cell bio exams
1/88
Earn XP
Description and Tags
exam 1,2 done, exam 3,4 pending
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
which of the following is not a shared feature of prokaryotes and eukaryotes
a. genetic information is encoded in DNA
b. the presence of organelles such as the ER and Golgi
c. the basic mechanisms of transcription and translation
d. the presence of a plasma membrane
e. the ability to respond to stimuli
b. the presence of organelles such as the ER and Golgi is not a shared feature
(prokaryotes lack these membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes possess them.)
under what conditions will a reaction occur spontaneously, in general?
a. if the Gibbs free energy is zero
b. if the Gibbs free energy change is positive
c. if the Gibbs free energy change is negative
d. if an enzyme is added to a reaction
e. if the change in internal energy is positive
c. if the Gibbs free energy change is negative
a reaction will occur spontaneously if the Gibbs free energy change is negative.
which of the following characteristics does not apply to water?
a. water is an asymmetric molecule
b. water is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with many types of molecules
c. the covalent bonds in water are highly polarized
d. water is essential for all chemical reaction in the cell
e. water form hydrophobic interactions
e. water forms hydrophobic interactions does not apply to water.
hydrophobic interactions occur between nonpolar substances in the presence of water, not with water itself.
which of the following statements is false about enzymes?
a. enzymes can be denatured at high temperatures
b. enzymes are reusable and are only needed in small amounts
c. enzymes add energy into the system which allows the acceleration of reaction rates
d. enzymes lower the Ea allowing for a chemical reaction to proceed
e. enzyme speed reaction rates by bringing substrates closer together
c. enzymes add energy into the system is false
enzymes do not add energy but lower the activation energy (Ea) needed for reactions to proceed.
which of the following is not a macromolecule formed by polymerization?
a. proteins
b. lipid
c. polynucleotide
d. polysaccharides
e. DNA
b. lipid is not a macromolecule formed by polymerization.
lipids are generally not polymers but are instead composed of smaller units such as fatty acids and glycerol.
You are interested in studying the function of a potential transcription factor called Hello303. You want to determine if Hello303 is expressed in the nucleus. What type of experiment would you perform to isolate the nucleus fraction from the rest of the cell?
a. Perform affinity chromatography
b. perform differential centrifugation
c. Perform SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
d. Perform Mass Spectrometry
e. there is no way to isolate the nucleus from the rest of a cell
b. perform differential centrifugation
this is the appropriate experiment to isolate the nucleus.
What type of protein secondary structure is characterized as being highly extensible because of its coiled structure?
a. globular
b. proline kink
c. B-pleated sheet a-helix
d. a-helix
e. Quaternary structure
c. a-helix
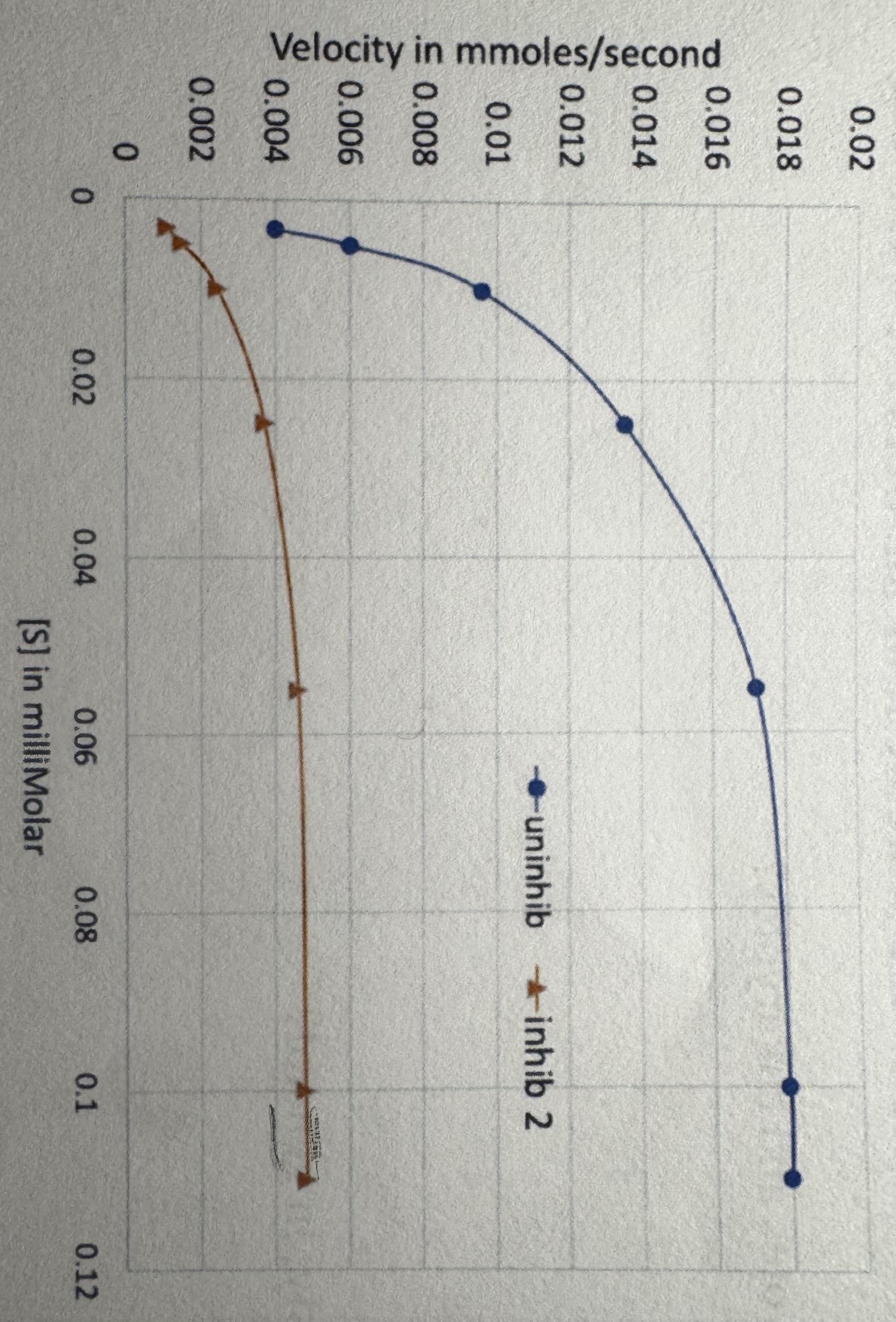
consider the reaction catalyzed by the enzyme ribulose biphosphate carboxylase. what is the appropriate Vmax of the reaction in the presence of inhibitor 2?
