ANAT FINAL
1/51
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
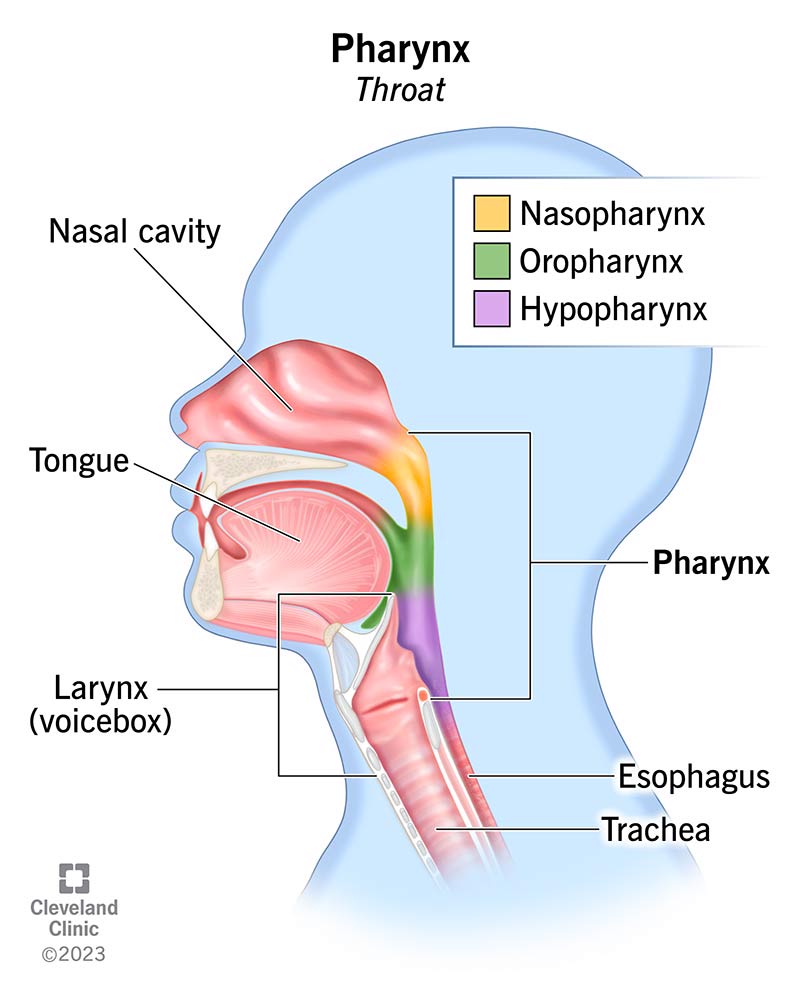
Pharynx
The second part of the digestive tract, connecting the mouth to the esophagus.
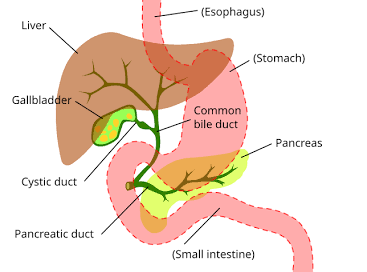
Bile
A substance produced by the liver that emulsifies fats in the intestine.
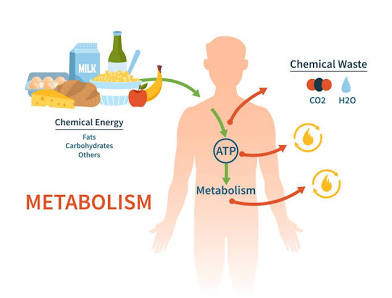
Metabolic Rate
The rate at which the body produces ATP (energy).
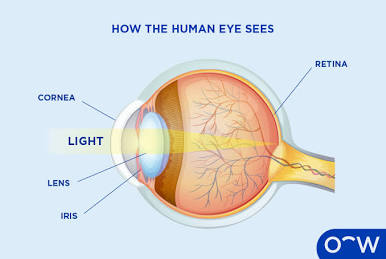
Cornea
The outermost layer of the eye that light passes through first.
