted in the yellow?
Fibrous Pericardium
29
New cards
The heart wall consists of what three layers?
epicardium ,myocardium and endocardium
30
New cards
What is a Epicardium and what is it made up of?
is a serous membrane covering the heart surface and is
simple squamous epithelium overlying a thin layer of areolar tissue.
simple squamous epithelium overlying a thin layer of areolar tissue.
31
New cards
The epicardium allows travel from?
The largest branches of the coronary blood vessels
32
New cards
The Largest branches of the Coronary blood vessels travel through ….?
The Epicardium.
33
New cards
What is the endocardium?
smooth inner lining of the interior of the heart (chambers) and blood vessels, compromised of endothelial cells
34
New cards
What does the endocardium consists of?
similar to epicardium
\
simple squamous eptithlieum overlying a thin areolar tissue layer. however it does not have a adipose tissue.
\
simple squamous eptithlieum overlying a thin areolar tissue layer. however it does not have a adipose tissue.
35
New cards
What is the myocardium?
between the endocardium and the epicardium
\
composed of cardiac muscle, thickest layer and performs the work of the heart
\
composed of cardiac muscle, thickest layer and performs the work of the heart
36
New cards
Name the Heart layers in in order! ( inner to outer)
endocardium,
myocardium,
Visceral Layer of the Serous pericardium ( a.k.a epicardium)
Pericardial Cavity
Parietal Layer of the Serous Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium
myocardium,
Visceral Layer of the Serous pericardium ( a.k.a epicardium)
Pericardial Cavity
Parietal Layer of the Serous Pericardium
Fibrous Pericardium
37
New cards
What is the fibrous skeleton?
framework of collagenous and elastic fibers and is spread in the walls between the heart chambers
38
New cards
How many functions does Fibrous Skeleton have?
4
39
New cards
What are the functions of the fibrous skeleton?
1. gives structural support for the heart, valves, and openings of the great vessels. Holds the orifices open and prevents them from excessively stretching when blood surges.
\
2. Anchors the cardiomyocytes and gives them something to pull against.
\
3. nonconductor of electricity/serves as electrical insulation between the atria and ventricle
\
4. aid in refilling of the heart with blood after each beat.
40
New cards
The heart heart has how many chambers?
4 Chambers
41
New cards
What are the four chambers of the heart
Right and Left Atria and the Right and left Ventricle
42
New cards
What does the right and left atria do?
They are superior and receiving chambers for blood returning to the heart auricles. ( by way of great veins)
43
New cards
what do the right and left ventricles do?
They are inferior chambers and pump blood into the arteries and keep it flowing around the body.
44
New cards
What is a interventricular septum ?
Thick Muscular wall that separates the right and left ventricles
45
New cards
What is Anterior Interventricular Sulcus (Interatrial Septum)
front of the heart sits on top of the inter-ventricular septum.
in the surface of an organ ( basically encircling the heart near the base )
and separates the atria (from the ventricles).
in the surface of an organ ( basically encircling the heart near the base )
and separates the atria (from the ventricles).
46
New cards
What is Posterior Interventricular Sulcus (interatrial Septum)
back of the heart and sits on top of the inter-ventricular septum.
in the surface of an organ ( basically encircling the heart near the base )
and separates the atria ( from the ventricles).
in the surface of an organ ( basically encircling the heart near the base )
and separates the atria ( from the ventricles).
47
New cards
What is a Trabeculae Carnae?
Internal Ridges in both right and left ventricles
48
New cards
What is the function of the Trabeculae Carnae?
stops the ventricular walls from sticking to each when the heart contracts.
allows the chambers to expand more when the refill.
allows the chambers to expand more when the refill.
49
New cards
What is Chordae Tendonae (Tendinous Cords)?
connect the Atrioventricular Valve cusps to conical papillary muscles on the floor of the ventricles.
50
New cards
What is the function of Chordae Tendinae?
stops the AV valves from flipping inside out of bulging into the atria when the ventricles contract.
\
\
\
\
51
New cards
Where is in the Chordae Tendinae?
Papillary Muscles
52
New cards
What are the Valves of the Heart?
AtrioVentricular Valves, Right AV, Left AV
Semilunar Valves, Pulmonary/Aortic Semilunar Valve.
Semilunar Valves, Pulmonary/Aortic Semilunar Valve.
53
New cards
What is the function of Papillary Muscles?
\
pillar-like muscles in the cavity of the ventricles with 2-3 attachments to heart floor/walls .
equally spread physical stress, coordinate timing of electrical conduction and provide redundancy..
\
or to be short
\
ensures proper cardiac valvular function.
pillar-like muscles in the cavity of the ventricles with 2-3 attachments to heart floor/walls .
equally spread physical stress, coordinate timing of electrical conduction and provide redundancy..
\
or to be short
\
ensures proper cardiac valvular function.