a. 0.018 mmoles/second
b. 0.005 mmoles/second
c. (1/0.018) mmoles/second
d. (1/0.005) mmoles/second
e. 0.1 milliMolar
b. 0.005 mmoles/second
Protein structure helps to determine protein function. Which of the following bonds hold amino acids together along the peptide back:
A. Hydrogen bonds
B. Ionic bonds
C. Van der Waals interactions
D. Covalent bonds
E. Multiple types of non-covalent interactions including ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and van der Waals interactions
D. Covalent bonds
Which of the following describes part of the cell theory?
A. Cells can arise spontaneously from molecular components.
B. Viruses are cells because they contain nucleic acids and can replicate.
All cells are generally the same size and shape.
All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
E. None of these statements are true about the cell theory.
D. All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
The first law of thermodynamics states that:
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be transduced from one form to another.
B. Energy can be created and transduced from one form to another.
C. Energy can be destroyed and can be transduced from one form to another.
D. Energy never changes forms.
E. Energy cannot be created or destroyed and cannot be transduced from one form to another.
A. Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be transduced from one form to another.
Which of the following statement is true about non-covalent bonds?
A. Non-covalent bonds only occur between the same type of macromolecule.
B. Non-covalent bonds are strong and require enzymatic activity for bonds to be broken.
C. Ionic bonds are a type of non-covalent bond that occurs between oppositely charged ions.
D. A non-covalent bond is a chemical bond in which electron pairs are shared between two atoms.
E. Hydrogen bonds are a type of non-covalent bond that describes the interaction forces between water and the phospholipid bilayer.
C. Ionic bonds are a type of non-covalent bond that occurs between oppositely charged ions.
If a red blood cell were added to a hypotonic solution, the cell would rapidly gain water and swell.
A. the cell would rapidly gain water and swell
B. the solute would leave the cell and enter the more dilute solution.
C. water cannot pass through the plasma membrane, so nothing would happen.
D. the cell would rapidly lose water and shrink.
a. the cell would rapidly gain water and swell
The limit resolution for a light microscope is about 220nm. What does this mean?
A. Structures bigger than this, like the lipid bilayer or ribosomes, can't be seen with any detail using a light microscope.
B. Structures bigger than this, like bacteria cells, mitochondria or chloroplasts, can't be seen with any detail using a light microscope.
C. Structures smaller than this, like the lipid bilayer or ribosomes, can't be seen with any detail using a light microscope.
D. This is better than the limit of resolution for an electron microscope.
E. This limit resolution refers to a 220 magnification.
C. Structures smaller than this, like the lipid bilayer or ribosomes, can't be seen with any detail using a light microscope.
What kind of organism reaches equilibrium?
A. a dead organism
B. a prokaryote
C. eukaryote
D. one with a low metabolic rate one that is actively metabolizing
A. a dead organism
What kind of membrane protein penetrates into the hydrophobic part of the lipid bilayer?
A. integral protein
B. lipid-anchored protein
C. peripheral protein
D. phosphatidylcholine
E. galactocerebroside
A. integral protein
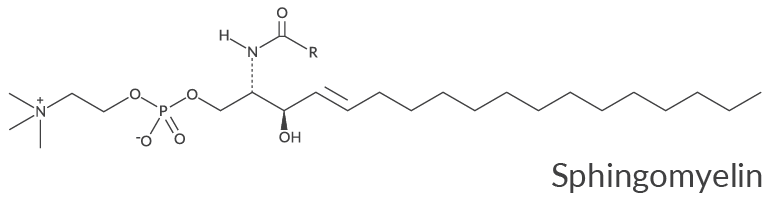
Name the following membrane component
a. sphingosine
b. phosphoglyceride
c. phosphatidylcholine
d. sphingomyelin
e. cholesterol
d. sphingomyelin
(you can tell cause the N(CH3)3 group at the end)
which of the equations sets represent coupled reactions?
a. A + B —> C + D (G = -4.6kcal/mole) and E + F —> G + H (G = -0.9kcal/mole)
b. A + B —> C + D (G = -4.6kcal/mole) and C + D —> E + F (G = -0.9kcal/mole)
c. A + B —> C + D (G = -4.6kcal/mole) and E + F —> C + D (G = -0.9kcal/mole)
d. all the above
b. A + B —> C + D (G = -4.6kcal/mole) and C + D —> E + F (G = -0.9kcal/mole)
People who have the A blood type possess ________
A. no enzymes capable of attaching galactose or N-acetylgalactosamine to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids
B. an enzyme that adds an N-acetylgalactosamine to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids.
C. an enzyme that adds a galactose to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids.
D. an enzyme that adds phospholipids to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids.
E. both an enzyme that adds an N-acetylgalactosamine to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids and an enzyme that adds a galactose to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids.
b. an enzyme that adds an N-acetylgalactosamine to the end of the oligosaccharide chain on RBC membrane glycolipids.
