Retina
1/199
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
200 Terms
in the retina, ______ energy is transformed to _________ energy
light energy is transformed to chemical energy
the retina extends from _________ to ____________
from optic disc to ora serrata
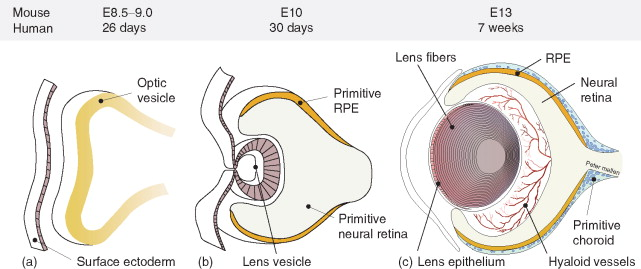
what embryological layer does the retina come from
neural ectoderm
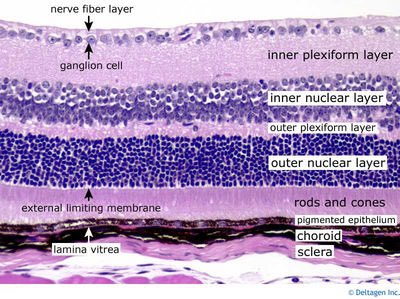
layers of the retina (outer to inner)
retina has 10 layers (RPE OO II GNI)
RPE, PR, ELM, ONL, OPL, INL, IPL, GCL, NFL, ILM
RPE histology
single layer of cuboidal pigmented cells
apical side of cells face the retina
basal side of cells are adjacent to bruch’s
BM adheres strongly to the choroid and forms the innermost part of Bruch’s membrane
what embryological structure is the RPE derived from
outer layer of optic cup
what is the role of the RPE
adheres to Bruch’s
takes waste out of retina: phagocytosis of outer PR segments
association of RPE with photoreceptors
the RPE does not have tight junctions with PRs
the apical side of the RPE has microvilli that extend to the PR layer and surround the PR outer segments, phagocytizing the PR outer segments and transporting them to the choriocapillaris as waste
the space between _________ and ____________ can lead to RDs
between the RPE and the neural retina
RPE adheres strongly to Bruch’s but neural retina can separate from RPE
6 functions of RPE
phagocytosis of PR outer segments
transfer of ions, water, and metabolites (nutrients & waste)
vitamin A storage and metabolism
blood-retinal barrier
absorbs light
produces growth factors (VEGF) for tissue maintenance
what organelle in RPE cells allows phagocytosis of photoreceptor outer segments
lysosomes
what happens when PR outer segments aren’t being digested by RPE cells
undigested PR material accumulates in the RPE cells and becomes lipofuscin
this can contribute to RPE cell death
what is lipofuscin
undigested PR outer segments in RPE cells
2 substances that are transported through the RPE
lactate & glucose
