nervous sytem and electrical activity
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Whats the general organization of the nervous system?
Has billions of cells
Neurons and glia are specialized for communication (Ex: generates electrical signals)
What’re the 2 main branches the nervous system splits off to?
Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
Central nervous system (CNS): Brain and spinal cord
Explain what afferent, efferent, and interneurons are in PNS
Afferent: Sensory division, sends info to the CNS through afferent (sensory) neurons
Efferent: Takes info from the CNS to target cells via efferent neurons
Interneurons are just how the central nervous system is referred to, it’s the integrating center
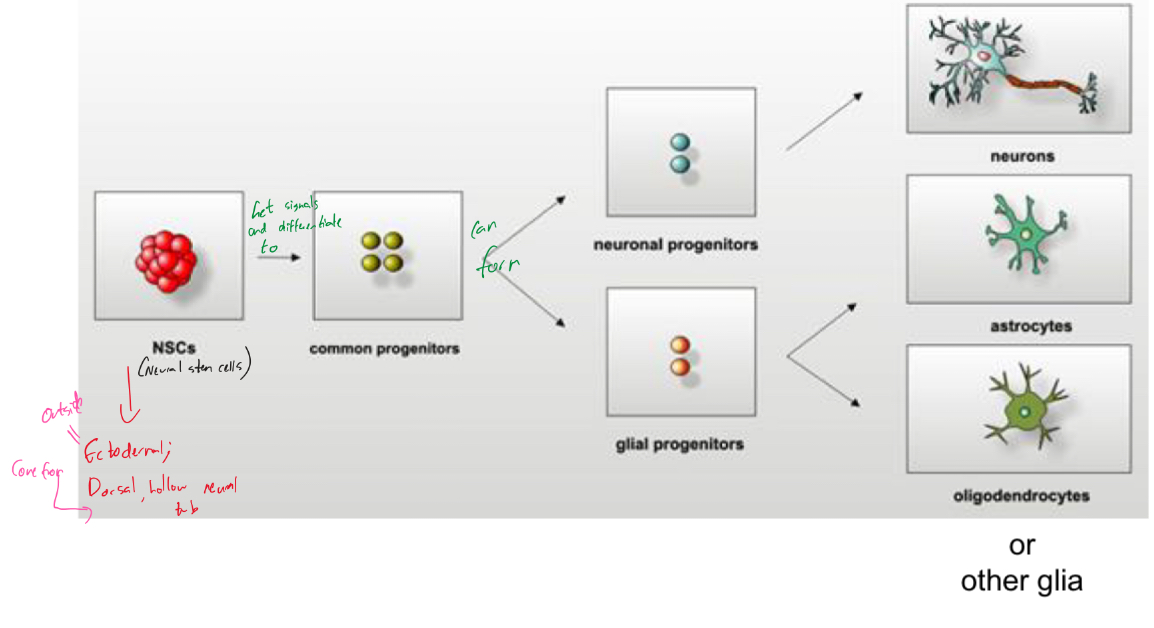
Explain and name the cells that form other cells in the nervous system
Whats the role of neurons?
Specialized to carry electrical signals and communicate with other cells
Secrete signaling molecules (neurotransmitters and neurohormones)
What’re some structures/ features of neurons?
Unique morphology (ex: axons, dendrites), can communicate with distant targets