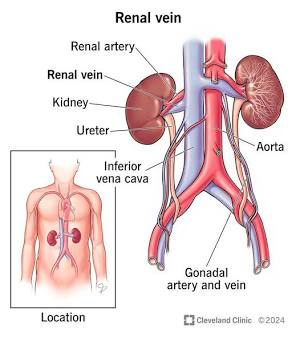
Renal Artery
A blood vessel that carries unfiltered blood to the kidney.
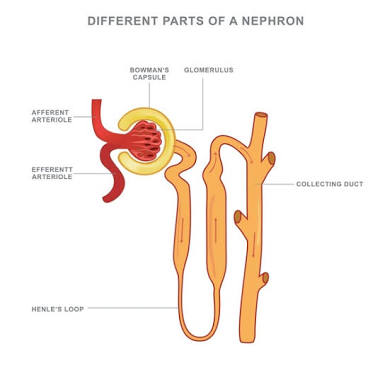
Collecting Duct
A structure in the kidney that collects urine from the nephrons.
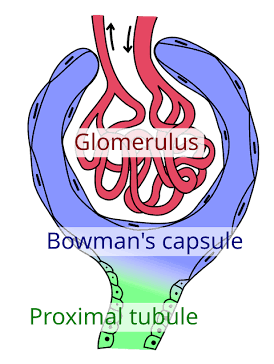
Glomerulus
A cluster of capillaries in the nephron where filtration begins.
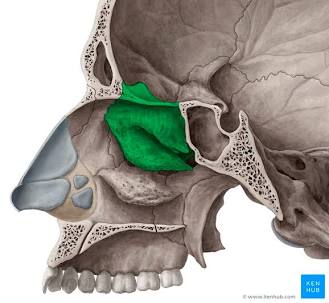
Ethmoid Bone
An internal cranial bone.
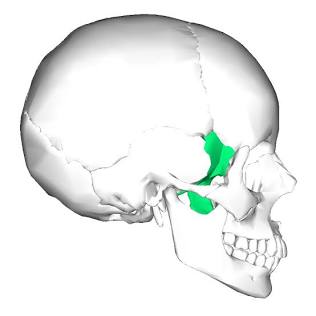
Sphenoid Bone
An internal cranial bone shaped like a bat.
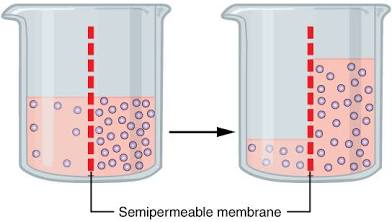
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
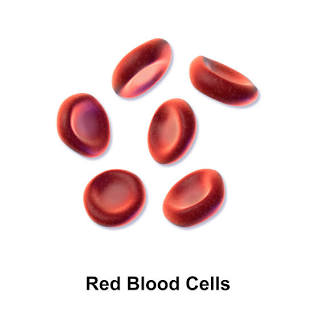
Red Blood Cells
Blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen.
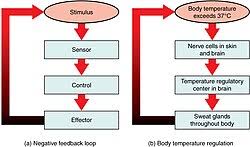
Negative Feedback
A regulatory mechanism that reduces hormone production when a set point is reached.
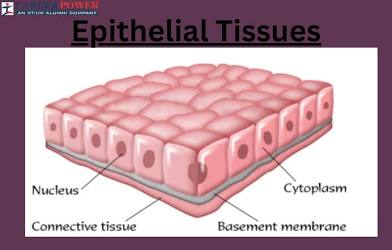
Epithelial Tissue
One of the four main tissue types of the body.

Connective Tissue
One of the four main tissue types of the body.
