Cell Signaling and Signal Transduction Mechanisms in Cell Biology
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
Signal transduction
The process by which cells receive external signals through receptor molecules and convert them into a cellular response.

Receptor
Molecules that receive external signals and initiate a cellular response.
Transduction
The process of converting a signal into another form, often involving stepwise regulation of intracellular signaling proteins.
Cellular response
The outcome of signal transduction, which can involve gene expression, membrane transport, metabolism, cell growth/death, etc.
Signal transduction cascade
Sequential biochemical events that transfer a signal through a series of reactions activating intermediate molecules to a final target.
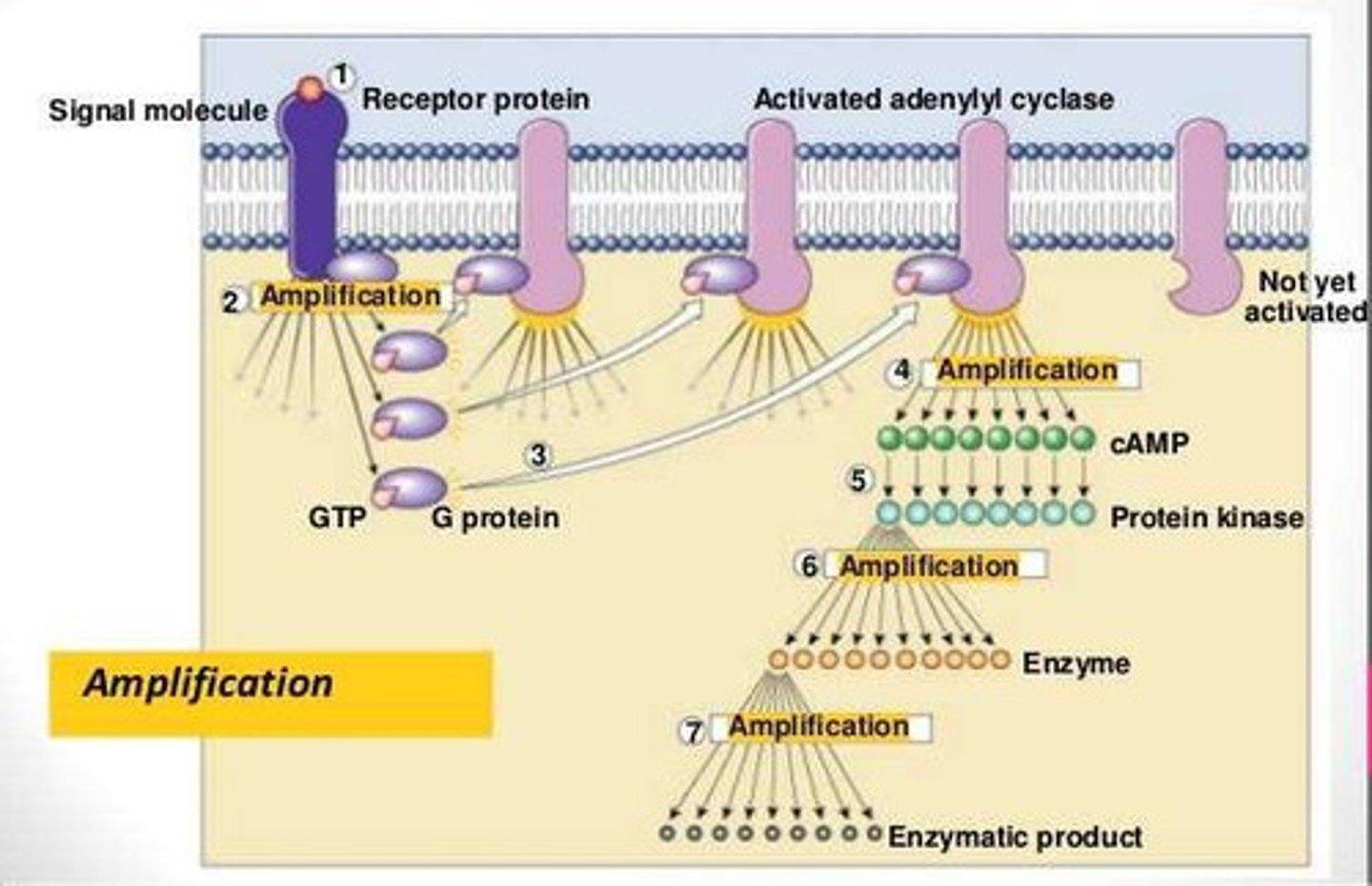
Amplification in signaling cascades
The process by which signaling cascades produce multiple intracellular activated molecules for every one receptor that is bound.