High density of ions channels which allows them to be electrically active/ send electrical signals
Special transport mechanisms to move materials from one end to the other (depend on cytoskeleton)
Secrete signaling molecules (neurotransmitters and neurohormones)
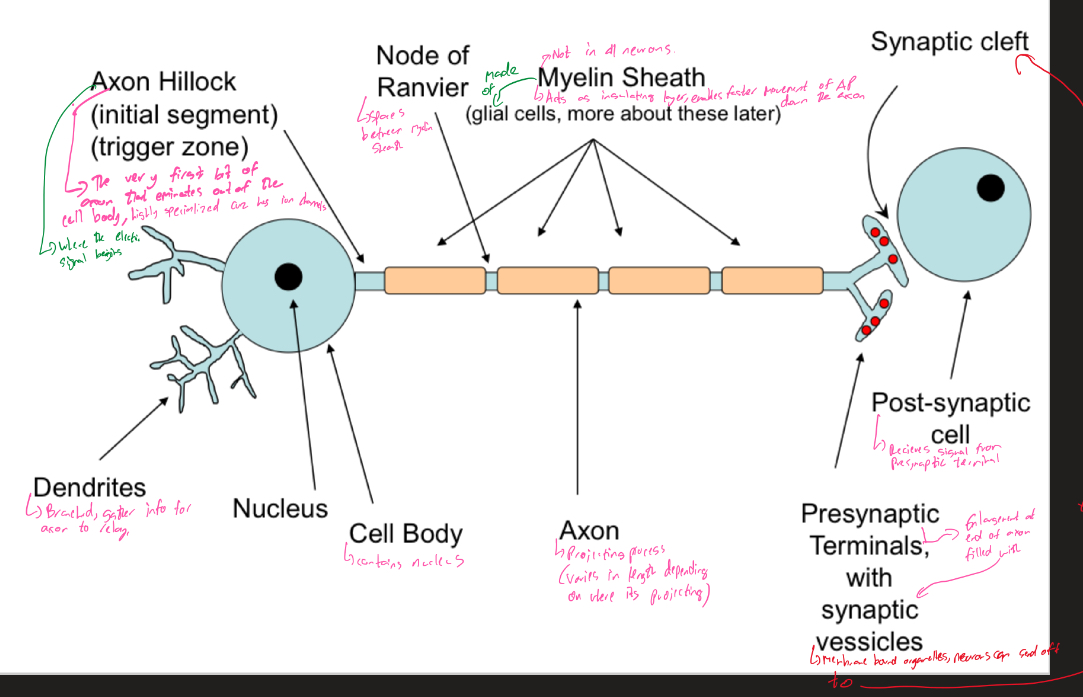
Explain the diagram of the neuron and what all the different parts of it do
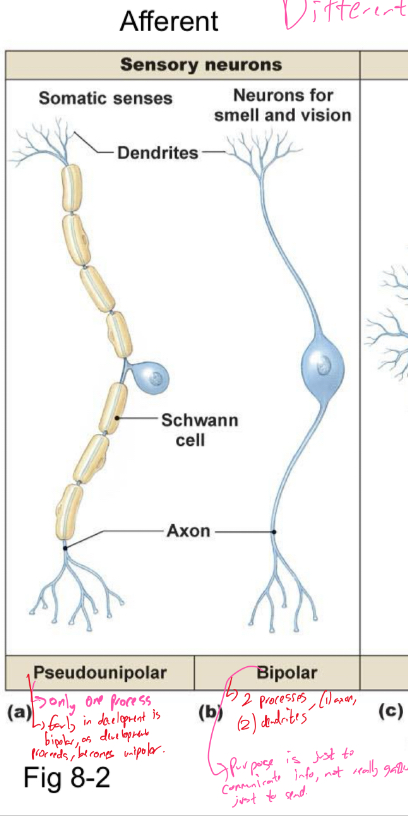
Explain afferent neurons and their functions
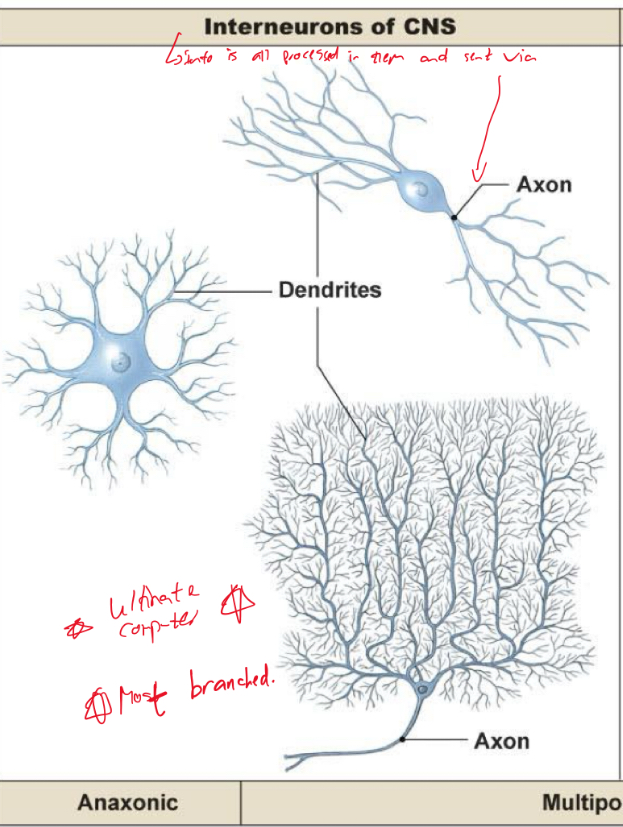
Explain interneurons
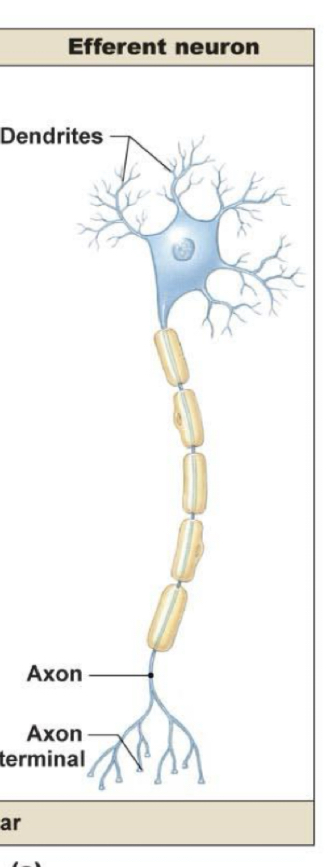
Explain efferent neurons
What’re the types of glia in CNS?
Oligodendrocytes
Ependymal cells
Microglia
Astrocytes
What do oligodendrocytes do?
Myelinate axons in brain and spinal cord (form myelin layer on the axons of brain + spinal cord)
What do ependymal cells do?
Line ventricles to prevent leakage of fluid in or around brain, make neural stem cells
What do microglia do?
They’re the immune cells of CNS
Phagocytosize cellular debris
They’re not derived from neural tissue but comes from mesoderm which makes blood tissue
What do astrocytes do?