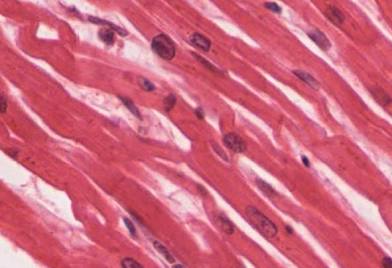
Muscle Tissue
One of the four main tissue types of the body.
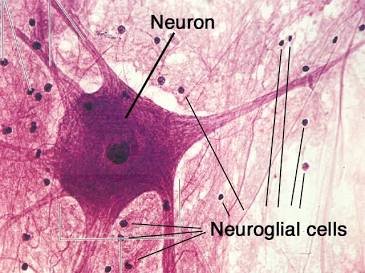
Nervous Tissue
One of the four main tissue types of the body.
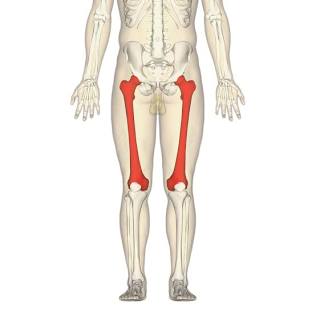
Femur
The primary bone of the leg.
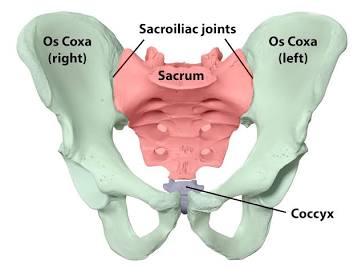
Os coxa
A bone made up of three fused bones.
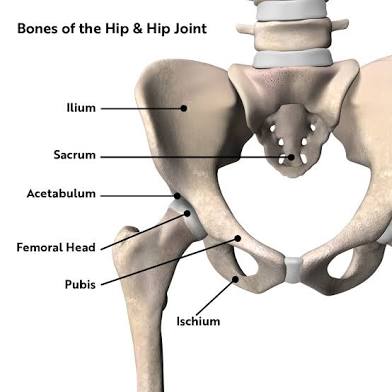
Hip
The joint linking the leg to the trunk of the body.
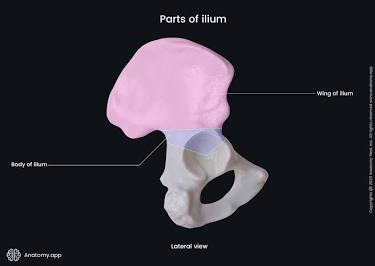
Ilium
The most superior bone of the hip.
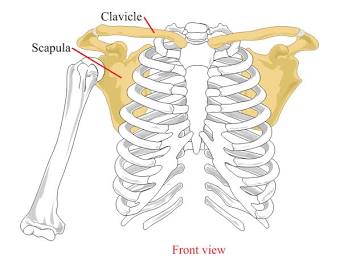
Pectoral Girdle
The skeletal structure comprised of the scapula and clavicle.
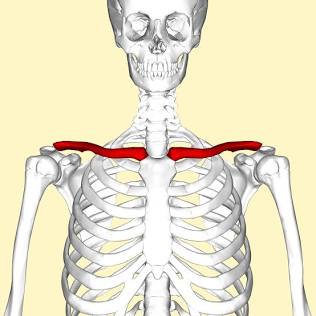
Clavicle
The collar bone.
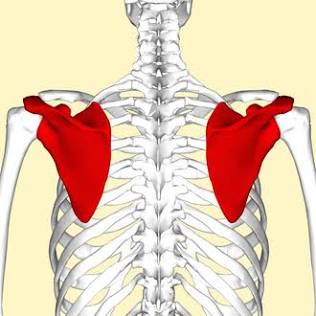
Scapula
The shoulder blade bone.
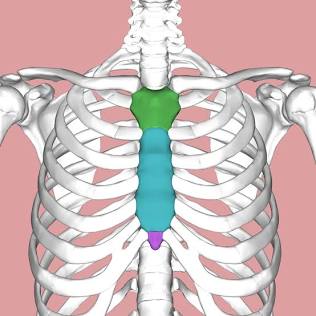
Sternum
The chestplate; articulates with ribs.
