Radioactivity
1/91
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
What is the radius of an atom?
about 1 x 10 to the power of -10 m
What is the basic structure of the atom?
a positively charged nucleus composed of both protons and neutrons surrounded by negatively charged electrons
How big is the nucleus compared to the atom?
Less than 1/10,000
Where is the mass of the atom concentrated?
in the nucleus
What is the mass number?
Number of protons and neutrons
What is the atomic number?
number of protons
What is an isotope?
atoms with the same number of protons but different number of neutrons
What was the first ever model of the atom?
tiny spheres that couldn't be divided
What was the plum pudding model?
Ball of positive charge with with negative electrons embedded in it
What was the model discovered by the alpha particle scattering experiment?
. nuclear model
. mass is concentrated in charged nucleus at centre
What was discovered after the nuclear model?
. Bohr discovered electrons orbiting at specific distances
What was discovered after electrons?
protons
What was discovered after protons
Chadwick discovered neutrons
What is radioactive decay?
. some atomic nuclei are unstable
. the nucleus gives out radiation as it changes to become more stable
. this is a random process
What is activity?
the rate at which a source of unstable nuclei decays
What is activity measured in?
Becquerels (Bq)
What is count-rate?
The number of decays recorded each second by a detector (e.g Geiger-Muller tube)
What may nuclear radiation be emitted?
. alpha particle
. beta particle
. gamma rays
. neutron
What is an alpha particle? (nature)
. 2 protons and 2 neutrons
. same as helium nucleus
What is a beta particle? (nature)
a high speed electron ejected from the nucleus as a neutron turns into a proton
What are gamma rays? (nature)
electromagnetic radiation from the nucleus
What does the top number next to a symbol mean when talking about radioactivity?
mass number
What does the bottom number next to a symbol mean when talking about radioactivity?
charge of particle
What is the charge of an alpha particle?
+2
What is the charge of a beta particle?
-1
What is the charge of a gamma ray?
no charge
What is the mass of an alpha particle?
4
What is the mass of a beta particle?
very small
What is the mass of a gamma ray?
0
What is the ionising power of an alpha particle?
high
What is the ionising power of a beta particle?
small
What is the ionising power of a gamma ray?
tiny
What is ionising radiation?
. can expel electrons from atoms near their path
. can lead to cell damage or mutations leading to cancer
What is the penetrating power of alpha particles?
. skin
. a sheet of paper
. <5cm of air
What is the penetrating power of beta particles?
. a few m of air
. a few mm of aluminium
. a few mm of lead
What is the penetrating power of gamma rays?
. a few m of concrete
. 3-5 cm of lead
. many km of air
What is the half-life of a radioactive isotope?
. the time it takes for the number of nuclei of the isotope in a sample to halve
OR
. the time it takes for the count rate (or activity) from a sample containing the isotope to fall to half its initial level
How can we calculate half life if radioactive decay is random?
. It is impossible to predict which nucleus will decay next or the exact time when a specific nuclei will decay
. Predicts when about half the nuclei will have decayed if the sample is large enough
How would you calculate the count rate after 3 half lives?
original count rate / (2 ^ 3)
What is radioactive contamination?
the unwanted presence of materials containing radioactive atoms on other materials
What is irradiation?
. the process of exposing an object to nuclear radiation
. irradiated object does not become radioactive
Why is irradiation hazardous?
. radiation is ionising
. could give cell damage, radiation sickness, or cancer
How can people protect themselves from irradiation?
. stay 2 m away
. wear lead apron
. use long tongs when handling to increase distance
Why is contamination hazardous?
. due to the decay of contaminating atoms
. type of radiation emitted affects level of hazard
. you become radioactive
. you irradiate people around you
. you receive a much higher dose of radiation
How can people protect themselves from contamination?
. Wear gloves
. Keep sources locked away when not being used
Where does background radiation come from?
. natural sources such as rocks and cosmic rays from space
. man-made sources such as the fallout from nuclear weapons testing and nuclear accidents
What is radiation dose measured in?
Sieverts (Sv)
How many Sv in a mSv?
1,000
What is the aim of radiotherapy (gamma knife)?
. Kill tumour / cancer
. Remove unwanted things in the body
How does radiotherapy work (gamma knife)?
. Multiple gamma rays are aimed at the tumour from different directions
. Patient is held in place so they can't move
What type of radiation is radiotherapy (gamma knife) and why?
. gamma
. it needs to penetrate into the body until the tumour
Does radiotherapy (gamma knife) have a long or short half life and why?
. Long half life
. Because the source is in the machine, which then works for many years
What are the risks of radiotherapy (gamma knife)?
Radiation damages healthy cells in the patient
How are the risks of radiotherapy (gamma knife) minimised?
Rays are sent from different directions, so the healthy cells receive low radiation dose but tumour received high radiation dose
What is the aim of radiotherapy (brachytherapy / beta implant)?
Kill tumour/cancer
How does radiotherapy (brachytherapy / beta implant) work?
. A radioactive source is implanted in the tumour
. The source usually emits beta
What type of radiation is radiotherapy (brachytherapy / beta implant) and why?
. Beta
. it needs to be quite ionising /not very penetrating so the radiation is absorbed locally by the tumour
Does radiotherapy (brachytherapy / beta implant) have a long or short half life and why?