how is lactate transported through the RPE
proton-lactate-water co-transporter moves lactate from the RPE to the choroid
lactate is a byproduct of anaerobic respiration
how is glucose transported through the RPE
glucose transporter moves glucose from the choroid to the RPE to supply the photoreceptors
what does the RPE store and metabolize
vitamin A and retinoids
recycles it between RPE and PRs
terminal complex
links together RPE cells to maintain the blood retinal barrier
includes zonulae occludens, zonulae adherens, and maculae adherens
function of RPE pigment granules
absorb light that was not absorbed by rods and cones
what do RPE cells produce
VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and PEDF (pigment epithelial derived factor)
function of VEGF and PEDF in RPE
VEGF maintains choriocapillaris function
PEDF is an antiangiogenic that balances the effects of VEGF
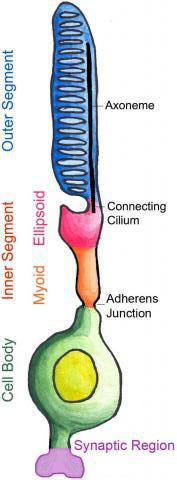
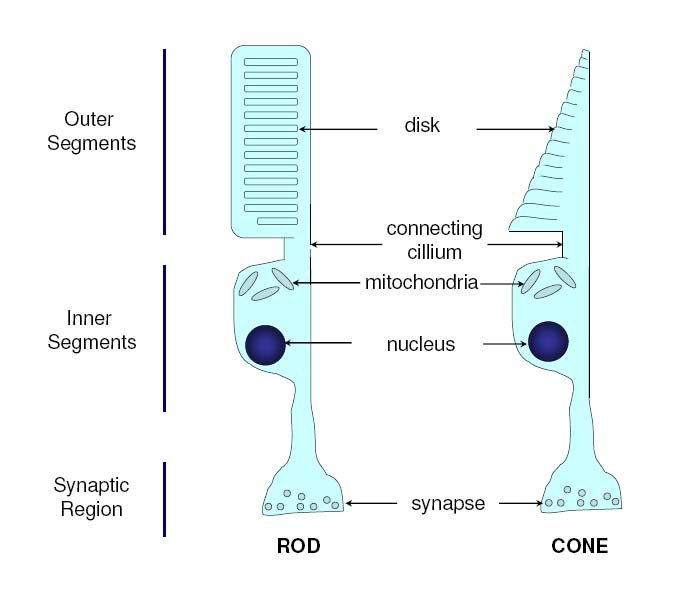
photoreceptor
special sensory cells with photopigments that absorb photons of light
contain inner and outer segment
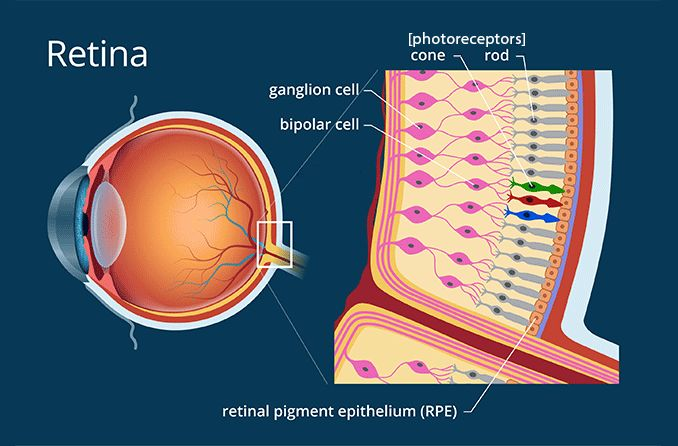
are there more rods or cones
rods (120 million)
only 6-8 million cones
function of photoreceptor inner segment
produces photopigments that are transported through the cilium to the outer segment where they are incorporated into discs
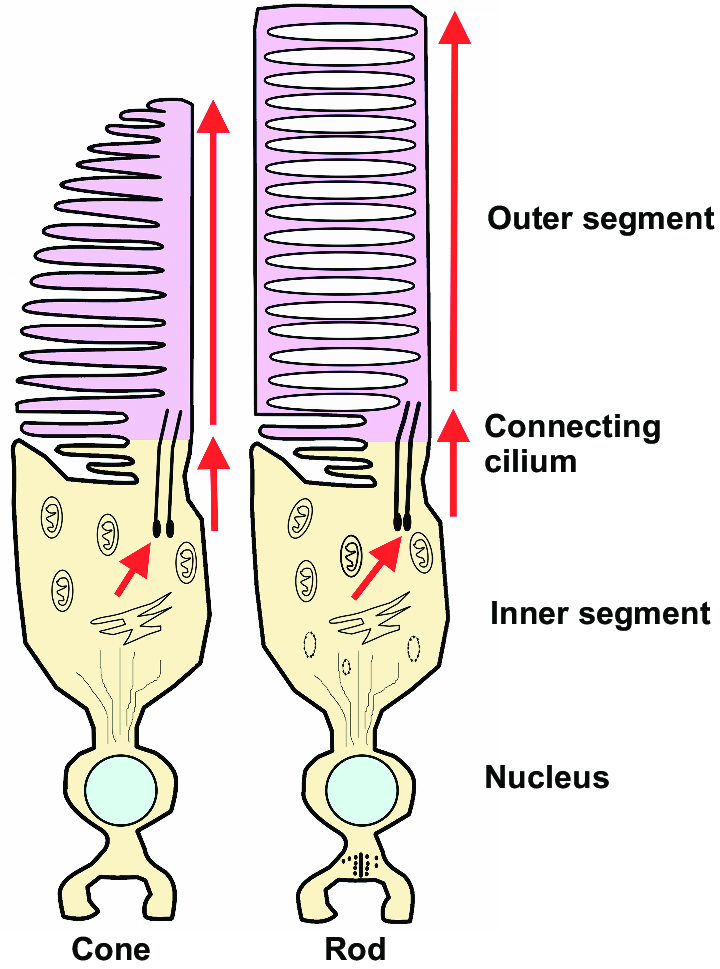
parts of photoreceptor inner segment
myoid, ellipsoid, cilium
myoid
inner layer of inner segment of PR
contains ER and golgi apparatus for protein synthesis
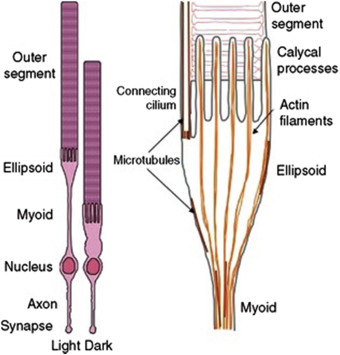
ellipsoid
outer layer of inner segment of PR
packed with mitochondria
cilium
connects outer and inner segments of PRs
myoid vs. ellipsoid
myoid: makes, inner portion of IS, makes proteins
ellipsoid: energy, outer portion of IS, filled with mitochondria
function of photoreceptor outer segment
has stacks of membranous discs that hold photopigments produced by the inner segment
think O looks like a disc
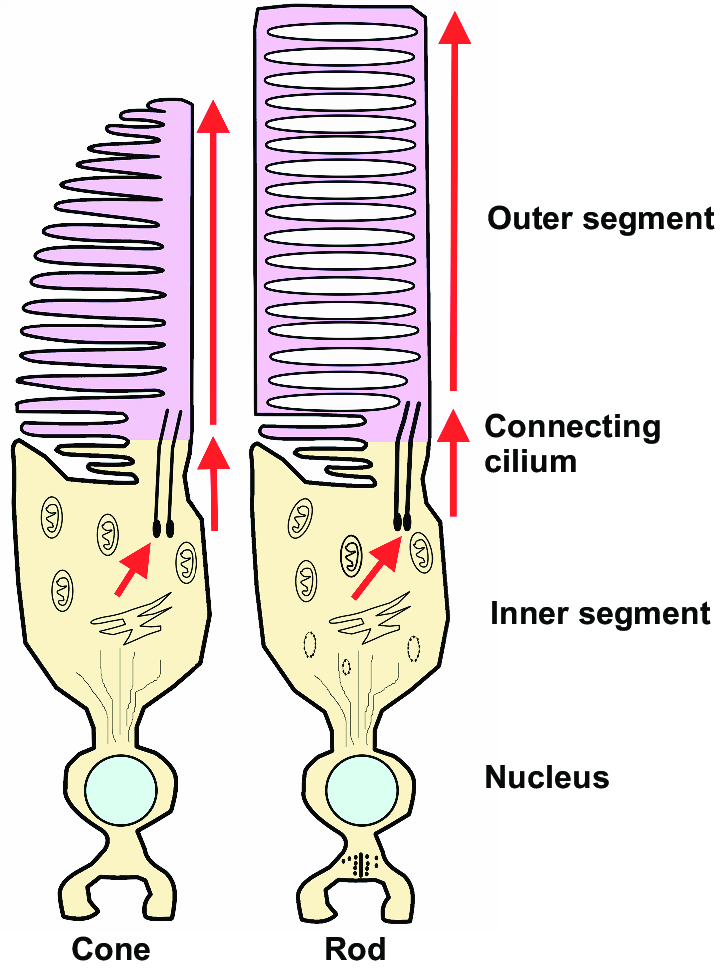
function of PR outer segment