Form a blood brain barrier
Produce trophic factors
Take up excess water and K+
Produce neural stem cells
Passes lactate to neurons
What’re the types of glia in PNS?
Satellite cells
Schwann cells
What do satellite cellls do?
Produce trophic factors specific for PNS
What do Schwann cells do?
They myelinate axons in peripheral nervous system
What do neurons contain?
High density of ions channels which channels
What’re ion channels classified according to?
The ions they carry
Where on the cell they are located
Gating mechanisms (most important)
What’re the different types of channel gating mechanisms and explain them.
Voltage gated ion channel: Open or close based on changes in changes in membrane potential via conformational changes. A threshold needs to be met for a conformational change to occur
Receptor channels: Need to bind to some sort of ligand to open typically a neurotransmitter, can also be gated by ligands on the intercellular side (=ligand gated ion channels
Phosphorylation gated
Stretch gated: Channel opens depending on how cell membrane stretch’s/ swells or depresses
Temperature gated: Responsible for us to sense chemicals like capsaicin
What does opening and closing or ion channels cause?
Causes rapid changes in membrane potential (this is the basis of electrical signalling
Explain graded potentials
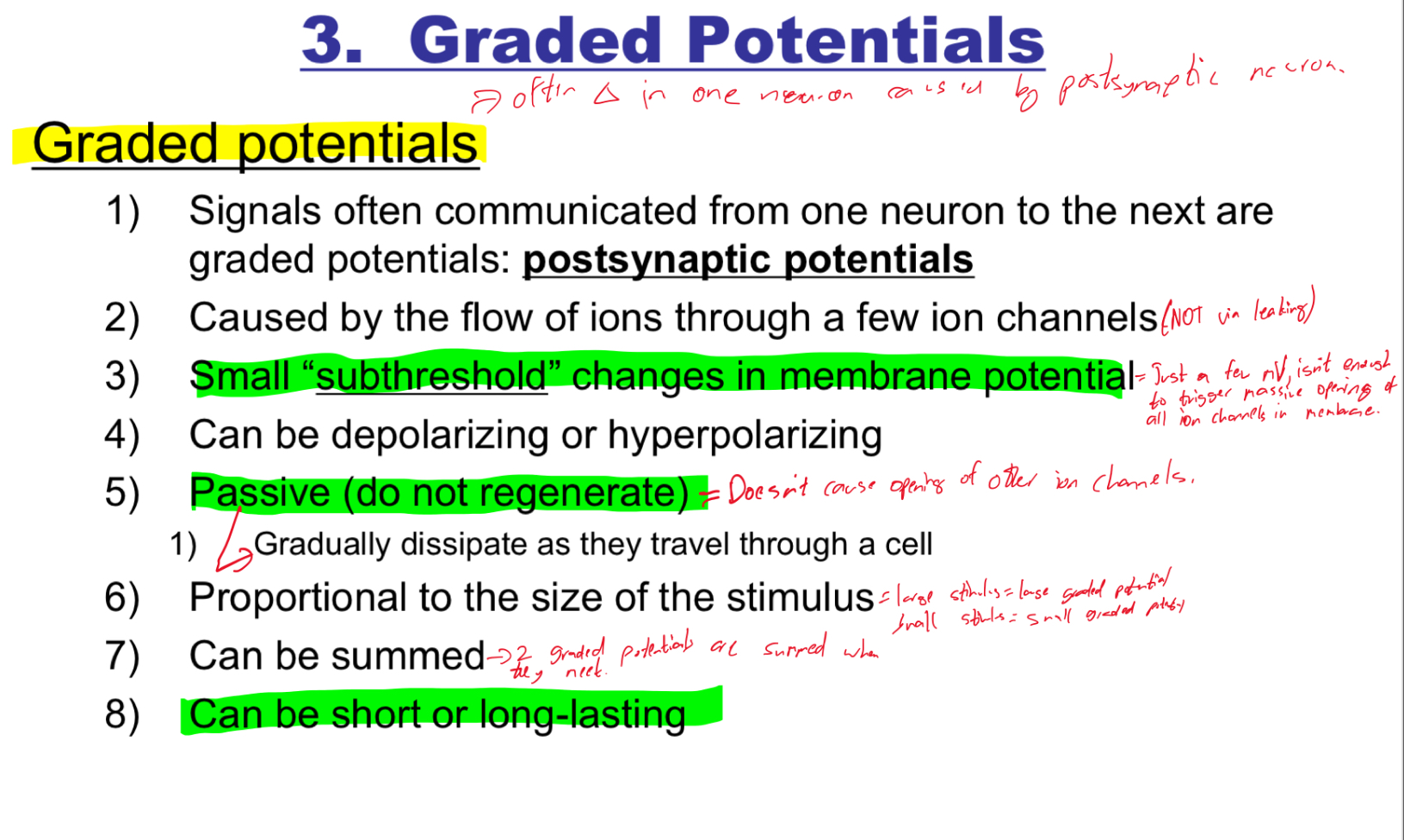
Explain how a graded potential travels like a ripple on a pond
It moves outward from the source and degrades as it moves farther away
Takes time to get from synapse to the axon hillock
Eventually degrades to nothing
Graded potential degrades the further away from the stimulus it gets
Why does the signal in a graded potential degrade?