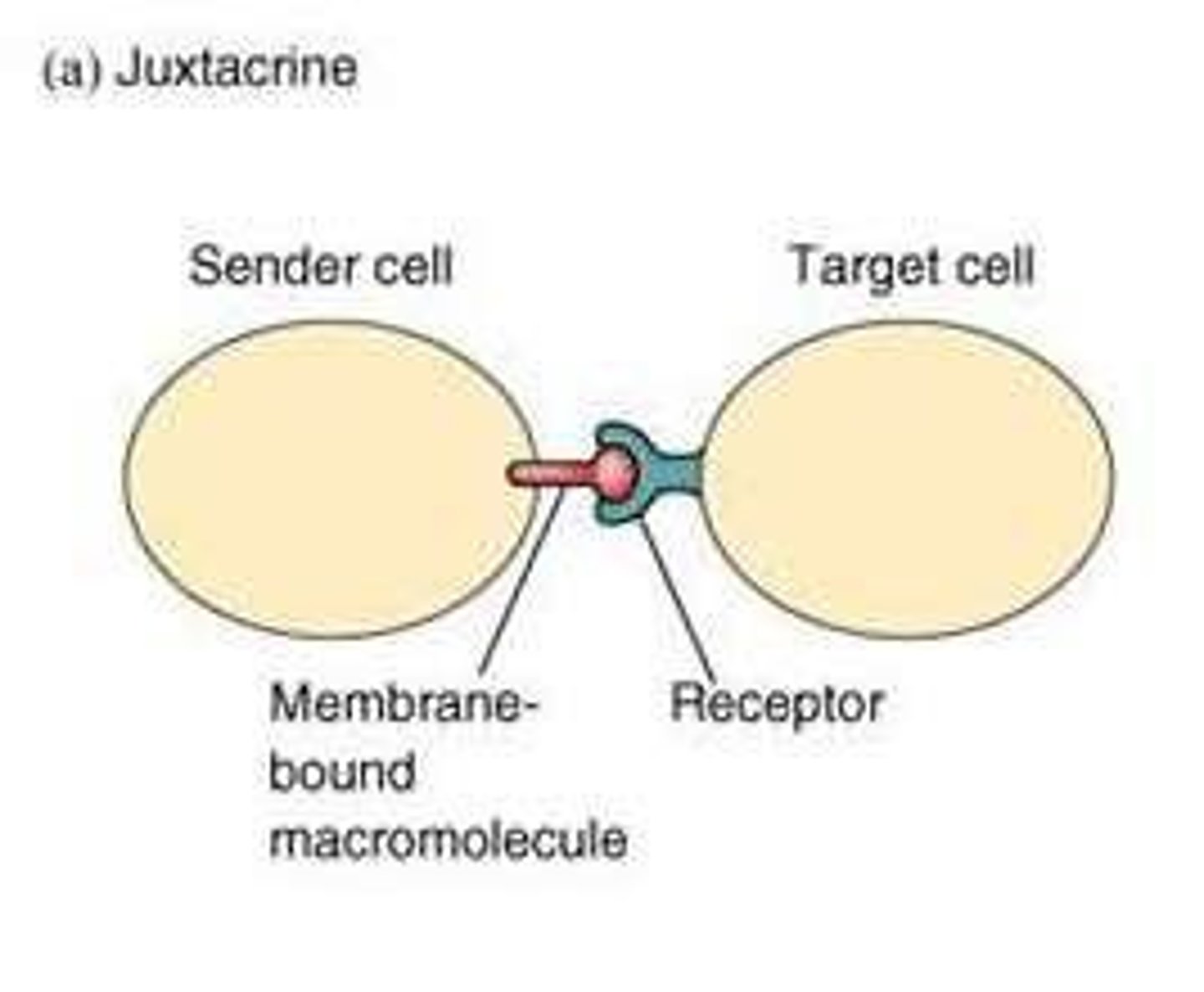
Juxtacrine signaling
Cell-cell communication that requires direct contact between cells via surface proteins.
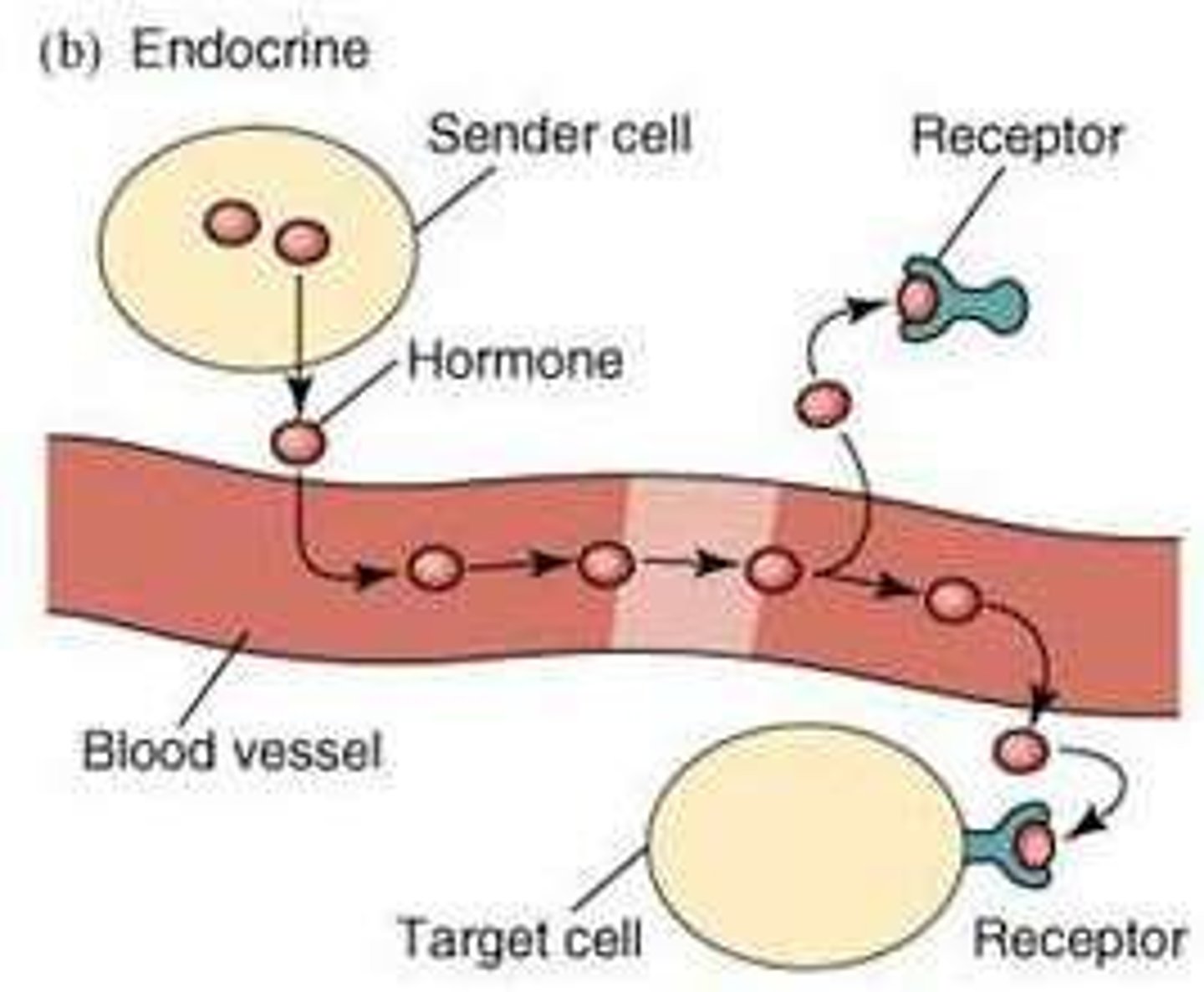
Endocrine signaling
Hormones secreted into the bloodstream at low concentrations (10^-12 - 