AP Psych - Unit 1 pt. 2 (research methods)
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/74
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
1
New cards
hindsight bias/I-knew it all along phenomenon
tendency to believe, after learning on outcome, that one would have froseen it
2
New cards
scientific method
a method of investigation involving observation and theory to test scientific hypotheses
3
New cards
theory
explains behaviors or events by offering ideas
4
New cards
hypothesis
a testable proposal intended to explain certain facts or observations
5
New cards
operational definitions
a carefully worded statement of the exact procedures(operations) used in a research study
6
New cards
replicate
reproduce or make an exact copy of (in this case an experiment)
7
New cards
descriptive methods
describes behaviors, often by suing case studies, surveys, or naturalistic observations
8
New cards
correlational
method associate different factors or variables
9
New cards
variables
anything that contributes to a result
10
New cards
experimental method
manipulate variables to discover their effects
11
New cards
case study
examines one individual or group in depth in hope of revealing things true of us all
12
New cards
case study strengths
gives us insight, can show us what can happen
13
New cards
case study weakness
misleading mistaken judgement; anecdotal cases can overwhelm general truth(ex: just because one persons grandpa lived a long age while smoking, does not mean smoking is not bad. studies show smoking is bad for health)
14
New cards
naturalistic observations
a descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate or control the situation
15
New cards
naturalistic observation stenghts
revelations that may not have been found in a lab setting, shows complexity, describes behavior
16
New cards
naturalistic observation weakness
does not explain behaviors
17
New cards
Hawthorne effect
when we know we are being watch, we change our behaviors
18
New cards
overconfidence
we think we know more than we do
19
New cards
false consensus effect
a person overestimated how many people agree with them (political views, interest, etc.)
20
New cards
the basic scientific attitudes
skepticism, curiosity, humility
21
New cards
surveys
looks cases in less depth, asking people to report their behavior or opinions
22
New cards
survey benefits
broad range of opinion
23
New cards
survey weakness
sampling bias, response bias, social desirability bias, wording effect
24
New cards
sampling bias
generalize from a few valid but unrepresentative cases
25
New cards
anecdotal fallacy
use of anecdotal evidence
26
New cards
population
all those in a group being studied, from which samples may be drawn
27
New cards
random sampling
what has to happen to make the samples not bais
28
New cards
random sample
a sample in which every element in the population has an equal chance of being selected
29
New cards
wording effect
the phrasing of the word can change the opinion of people (ex: "gun safety" vs "gun control"
30
New cards
correlate
a measure of the extent to which two factors vary together, and thus of how well either factor predicts the other
31
New cards
correlation coefficient
a statistic representing how closely two variables co-vary; it can vary from -1 through 0 to +1
32
New cards
correlation research strenghts
can predict how well one variable predicts another
33
New cards
correlation research weakness
does not specify cause and effect
34
New cards
illusory correlation
perceiving a relationship where none exits, or perceiving a stronger-than-actual relationship
35
New cards
regression toward the mean
tendency for extreme or unusual scores or events to fall back (regress) toward the average
36
New cards
experiment
a research method in which an investigator manipulates one or more factors (independent variables) to observe the effect on some behavior or mental process (dependent variables) By random assignment of participation, the experimenter aims to control other relevant factors
37
New cards
experimental group
in an experiment, the group exposed to the treatment, that is, to one version of the independent variable
38
New cards
experimental research strenghts
control variables, determine effects
39
New cards
experimental weaknesses
