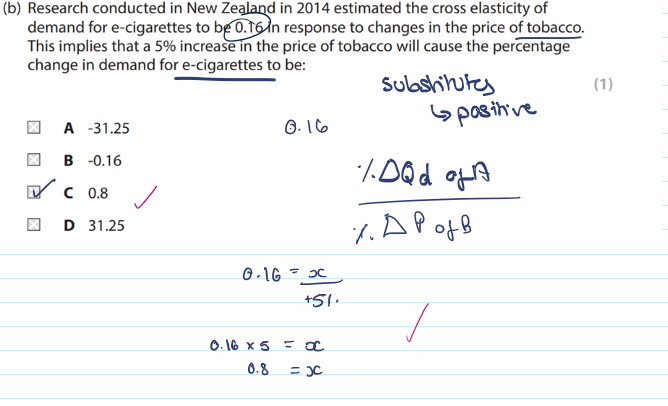1.2.3 Price, income and cross elasticity of demand
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
It measures the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a change in price of a good.
What is the formula for PED?
(% change in quantity demanded) / (% change in price)
If the original price pf a product was £5 and 100 were sold and the new price is £3 and 120 are sold what is the PED?
120-100 = 20
3-5 = -2
(20/100) x 100 = 20%
(-2/5) x 100 = -40%
so the PED = 20%/-40% = -0.5
What is true for all values of PED (price elasticity of demand) for normal goods? Why?
They are always negative
Because a rise in price level usually leads to a fall in output
(increased prices leads to a fall in demand therefore suppliers supply less so output falls consequently)
What is unitary elastic PED?
And what does it look like on a diagram?
Where PED= -1
Demand changes proportionately with price
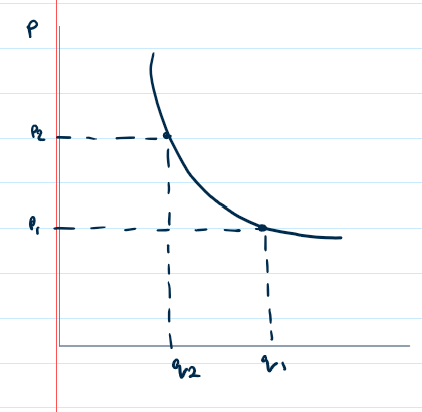
What is relatively elastic PED?
What would this look like on a diagram?
where PED < -1
The good is price elastic - demand is very responsive to changes in price

What are some examples of price elastic products?
Goods with many substitutes
Anything to do with travel
Anything which will take a big proportion of ones income
What is relatively price inelastic?
What doe this look like on a diagram?
The PED value is between 0 and -1
the good is price inelastic - demand is not very responsive to changes in price

Give some examples of price inelastic goods
Necessity foods such as bread, milk, toothpaste ect
demerit goods such as tobacco, alcohol
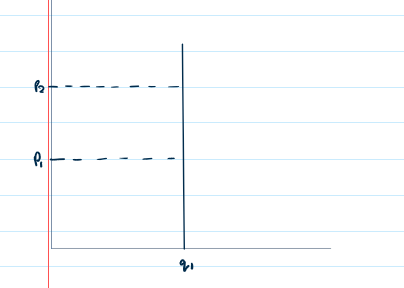
What is perfectly inelastic?
What does this look on a diagram?
PED = 0
the good is perfectly inelastic (doesn’t change)
a change in price will have no influence on quantity demanded
What is perfectly elastic?
What does this look like on a diagram?
PED value = negative infinity
the good is perfectly elastic - any change in price will see quantity demanded fall to zero

Question: Julian raises the price of his rugby shorts from £50 to £55. He known that his price elasticity of demand is -6.
a) What will the change in demand be?
b) What does this suggest about the price elasticity of demand?

