CH13 LEC: ALKENES, ALKYNES, AROMATICS
1/98
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
alkene definition
unsaturated hydrocarbon w/ at least 1 C=C
Alkenes are able to undergo which reaction and why?
addition rxns due to C=C presence
alkenes are ___ reactive than alkanes
more
alkenes general molecular formula
CnH2n
alkene suffix
-ene
what is the smallest alkene
ethene (C2H4)
alkyne definition
unsaturated hydrocarbon molecules with at least 1 C≡C
alkynes general molecular formula
CnH2n-2
alkyne suffix
-yne
smallest alkyne
ethyne (C2H2)
benzene is the ___ compound of the large ___ family of compounds
parent
aromatic
benzene compound description
contains 6-membered ring, C or other atoms, w/ alternating single and double bonds
heterocyclic aromatic compounds definition
when elements, other than C, are also members of a ring structure
also called heterocycle rings or heterocyclic compounds
5 nucleotide bases
adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracil
nucleotide bases purpose
form components of DNA & RNA
2 categories of nucleotide bases
pyrimidines
purines
pyrimidines definition
a single 6-membered ring (2 Cs replaced by 2 Ns)
purines definition
pyrimidine ring fused to a 5-membered ring
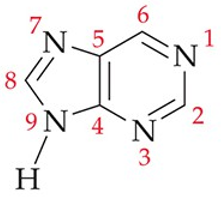
recognize this structure
purine (parent)
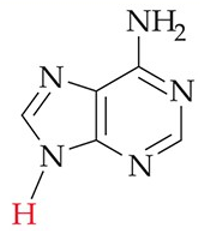
recognize this structure
adenine (A) (DNA, RNA)
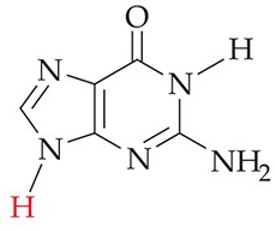
recognize this structure
guanine (G) (DNA, RNA)
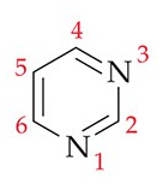
recognize this structure
pyrimidine (parent)
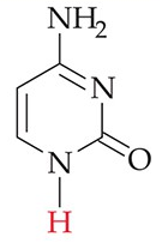
recognize this structure
cytosine (C) (DNA, RNA)
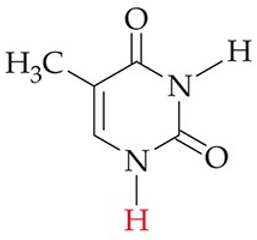
recognize this structure
thymine (T) (DNA, some RNA)
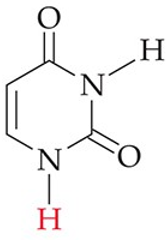
recognize this structure
uracil (U) (RNA)
3 amino acid sidechains
phenylalanine, tryptophan, tyrosine
also called: aromatic amino acids
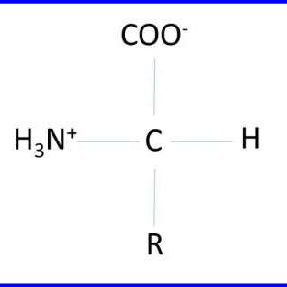
recognize this structure
general amino acid structure
amino acid links to ___ from a central C
4 groups
what determines the key characteristics of an amino acid?
the sidechain
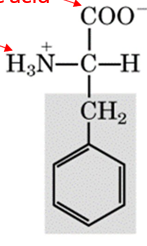
recognize this structure
phenylalanine
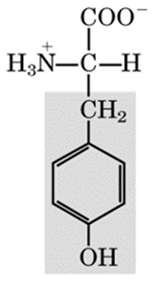
recognize this structure
tyrosine
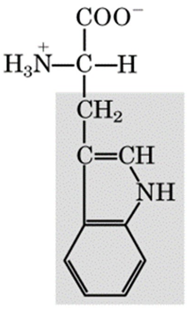
recognize this structure
tryptophan
what is the relationship b/t tyrosine and phenylalanine?
tyrosine is derived from phenylalanine — making these two interchangeable to some degree in proteins and metabolism
why can you not add more Hs to a benzene ring?
