AP Psych - Developmental Psychology
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
1
New cards
behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and enviromental influences on behavior
2
New cards
enviroment
every nongenetic influence
3
New cards
chromosomes
threadlike structures made of **DNA** that contain **genes**
4
New cards
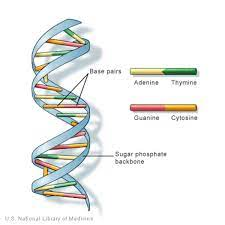
DNA
molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
5
New cards
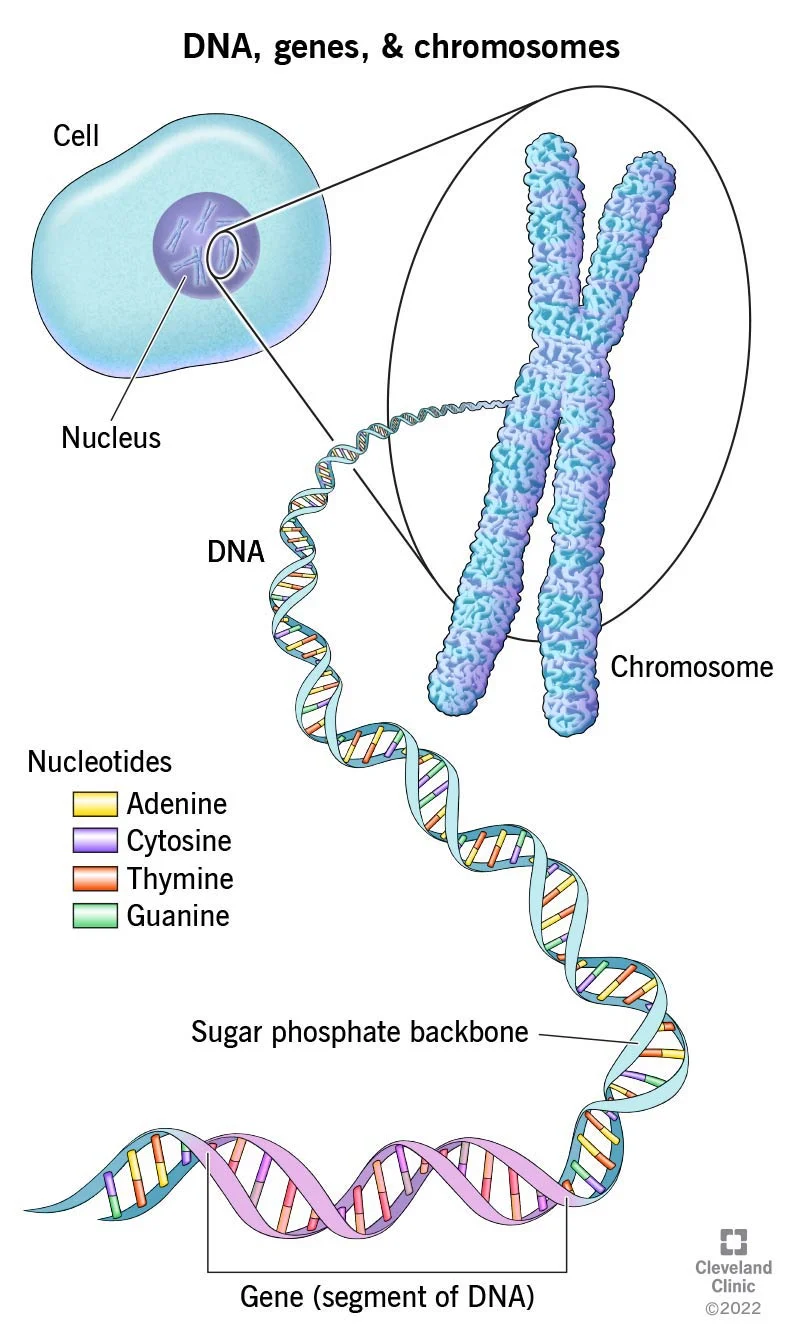
genes
small segments of DNA
6
New cards
genome
the complete instuctions for making an organism, consisting of all the genetic material in that organism’s chromosomes
7
New cards
identical twins
twins who develop from a single fertalized egg that splits into two
8
New cards
fraternal twins
twins who develop from seperate fertilized eggs
9
New cards
temperment
a person’s characteristic emotional reactivity and identity
10
New cards
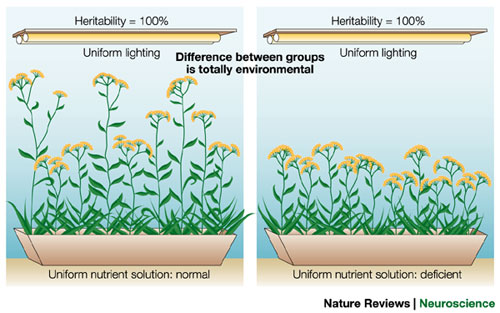
heritability
the proportion of variation among individuals we can attribute to **genes**
11
New cards
molecular genetics
subfield of biology that studies the molecular structure and function of **genes**
12
New cards
evolutionary psychology
study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using priciples of **natural selection**
13
New cards
natural selection
the principle that, among a range of inherited trait variations, those that lead to increased reproduction and survival are most likely to be passed on to succeding generations
14
New cards
mutation
a random error in gene replication that leads to a change
15
New cards
culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
16
New cards
norm
an understood rule for accepted an expected behavior
17
New cards
individualism
prioritizing one’s own goals over group goals and defining one’s identity interms of personal attributes rather than group identification
18
New cards
collectivism
prioritizing the goals of one’s group and defining one’s identity accordingly
19
New cards
social learning theory
theory that we learn social behavior by observing and imitating and by being rewarded and punished
20
New cards
developmenal psychology
a branch of psychology that studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the life span
21
New cards
zygote
* fertilized egg
* conception - 2 weeks
* conception - 2 weeks
22
New cards
embryo
* developing organism
* 2 weeks - 8 weeks
* 2 weeks - 8 weeks
23
New cards
fetus
* developing organism
* 9 weeks - birth
* 9 weeks - birth