10^-9 M) without cell-cell contact, requiring high affinity receptors.
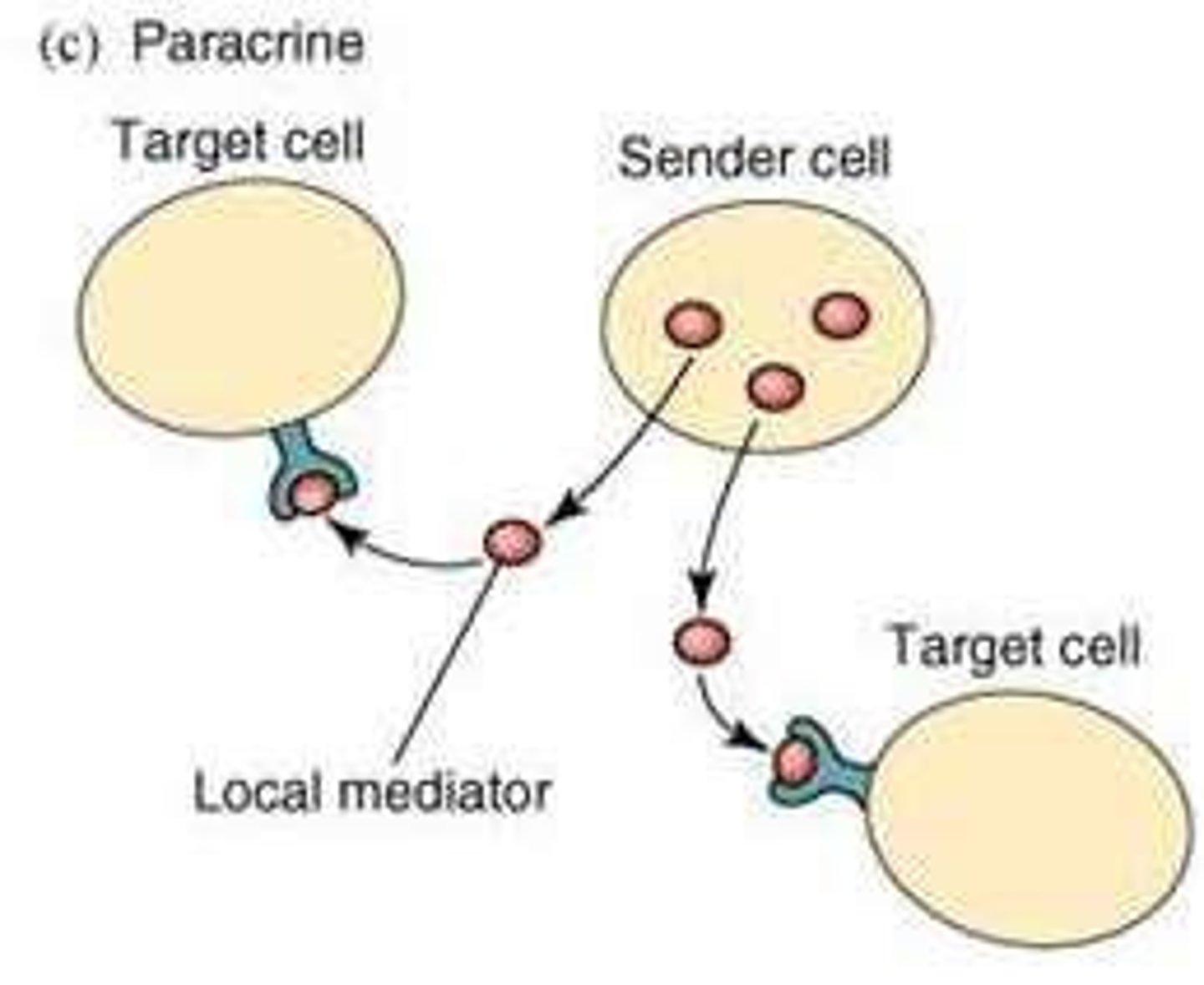
Paracrine signaling
Secreted ligands that target nearby cells at relatively high local concentrations (10^-9 - 10^-6 M) with lower affinity receptors and rapid responses.