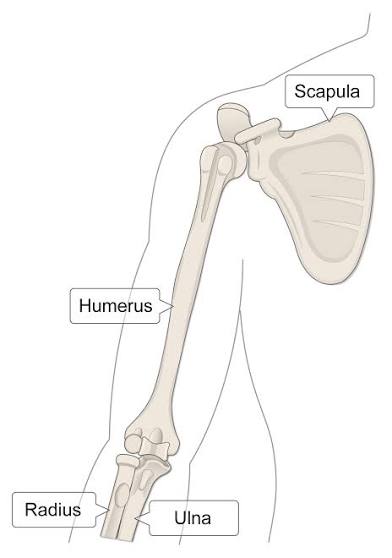
Humerus
The bone of the arm.
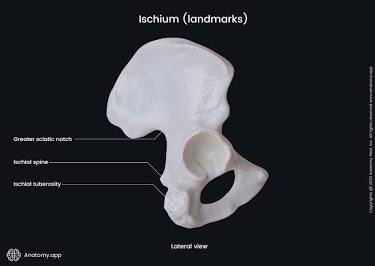
Ischium
The most inferior bone of the hip.
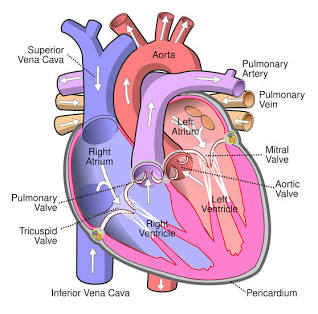
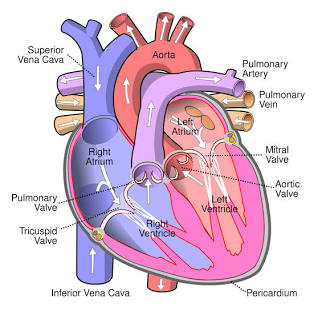
Right Atrium
Receives blood from the inferior vena cava.
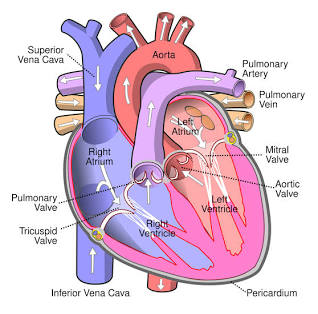
Tricuspid Valve
Valve between the right atrium and right ventricle.
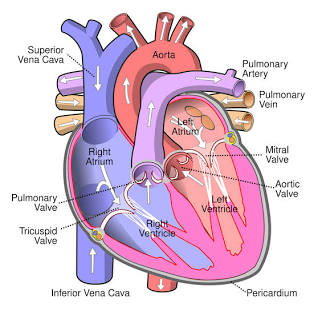
Right Ventricle
Pumps blood to the pulmonary arteries.
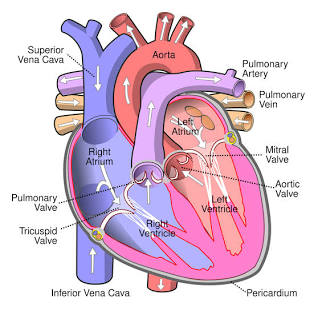
Pulmonary Arteries
Carries blood to the lungs.
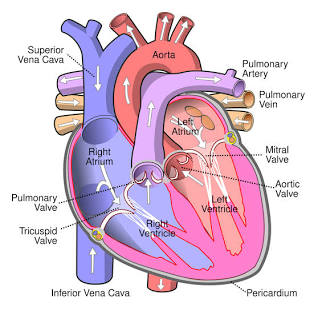
Pulmonary Veins
Carry blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
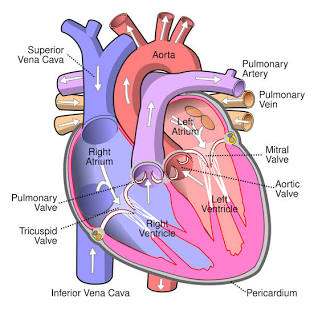
Left Atrium
Receives blood from the pulmonary veins.