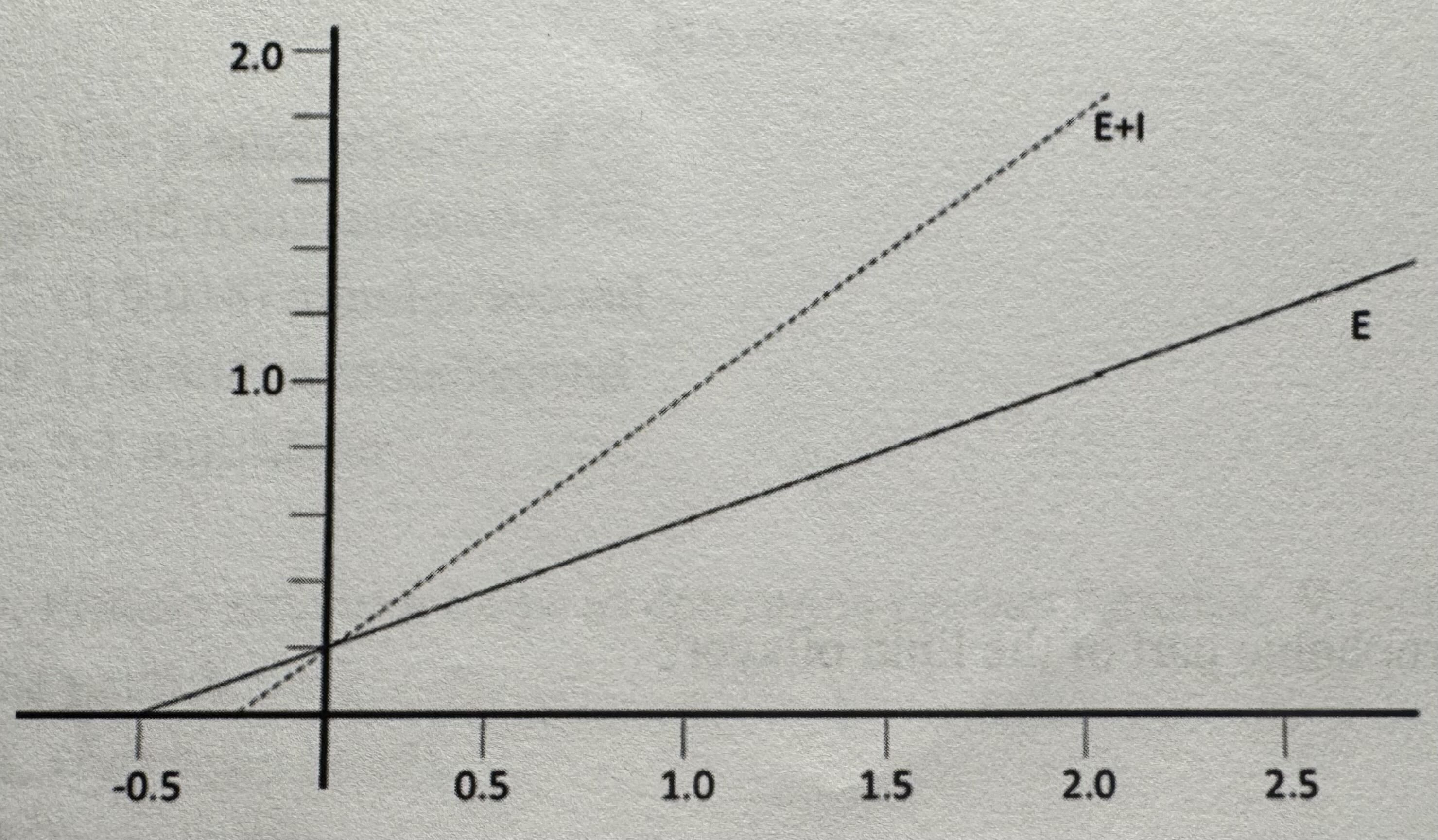
The graph below is a Lineweaver-Burke plot of an enzyme catalyzed reaction (E) and an enzyme-catalyzed reaction in the presence of an inhibitor (E+I). Use it to answer the question below. Based on the line shown for the enzyme in the presence of inhibitor (E+I), what type of inhibitor is this? How did you determine what type of inhibitor is shown?
a. competitive inhibitor; The Vmax for E+I is lower than E alone and the Km is the same for both reactions
B. competitive inhibitor; The Vmax for E+I is the same as E alone and the Km is higher than E alone
C. noncompetitive inhibitor; The Vmax for E+I is lower than E alone and the Km is the same for both reactions
D. noncompetitive inhibitor; The Vmax for E+I is the same as E alone and the Km is higher than E alone
E. There is not enough information from this graph to determine what type of inhibitor it is.
B. competitive inhibitor; The Vmax for E+I is the same as E alone and the Km is higher than E alone
What is a major advantage of conventional fluorescent microscopy compared to electron microscopy?
A. fluorescent microscopy can only be used on living cells.
B. fluorescent microscopy uses lenses to focus the light.
C. fluorescent microscopy results in higher resolution images.
D. fluorescent microscopy provides higher magnification.
E. fluorescent microscopy can be used on very thin specimens or sections of tissue.
a. fluorescent microscopy can only be used on living cells.
Which of the following statements is true about the Na/K ATPase pump.
A. The Na/K ATPase pump is responsible for the excess of K* outside and Na* inside the cell.
B. The Na/K ATPase pumps ions with their concentration gradient.
C. Different affinities for K* and Na* are achieved by the steep concentration gradients across the membrane.
D. The Na/K ATPase pump must have a higher binding affinity for Na* inside the cell and a lower binding affinity for Nat outside of the cell.