The cell membrane is leaky to ions
Electrical resistance in the cytoplasm
Explain action potentials

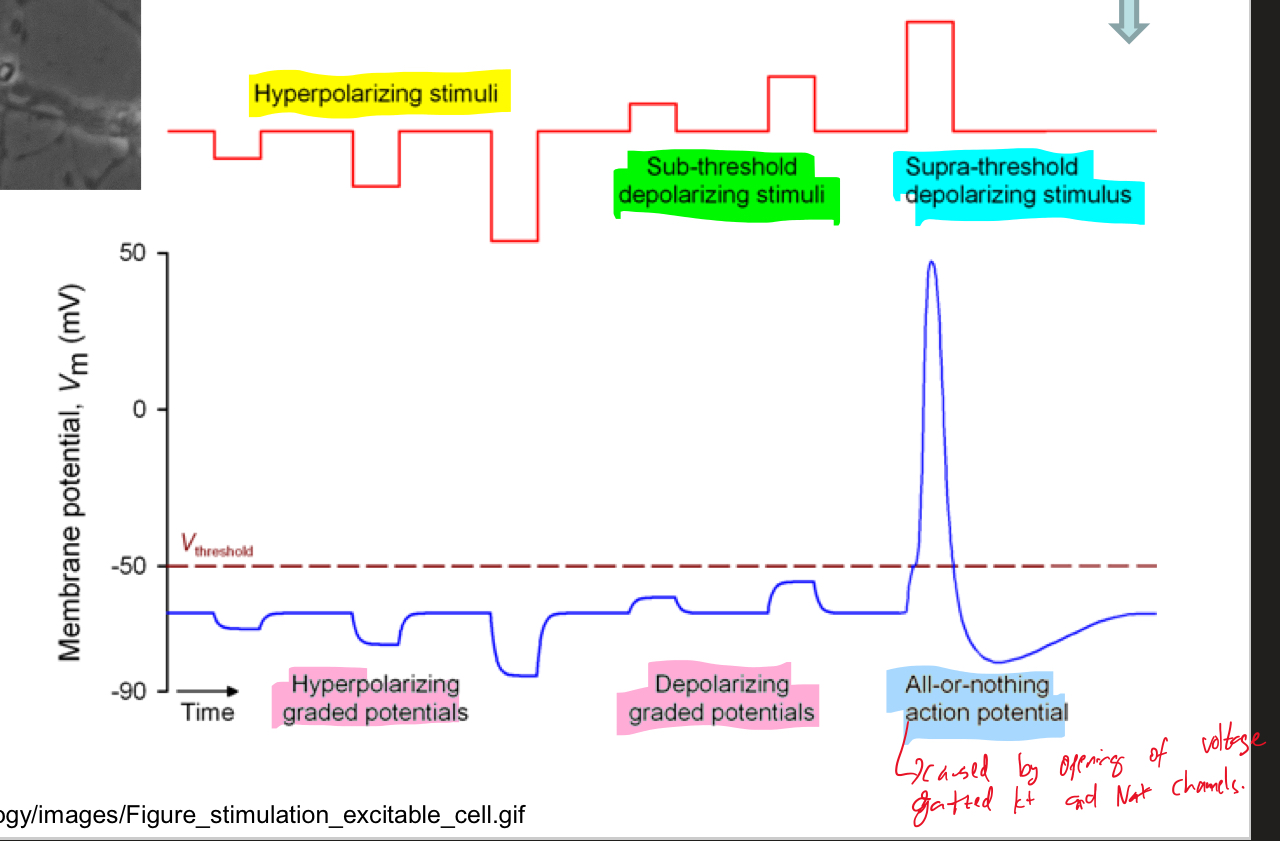
Be able to explain this diagram and the various stimuli
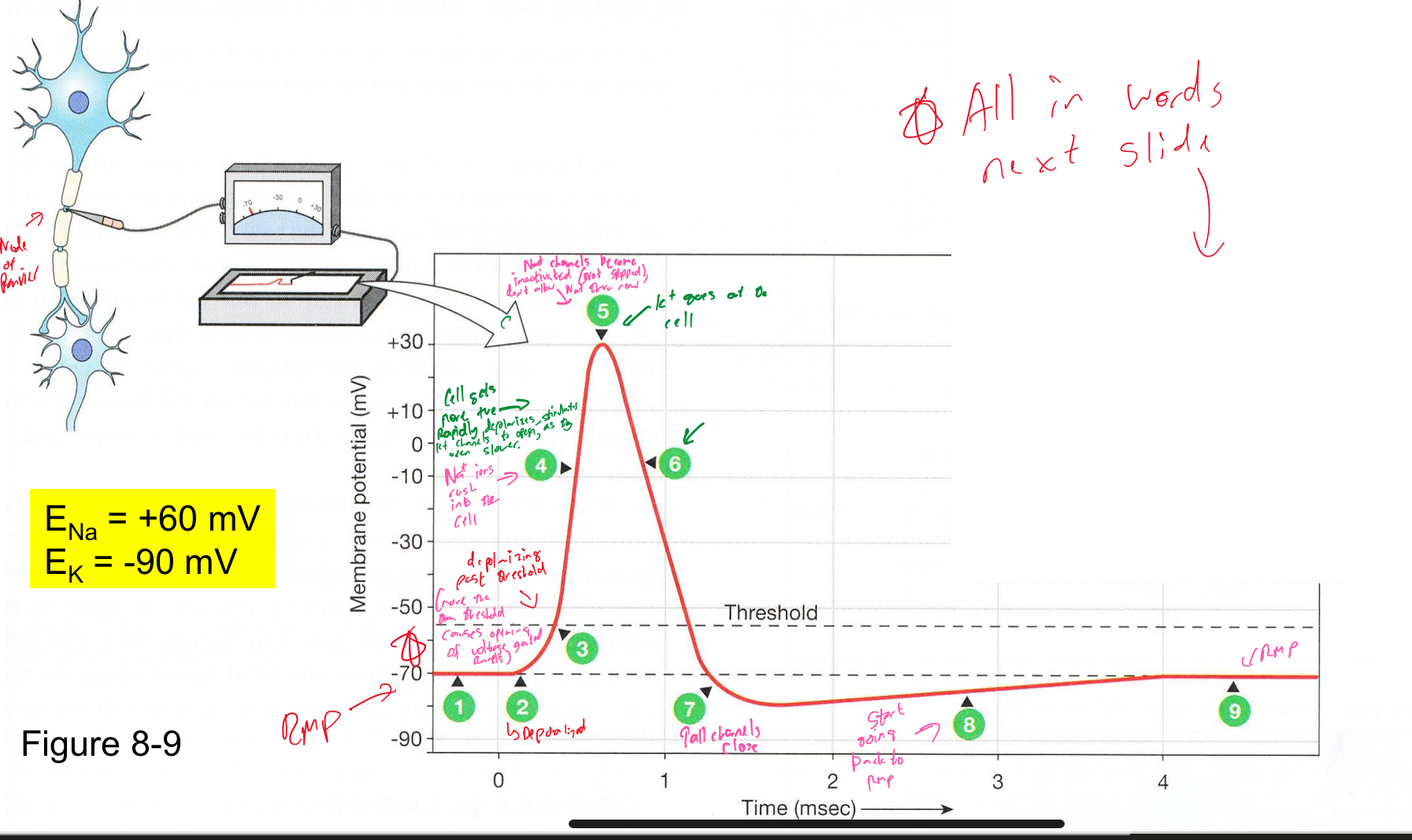
Explain what’s happening in this diagram

Explain what the recovery from inactivation is
It’s what occurs during the afterhyperpolarization (caused by the K+ leaving the cell), the 2 Na+ channels reset to their original positions
Its critical in determining refractory periods, stops action potentials from happening too quickly
Does the NaTPase every stop?
No, it doesnt stop ever during the entire process of the action potentials cuz it doesnt care about membrane potential, the important part is theres ATP.
Just used to maintain Na levels in the cell
Explain the change in concentration a single action potential can cause?
It doesnt really cause a change in concentration as it doesnt move enough Na+ across to cause a change in concentration in the cell
What’re the 2 refractory periods over the course of an action potential?