produces discs that surround photopigment molecules
do rods or cones have more discs
cones (1000-1200 per cone)
rods have 600-1000 discs
discs in rods vs. cones
cones: continuous, discs are continuous with plasma membrane
rods: discs are free floating, not continuous with membrane
path of disc photopigments through the photoreceptors
formed in inner segment
assembled into discs at the base of the outer segment
shed by the tip of the outer segment
phagocytosis by the RPE
function of rods
scotopic vision
detect objects under low illumination
function of cones
photopic vision, color vision
rod photopigment and wavelength it absorbs photons
rhodopsin
507 nm
rhodopsin (does/does not) detect color
does not
iodopsins
the 3 cone photopigments
each contain the same chromophore (11-cis retinal)
each differ in their protein (opsin) component
what is the chromophore in all 3 cone photopigments
11-cis retinal
name of the 3 cone photopigments and which wavelength they absorb photons
cyanolabe (blue): 426 nm
chlorolabe (green): 530 nm
erythrolabe (red): 557 nm
what is difference between the 3 cone photopigments
their protein (opsin) composition
where is rod density greatest
5 mm or 20 degrees from the fovea concentrically
rod ring
area where rod density is the greatest
5 mm or 20 degrees from the fovea
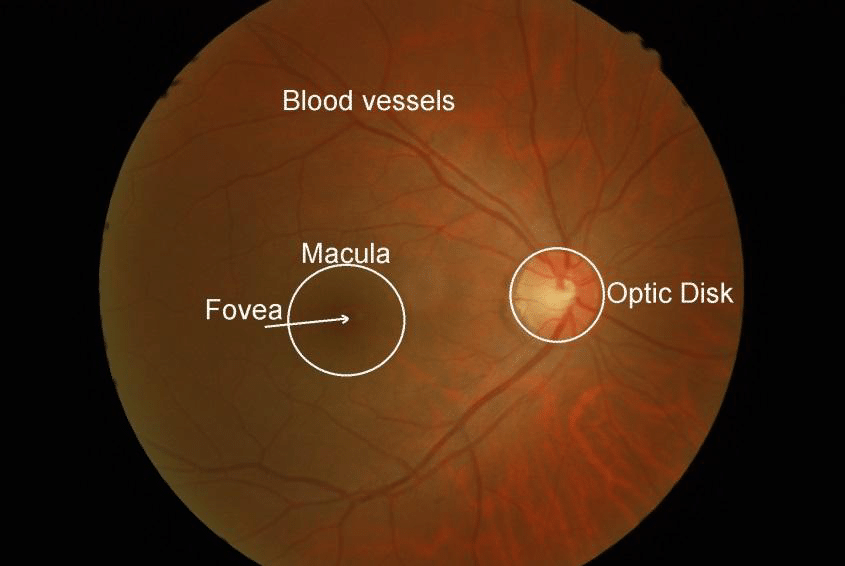
where are cone photoreceptors most concentrated
fovea
contains only cones
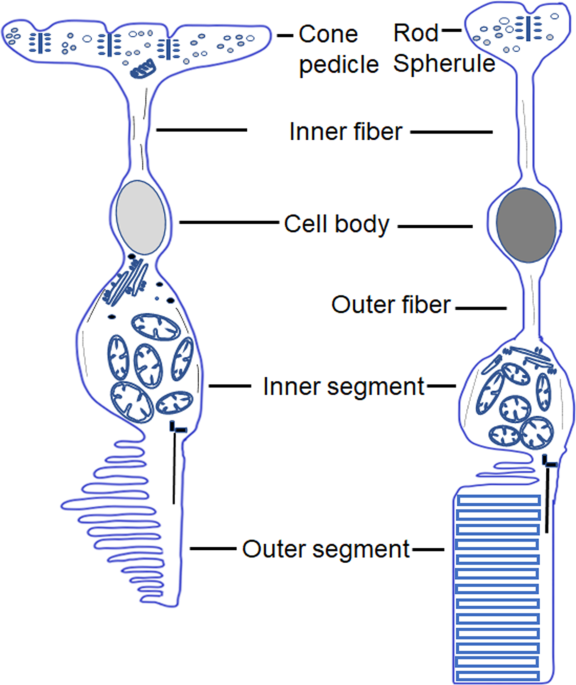
where rods terminate vs. where cones terminate
rods: spherules
cones: pedicules
location of fovea in relation to ON
5 mm temporal and 0.4 mm inferior to the center of the ON
the ELM (is/is not) a true membrane
is not
the ELM (has/does not have) cells
does not have
the ELM is formed by attachments between what
Muller cells and inner segments of photoreceptors
function of the ELM
provides structure to the retina and acts as a barrier against large metabolites
what does the outer nuclear layer consist of
cell bodies of rods and cones
what happens in the OPL
