Motion
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The s-t and v-t graph flashcards are about what their shape means
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Method to answer projectiles questions
Sketch the situation and add any values known.
Split into vertical and horizontal motion.
Use suvat for vertical.
Decide which direction you are taking as positive.
Velocity remains constant in the horizontal directions
For max height problems velocity at top is zero.
Define thinking distance
The distance travelled between the moment when you first see a reason to stop, to the moment when you use the brake
Define breaking distance
The distance travelled from the time the brake is applied until the vehicle stops.
Define stopping distance
Thinking distance + breaking distance
Total distance travelled from when the driver first sees a reason to stop to when the vehicle stops
Factors that affect thinking distance
Speed of the vehicle
Alertness of driver - are they tired? are they under the influence of alcohol or drugs?
Factors that affect breaking distance
Speed of the vehicle
Condition of brakes
Condition of tyres
Factors that affect stopping distance
Speed of the vehicle
Alertness of driver - are they tired? are they under the influence of alcohol or drugs?
Condition of brakes
Condition of tyres
Average speed (definition & equation)
The rate of change in distance calculated over a complete journey
Equation: ___ = distance travelled / time taken
Instantaneous speed
The speed at at the moment it is measured; the speed over an infinitesimal interval of time
Displacement
The direct distance between an object’s starting and ending positions in a particular direction
Is a vector quantity
Velocity
The ratge of change of displacement
Is a vector quantity
Acceleration
The rate of change of velocity
Is a vector quantity
What does the gradient of a displacement-time graph equal?
Equals the velocity (of the object)
What does the gradient of a velocity-time graph equal?
Equals the acceleration (of the object)
What does area under a velocity-time graph equal?
Equals the displacement (of the object)
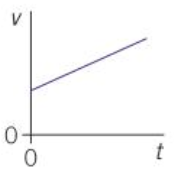
Straight line of constant, positive gradient on a v-t graph means…
Constant positive acceleration
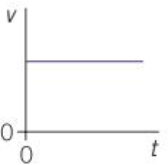
A straight line of zero gradient on a v-t graph means…
Constant velocity / zero acceleration
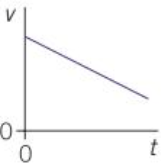
A straight line of constant, negative gradient on a v-t graph means…
Constant negative acceleration (deceleration)
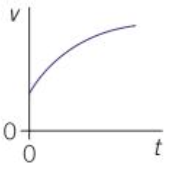
A curve of changing gradient on a v-t graph means…
Acceleration is changing
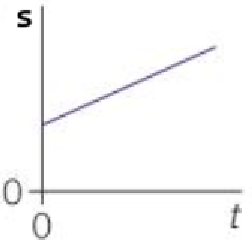
A straight line of constant, positive gradient on a s-t graph means…
Constant positive velocity
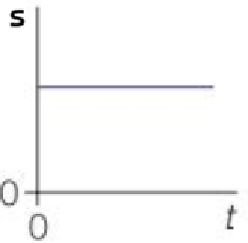
A straight line of zero gradient on a s-t graph means…
Constant displacement / zero velocity
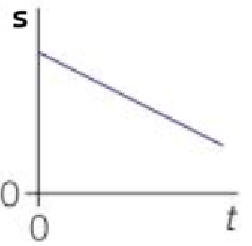
A straight line of constant, negative gradient on a s-t graph means…
Constant negative velocity
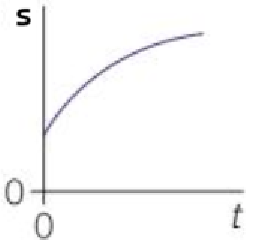
A curve of changing gradient on a s-t graph means…
Velocity is changing (object is accelerating)
Equipment for determining g using manual timing
Ruler
Spherical object
Stopwatch
Method & analysis for determining g using manual timing (graphical analysis)
Method:
Drop the object from a height measured with the ruler
Use the stopwatch to time how long it takes the object to reach the ground and record it along with the height
Repeat this for a number of heights and record the results
Analysis:
Plot a graph or height against time2, and draw a line of best fit.
Calculate the gradient (m) of this line
s = ut + ½at2 and innitial velocity u = 0, so s = ½at2
As such the gradient m is ½a, so a = 2m
Method & analysis for determining g using manual timing (non-graphical analysis)
Method:
Drop the object from a height measured with the ruler
Use the stopwatch to time how long it takes the object to reach the ground
Analysis:
s = ut + 1/2at2 and innitial velocity u = 0, so s = ½ at2.
a=g, so s = ½ gt2
Rearrange this to get g = 2s/t2, which we can be used to calculate our value of g.
Equipment for determing g using 2 light gates
object to drop, e.g. a piece of plasticine
stop clock
data logging system
2 light-gates
ruler
Method to determine g using 2 light gates
Set up the data logger with two light gates vertically above each other.
Measure distance between light gates using ruler
Drop the interupt card from just above the top light gate and record time shown on data logger
Repeat a number of times and record time to fall for each
Analysis for determing g using 2 light gates
Calculate the average time taken to fall between light gates
s = ut + 1/2at2 and innitial velocity u = 0, so s = ½ at2.
a=g, so s = ½ gt2
Rearrange this to get g = 2s/t2, which we can be used to calculate our value of g.
Diagram & method for determining g using an electromagnet and timer
An electromagnet holds a small steel ball above a trapdoor. When the current is switched off, a timer is triggered, the electromagnet demagnetises, and the ball falls. When it hits the trapdoor, the electrical contact is broken and the timer stops. Record the height of fall (h) using the ruler.
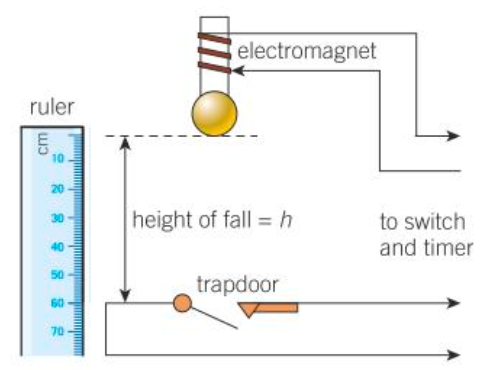
Analysis for determining g using an electromagnet and timer
s = ut + 1/2at2 and innitial velocity u = 0, so s = ½ at2.
a=g and s=h, so h = ½ gt2
Rearrange this to get g = 2h/t2, which we can be used to calculate our value of g.