Chapter 9: Electromagnetic Induction
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/15
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
1
New cards
**Motional EMF**
The simple act of moving a conducting rod in the presence of an external magnetic field creates an electric field within the rod.
2
New cards
**Faraday’s**
Whose discovery found that a current is induced when the magnetic flux passing through the coil or loop of wire changes.
3
New cards
**weber (Wb)**
The SI unit for Magnetic Flux which is equivalent to one Tesla meter-squared.
4
New cards
**Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction**
states that: The magnitude of the emf induced in a circuit is equal to the rate of change of the magnetic flux through the circuit.
5
New cards
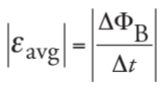
**Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic Induction**
6
New cards
**Lenz’s Law**
states that: The induced current will always flow in the direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux that produced it.
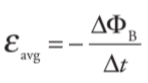
7
New cards
**flux** ( **ϕ** )
tells the amount of something that goes through a surface
8
New cards
**magnetic flux**
depends on the strength of the magnetic field, the surface area through which the field passes, and the angle between the two
9
New cards
**Faraday’s Law of Induction**
says that if the wire is formed in a loop, an electromagnetic force is produced if the magnetic flux changes with time.
10
New cards
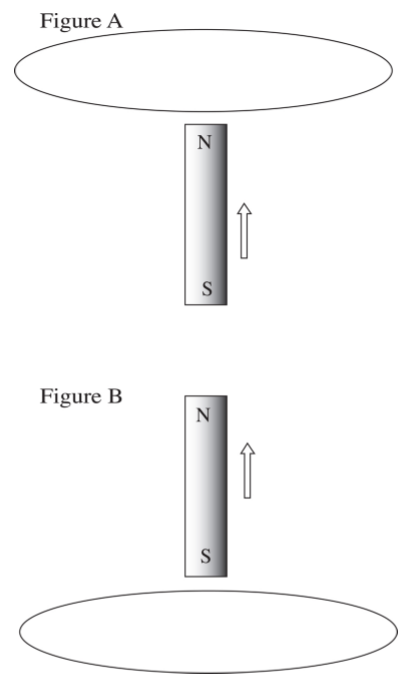
A bar magnet is moved as a constant speed through a loop of wire. Figure A shows the bar magnet when it is as a position below the loop of wire and figure B shows the loop of wire after it has passed completely through the loop.
Which of the following best describes the direction or directions of the current induced in the loop when the loop is looked at from above? Note that when looking at the loop from above, the bar magnet will be moving toward the viewer.
Which of the following best describes the direction or directions of the current induced in the loop when the loop is looked at from above? Note that when looking at the loop from above, the bar magnet will be moving toward the viewer.
**First clockwise, then counterclockwise**
11
New cards
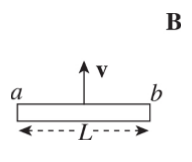
A metal rod of length L is pulled upward with constant velocity v through a uniform magnetic field B that points out of the plane of the page.
What is the potential difference between points *a* and *b*?
What is the potential difference between points *a* and *b*?
***vBL*****, with point** ***b*** **at the higher potential**
12
New cards
**Shrinking the size of a loop of wire in constant magnetic field**
induces an emf in the wire
13
New cards
An emf will be induced when moving the loop of wire _______________ through the magnetic field.
**perpendicularly**
14
New cards
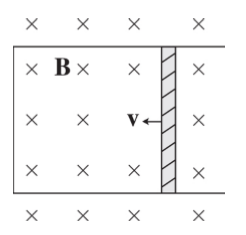
A conducting rod of length 0.2 m and resistance 10 ohms between its endpoints slides without friction along a U-shaped conductor in a uniform magnetic field B of magnitude 0.5 T perpendicular to the plane of the conductor, as shown in the diagram.
If the rod is moving with velocity **v = 3 m/s** to the left, what is the magnitude and direction of the current induced in the rod?
If the rod is moving with velocity **v = 3 m/s** to the left, what is the magnitude and direction of the current induced in the rod?
**Current: 0.03 A** \n **Direction: down**
15
New cards
The most effective airflow is when the loop is completely **_____________.**
**perpendicular**
16
New cards
An induced current can be created three different ways:
1. Changing the area of the loop of wire in a stationary magnetic field
2. Changing the magnetic field strength through a stationary circuit
3. Changing the angle between the magnetic field and the wire loop