Absolute Refractory
Relative Refractory
Explain the absolute refractory period
Occurs from the rising phase to the falling phase
In this phase, regardless of what you do to a neuron, and action potentials wont happen cuz it’s already depolaruzing as fast as it can
Explain relative refractory
Occurs during recovery phase
Can make a neuron fire an action potential, but you just have to stimulate it more than you did before the action potential
What’re the 3 patterns of action potentials?
Single AP
Tonic AP
Bursting AP
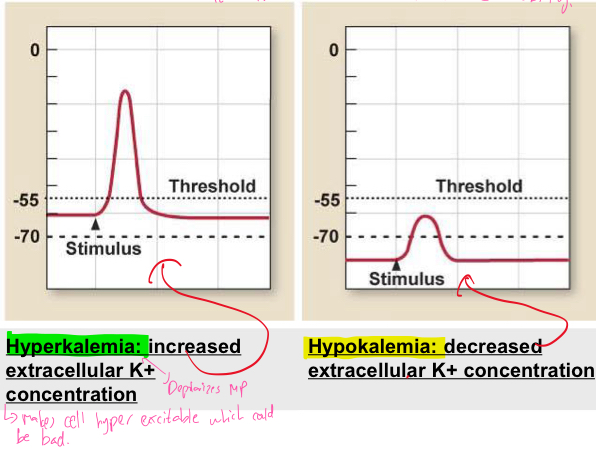
What does change in extracellular [K+] do?
It influences generation of action potentials
It does this by causing a decrease in excitability of neurons as it affects MP which affects excitability
Explain what occurs in hyperkalemia and hypokalemia
Hyperkalemia: Increased extracellular K+ concentration as it depolarizes MP and makes cell hyper excitable which could be bad
Hypokalemia: Decreased extracellular K+ concentration
What does an unmyelinated axon look like and where is the AP on it conducted?