E All of the above statements are true.
D. The Na/K ATPase pump must have a higher binding affinity for Na* inside the cell and a lower binding affinity for Nat outside of the cell.
Fats that remain solid at room temperature are most likely to be
A. Saturated
B. Unsaturated
C. Polysaturated
D. Transaturated
E. None of these answers are correct
a. saturated
Which of the following strategies are used in the cell to promote reactions with a large deltaGo’ to occur?
A. The cellular concentration of the reactants may increase to promote the reaction.
B. The cellular concentration of the products may decrease to promote the reaction
C. The reaction may be coupled to ATP hydrolysis
D. All of these strategies may be used by the cell
E. None of these strategies may be used by the cell
d. All of these strategies may be used by the cell
While culturing some cells, you raise the temperature. What happens immediately to the membrane fluidity?
A. The membrane becomes more fluid
B. The membrane becomes less fluid.
C. The membrane becomes more hydrophilic.
D. The membrane becomes more hydrophobic.
E. Nothing happens to the membrane because temperature does not affect fluidity.
A. The membrane becomes more fluid
Which of the following molecules is able to pass through the plasma membrane without being mediated by a protein?
A. potassium ions
B. glucose
C. oxygen
D. acetylcholine
E. dopamine
c. oxygen
Facilitated diffusion through a biological membrane is:
A. driven by ATP.
B. endergonic.
C. driven by a difference of solute concentration.
D. generally irreversible.
E. driven by a difference in membrane potential
c. driven by a difference of solute concentration.
A channel that opens in response to the binding of a specific molecule, which is not the solute that passes through the channel, is called a
A. voltage-gated channel
B. electric-gated channel
C. mechanosensory gated channel ligand-gated channel
D. ligand gated channel
E. pump
D. ligand gated channel
You have discovered a peripheral membrane protein and called it NPC303! In order to perform functional studies you need to separate the protein from the membrane by using a buffer that has
A. a high salt concentration.
B. a high salt and then placing it in a nonpolar solvent
C. enzymes that dissociate the inositol-containing phospholipids. an ionic detergent and placing it in water.
D. an ionic detergent and placing it in water
E. a polar, non-ionic detergent and placing it in water with the detergent.
D. an ionic detergent and placing it in water
What kind of membrane protein is found entirely outside the bilayer and is covalently linked to a membrane lipid situated within the bilayer?
A. integral protein
B. lipid-anchored protein
C. glycoprotein
D. peripheral proteins
E. transmembrane protein
B. lipid-anchored protein
which of the following statements is true about the eukaryotic voltage gated K+ channel?
a. it is activated by a ligand binding to the cytoplasmic domain of the protein
b. it transports K+ ions from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration
c. it uses the energy of ATP hydrolysis to pump K+ across the membrane
d. it is activated by a change in membrane potential
e. it doesn’t gave a selectivity filter and therefore transports both K+ and Na+ ions
d. it is activated by a change in membrane potential
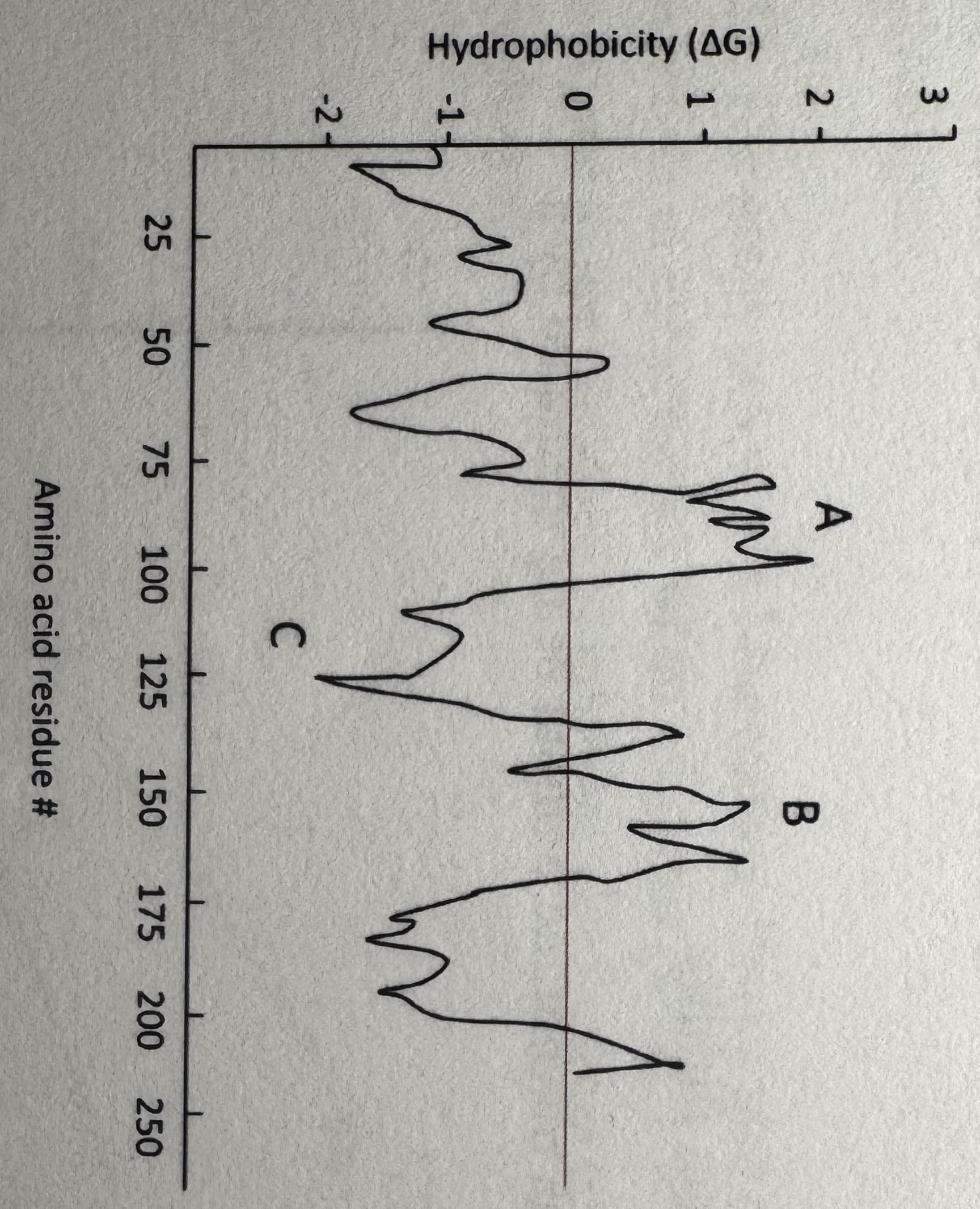
Below is a hydropathy plot for an integral membrane protein. Which of the region(s) on the graph have the greatest likelihood of representing a transmembrane domain(s)?