b/c there is only 1.5 e- in the double bond
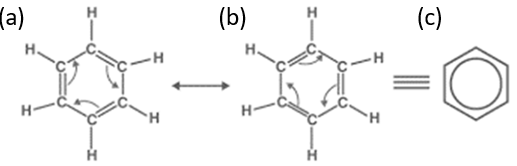
resonance structures of benzene
the e- are delocalized or shared throughout the ring structure — across the single & double bonds
contributes to increased stability, resulting in lower reactivity
can exist as 2 structures, A. and B., and written as C.
saturated molecule definition
all Cs are linked together by only single bonds
each C bonds to 4 groups
no more Hs can be added
unsaturated molecule definition
contains one or more double or triple bonds
addition Hs can be incorporated, leading to conversion of a multiple bond to a single bond
every time you make a C=C, 2 Hs are removed
Addition rxn definition
for unsaturated hydrocarbons, more Hs can be added to multiple bonds to form single bonds and saturated hydrocarbons
in naming alkenes and alkynes, number the chain starting from ___.
the end closer to the multiple bond
in naming alkenes and alkynes, use the ___ to indicate the location of the functional groups
smaller number
in naming alkenes and alkynes, the longest chain chosen for the root name must include ___.
both C atoms of the double/triple bond, even if the chain is longer w/out — you choose the shorter chain that includes these bonds
in naming alkenes and alkynes, if a double/triple bond and an alkyl substituent are both present, the ____ has the lowest number.
alkene/alkyne group
priority to family name first, then to the substituent
in naming alkenes and alkynes, if the double/triple bond is equal distance from each end, number so the ___ has the lowest number.
1st substituent
in naming alkenes and alkynes, if more than one double/triple bond is present, indicate their position by using the ___.
number of the 1st C of each bond, and use the suffix — -diene, triene, tetraene, diyne, triyne, tetrayne, etc.
trivial or common names definition
informal names given to compounds that are often simpler and more user friendly than their IUPAC names
Common name of ethene (H2C=CH2)
Ethylene
common name of propene (CH3CH=CH2)
propylene
common name of ethyne (HC≡CH)
acetylene
cycloalkenes definition
hydrocarbons that contain 1 or more C=C in a ring
in naming cycloalkenes, number the double bond Cs ___, and the 1st substituent has ___.
1 & 2
the lowest possible number
in naming cycloalkenes, if there is an alkyl substituent on one of the C=C, that C is ___.
#1
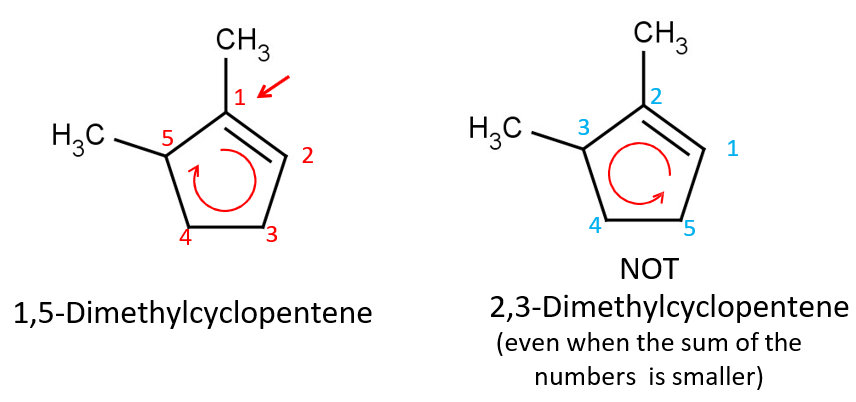
NOTE: sometimes this can lead to a deviation from the Lowest Sum Rule, and you end up choosing the larger sum b/c the positioning is prioritized. (see pic for example)
in naming aromatic compounds w/ 1 substituent, substituted benzenes are named using the substituent as ___.
the prefix followed by -benzene as the parent. no number is needed for mono-substituted benzenes b/c it is always 1.