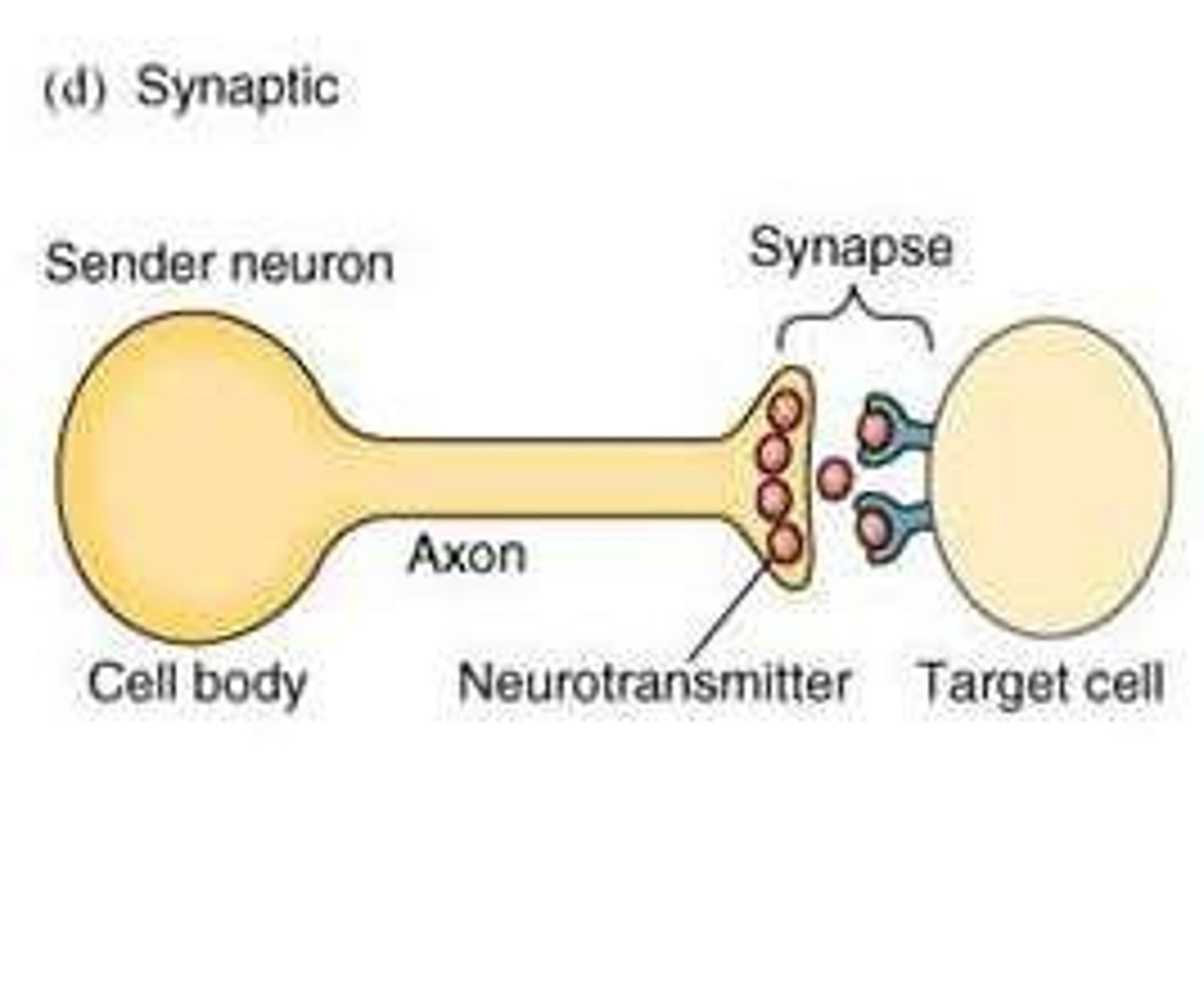
Synaptic signaling
A type of paracrine signaling that occurs at synapses between neurons and targets, characterized by very high local concentrations (10^-6 - 10^-3 M) and rapid response times.