synapses between rod spherules/cone pedicles and dendrites of horizontal and bipolar cells
what are spherules and pedicles
synaptic terminals of rods and cones
synaptic terminal of cone
pedicle
synaptic terminal of rod
spherule
what cells do rods and cones synapse with in the OPL
bipolar and horizontal cells
how (specifically) do rods synapse
each rod spherule connects to 1-4 rod bipolar cell dendrites
rod spherules can also connect to horizontal cell dendrites
rod bipolar cells only connect with rod PRs
how (specifically) do cones synapse
each cone pedicle has a synaptic triad of either:
3 horizontal cell dendrites
2 horizontal cell dendrites and 1 bipolar cell dendrite in the middle in an invagination in the cone pedicle
cone pedicles can synapse with midget, flat, or diffuse flat bipolar cells
are rod spherules or cone pedicles larger
cone pedicles
where is the site of the first synapse of the visual pathway
OPL
what is Henle’s fiber layer
the OPL in the macula
where does the OPL receive its blood supply
only retinal layer to receive dual blood supply from the choroid and the retina (CRA)
retinoschisis
splitting of the OPL
where are hard exudates located
OPL
what cells can be found in the INL
amacrine, bipolar, horizontal, interplexiform, Muller
role of bipolar cells
carry signals from PRs to RGCs
where and what do bipolar cells synapse with
OPL: PRs
IPL: RGCs
4 types of bipolar cells
rod, midget, flat, diffuse flat
midget bipolar cells
have a 1:1 connection with cones and a 1:1 connection with RGCs
resolve very fine details (20/20 vision)
found in the fovea
which cells are responsible for fine vision and found in the fovea
midget bipolar cells
flat bipolar cells
connect with several cone PRs
do flat or diffuse flat bipolar cells connect with more PRs
diffuse flat
where do horizontal cells synapse and with what
synapse in the OPL
lateral signals between PRs, bipolar cells, and other horizontal cells
modification of information that reaches the bipolar cells by horizontal cells
lateral inhibition
horizontal cells provide ________ to PRs