Fill in the gap:
If a good has a large number of substitutes (for example ….).
Demand will be relatively …
Because …
If a good has a large number of substitutes (for example pasta).
Demand will be relatively elastic
Because types of pasta will be very responsive to changes in price as there are are may to choose from. If one brand increases its prices, consumers will very easily move to another brand of pasta.
Gap fill
If a good has strong consumer loyalty (for example …).
Demand will be relatively …
Because …
If a good has strong consumer loyalty (for example apple.).
Demand will be relatively inelastic
Because consumers want this product at all costs - people who are loyal to the brand/ product will continue to buy their products despite changes in prices
Gap fill
If a good is a necessity (for example ….).
Demand will be relatively …
Because …
If a good is a necessity (for example shower gel).
Demand will be relatively inelastic
Because consumers require these products so will have to buy them no matter the price
gap fill
If a good accounts for a large proportion of income (for example ….).
Demand will be relatively …
Because …
If a good accounts for a large proportion of income (for example plane flights).
Demand will be relatively elastic
Because purchasing or not purchasing these products can cause significant changes in ones disposable income
Gap fill
If a good is a habit forming good (for example …).
Demand will be relatively …
Because …
If a good is a habit forming good (for example cigarettes).
Demand will be relatively inelastic
Because consumers who purchase these goods will continue to buy them regardless of changes in prices because it is necessary for their habit/ addiction
Gap fill
If a good can only be substituted in the long-term (for example …).
Demand will be relatively …
Because …
If a good can only be substituted in the long term (for example rise in oil prices).
Demand will be relatively elastic
Because over time people will begin to search for substitutes
For example a rise in oil rises - consumers will continue to use oil in the short run regardless of changes in price because they have no other option (so relatively price inelastic). However in the long run they can switch to alternative forms of heating such as using solar panels.
What is revenue + the equation
money received for selling goods/ services
Revenue = price x quantity
When a good have a low PED value what effect will this have on the total revenue form the good?
When a good has a low PED value it is price inelastic - a rise in price will cause the total revenue to increase

Use the following data this case study on apple to show the effect of price inelasticity of apples product on its revenue

If a product has a high PED what effect will this have on the total revenue for this product?
When a good high PED value it is price elastic - a rise in price will cause the total revenue to decrease
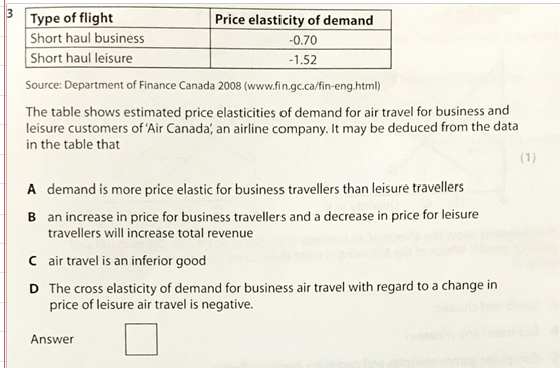

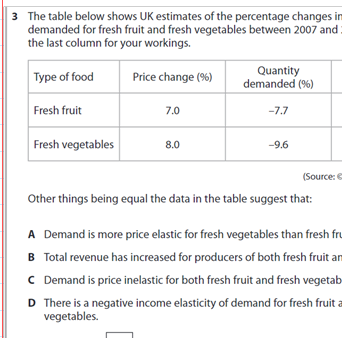
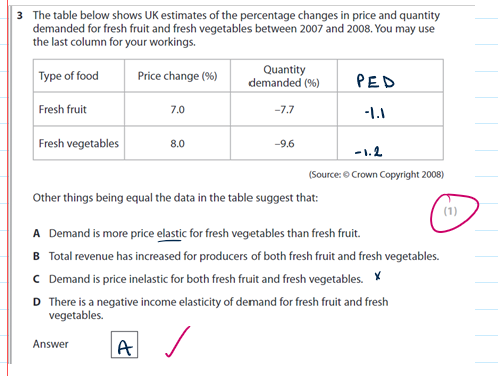
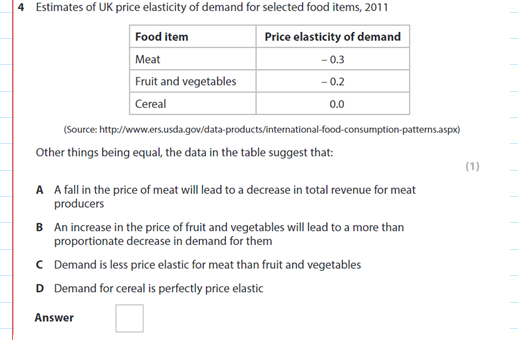
A