54
New cards
What is the function of atrioventricular ( AV ) valves?
control the blood flow opening between the atria and ventricles
55
New cards
The right AV (tricuspid) valve has how many cusps?
three cusps
56
New cards
The left AV ( Mitral ) ) valve
has two cusps
57
New cards
What is the right AV valve called
Tricuspid VALVE
58
New cards
What is the left AV valve called
Mitral VALVE
59
New cards
What do semilunar valves consist of?
Pulmonary semilunar valves and Aortic semilunar valves
60
New cards
What is the function of semilunar valves
regulates the flow of the blood from the ventricles into the great arteries and open and close because of blood flow and pressure
61
New cards
What is the pulmonary semilunar valve
controls the opening from the right ventricle and/nto the pulmonary trunk. has 3 cusps
62
New cards
What is the Aortic semilunar Valve
controls the opening from the left ventricle into the aorta, has three cusps
63
New cards
What happens when ventricles relax?
Pressure drops inside the ventricles
\
Semilunar valves close as blood attempts to back \\n up into the ventricles from the vessels
\
AV valves open
\
Blood flows from atria to ventricles
\
Semilunar valves close as blood attempts to back \\n up into the ventricles from the vessels
\
AV valves open
\
Blood flows from atria to ventricles
64
New cards
What happen when ventricles contract?
AV valves close as blood attempts to back up into the atria
\
Pressure rises inside of the ventricles
\
Semilunar valves open and blood flows into great vessels
\
Pressure rises inside of the ventricles
\
Semilunar valves open and blood flows into great vessels
65
New cards
What are the two arteries that provide Arterial Supply?
Right Coronary Artery and Left Coronary Artery, Both branch off the Ascending Aorta
66
New cards
In the RCA, What 2 branches exist and where are they located?
Right Marginal Branch and Posterior inter-ventricular branch.
located along the coronary sulcus under the right auricle.
located along the coronary sulcus under the right auricle.
67
New cards
Right Coronary Artery supplies the …
right atrium and sinuatrial node (pacemaker)
68
New cards
In the RCA, The Right Marginal Branch is located where and what is it?
Runs towards the Apex of the heart
Supplies lateral aspect of right atrium and ventricle
Supplies lateral aspect of right atrium and ventricle
69
New cards
In the RCA, The Posterior Inter-Ventricular Branch is located where and what does it do ?
\
Travels down the corresponding sulcus
\
Supplies posterior walls of ventricles
\
RCA --→ continues right margin of the heart--→posterior side----→sends a small branch----→ to the atrioventricler node ------→ becomes posterior InterV branch
\
Travels down the corresponding sulcus
\
Supplies posterior walls of ventricles
\
RCA --→ continues right margin of the heart--→posterior side----→sends a small branch----→ to the atrioventricler node ------→ becomes posterior InterV branch
\
70
New cards
The Left Coronary Artery divides into how many branches and what are they
2,
The Anterior Inter-Ventricular branch and the Circumflex Branch
The Anterior Inter-Ventricular branch and the Circumflex Branch
71
New cards
In the L.C. A, What does the Anterior inter -ventricular Branch do and where is it located
\
Artery supplies blood to both ventricles and the anterior two- thirds of the inter-ventricular septum.
\
travels down the anterior ventricular sulcus to the apex, rounds the bend and travel shortly up the posterior side of the heart. Joins the posterior interventricular branch (or L.A.D)
Artery supplies blood to both ventricles and the anterior two- thirds of the inter-ventricular septum.
\
travels down the anterior ventricular sulcus to the apex, rounds the bend and travel shortly up the posterior side of the heart. Joins the posterior interventricular branch (or L.A.D)
72
New cards
In the L.C.A, What does the Circumflex Branch do?
Supplies Blood to the left atrium and posterior \n wall of left ventricle
73
New cards
Describe the location of the Circumflex Branch
continues around the left side of the heart in the coronary sulcus and gives off left marginal branch and then ends on the posterior side of the heart.
74
New cards
The clinical name for Posterior interventricular branch is …..?
Left Anterior Descending (LAD) Branch.
75
New cards
Describe the location of The Left Marginal Branch
passes down the left margin of the heart and furnishes the blood to the left ventricle
76
New cards
The function of the circumflex branch ?
supplies the blood to the left atrium and posterior wall of the left ventricle
77
New cards
What is Venous Drainage?
route of blood leaving the organ
78
New cards
Coronary blood returns to the ????? ????? by way of the ????? ?????
Right Atrium, Coronary Sinus
79
New cards
The Coronary Sinus has three main veins/inputs that makes coronary blood return to the Right Atrium.. What are the three main veins/inputs?
Great Cardiac Vein , Posterior Inter ventricular Vein and the Left Marginal Vein
80
New cards
What is the Great Cardiac vein and what is its function?