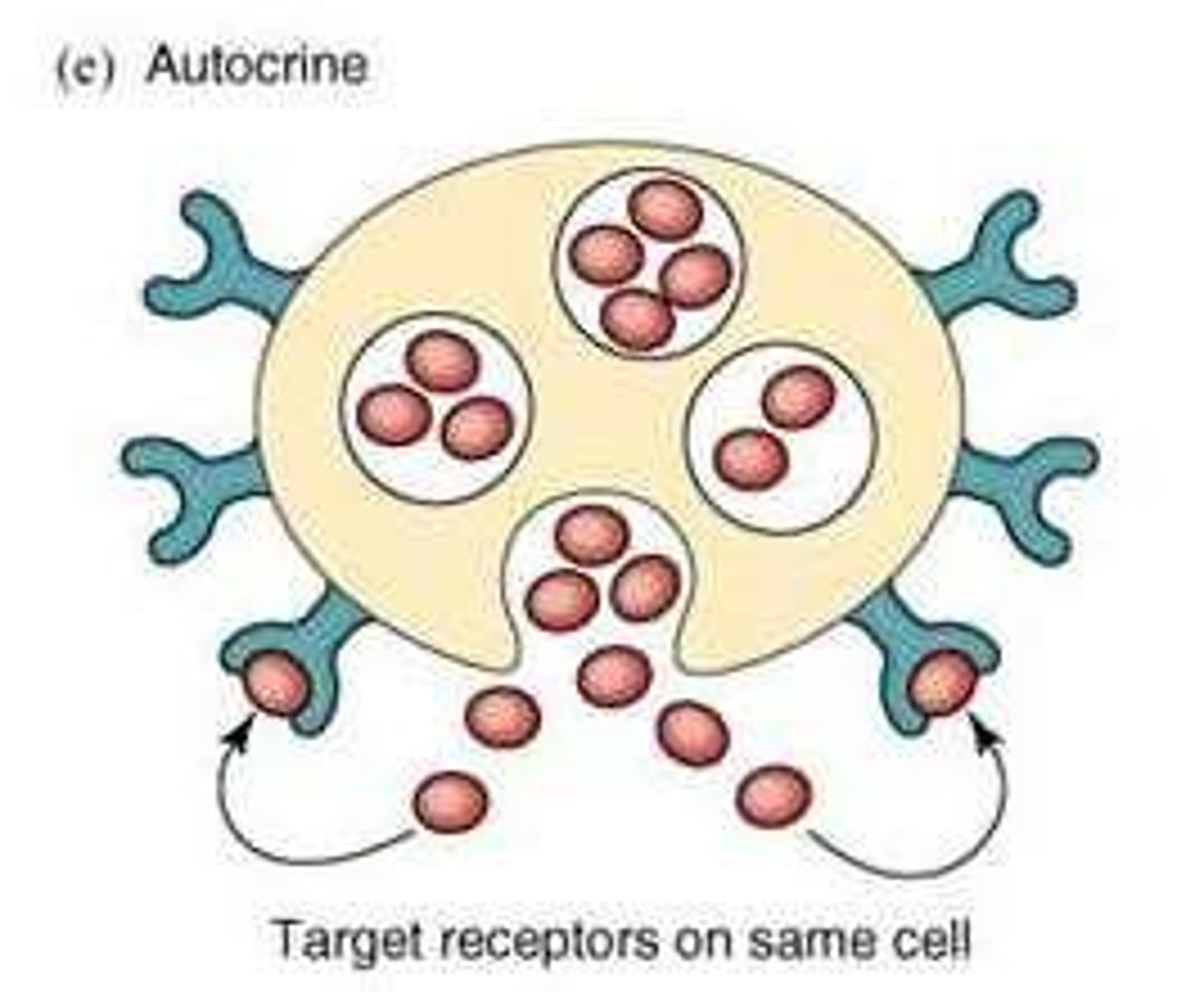
Autocrine signaling
A form of signaling where the sender and target are the same cell, with response times similar to paracrine signaling.
First messengers
Secreted molecules that act as ligands for receptors, which can be large (e.g., proteins) or small (e.g., amino acids, lipids).