Has no myelin sheath
AP conducted From the soma to the terminals
Explain what local current flow is
Plays on the idea of ions being attracted to opposite charges
When a section of the axon depolarizes, positive charges move by local current flow into adjacent sections of the cytoplasm. On the extracellular surface, the positive charges flow toward the depolarized region (relatively negative)
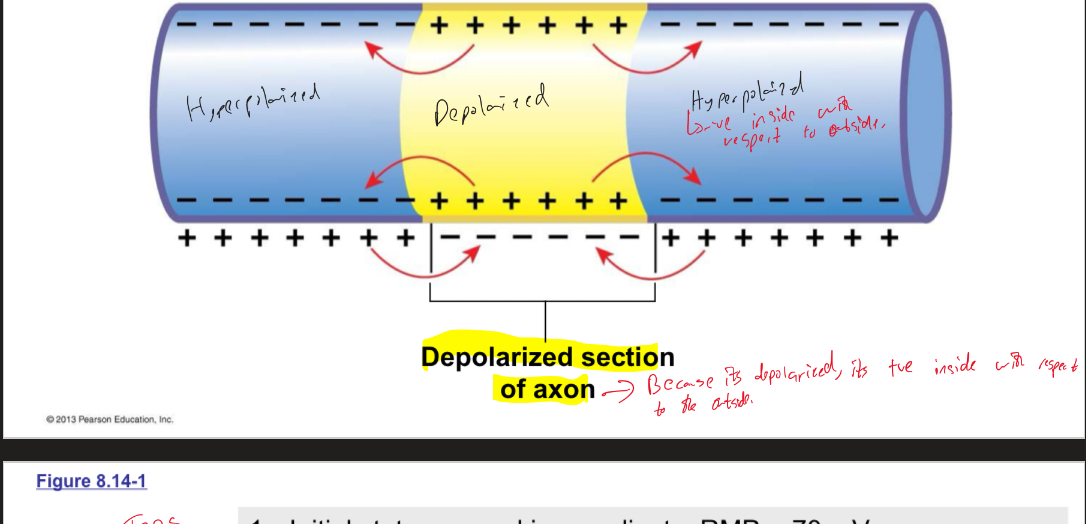
Explain what the steps of continuous conduction in unmyelinated axons are
Initial state: RMP ~ 70(normal), high density of Na+ channels at the axon hillock (trigger zone). Voltage gated Na+ and K+ channels along axon. Starts as graded potential above threshold reaches trigger zone
Na+ rushes into axon as voltage gated Na+ channels open, causing depolarization
Positive charges flows into adjacent sections of the axon by local current flow, causing depolarization of nearby axon to its threshold (hillock now refractory)
Local current flow from the active region causes new sections of the membrane to depolarize. AP moves down the axon as a traveling wave of depolarization
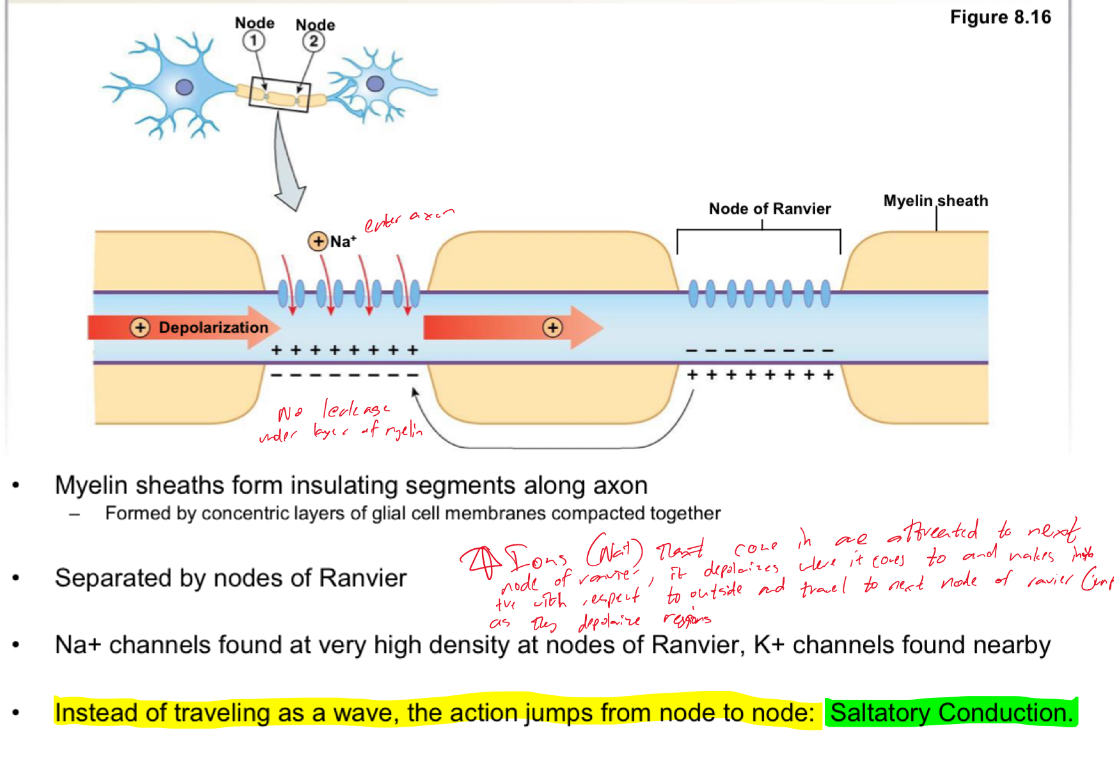
What kind of conduction of APs occur on myelinated axons?