\n Collects blood from the anterior portion of the heart and
Travels alongside anterior inter-ventricular artery
\
In Detail:
* Carries blood from the apex towards the coronary sulcus, then arcs around the left side of the heart and empties into the coronary sinus
Travels alongside anterior inter-ventricular artery
\
In Detail:
* Carries blood from the apex towards the coronary sulcus, then arcs around the left side of the heart and empties into the coronary sinus
81
New cards
What is the function of the Posterior Inter-ventricular Vein?
collects blood from the posterior portion of the heart.
found in the posterior inter-ventricular sulcus
\--------
also carries blood from the apex upwards and drains into the coronary sinus
found in the posterior inter-ventricular sulcus
\--------
also carries blood from the apex upwards and drains into the coronary sinus
82
New cards
What does the Left Marginal Vein do and where is it located?
empties into the coronary sinus and is
near the apex up the left margin.
near the apex up the left margin.
83
New cards
What does the coronary sinus do and where is it?
\
Collects blood from coronary veins and empties into right atrium
\
Large transverse vein in the coronary sulcus on the posterior side of the heart
Collects blood from coronary veins and empties into right atrium
\
Large transverse vein in the coronary sulcus on the posterior side of the heart
84
New cards
What is a Cardiomyocyte?
The muscle cells of the heart.
85
New cards
What do cardiomyoctyes look like ?
Muscle cells of the heart and have one central nucleus, striated, short and thick branched cells
86
New cards
What are intercalated discs?
join cardiocytes end to end with three features:
\
1.Interdigitating folds ( Plasma Membrane)
\
2\.Mechanical Junctions ( Fascia Adherens,Desmosomes)
\
3\.Electrical Junctions ( gap junction )
\
1.Interdigitating folds ( Plasma Membrane)
\
2\.Mechanical Junctions ( Fascia Adherens,Desmosomes)
\
3\.Electrical Junctions ( gap junction )
87
New cards
What do Intercalated disc look like?
visible as a dark line
88
New cards
Intercalated discs have how many distinctive junctions/features
3 junctions
89
New cards
What is a function of a fascia adherens?
(mechanical junction:tightly join cardiocytes)-actin of the thin myofilaments is anchored to the plasma memebrane
and each cell is linked to the next by transmemebrane proteins.
and each cell is linked to the next by transmemebrane proteins.
90
New cards
What is a function of desmosomes?
(mechanical junctions) patches of mechanical linkage prevent the contracting cardiocytes from being pulled apart from each other
91
New cards
What is the function of Gap Junctions
(Electrical Junction) makes channels that allow the ions to flow between cells; allows cardiocmyoctye to stimulate their neighbors.
\
Entire myocardium of either two atria or two ventricles acts like single, unified cell.
\
Entire myocardium of either two atria or two ventricles acts like single, unified cell.
92
New cards
What is the (Cardiac) Conduction System?
coordinates the heartbeat / composed of an internal pacemaker and has nerve-like conduction pathways through the myocardium
generates and conducts rhythmic electrical signals.
\
\
generates and conducts rhythmic electrical signals.
\
\
93
New cards
Put the conduction system nodes and bundles in order from first to last .
1. SA NODE FIRES
2. EXCITAION SPREADS THROUGH THE ATRIAL MYOCARDIUM
3. AV NODE FIRES
4. EXCITATION SPREADS DOWN AV
5. PURKINJE FIBERS DISTRIBUTE EXCITATION THOUGH VENTRICULAR MYOCARDIUM
94
New cards
What is a SA node and where is it located?
Sinautrial Node, patch of modified cardiomyocytes and acts a natural pacemaker that intitates each heartbeat and determines the heart rate.
\
located in the right atrium, under the epicardium, near the superior vena cava.
\
located in the right atrium, under the epicardium, near the superior vena cava.
95
New cards
What is the 1st stage of the conduction system ?
The Sinuatrial NODE makes an appearance
96
New cards
What happens in the 2nd stage of the cardiac conduction system
Signals from the SA Node spread throughout the atria
97
New cards
What happens in the third stage of the conduction system
Atrioventricular Node acts as an electrical gateway to the ventricles. while fibrous skeleton acts as an insulator to prevents currents from getting to ventricles by \n any other route.
98
New cards
What happens in the fourth stage of conduction system?
AV Bundles forks into right and left bundle branches,
Bundle branches pass through the interventricular septum and descend towards the apex.
Bundle branches pass through the interventricular septum and descend towards the apex.
99
New cards
What happens in the fourth stage of cardiac system
Nerve-like processes spread throughout ventricular myocardium. Cardiocytes then pass signal from cell \n to cell through gap junctions
\
In more detail:
* Purkinje fibers are at the apex of the heart , they turn upwards and spread though the ventricular myocardium and distribute electrical excitation tot he cardiomyocytes of the ventricles. once completed, the cardiomyotyes encourage it by passing ions from cell to cell through their gap junctions
\
In more detail:
* Purkinje fibers are at the apex of the heart , they turn upwards and spread though the ventricular myocardium and distribute electrical excitation tot he cardiomyocytes of the ventricles. once completed, the cardiomyotyes encourage it by passing ions from cell to cell through their gap junctions
100
New cards
What is a Sinus Rhythm?
The normal heartbeat by the SA NODE (70 to 80 heartbeats)