a. A only
b. B only
c. C only
d. A and B
e. A, B, and C
d. A and B
In colder weather, a bird's cells would need to _________ in order to best modify the fatty acid composition of lipid membranes and maintain membrane fluidity homeostasis.
A. increase incorporation of saturated fatty acids
B. increase incorporation of unsaturated fatty acids
C. decrease incorporation of saturated fatty acids
D. both an increase in incorporation of unsaturated fatty acids and a decreased incorporation of saturated fatty acids would be optimum
E. both a decrease in incorporation of unsaturated fatty acids and an increased incorporation of saturated fatty acids would be optimum.
D. both an increase in incorporation of unsaturated fatty acids and a decreased incorporation of saturated fatty acids would be optimum
During active transport, the positive delta G created by moving something up its concentration gradient (to where it is already higher) is overcome by.
A. coupling this movement with something with a larger negative delta G, like ATP hydrolysis.
B. coupling this movement with something with a large positive delta G, like ATP hydrolysis.
C. cells going to equilibrium.
D. passive transport of the moving substance back down the concentration gradient.
E. the opening of voltage-gated channels.
A. coupling this movement with something with a larger negative delta G, like ATP hydrolysis.
The sodium-potassium pump takes the cell interior more ____ by pumping ____ sodium ions out of the cell for every ____ potassium ions pumped in.
A. negative, 3, 2
B. negative, 2, 3
C. positive, 3, 2
D. positive, 2, 3
E. none of the above
A. negative, 3, 2
Liposomes formed in water are impenetrable to water - that is, water cannot get in or out. If you made liposomes that contained lipids and the aquaporin protein complex (and assuming it was folded correctly), then moved the liposomes taquaporin to a more hypotonic solution, what do you predict would happen?
A. The aquaporins would precipitate out of solution, leaving the liposomes intact.
B. Water would not move into the liposomes and no distribution of water across the membrane would occur.
C. Water would move out of the liposomes through the aquaporin due to osmosis and cause the liposome to shrink or collapse.
D. Water would move into the liposomes through the aquaporin due to osmosis and cause the liposome to swell or break open.
E. Aquarporin is not the transporter for water and thus no water would cross the membrane.
D. Water would move into the liposomes through the aquaporin due to osmosis and cause the liposome to swell or break open.
Individuals with Huntington's disease experience progressive neurodegeneration symptoms. Huntington's disease is caused by a mutation in the huntingtin (HTT) gene. As a scientist, you want to explore its role in neuronal communication, which cell type would you choose:
A. Immortalized HeLa cells
B. Primary neurons isolated from Huntington's disease patients.
C. Embryonic stem cells isolated from Huntington's disease patients
D. Induce pluripotent stem cells to differentiate into neurons isolated from Huntington's disease patients.
D. Induce pluripotent stem cells to differentiate into neurons isolated from Huntington's disease patients.
A transport system that moves one solute into the cell and another one out of the cell during a single cycle accompanied by the expenditure of energy through ATP hydrolysis could be called
A. an active antiport
B. an active uniport
C. a passive antiport
D. an active symport
E. a passive symport
A. an active antiport
The electron microscopy method in which two leaflets of the lipid bilayer are split and metal-coated, provided evidence for proteins being embedded through the plasma membrane.
A. freeze-fracture
B. Western blotting
C. Confocal microscopy
D. FRAP
E. X-ray crystallography
A. freeze-fracture
You are working in the lab studying the interaction between two proteins called Hello and Goodbye. You want to determine the association between these two proteins under different drug conditions. What type of experiment would be best to determine the relative distance between Hello and Goodbye under individual drug treatments?
A. Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching
B. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
C. SDS-Page gel followed by immunoblotting using specific antibodies.
D. Mass Spectrometry
E. Liquid Chromatography
B. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer
Molecules which absorb photons of a specific wavelength and release a portion of the energy in longer wavelengths are called
A. fluorophores
B. absorbers
C. antibodies
D. donors
E. emitters
A. fluorophores
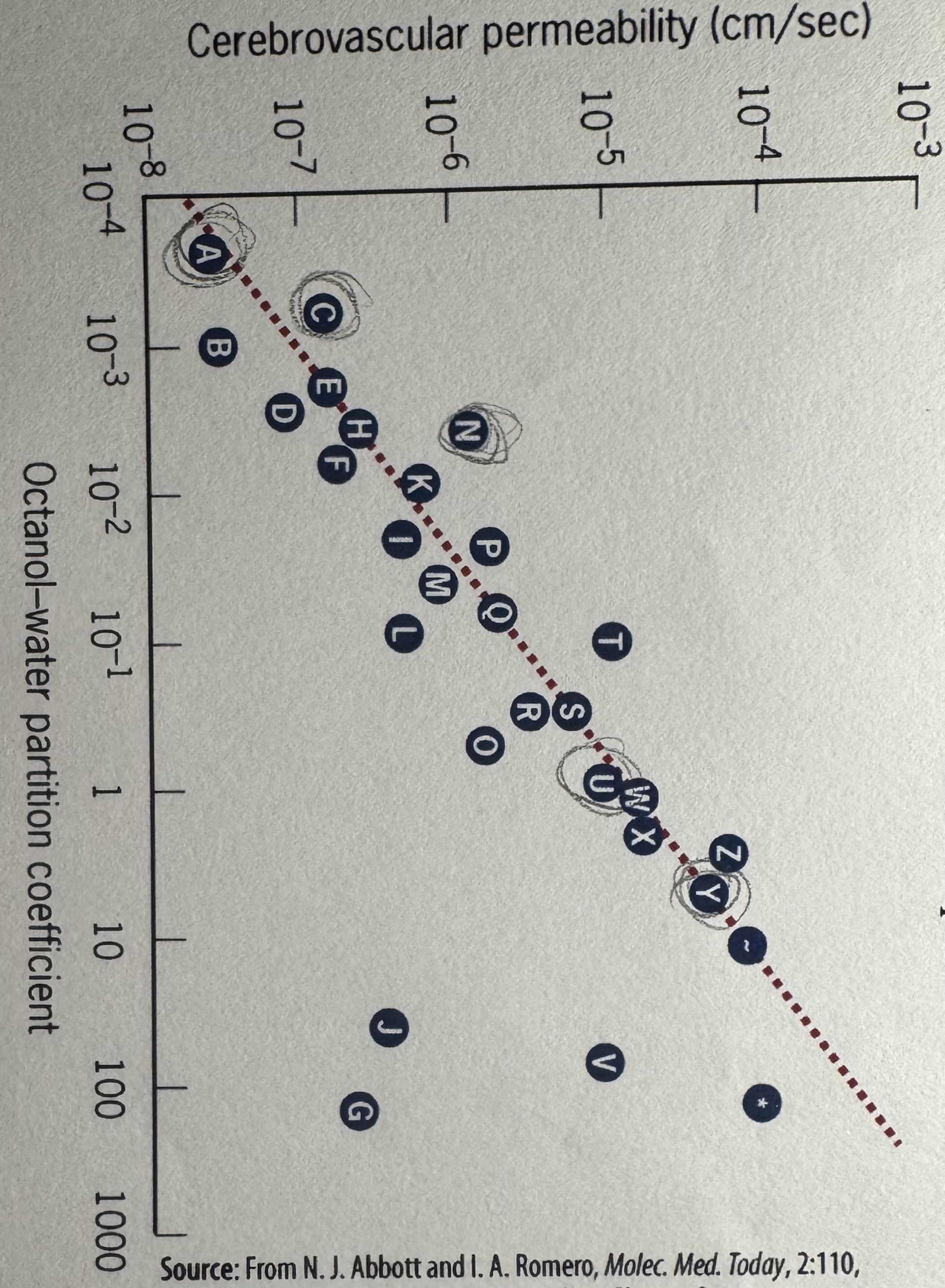
Using the partition coefficient plot, which of the following molecules is most likely to pass through the plasma membrane without being helped by any protein/transporter?
A. mannitol
B. sucrose
C. antipyrine
D. glycerol
E. metronidazole
C. antipyrine
How would you describe the phospholipid movement of a cell membrane?
A. Transverse movement is fast, lateral movement is slow.
B. Transverse movement is slow, lateral movement is fast.
C. Transverse and lateral movement are both slow.
D. Transverse and lateral movement are both fast.
B. Transverse movement is slow, lateral movement is fast.
Which of the following examples best describes the active transport of a solute?
A. Water molecules moving through aquaporin.
B. Glucose transport using the GLUT4 transporter.
C. Transport of O2 through the plasma membrane.
D. Movement of H+ through a proton pump.
E. All of these are examples of active transport.
D. Movement of H+ through a proton pump.
the cell employs ___ to make microfilaments more stable.
a. capping proteins
b. arp 2/3 complexes
c. myosins
d. monomer-sequestering protein
e. none of these
a. capping proteins
embryo development requires neural crest cells to migrate to proper locations. if you experimentally make fibronectin protein unavailable in the extracellular matrix, what happens?
a. neural crest cell migration is disturbed
b. neural crest cells convert into epithelial cells
c. neural crest cells divide
d. neural crest cells die
e. neural crest cells migrate as usual
a. neural crest cell migration is disturbed
what kind of molecule does not pass through the gap junction?
a. cAMP
b. Na+ ions
c. ATP
d. Ca2+ ions
e. ribosomal RNA
e. ribosomal RNA
what term refers to the fact that growing and shrinking microtubules can coexist and that a given microtubule can switch back and forth between growing and shortening?
a. dynamic instability
b. dynamic equilibrium
c. catastrophe
d. flagellar transport
e. treadmilling
a. dynamic instability
all collagen family members consist of ___ chains arranged in a ____ in at least part of their length.
a. 3, double helix
b. 2, double helix
c. 3, triple helix
d. 3, triple lattice
e. 2, triple helix
c. 3, triple helix
how do mitochondria generate and store energy to produce ATP during aerobic respiration?