Saltatory conduction: action jumps from node of ranvier to next rode of ranvier cuz of myelin sheath.
Not continuous
Explain what myelin sheath on PNS looks like and contains
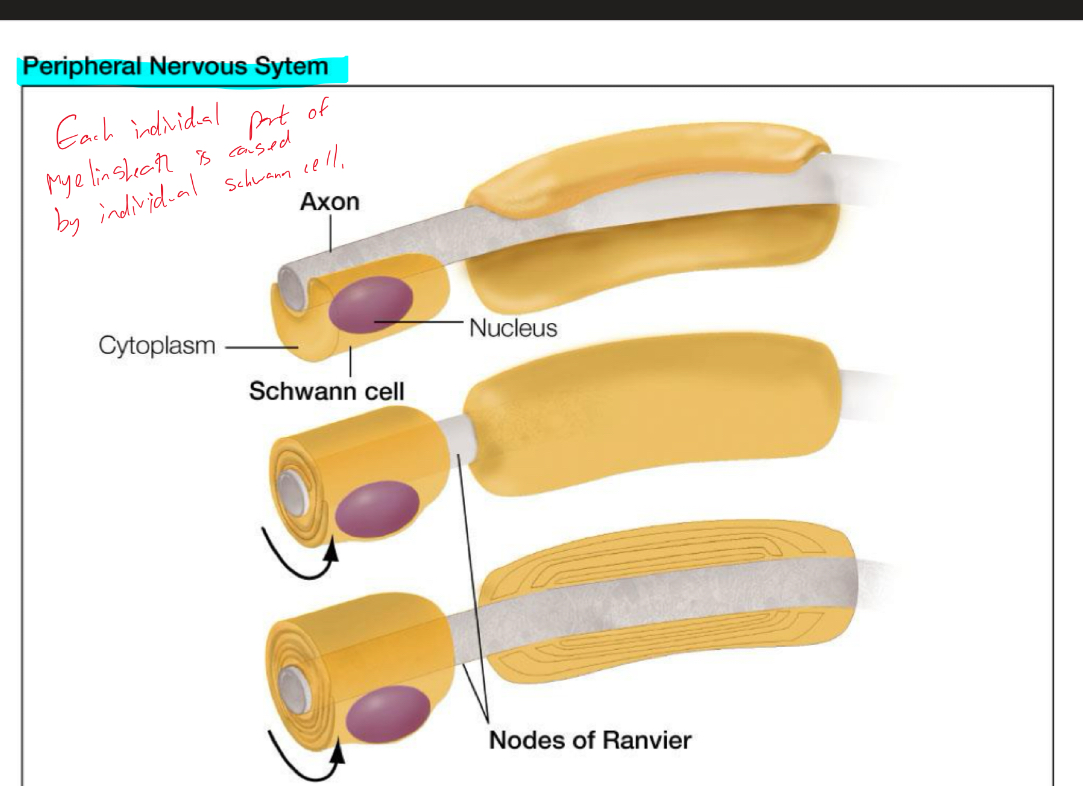
Explain what myelin sheath on CNS looks like and contains
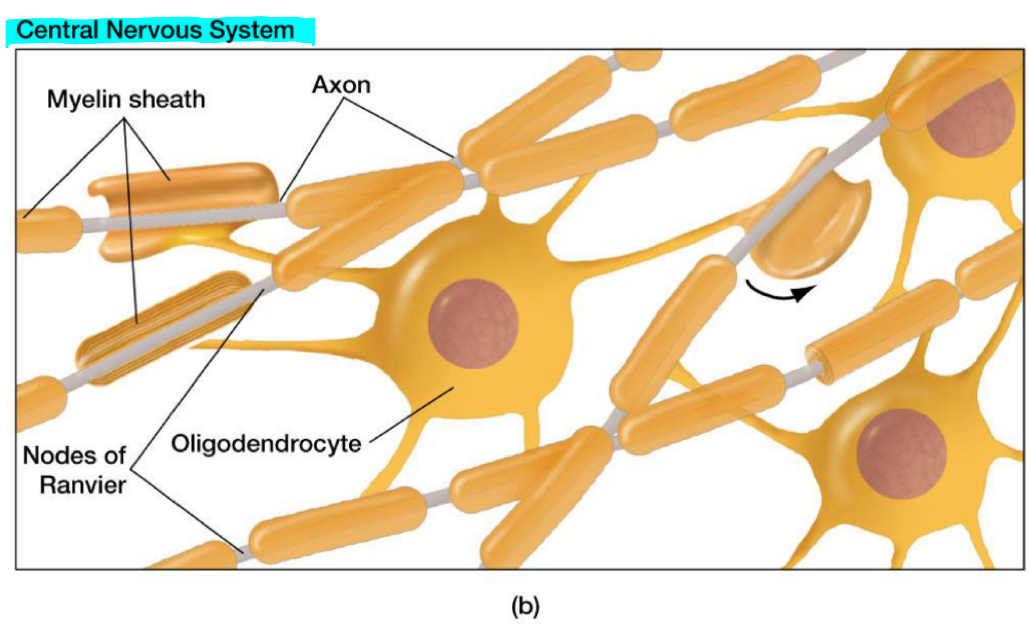
What is myelin formed from and what roles does it play?