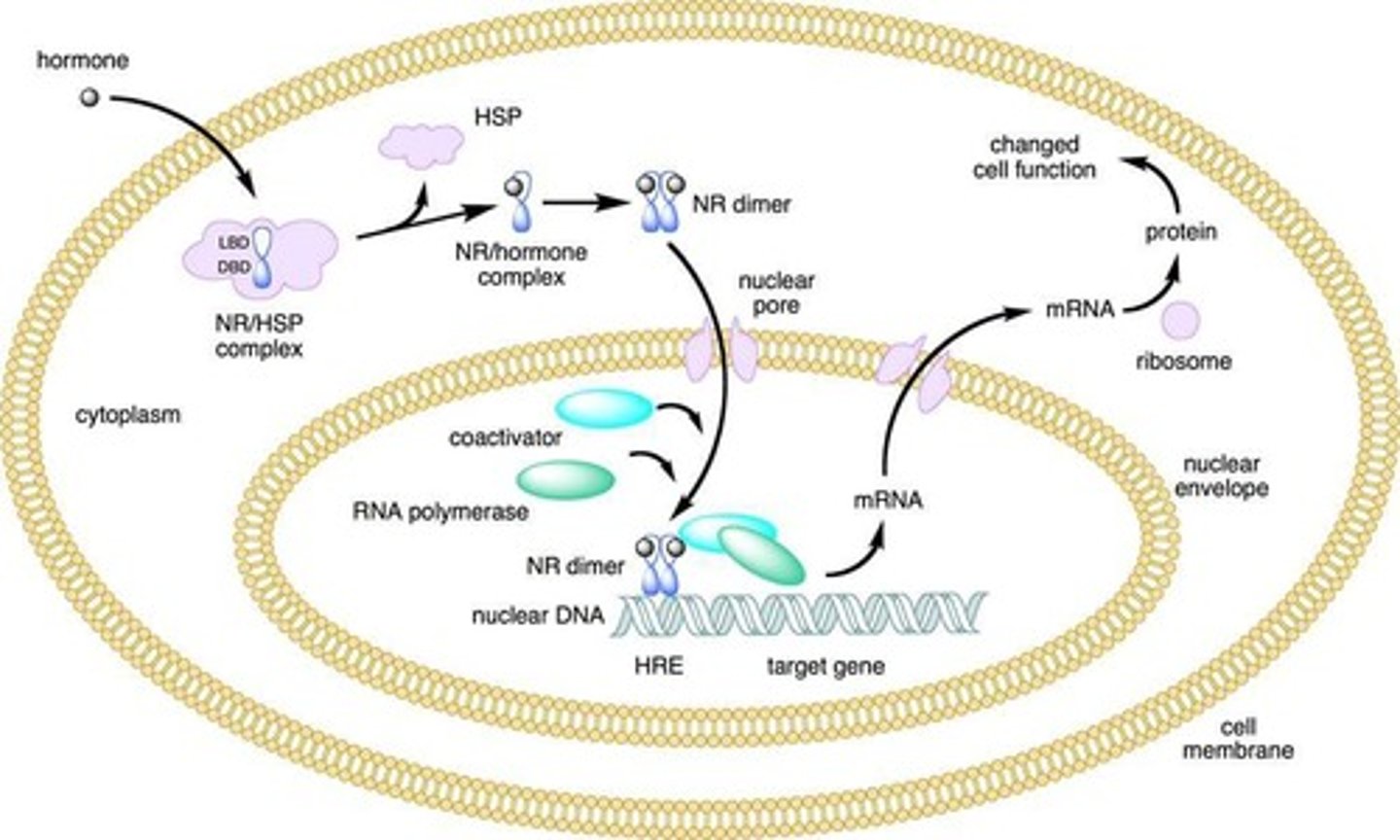
Intracellular receptors
Receptors located inside the cell that respond to hydrophobic ligands such as steroid hormones and thyroid hormones.
Integral membrane proteins
A type of receptor that spans the plasma membrane and interacts with external signals.
Hydrophobic ligands
Ligands that can diffuse through the plasma membrane and bind to intracellular receptors.
Lipid-soluble hormones
Hormones that can pass through the plasma membrane to bind intracellular receptors, leading to altered gene expression.
Response time for endocrine signaling
Minutes to hours, depending on the hormone and its receptor.
Response time for paracrine signaling
Seconds to minutes, characterized by rapid and transient responses.
Response time for synaptic signaling
Milliseconds, due to the short distance between neurons and targets.
Response time for autocrine signaling
Similar to paracrine signaling, typically rapid.
Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal conditions among tissues and organs, facilitated by signal transduction.
Intracellular receptor example
Hormonal nuclear receptor
HRE
Highly specific to given hormone/NR
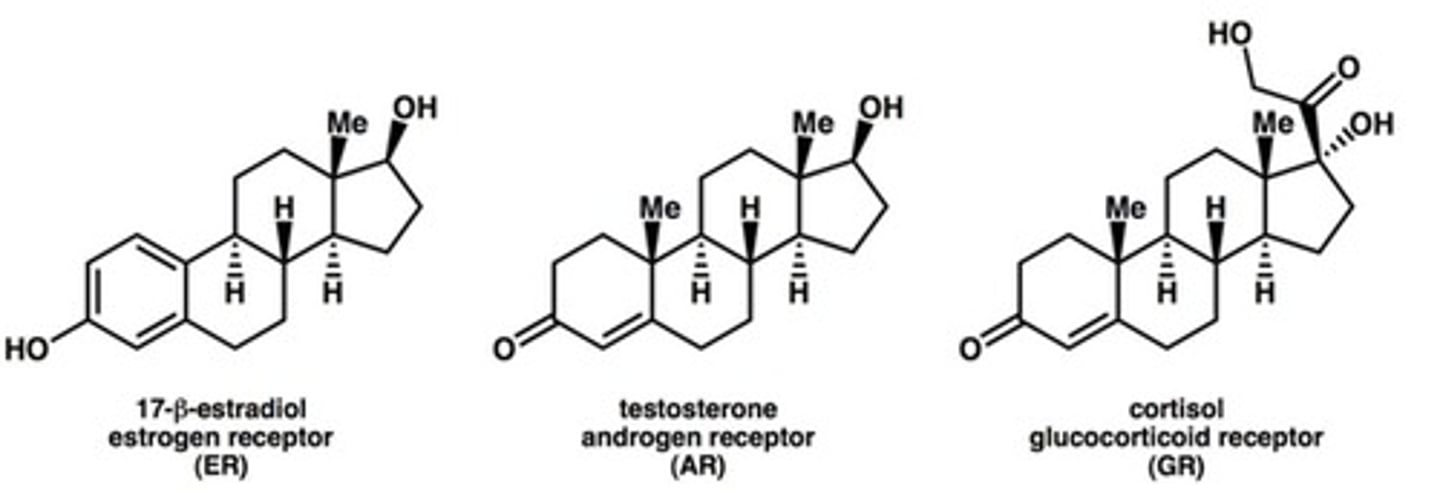
Steroid nuclear receptors
Initiate the signaling processes activated by steroid hormones (e.g. estrogen, glucocorticoid, progesterone, androgen)
Gene expression changes
Results in changes in gene expression over hours to days
Nuclear receptor proteins
Certain steroid receptors that are transcription factors
Unique property of nuclear receptors
Direct interaction with DNA and control of gene expression
Nuclear receptors' role
Key to embryonic development, adult homeostasis, and metabolism
Receptor binding process
After receptors bind their steroid, the receptor binds to specific sites on DNA, associates with coactivators, and activates transcription