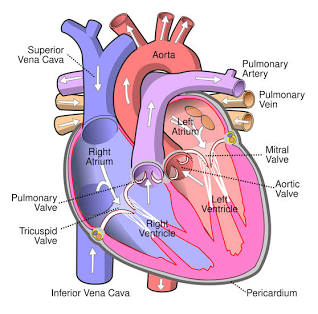
Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve
Valve between the left atrium and left ventricle.
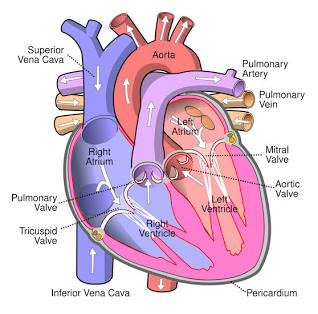
Left Ventricle
Pumps blood to the aorta.
Aorta
The largest artery in the body.
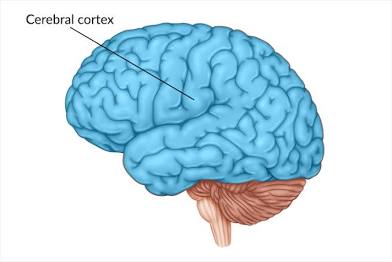
Cerebral Cortex
The conscious part of the brain.
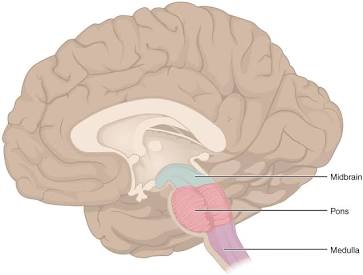
Brainstem/Medulla
The autonomic, unconscious part of the brain.
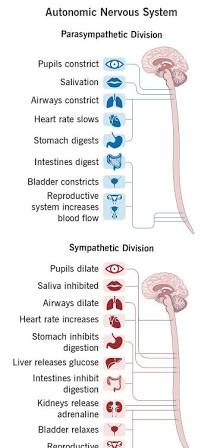
Sympathetic Nervous System
Responsible for fight, flight, or fear responses.
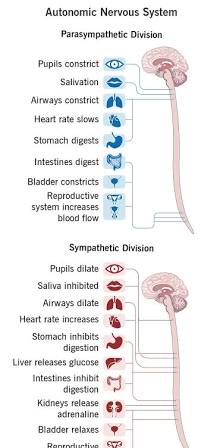
Parasympathetic Nervous System
Responsible for rest and digest responses.
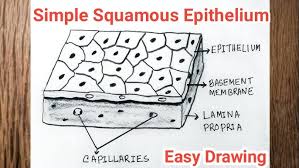
Simple Squamous Epithelial
Tissue cells that permit gas exchange.
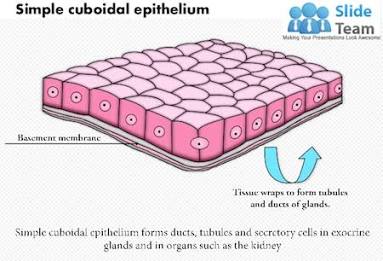
Simple Cuboidal Epithelial
Tissue cells that line nephron tubules.
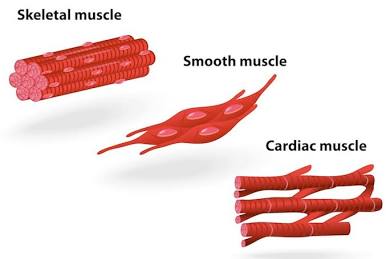
Smooth Muscle
Tissue cells that cause peristalsis.