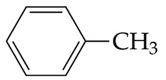
recognize this structure by its common & IUPAC name
common name: toluene
IUPAC: methylbenzene
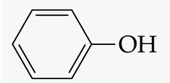
recognize this structure by its common & IUPAC name
common name: phenol
IUPAC: hydroxybenzene
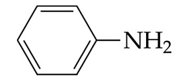
recognize this structure by its common & IUPAC name
common name: aniline
IUPAC: aminobenzene
ortho (o) definition
indicates position of 2 substituents on benzene ring: 1,2— (2 substituents next to each other)
meta (m) definition
indicates position of 2 substituents on benzene ring: 1,3— (separated by one carbon)
para (p) definition
indicates position of 2 substituents on benzene ring: 1,4— (across from each other on the ring)
phenyl group definition
what benzene rings are called when they act as a substituent group attached to another parent compound
conformers arise from what?
unrestricted rotation around a C—C single bond
T/F: 2 molecules having the same structure do not always have the same IUPAC name.
False; they always do
in cis— or trans— structures, the C=C is ___ and cannot be ___.
rigid
rotated unless by breaking the double bond
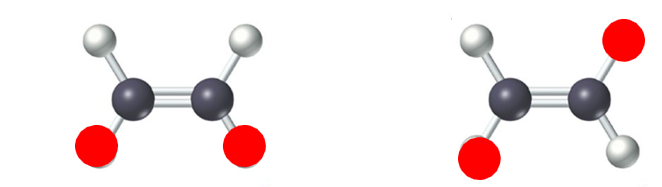
know this is cis and which is a trans structure

another name for cis-trans isomer
geometric isomer
cis means ___ side.
same
trans means ___ side.
opposite
cis shape
bent
trans shape
more linear
When one of the C=C is bound to the ___, cis-trans isomerism is impossible.
same group
cis-isomer definition
when identical or larger groups are on the same side of the C=C
trans-isomer definition
when identical or larger groups are on the opposite sides of C=C
the formation of cis-trans isomers in alkenes depends upon the___.
groups bound to C=C
alkenes w/ —C=CH2 ___ as cis-trans isomers
do not exist
alkenes w/ —C=CR2, where the R-groups are identical, ____ as cis-trans isomers
do not exist
what are the five major reactions
addition, elimination, substitution, rearrangement, oxidation & reduction
addition reaction definition
a reaction X—Y is added to the multiple bond of an unsaturated reactant to yield a saturated product
name this reaction: 2 reactants form 1 product
addition rxn
elimination reaction definition
saturated reactant yields an unsaturated product by losing a group from each of the 2 adjacent Cs; forming a double bond in place of a single bond
name this reaction: 1 reactant forms 2 products
elimination reaction
why type of reaction is a dehydration reaction?
elimination reaction
dehydration reaction definition
removal of H2O
what is this reaction: alcohol → alkene + water
elimination reaction: dehydration of alcohols
substitution reaction definition
an atom or group of atoms in a molecule is replaced by another atom or group of atoms in a molecule
name this reaction: 2 reactants form 2 products
substitution reaction
a common substitution rxn of alkanes is ___.
halogenation
rearrangement reaction definition
type of o-chem rxn in which the structure of a molecule is reorganized to form a new isomer. the atoms/groups shift to different connectivity / positions w/out adding or removing any atoms.
name this reaction: 1 reactant forms 1 product
rearrangement reaction
the reactants and products of a rearrangement reaction are ___.
constitutional isomers
oxidation reaction definition
addition of O atom(s) OR removal of H atom(s)
reduction reaction definition
removal of O atom(s) OR addition of H atom(s)
due to the presence of multiple bonds, alkenes and alkynes are ___ than related alkanes
more reactive
the most common rxns involving C-C multiple bonds are ___.
addition reactions
common addition rxns involving C—C multiple bonds
hydrogenation
halogenation
hydrohalogenation
hydration
benzene doesn’t undergo ___ b/c that would necessitate disrupting its delocalized e- system, resulting in a loss of its inherent stability
addition reactions
hydrogenation reaction definition
H is added to a multiple bond yielding a saturated product
alkenes and alkynes react w/ H to yield alkanes
halogenation reaction definition
the addition of a halogen (Cl2, Br2, etc.) to an alkene yields a dihaloalkane
hydrohalogenation reaction definition
alkenes react w/ hydrogen halides (HBr, HCl, etc.) to yield alkyl halides (IUPAC haloalkanes)
hydration reaction definition
alkenes react w/ H2O to yield alcohols
Markovniko’s Rule
in the addition of H—X (such as HBr, HCl, or H2O) to an asymmetrical alkene, the H will add to the C of the double bond that already has the greater number of Hs, while the X will add to the C w/ fewer Hs.