. short
. just for the duration of the treatment
What are the risks of radiotherapy (brachytherapy / beta implant)? (check)
Ionising radiation damages healthy cells and can cause cancer
How are the risks of radiotherapy (brachytherapy / beta implant) minimised?
. Have a short half life, so the source is radioactive for not too long
. Use a small amount
What is the aim of Radioactive tracers / PET scans?
. Find out where the tumour or other problem is
. Medical imaging
How do Radioactive tracers / PET scans work?
. Inject the patient with a radioactive tracer (a chemical used by body with a radioisotope)
. We use a special camera to detect where the radiation comes from
What type of radiation is Radioactive tracers / PET scans and why?
. Gamma
. so the radiation can travel through the body (high penetrating power)
Do Radioactive tracers / PET scans have a long or short half life and why?
. Long half life
. So the radioactive source doesn’t need to be replaced so oftenly
What are the risks of Radioactive tracers / PET scans?
Ionising radiation damages healthy cells and can cause cancer
How are the risks of Radioactive tracers / PET scans minimised?
. Don't use this if pregnant
. Short half-life is used
What is the aim of Sterilisation by irradiation?
Kill bacteria and micro-organisms on food and medical equipment
How does Sterilisation by irradiation work?
. Gamma rays are projected on the food/medical equipment
. The food/equipment is already in its package
What type of radiation is Sterilisation by irradiation and why?
. Gamma
. Very penetrating so bacteria everywhere is killed
Does Sterilisation by irradiation have a long or short half life and why?
Long half life so the machine works for a long time
What are the risks of Sterilisation by irradiation?
. THE FOOD/EQUIPMENT DOES NOT BECOME RADIOACTIVE
. Risk is for the workers only: radiation exposure
How are the risks of Sterilisation by irradiation minimised?
. Workers use protective equipment like lead aprons, they stay away/in another room
. Their radiation dose is monitored and they will be affected to another activity if too high
What is the aim of Smoke alarm?
Detect smoke before there's a fire
How does Smoke alarm work?
. A radioactive material fires alpha particles at a smoke detector
. If there is smoke between the radioactive material and the smoke detector, then fewer alpha particles will reach the detector
. This will set off the alarm
What type of radiation is Smoke alarm and why?
. Alpha
. because it is the most ionising radiation
Does Smoke alarm have a long or short half life and why?
. Long half-life
. to make sure the smoke alarm keeps working for a long time
What are the risks of Smoke alarm?
No risks unless you eat your smoke alarm
How are the risks of Smoke alarm minimised?
Alpha is absorbed by the packaging as it is least penetrating
What is nuclear fission?
the splitting of a large and unstable nucleus e.g uranium or plutonium
What generally causes fission to occur?
the unstable nucleus absorbs a neutron
What happens when fission occurs?
. Nucleus splits into 2 smaller nuclei, roughly equal in size
. Emits 2 or 3 neutrons plus gamma rays
. Energy is released by the fission reaction
What do all the fission products have in common?
All have kinetic energy
What fuel is generally used in nuclear fission?
. Uranium 235
. Plutonium 239
What can happen after fission has occurred?
The neutrons may go on to start a chain reaction
Why might we want and not want to control a chain reaction?
. Want: In a nuclear reactor to control energy released
. Don't want: In a nuclear weapon as explosion is caused by uncontrolled chain reaction
What does a moderator do in a nuclear reactor?
material that slows down neutrons to ensure they're absorbed
What do control rods do in a nuclear reactor?
absorbs the neutrons to control the rate of reaction
What is nuclear fusion?
. The joining of 2 smaller nuclei to form a larger nucleus
. In this process some of the mass may be converted into energy
What conditions are needed for fusion to occur?
. very high temps
. very high pressure
. mostly happens in stars
Why is fusion better than fission?
. Can't melt down
. Doesn't produce nuclear waste
. Higher energy density
Diagram of nuclear reactor and key terms

fuel rods
control rods
moderator e.g. water
coolant e.g. water
steam to turbines
concrete shield
pump
steel vessels (the thing that keep in fuel, control rods and water
Diagram of controlled chain reaction in fission
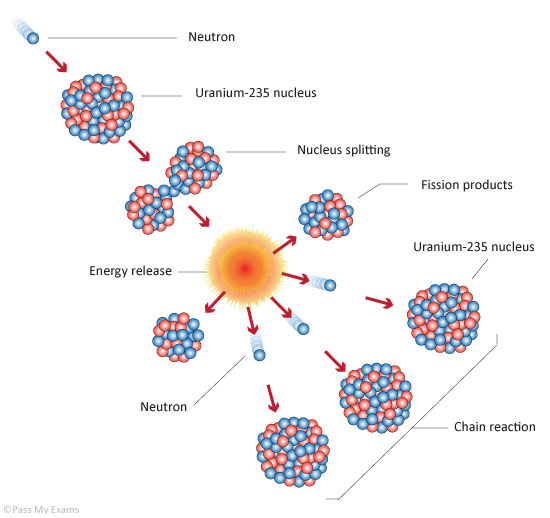
There would also be moderators (water) that slow down the neutrons to make sure they get absorbed and control rods that absorb neutrons to control the rate of reaction.