confounding variable. ethical on some issues, lack ecological validity
40
New cards
control group
the group not exposed to the treatment
41
New cards
random assign
assigning participants to experimental and control groups by chance, thus minimizing preexisting differences between the different group
42
New cards
double blind procedure
an experimental procedure in which both the research participants and the research staff are ignorant(blind) about whether the research participants have received the treatment or a placebo
43
New cards
placebo effect
any effect that seems to be a consequence of administering a placebo; the change is usually beneficial and is assumed result from the person's faith in the treatment or preconceptions about what the experimental drug was supposed to do (ex: phony drug makes people have better moods)
44
New cards
independent variable
factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied
45
New cards
confounding variables
a factor other than the factor being studied that might influence a study's results
46
New cards
dependent variable
the outcome that is measured; the variable that may change when the independent variable is manipulated
47
New cards
operational definitinos
specify the procedures that manipulate the independent variable or measure the dependent variable
48
New cards
validity
experiment will test what it is suppose to test
49
New cards
placebo
introduce something fake to the control group to keep anominity
50
New cards
quasi-experimental design
subjects not randomly assigned to groups
51
New cards
ethical guidelines
informed consent, rights to withdraw, avoid deception, debrief, confidentiality, privacy, protect from physically & mental harm, advise participants when psychological or physical problems are discovered, consider implication and psychological consequence, monitor work of other colleagues
52
New cards
informed consent
giving potential participants enough information about a study to enable them to choose whether they wish to participate
53
New cards
debrief
the post experimental of a study including its purpose and any deceptions to its participants
54
New cards
descriptive statistics
numerical data used to measure and describe characteristics if group, includes measure of central tendency and measures of variation
55
New cards
histograms
a bar graph depicting a frequency distribution
56
New cards
mode
most frequently occurring score (s) in a distribution
57
New cards
mean
average of a distribution; add the scores then divide by number of scores
58
New cards
median
middle score in a distribution
59
New cards
skewed
a representation of scores that lack symmetry around their average value
60
New cards
range
differences between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
61
New cards
standard deviation
a computed measure of how much scores vary around the mean score; better for averages
62
New cards
dimodal distribution
it has two peaks or humps (modes)
63
New cards
normal curve/distribution
bell-shaped distribution often symmetrical
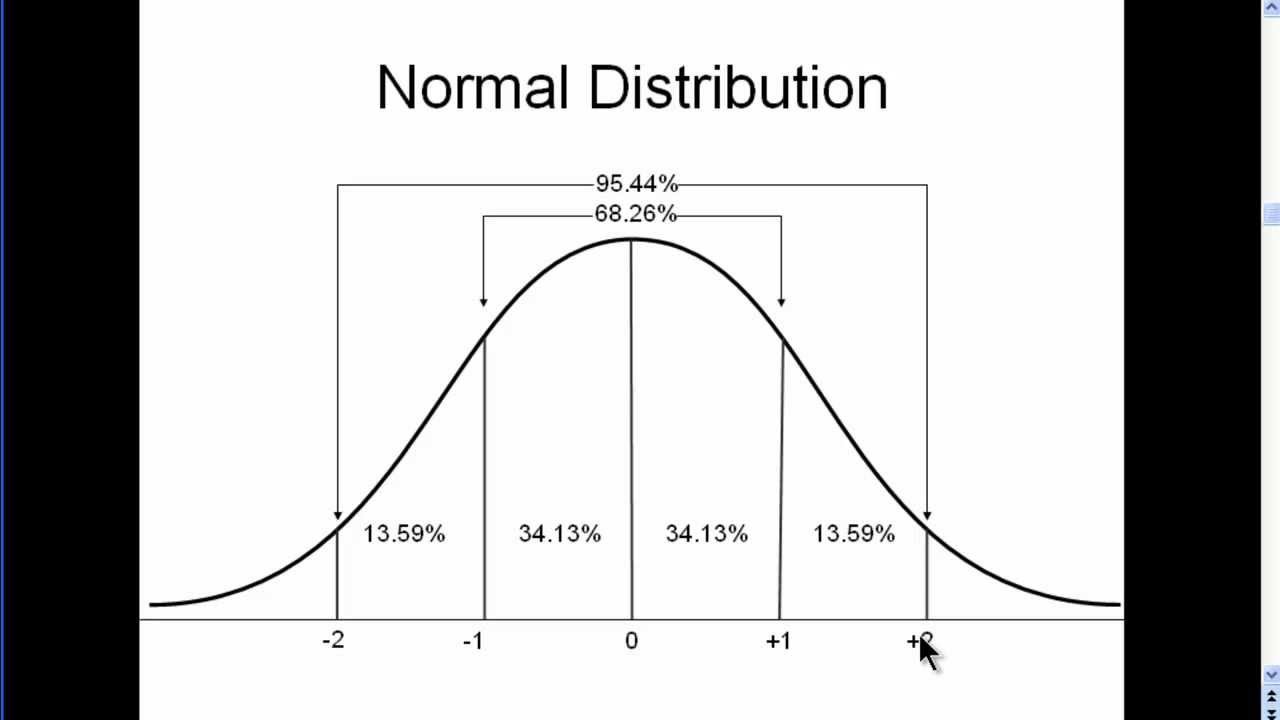
64
New cards
inferential statistics
numerical data that allow one to generalize - to infer from sample data the probability of something being true of a population
65
New cards
statistical significance
a statistical statement of how likely it is that an obtained result occurred by chance
66
New cards
scatterplot
show us relationship
67
New cards
ex: 2, 5, 8: mean = 5, 2-5 = -3, 5-5 = 0, 8-5 = 3, -3^2 + 0^2 + 3^2 = 18, 18/3 = 6
how to calculate standard deviation
68
New cards
data clustered around the mean
What does a small Standard Deviation mean?
69
New cards
mean
What measure greatly affects measure of central tendency
70
New cards
central tendency
single score that represents a whole set of scores
71
New cards
range (i believe idk)
What measure greatly affects measure of central variation/dispersion
72
New cards
Measure of central tendency shows where the center or middle of the data set is located, whereas measure of variation shows the dispersion among data values.
Central tendency vs measure of variation
73
New cards
positive correlation
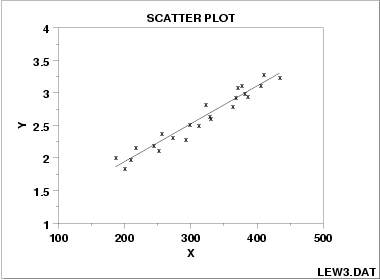
74
New cards
negative correlation
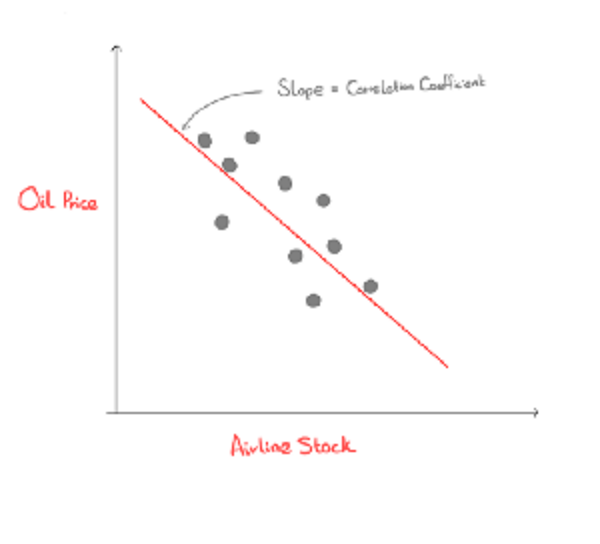
75
New cards
no correlation