a. by increasing mitochondrial Ca2+ concentration
b. by producing reactive oxygen species
c. by generating a proton electrochemical gradient
d. by generating a heat gradient
e. by generating a Na+ electrochemical gradient
c. by generating a proton electrochemical gradient
you coat a petri dish with fibronectin and proteoglycans and then culture cells on the dish. the cells adhere to the dish. you repeat the experiment, but this time, add abundant RGD tripeptides to the culture dish as the cells are added. what happens?
a. the cells die immediately
b. the cells divide immediately
c. the cells do not adhere to the dish
d. the cells adhere as they usually do
c. the cells do not adhere to the dish
in a severely over contracted muscle, which band or zone may disappear?
a. a band
b. i band
c. h zone
d. a band and h zone
e. i band and h zone
e. i band and h zone
in an overstretched myofibril where sarcomeres are 50% longer, do you expect the contractile strength to be
a. the same
b. greater
c. reduced
c. reduced
during muscle contraction,
a. the length of the I bands is decreased
b. the length of the A band is increased
c. both thick and thin filaments are shortened
d. there is no changes in the length of A and I bands
a. the length of the I bands is decreased
when ATP formation is driven by energy released from electrons removed during substrate oxidation. the process is called ____.
a. ATP phosphorylation
b. oxidative phosphorylation
c. electron transportation
d. electrochemical gradient formation
b. oxidative phosphorylation
which of the following features unlikely play a role in the dynamic assembly and disassembly of cytoskeletons?
a. covalent bonds hold cytoskeletons building units together
b. cytoskeletons have filamentous structures
c. the binding affinity between the building units in existing cytoskeletal filaments is changeable
d. cytoskeleton are polymers
e. none of these (all features are good for cytoskeletal dynamics)
a. covalent bonds hold cytoskeletons building units together
what substance joins proteoglycans together into gigantic complexes called proteoglycan aggregates?
a. fibronectin
b. hyaluronic acid
c. laminin
d. oligosaccharide
b. hyaluronic acid
in an in-vitro ATP production experiment, your test tube has purified live mitochondria. what substrate would you add to the tube to allow mitochondria to make ATP?
a. fructose-6-phosphate
b. pyruvate
c. glycogen
d. lactic acid
e. glucose
b. pyruvate
which parts of the ATP synthase act as rotors during ATP synthesis?
a. C ring and gamma subunit
b. beta subunit
c. alpha and beta subunits
d. peripheral stalk
a. C ring and gamma subunit
which of the following statements about myosin is NOT true?
a. the fibrous tail of myosin II plays a structural role in forming the thick filaments in muscle cells
b. myosin-mediated contraction is essential in separating two daughter cells during cell division
c. unconventional myosins can walk on actin filaments and carry cargo
d. unconventional myosins differ from the conventional type of myosins in that they move toward the minus end of an actin filament
e. none of the above (all are true)
d. unconventional myosins differ from the conventional type of myosins in that they move toward the minus end of an actin filament
which of the following sets of molecules are necessary for mitochondria to be appropriately positioned within the cell?
a. microtubules, myosin, ATP, GTP
b. microtubules, kinesin, ATP
c. actin filaments, dynein, ATP
d. intermediate filaments, dynein, ATP
e. none of the above is needed because mitochondria always stay in the same positions
b. microtubules, kinesin, ATP
cytoskeleton proteins, including microtubules and actin filaments, are unevenly distributed in polarized cells, such as epithelial and nerve cells.
a. false
b. true
b. true
actin binding proteins (not myosins) play various important roles. which of the following functions is not provided by actin-binding proteins?
a. promoting polymerization for actin filament growth
b. creating strong structures (actin filament network) by cross-linking and bundling
c. stabilizing the length of an actin filament
d. transporting actin filaments to the desired cellular location
e. facilitating nucleation
d. transporting actin filaments to the desired cellular location
what is thought to promote the release of cells from an epithelium and their transformation into mesenchymal (migrating) cells?
a. a reduction in the expression of E-cadherin genes
b. an increase in the expression of E-cadherin genes
c. degradation of the cellular cytoskeletons
d. the cytoplasm taking on an anti-adhesive character
a. a reduction in the expression of E-cadherin genes
which of the following about the focal adhesion is incorrect?
a. it helps to adhere epithelial cells to the basal membrane
b. it connects to microtubules to develop interaction with the extracellular matrix
c. it connects to actin filaments using integrins and various adaptors
d. it may play a role in collecting information about the chemical properties of the extracellular environment
b. it connects to microtubules to develop interaction with the extracellular matrix
the functions of the cytoskeleton include
a. generating forces needed for cellular locomotion
b. serving as an internal framework to position organelles
c. making up the core structure of cilia and flagella
d. serving as a scaffold to provide structural support and maintain cell shape
e. all of these are correct
e. all of these are correct
motor proteins, including myosin, dynein and kinesin, utilize energy stored in the proton electrochemical gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane transport cytosolic pyruvate and ADP into the matrix
a. true
b. false
b. false
motile cells in culture, when treated with cytochalasin D, which blocks plus ends of actin polymerization, will
a. keep extending protrusions
b. adhere more strongly to the culture dish
c. stop extending protrusions and freeze
d. immediately die by apoptosis
c. stop extending protrusions and freeze
what is the terminal electron acceptor of the electron transport chain in cells undergoing aerobic respiration?
a. H2O2
b. CO2
c. water
d. CO
e. O2
e.O2
The intermediate filaments _____
a. are rope like and more flexible compared to microtubules
b. required both phosphorylation and GTP for polymerization
c. do not directly associate with motor proteins, such as dyneins and kinesins for cellular transportation
d. are made up for 5 polypeptides that share a similar a-helix structure
e. two of the answers are correct
e. two of the answers are correct (a. and c.)
types of electron carriers for the electron transport chain in the mitochondria include all of the following except _______.
