Ultrasound Physics Ch 8: Transducers
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What 2 functions do ultrasound transducers perform?
- During transmission, electrical energy from the system is converted into sound
- During reception, the reflected sound pulse is converted into electricity
What is the piezoelectric effect?
describes the property of certain materials to create a voltage when they are mechanically deformed or when pressure is applied to them
What is the reverse piezoelectric effect?
when piezoelectric materials change shape when a voltage is applied to them
What are piezoelectric materials or ferroelectric?
materials that convert sound into electricity and vice versa
What piezoelectric materials are commonly used in clinical transducers?
- lead zirconate titanate (PZT)
- they are synthetic or man-made
PZT in an ultrasound transducer is also known as the
ceramic, active element, or crystal
What are the 7 components of an ultrasound transducer?
. wire(cable)
. Case (housing unit)
. electric shield
. acoustic insulator
. PZT or active element
. matching layer
. backing material (damping element)
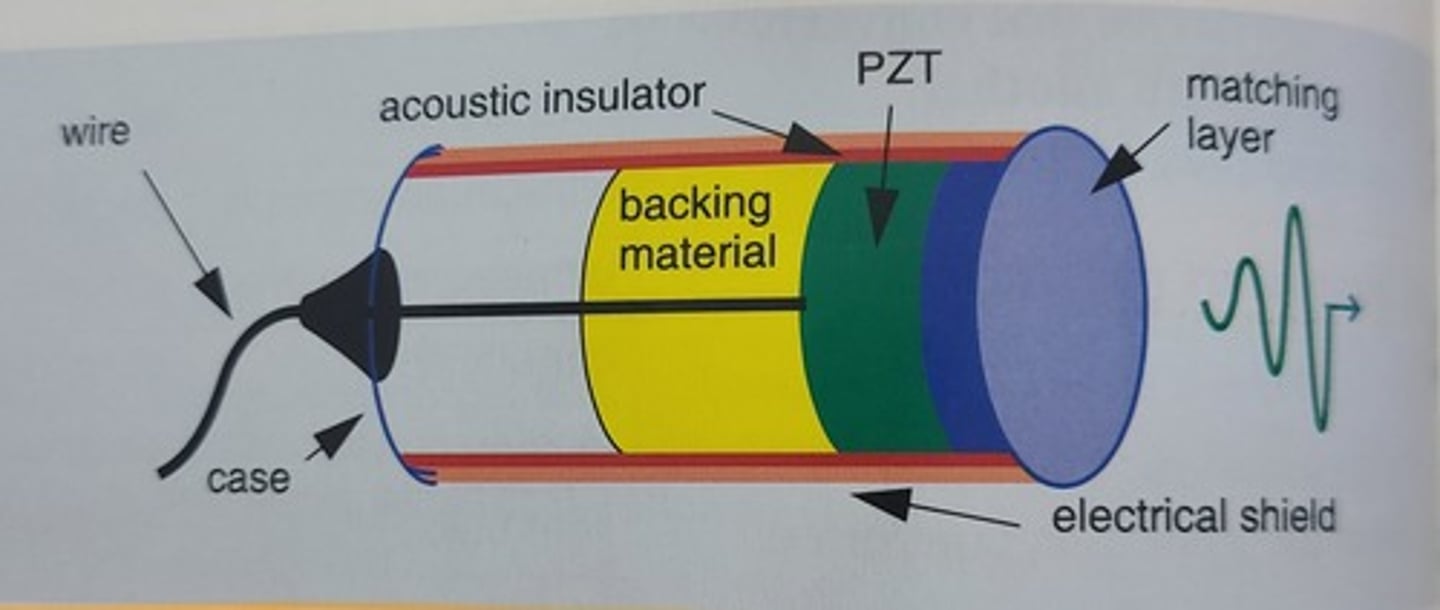
What does the case of a transducer do?
- protects the internal components from damage
- insulates the patient from electrical shock
What does the electric shield of a transducer do?
. a thin metallic barrier lining inside of the case
. prevents spurious electrical signals in the air from entering the transducer
. prevents electrical noise from contaminating the important electrical signals used to create dx images
What is the acoustic insulator and what does it do?
- A thin barrier of cork or rubber that isolates or "uncouples" the internal components of the transducer from the case.
- Prevents vibrations in the case from inducing an electrical voltage in the PZT of the transducer.
What is the PZT or active element
-the piezoelectric crystal itself
- the characteristics of the sound beam emitted by the transducer are related to the dimensions of the active element
- PZT is one-half (1/2) wavelength thick
What is the wire in a transducer
-provides an electrical connection between the PZT and the ultrasound system
- active element requires electrical contact so that during transmission, the voltage from the US system can cause the crystal to vibrate and produce an ultrasonic wave
- During reception, the crystal's vibrations produces a voltage that must return to the system for processing into an image
What is the matching layer? (cork, most common)
-Increases the efficiency of sound energy transfer between the active element and the body
-Protects the active element
- it is one-quarter (1/4) wavelength thick
What is backing material (damping element)?
-Reduces the "ringing" of the PZT pulse
-Epoxy resin containing tungsten filaments
-Enhances Axial Resolution
-Similar Impedance to PZT
- when electrical spike excites the PZT, the backing material restricts the extent of PZT deformation
- emitted sound pulse is dampened, thus, it is short in duration and length
The impedance of PZT is about _______ than the impedance of skin.
20 times greater
The matching layer decreases reflection at the PZT/skin boundary, thereby....
increasing the percentage of transmitted sound between the active element and the skin
The impedance of gel is between that of the matching layer and biologic media. Meaning that gel further......
increases the percentage of sound transmitted into and out of the body.
- commonly described as "coupling" the transducer to the patient
What is the decreasing order of impedance?
PZT > matching layer > gel > skin