Case 10 pharmacology part 1
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:56 PM on 11/22/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
1
New cards
What is ACh function on the CNS?
- Alterness
- Attention
- Memory
- Attention
- Memory
2
New cards
How is ACh synthesised?
Choline + acetyl CoA -> ACh using the enzyme choline acetyl transferase
3
New cards
Where is ACh located in the CNS?
- Basal forebrain
- Cerebral cortex
- Hippocampus
- Cerebral cortex
- Hippocampus
4
New cards
What condition does an impaired levels of ACh cause?
Myasthenia gravis- autoantibodies to ACh receptors
5
New cards
ACh is also the neurotransmitter (NT) of the...
neuromuscular junction
6
New cards
What is ACh the final NT of?
ACH is the final NT in parasympathetic innervation pathways of the ANS
7
New cards
How is ACH recycles/ reuptaked?
ACh broken down to choline which is transported back into the pre-synaptic cleft for re-cycling into fresh ACh.
8
New cards
How is ACh cleared?
Acetylcholine esterase breaks ACh down before it activates receptors.
9
New cards
What are the ACh receptors?
1. Nicotine ACH R-ligand gated ion channels (fast)
2. Muscarinic ACh R-G protein coupled (slow)
3. Use 2nd messengers
2. Muscarinic ACh R-G protein coupled (slow)
3. Use 2nd messengers
10
New cards
What is noradrenaline function on the CNS?
- Alterness
- Arousal
- Action readiness
- Arousal
- Action readiness
11
New cards
How is noradrenaline synthesised?
Tyrosine -> Levodopa -> dopamine -> noradrenaline
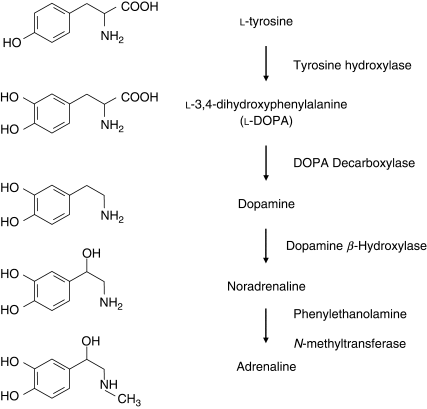
12
New cards
Where is noradrenaline located in the CNS?
- Medulla
- Solitary nucleus
- Locus coeruleus
- Solitary nucleus
- Locus coeruleus
13
New cards
What condition does an impaired levels of noradrenaline cause?
Sympathetic hyper-activation (multiple systems)
14
New cards
What is noradrenaline's role on the sympathetic nervous system?
- It is the major NT in the SNS
- Plays a major role in sympathetic innervation to the cardiovascular system
- Controls vasomotor tone by activating alpha-adrenoceptors on VSMC.
- Plays a major role in sympathetic innervation to the cardiovascular system
- Controls vasomotor tone by activating alpha-adrenoceptors on VSMC.
15
New cards
How is noradrenaline recycles/ reuptake?
Noradrenaline (NorAd) transport into pre-synaptic cell or glia by noradrenaline transporters (NET).
16
New cards
How is NorAd cleared?
NorAd broken down by monoamine oxidase in cytosol (NOT synaptic cleft) + by catechol-O- methyltransferase
17
New cards
What are the NorAd receptors?
1. beta-adrenoceptors (1-3)
2. Gs- coupled
3. Alpha-adrenoceptor 1 (Gq- coupled)
4. Alpha- adrenoceptor 2 (Gi/O coupled)
2. Gs- coupled
3. Alpha-adrenoceptor 1 (Gq- coupled)
4. Alpha- adrenoceptor 2 (Gi/O coupled)
18
New cards
What is dopamine function on the CNS?
- Executive function
- Motor control
- Motivation
- Motor control
- Motivation
19
New cards
How is dopamine synthesised?
Phe -> Thy -> Levodopa -> Dopamine
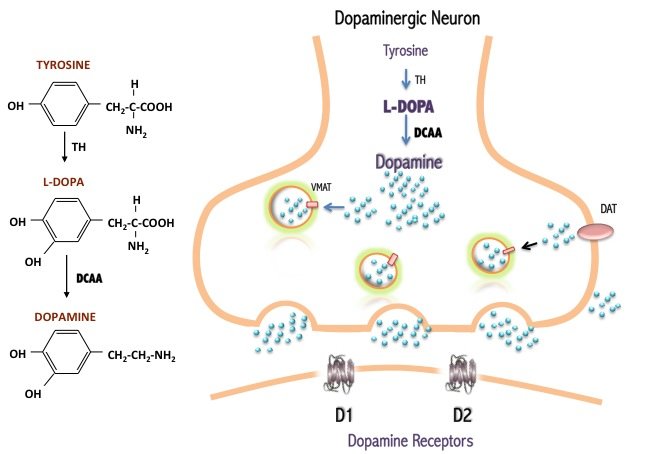
20
New cards
Where is dopamine located in the CNS?
- Substantia nigra
- hypothalamus
- VTA
- Arcuate nucleus
- Zona incerta
- hypothalamus
- VTA
- Arcuate nucleus
- Zona incerta
21
New cards
What condition does an impaired levels of dopamine cause?
- Parkinson's disease (destruction of dopaminergic neurons in the substantial nigra)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain ageing
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain ageing
22
New cards
What type of behaviour is dopamine important in?
- Reward-motivaiton behaviour
- Many addictive drugs block dopamine re-uptake + increase its release
- Many addictive drugs block dopamine re-uptake + increase its release
23
New cards
What does dopamine also influence?
- Motor control
- lactation (inhibit)
- nausea
- lactation (inhibit)
- nausea
24
New cards
How is dopamine recycles/ reuptake?
Dopamine transport into the presynaptic cleft or glia via dopamine transporters + monoamine transporters
25
New cards
How is dopamine cleared?
Dopamine is broken down by monoamine oxidase in the cytosol (NOT cleft) + catechol- O methyl transferase
26
New cards
What are the dopamine receptors?
- 5 subtypes (all GPCR)
- Different effects due to 2nd messenger system triggered after dopamine activation of receptors.
- Different effects due to 2nd messenger system triggered after dopamine activation of receptors.
27
New cards
What is noradrenaline function on the CNS?