a. acetyl Co-A
b. cytochromes
c. flavoproteins
d. ubiquinone
a. acetyl Co-A
which is NOT true regarding glycolysis of one glucose molecule?
a. it involves multiple enzymatic reactions in the mitochondrial matrix
b. it produces 2 pyruvates
c. it changes 2NAD+ to 2 NADH
d. the initial reactions consume 2 ATP but the later reactions produce 2 ATP
a. it involves multiple enzymatic reactions in the mitochondrial matrix
which of the following statements about the TCA cycle is incorrect?
a. it releases CO2
b. it produces the reduced form of coenzyme NADH and FADH2
c. it extracts the energy stored in fatty acids, proteins, and carbohydrates
d. it uses pyruvate as a starting reactant
d. it uses pyruvate as a starting reactant
which of the following is an essential step during oxidative phosphorylation?
a. high energy electrons are passed from FADH2 and NADH to electron carriers
b. transfer of glucose into mitochondrial matrix
c. transfer of electrons from NADH products produces two molecules of ATP
d. protons produce ATP during electron transport
a. high energy electrons are passed from FADH2 and NADH to electron carriers
in an experiment, you make actin filament polymers in vitro. you added purified G-actin, ATP, ADP, GTP, GDP, and a buffer solution to your test tube. after the polymers are formed, which molecule will be depleted (ie. found at a much lower concentration)?
a. GDP
b. GTP
c. ATP
d. ADP
e. none of the above
c. ATP
phosphorylation and dephosphorylation are involved in the assembly and disassembly of _____.
a. f-actin
b. microfilaments
c. intermediate filaments
d. microtubules
c. intermediate filaments
a new type of “alien microtubules (aMTs)” has been discovered by scientists. the aMTs are comprised of heterodimers of tubulin A and B molecules. also, aMTs polymerize in the presence of GTP and have 11 protofilaments arranged in a hollow tube. which of these characteristics of aMTs makes them different from typical eukaryotic microtubules?
a. using GTP instead of ATP
b. the number of protofilaments
c. heterodimers instead of polymers of one subunit
d. the hollow tube
e. all of the above
b. the number of protofilaments
a glucose molecule completely catabolized by glycolysis and the TCA cycle can produce a net total of ___ ATPs
a. 36
b. 2
c. 50
d. 72
a. 36
each microtubule is a polarized polymer. its polymerization (incorporating new tubulins) can occur in both the minus and the plus ends when associating with a centrosome.
a. true
b. false
b. false
GTP hydrolysis in a ____ increases its chance for ____.
a. microfilament, disassembly
b. intermediate filament, forming tetramer
c. microtubule, polymerization
d. microtubule, disassembly
d. microtubule, disassembly
____ are members of an integral membrane glycoprotein family that bind to specific sugar arrangements in oligosaccharides that project from the surfaces of other cells
a. integrins
b. calmodulins
c. selectins
d. immunoglobulin superfamily proteins
e. cadherins
c. selectins
which of the following statements about fast twitch fibers in skeletal muscle are true?
a. they are rich in mitochondria
b. they tend to generate less force than slow twitch fibers
c. they can generate most of their ATP anaerobically
d. they can contract continuously to generate a lot of force for hours without any fatigue
c. they can generate most of their ATP anaerobically
microscope beads are attracted with dynein and subjected to an in vitro mobility assay. in what direction and along what cytoskeletal element are they seen to move?
a. toward the plus end of the intermediate filament
b. toward the plus end of the microfilament
c. toward the minus end of the microtubule
d. toward the minus end of the microfilament
e. toward the plus end of the microtubule
c. toward the minus end of the microtubule
an enzyme family called matrix metalloproteinases degrades the extracellular matrix
a. true
b. false
a. true
the number of mitochondria can be increased ______
a. by spontaneous self-assembly through a fusion process
b. by budding off from the rough endoplasmic reticulum
c. by budding off from the Golgi apparatus
d. through the fission of preexisting mitochondria
d. through the fission of preexisting mitochondria
which of the following structures facilitates the rapid nucleation of microtubules inside a cell?
actin binding protein
centrosomes
basal bodies
cilia
flagella
a. 2, 3, 4
b. 3, 5
c. 2, 3
d. 1, 2, 3
c. 2, 3
you are studying a cell-to-cell connection in a cultured cell cluster. you inject fluorescein, a small fluorescent dye, into a single cell in the cluster. after a brief period, the dye spreads to cells neighboring the injected cell. you conclude that this is due to _____ that connect the cells.
a. cell-matrix junctions
b. adherens junctions
c. desmosomes
d. tight junctions
e. gap junctions
e. gap junctions
Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) experiments are commonly used to study cytoskeletons' dynamic assembly and disassembly. You genetically tagged microtubules with GFP in cultured cells to test the effect of a cancer drug, vinblastine, on the microtubule dynamics. You added the drug immediately after photobleaching a cytosolic region. You found that GFP signals in the photobleached area recover minimally after 5 minutes. Still, the GFP-labeled filaments in the non-photobleached area are unchanged. You conclude that vinblastine
a. stabilizes microtubules, preventing them from dynamic assembly and disassembly
b. promotes microtubule disassembly, making microtubules difficult to assemble and elongate
c. caps the minus end, preventing the addition of new aB-tubulin dimers to existing microtubules
d. blocks the basal body complex, making it unavailable for microtubules to assemble
a. stabilizes microtubules, preventing them from dynamic assembly and disassembly
what advantage do the cristae confer on the mitochondria?
a. they allow mitochondria to control TCA cycle better
b. they significantly increase the surface area for proteins involving electron transport and ATP synthesis
c. they allow mitochondria to have cytoskeletal support
d. they allow enzymes of the TCA cycle to react with substrates
b. they significantly increase the surface area for proteins involving electron transport and ATP synthesis