inhibitory feedback
horizontal cells provide ____________ to bipolar cells
inhibitory feed forward
interplexiform cells
carry information vertically between the IPL and the OPL
role of amacrine cells and what cells they synapse with
amacrine cells carry information laterally in the IPL
connect bipolar, interplexiform, amacrine, and RGCs
most common glial cells in the retina
muller cells
role of muller cells and where they stretch through
stretch from the ILM to the ELM
provide structural and nutritional support in the retina
what 2 cells in the retina provide inhibitory feedback
amacrine and horizontal cells
both carry info laterally
1st, 2nd, and 3rd order neurons of the retina
1st: PRs
2nd: bipolar cells
3rd: RGCs
what happens in the IPL
bipolar cells synapse with RGCs
amacrine cells modify the synapse via temporal input
what do bipolar cells synapse with in the IPL
one process from an amacrine cell
one dendrite from a ganglion cell
bipolar cells ______ the stimulation of RGCs
amacrine cells ______ the stimulation of RGCs
bipolar cells increase
amacrine cells decrease
the 2 cells have opposite effects on RGCs
what is in the GCL
location of ganglion cell bodies
path of RGC axons
each RGC has a singular axon that travels within the ON and ends in the LGN or other areas of the brain
where are there no RGCs
foveola
there are ____ RGC layers in the outer macular region
there are ____ RGC layers in the rest of the retina
4-7 in outer macula
1-2 in rest of retina
2 main categories of RGCs
P-cells (parvocellular)
M-cells (magnocellular)
are P-cells or M-cells larger
M-cells
have larger diameter axons
are P-cells or M-cells more common
P-cells
role of P-cells
sensitive to color and fine detail
role of M-cells
sensitive to dim changes in illumination and motion
where do P-cells project to
parvocellular layers of LGN: 3, 4, 5, 6
where do M-cells project to
magnocellular layers of LGN: 1, 2
2 types of P-cells
P1 cells: midget ganglion cells
P2 cells
are P1 or P2 cells larger
P2
what is the most common RGC
P1 cells/midget ganglion cell