A

What is income elasticity of demand + equation
measures how demand responds to a change in any other variable
YED = (% change in quantity demanded) / (% change in income)
For normal goods (e.g mobile phones, steak, air travel, foreign holidays) what is the relationship between YED?
There is a positive relationship so YEP is always positive
What is a normal good?
A normal good means an increase in income causes an increase in demand and a decrease in income causes a decrease in demand
If YED is > 1 what is the product considered as?
a luxury good
If the YED < 1 what is the product considered as?
a necessity good
If the YED value is less than 0 what does this mean?
there is an inverse relationship (as income rises, demand of the good falls) - considered an inferior good
Daniel’s demand for visits to the bowling alle rose from 3 a month to 5 a month when he received a 10% salary increase. What is the YED
5-3=2
2/3×100= 66.67
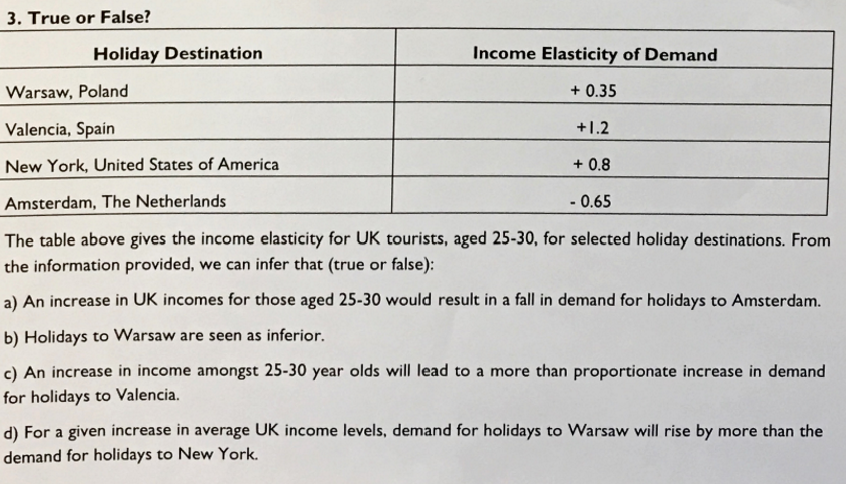
How might firms be able to make use of YED estimates?
Firms use YED to estimate when planning output
When a good has a high YED (elastic) - demand is sensitive to living standards of consumers
E.g
In an economic boom - income increases = proportionately larger increase in demand - so producers may increase production of luxury goods.
However in a recession - income decreases = proportionately large decrease in demand - so producers may increase production of inferior goods


What is cross elasticity of demand + equation
it measure the responsiveness of demand for one good (A) to a change in the price of another good (B)
XED = (%change in demand for A) / (% change in price of B)
Define a substitute good and give 3 examples
are products that can be used as alternatives to one another to satisfy a particular need or wants. - when the demand for one substitute increases the demand for the other substitute decreases
E.g apples vs oranges, sweets vs chocolates, butter vs jam
If two goods (X and Y) are substitutes; if the price of good ‘X’ rises what will happen to the demand for good ‘Y’ ? And what does this tell you about their relationship
The demand for good Y will increase.
This indicates that there is a positive relationship
(the closer the substitute the larger the XED)
If the XED >1 what does this tell you about the substitutes?
They are close substitutes
E.g a 10% rise in the price of bus travel will clause a 20% rise in the demand for rail travel, XED = 2 therefore close substitute (bc 2>1)
Define a complementary good and give 3 examples
goods or services that are used together - when the demand of one of them increases the demand for the other increases also.
E.g strawberries are cream, peanut butter and jelly, tennis ball and tennis racket
If two goods (X and Y) are complements what effect will a rise in the price of good X have on the demand for good Y? And what does this tell you about their relationship?
it will cause a fall in the demand for Y.
they have a negative relationship
IF the XED of the complement good is < -1 what does this tell you?
that the two goods are close complements
E.g a 10% tise in the price of DVD platers will cause a 12% fall in demand for DVDs, XED = /12/10 = -1.2 (therefore they are close complements -1.2< -1
If there is no relationship between the good what will the WED be?
0
If goods are complements what might businesses do?
Bundle them together and sell them as a package e.g meal deals or 2 for 1 cinema tickets
Take over businesses that sell complements or work more closely with them
If goods are substitutes then how might businesses take advantage of this?
use brand proliferation to weaken the degree of substitutability e.g Apple
engage in heavy advertising/ price wars e.g supermarkets
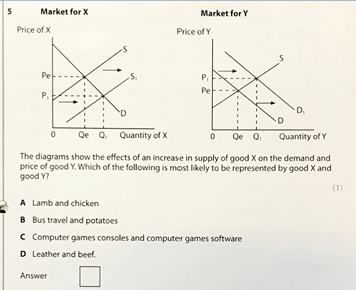
complement goods - C

substitutes - C

A

Substitutes - A