Myelin is formed from concentric layers of glial cell membrane
Layers of this membrane are excellent insulators
Myelination increases electrical efficiency of axons
Explain diagram of AP moving down myelinated axon
Ions (Na+) that come in are attracted to next node of ranvier, it depolarizes where it comes to and makes it positive with respoect to outside and travels to next node of ranvier (jumps to) as they depolarize regions
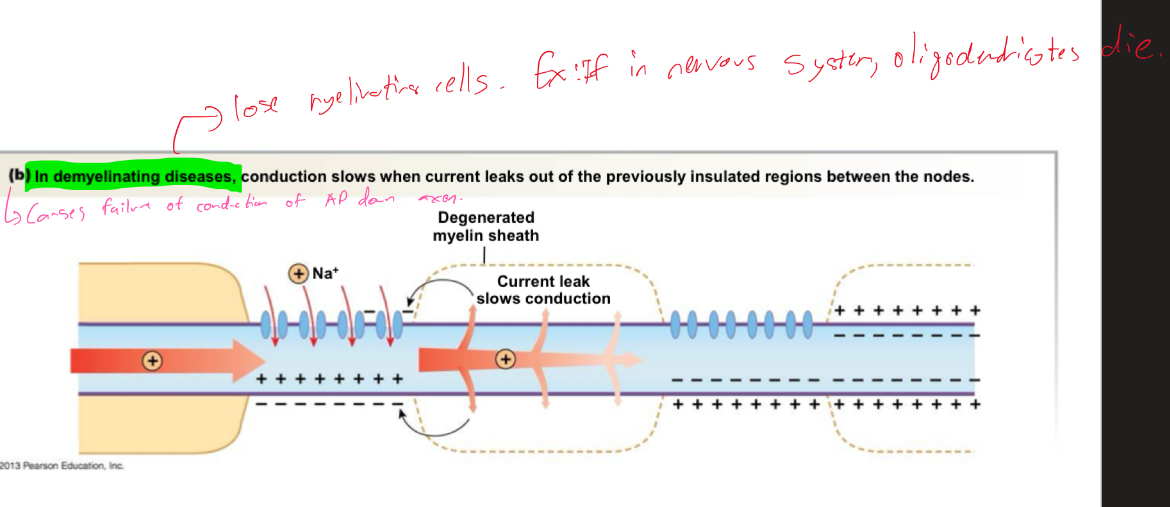
Explain the diagram of what happens to APs in demyelinating diseases
What’re the 2 ways to speed up velocity of action potentials along an axon?
Myelination: Increases velocity because insulated areas have less leakage of Na+ and K+
Increase axon diameter: Increases velocity because as the axon radius becomes larger, internal resistance decreases (inverse square relationship)
What’re the advantages of myelinated axons over unmyelinated axons?
Myelination allows for faster conduction, but axons take up less space = more processing power
Saltatory = better
Can fit more myelinated axons into the same place
What’re some demyelinating diseases?
Multple sclerosis
Giuliann Barre syndrome/ AIDM
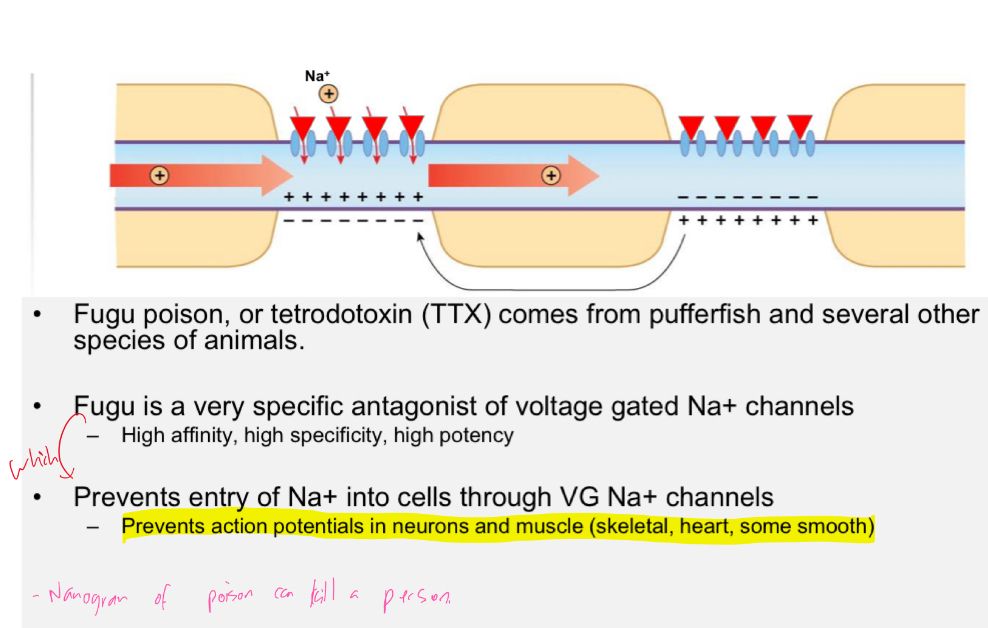
Fugu poison
Explain them all
Whats the difference between multiple sclerosis and giullain barre syndrome?
Multiple sclerosis = CNS
Guillan Barre = PNS
Explain the mech of how fugu poison works