24
New cards
tetrogens
agents, such as chemicals and viruses, that can reach the embryo or fetus during prenatal development and cause harm
25
New cards
fetal alcohol syndrome (FAS)
physical and cognitive abnormalities caused by a pregnant person’s heavy drinking
26
New cards
habituation
decreasing responsiveness with repeated stimulation
27
New cards
maturation
biological growth processes that enable changes in behavior
28
New cards
cognition
all the mental activities associated w/ thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
29
New cards
schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
30
New cards
assimilation
interpreting our new experience in terms of our existing **schemas**
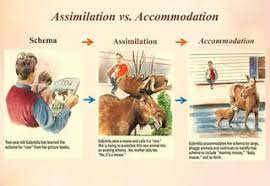
31
New cards
accommodation
adapting our curent understandings (**schemas**) to incorporate new information
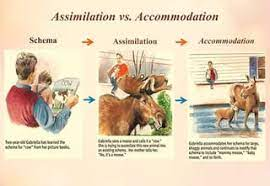
32
New cards
Piaget’s Stages of Cognitive Deveopment
__**Sensorimotor**__
* birth - 2 years
* experiencing the world through senses and actions (looking, hearing, touching, mouthing, grasping)
* **object permanence, stranger anxiety**
__**Preoperational**__
* 2 - 6/7 years
* represinting things with words and images, using intuitive rather than logical reasoning
* **pretend play, egocentricism** (difficulty percieving things from another’s point of view)
__**Concrete operational**__
* 7 - 11 years
* thinking logicially about concrete events, grasping concrete analogies and performing mathmatical transformations
* **conservation** (properties like volume remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects), **mathmatical transformations** ( 8 + 4 = 12, 12 - 4 = ?)
__**Formal operational**__
* 12 - adulthood
* abstract reasoning
* abstract logic, potential for mature moral reasoning
* birth - 2 years
* experiencing the world through senses and actions (looking, hearing, touching, mouthing, grasping)
* **object permanence, stranger anxiety**
__**Preoperational**__
* 2 - 6/7 years
* represinting things with words and images, using intuitive rather than logical reasoning
* **pretend play, egocentricism** (difficulty percieving things from another’s point of view)
__**Concrete operational**__
* 7 - 11 years
* thinking logicially about concrete events, grasping concrete analogies and performing mathmatical transformations
* **conservation** (properties like volume remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects), **mathmatical transformations** ( 8 + 4 = 12, 12 - 4 = ?)