FDA approved drugs targeting nuclear receptors
Targets of 10-20% of FDA approved drugs
Heterodimer nuclear receptor example
Retinoid X receptor LXR-β and liver X receptor RXR-α bound to DNA response element
DBD-hinge-LBD
DNA binding domain; ligand binding domain
Estrogen receptor α
Over expressed in ~70% breast cancer
Tamoxifen
ER antagonist in breast tissue
Intracellular receptor example 2
Thyroid nuclear receptor
Thyroid hormone
A lipid-soluble hormone that diffuses through the plasma membrane
Dimerization of receptor
Thyroid hormone binds receptor and promotes dimerization of receptor
Coregulatory proteins
Recruitment of coregulatory proteins promotes DNA binding and specific recognition of thyroid response element (TRE)
Signaling outcome of thyroid hormone
To turn on or off transcription
Second type of receptor for first messenger ligands
Integral membrane proteins
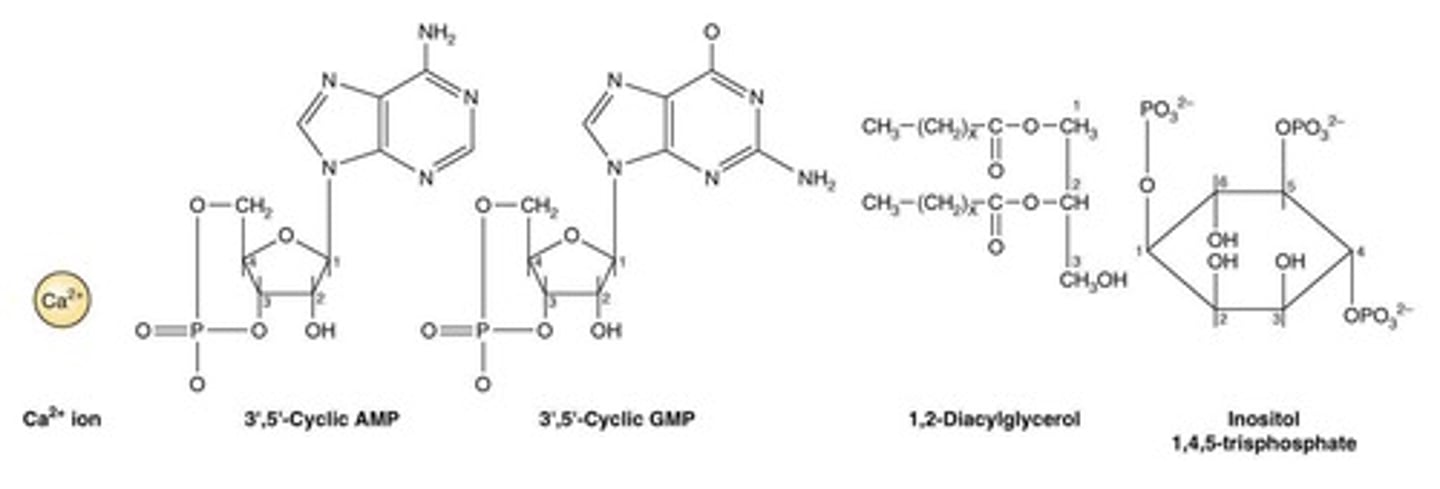
Second messengers
Small, intracellular molecules that transmit and amplify the initial signal from extracellular 1st messenger binding to receptors
Examples of second messengers
Inorganic ions or organic products of enzyme-catalyzed reactions (e.g. Ca2+, cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, Diacylglycerol, Phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-triphosphate)
Protein phosphorylation
Modification by phosphorylation controls protein-protein interactions and enzymatic activity
Phosphorylation
Modification by phosphorylation controls protein-protein interactions and enzymatic activity.
Protein Kinase
An enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from ATP to proteins.
Phosphatase
An enzyme that removes phosphate groups from proteins, reversing the action of kinases.
Enzymatically inactive
A state of a protein where it does not catalyze reactions.