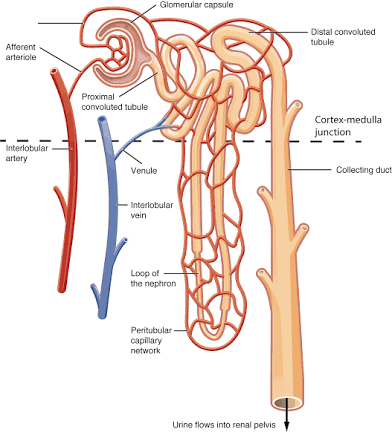
Nephron
The kidney's basic unit of filtration.
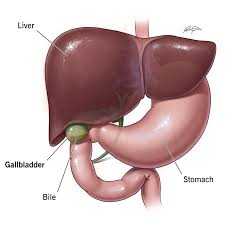
Gall Bladder
Organ that stores bile.
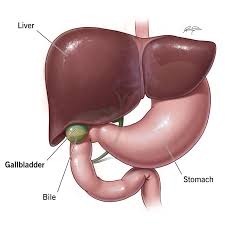
Liver
Organ that makes bile.
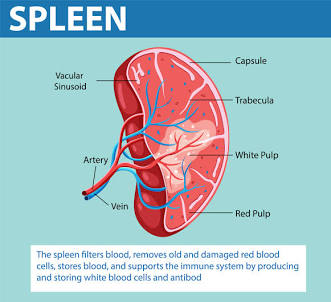
Spleen
Organ that recycles old red blood cells.
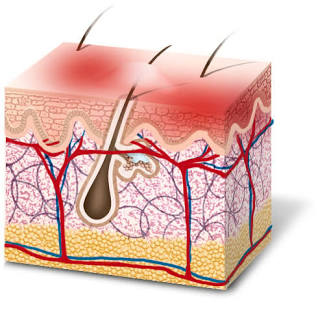
Skin
The body's most superficial organ.
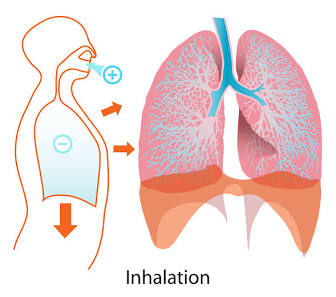
Inhalation
The result of diaphragm contraction.
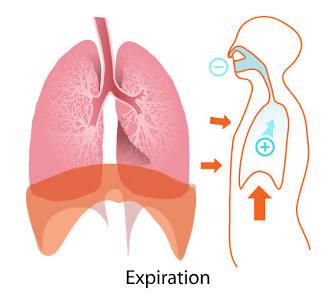
Exhalation
The result of diaphragm relaxation.
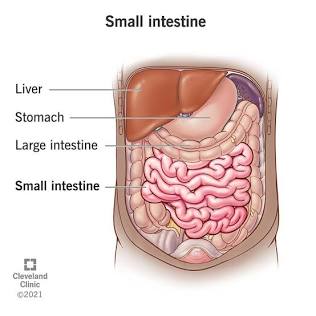
Small Intestine
Where most nutrients are absorbed.
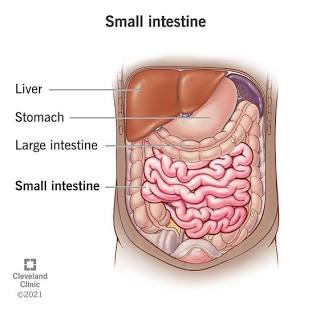
Large Intestine
Where most osmosis occurs in the GI tract.
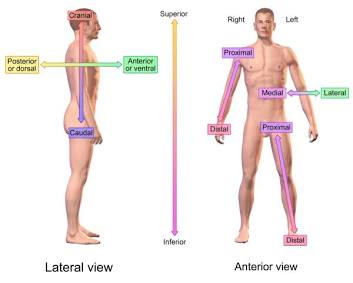
Proximal
Relatively closer to the trunk or point of origin . For example: Knee is __ to the foot.