__**Formal operational**__
* 12 - adulthood
* abstract reasoning
* abstract logic, potential for mature moral reasoning
33
New cards
attachment
* an emotional tie with another person
* seen in young children through seeking closeness with a caregiver and showing distress upon separation
* seen in young children through seeking closeness with a caregiver and showing distress upon separation
34
New cards
critical period
optimal period when certain events must take place to facilitate proper development
35
New cards
imprinting
the process by which certain animals form attachments during a **critical period** very early in life
36
New cards
basic trust
according to **Erik Erikson**, a sense that the world is predictable and trustworthy
* said to be formed during infancy through responsive caregivers
* said to be formed during infancy through responsive caregivers
37
New cards
self-concept
our understanding and evaluation of who we are
38
New cards
cross-sectional study
a study in which people of different ages are compared w/ one another
39
New cards
longitudinal study
research in which the same people are studied and retested over a long period
40
New cards
crystalized intelligence
* our accumulated knowledge and verbal skills
* tends to increase with age
* tends to increase with age
41
New cards
fluid intelligence
* our ability to reason speadily and abstractly
* tends to decrease during late adulthood
* tends to decrease during late adulthood
42
New cards
social clock
the culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
43
New cards
Jean Piaget
* cognitive development
* stage theorist
* **sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, formal operational**
* stage theorist
* **sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, formal operational**
44
New cards
Lev Vygotsky
* Soviet psychologist
* believed that cognitive abilities aren’t biologicially determined, but rather shaped by the use of language and tools in the process of interacting w/ the cultural and social enviroment
* **zone of proximal development** - the gap btwn what a child is currently able to do unsupported and the level they are capable of reaching with tools provided by others (friends, adults, technology)
* **inner speech -** communication w/ oneself
* believed that cognitive abilities aren’t biologicially determined, but rather shaped by the use of language and tools in the process of interacting w/ the cultural and social enviroment
* **zone of proximal development** - the gap btwn what a child is currently able to do unsupported and the level they are capable of reaching with tools provided by others (friends, adults, technology)
* **inner speech -** communication w/ oneself
45
New cards
Erik Erikson
* German-American psychologist/psychoanalyst
* personality development - **psychosocial**
* stages of psycho-social development
* __**trust vs. mistrust**__
* infancy (1st year)
* if needs are dependable met, infants develop a sense of basic trust
* __**autonomy vs. shame and doubt**__
* toddler (2nd year)
* toddlrs learn to exercise will and do things for themselves, or they will doubt their abilities
* __**initiative vs. guilt**__
* preschooler (3 - 5 years)
* preschoolers learn to initiate tasks and carry out plans, or they feel guilty about plan to be independent
* __**competence vs. inferiority**__
* elementary (6 years - puberty)
* children learn the pleasure of applying themselves to tasks, or they feel inferior
* __**identity vs. role confusion**__
* adolescence (teens - 20’s)
* teenagers work at refining a sense of self by testing roles and then integrating them to form a single identity, or they become confused about who they are
* __**intimacy vs. isolation**__
* young adult (20's - 40’s)
* young adults find close relationships and gain the capacity for intimate love, or they feel socially isolated
* __**generativity vs. stagnation**__
* middle adult (40’s - 60’s)
* the middle-aged discover a sense of contributing to the world, or they may feel a lack of purpose
* __**integrity vs. despair**__
* late adult (late 60’s onward)
* when reflecting on their life, the older adult may feel a sense of satisfaction or failure
* personality development - **psychosocial**
* stages of psycho-social development
* __**trust vs. mistrust**__
* infancy (1st year)
* if needs are dependable met, infants develop a sense of basic trust
* __**autonomy vs. shame and doubt**__
* toddler (2nd year)
* toddlrs learn to exercise will and do things for themselves, or they will doubt their abilities
* __**initiative vs. guilt**__
* preschooler (3 - 5 years)
* preschoolers learn to initiate tasks and carry out plans, or they feel guilty about plan to be independent
* __**competence vs. inferiority**__
* elementary (6 years - puberty)