Enzymatically active
A state of a protein where it catalyzes reactions.
Downstream signaling
The process by which signals are transmitted within a cell after receptor activation.
GTP-binding regulatory proteins
Proteins that bind and hydrolyze GTP, functioning as molecular switches.
G proteins
Molecular switches that exist in OFF/ON states and interact with downstream signaling proteins.
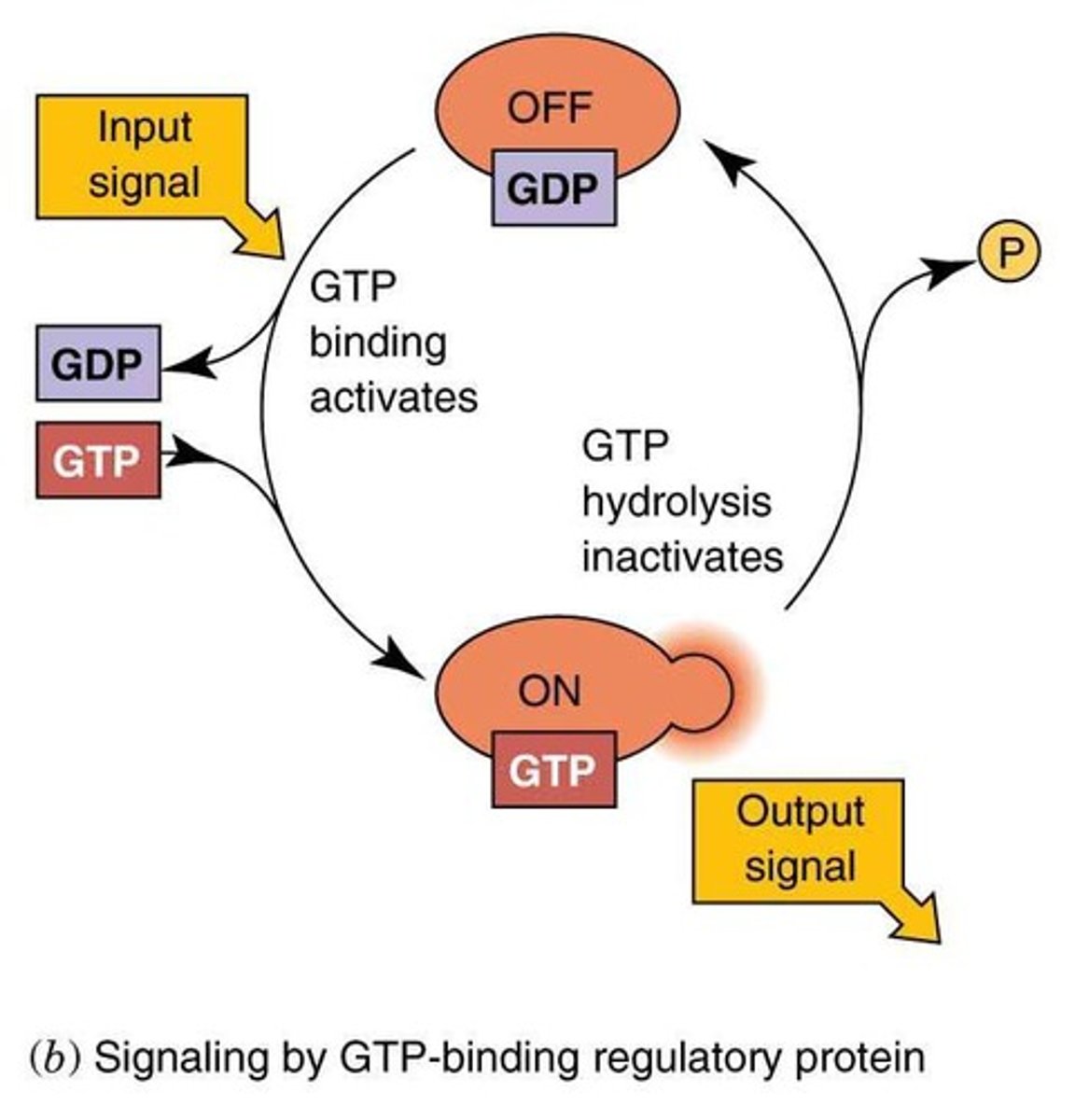
GDP-bound form
The inactive conformation of a G-protein when bound to GDP.
GTP-bound form
The active conformation of a G-protein when bound to GTP.
Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs)
Proteins that catalyze the exchange of GDP for GTP on G-proteins.
GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs)
Proteins that facilitate GTP hydrolysis, turning off the G-protein signal.
Receptor Binding
The interaction between a ligand and its receptor, initiating a signaling cascade.
Spare receptors
Receptors that are not fully occupied by ligands but still contribute to signaling.
Termination of signaling
The process of stopping a signal, which can involve reducing ligand availability or receptor desensitization.
Rapid re-uptake
The mechanism by which neurotransmitters are quickly taken back into the presynaptic neuron.
Acetylcholine esterase
An enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft.
Receptor desensitization
A decrease in receptor responsiveness to the same concentration of agonist.
Protein-protein interactions
Interactions between proteins that can be modulated by phosphorylation.
Amplification
The process by which a small signal is enhanced to produce a larger cellular response.