* children learn the pleasure of applying themselves to tasks, or they feel inferior
* __**identity vs. role confusion**__
* adolescence (teens - 20’s)
* teenagers work at refining a sense of self by testing roles and then integrating them to form a single identity, or they become confused about who they are
* __**intimacy vs. isolation**__
* young adult (20's - 40’s)
* young adults find close relationships and gain the capacity for intimate love, or they feel socially isolated
* __**generativity vs. stagnation**__
* middle adult (40’s - 60’s)
* the middle-aged discover a sense of contributing to the world, or they may feel a lack of purpose
* __**integrity vs. despair**__
* late adult (late 60’s onward)
* when reflecting on their life, the older adult may feel a sense of satisfaction or failure
46
New cards
Lawrence Kohlberg
* American psychologist
* stages of moral development
* __**preconventional**__
* 7 - 11 years
* moral judgements to obtain rewards and avoid punishment
* __**conventional**__
* 11 on
* moral decisions based on what they think others will think of them, based on rules/laws
* __**principled**__
* occasionally after 13
* judge actions on the basis of ethical principles, rather than the consequences
* stages of moral development
* __**preconventional**__
* 7 - 11 years
* moral judgements to obtain rewards and avoid punishment
* __**conventional**__
* 11 on
* moral decisions based on what they think others will think of them, based on rules/laws
* __**principled**__
* occasionally after 13
* judge actions on the basis of ethical principles, rather than the consequences
47
New cards
Carol Gilligan
* American psychologist
* stages of moral development, critiqued **Kohlberg** for only studing moral reasoning of boys
* __**Morality as Individual Survivor**__
* follows rules to obtain rewards and avoid punishments
* __**Morality as Self-Sacrifice**__
* obtained after becoming aware of the needs of others
* believes that they must sacrifice their own needs and meet the needs of others
* __**Morality as Equality**__
* the person views their own needs as equal to those of others
* believes that everyone’s needs should be met when possible, and that sacrifices should be shared
* stages of moral development, critiqued **Kohlberg** for only studing moral reasoning of boys
* __**Morality as Individual Survivor**__
* follows rules to obtain rewards and avoid punishments
* __**Morality as Self-Sacrifice**__
* obtained after becoming aware of the needs of others
* believes that they must sacrifice their own needs and meet the needs of others
* __**Morality as Equality**__
* the person views their own needs as equal to those of others
* believes that everyone’s needs should be met when possible, and that sacrifices should be shared
48
New cards
Harry Harlow
* American psycholgist
* **cloth/wire monkey** experiments
* the importance of caregiving and companionship to social and cognitive developments
* **cloth/wire monkey** experiments
* the importance of caregiving and companionship to social and cognitive developments
49
New cards
Sigmund Freud
* Psychoanalyst
* Unconscious
* **Id, ego, superego**
* **Free association**
* Unconscious
* **Id, ego, superego**
* **Free association**
50
New cards
Mary Ainsworth
* American-Canadian developmental psychologist
* **strange situation** procedure
* **attachment styles**
* **strange situation** procedure
* **attachment styles**
51
New cards
Jerome Kagan
* American psychologist
* showed that an infants **temperament** is quite stable over time + that certain behaviors in infancy are preductive of behaviors patterns in adolescence
* showed that an infants **temperament** is quite stable over time + that certain behaviors in infancy are preductive of behaviors patterns in adolescence
52
New cards
Judy DeLoache
* American psychologist
* **dual representation -** the concept that the ability to use a symbolic object (such as a map or a model) arises from mentally representing the object in two different ways, as an actual object and as a symbol for the object
* **dual representation -** the concept that the ability to use a symbolic object (such as a map or a model) arises from mentally representing the object in two different ways, as an actual object and as a symbol for the object
53
New cards
Karen Wynn
* Canadian psychologist
* cognative capabilities of infants and young children
* cognative capabilities of infants and young children
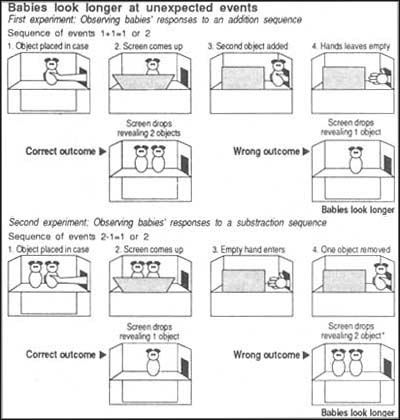
54
New cards
Diana Baumrind
* clinical and developmental psychologist
* parenting styles
* **authoritarian, permissive, authoritative**
* parenting styles
* **authoritarian, permissive, authoritative**
55
New cards
Konrad Lorenz
* American zoologist, ethologist, ornithologist
* instinctive behavior in animals
* **imprinting**
* instinctive behavior in animals
* **imprinting**