Kent State, Physical Geography, Exam 1, Chapters 1-3 Study Guide
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
What is physical geography
Integrating knowledge about a wide variety of features and processes involving all four of Earth's major subsystems
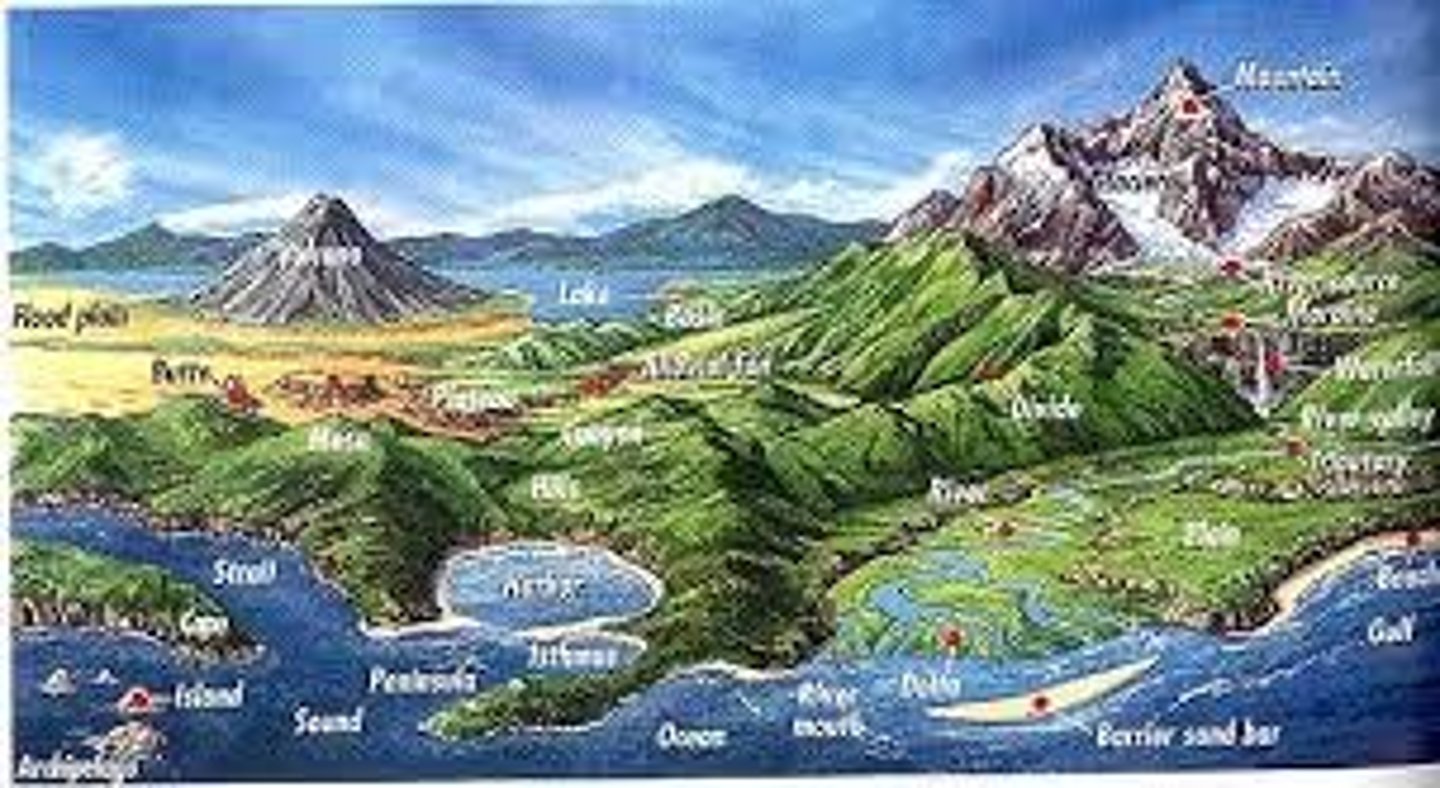
spatial meaning
the arrangement of features in a space
the spatial perspective
observing variations in geographic phenomena across space, (location, characteristics, spatial distribution and pattern, spatial interaction)
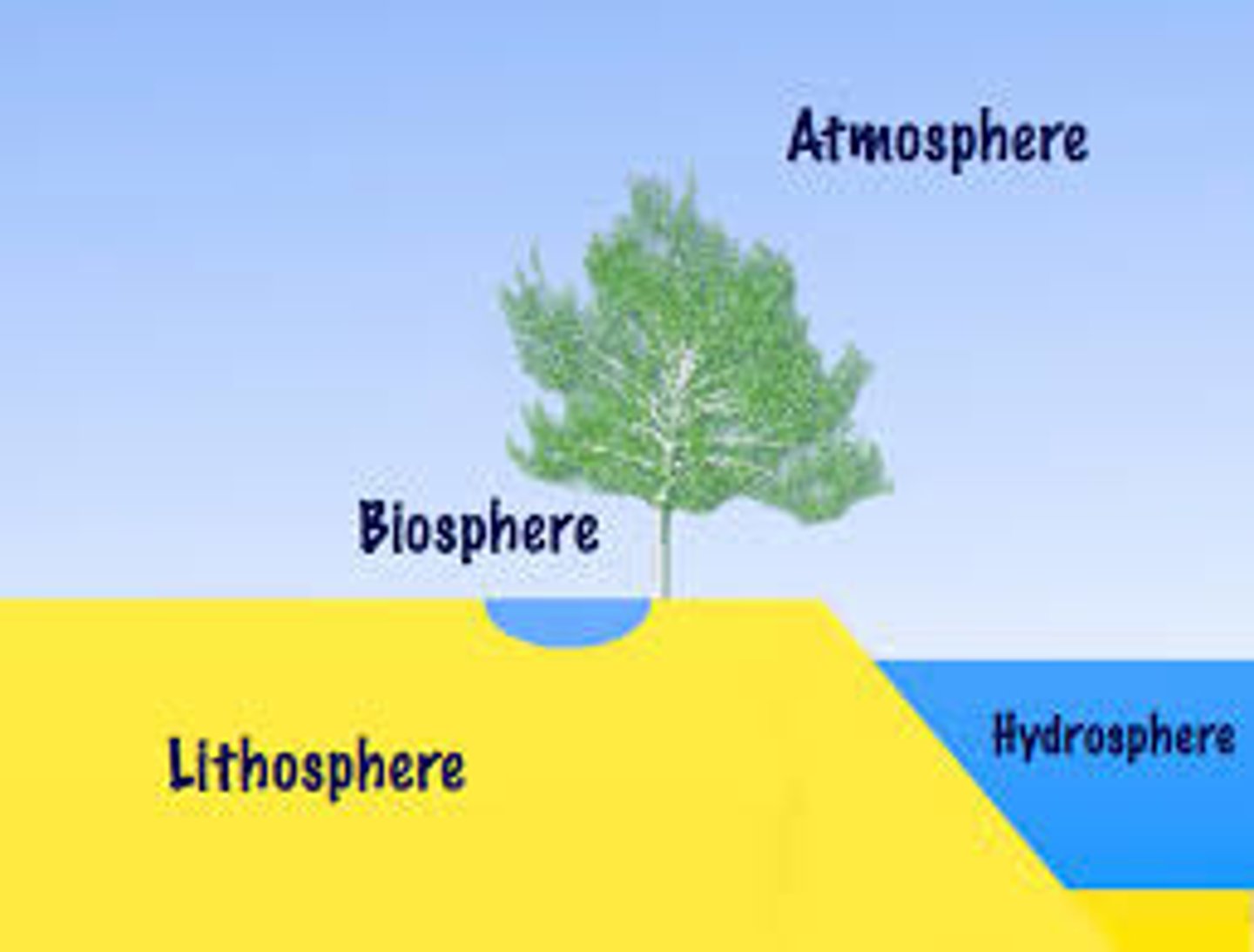
Four major subsystems of earth
atmosphere (air), lithosphere (land), biosphere (life), hydrosphere (water)
scientific method
A series of steps followed to solve problems including collecting data, formulating a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis, and stating conclusions.

Closed System vs. Open System
Closed=Energy can move in or out, but not matter. (earth)
open=Both energy and matter can move in or out.
Positive feedback
amplifying change (Global Warming melting)
negative feedback
a mechanism of response in which a stimulus initiates reactions that reduce the area back to normal
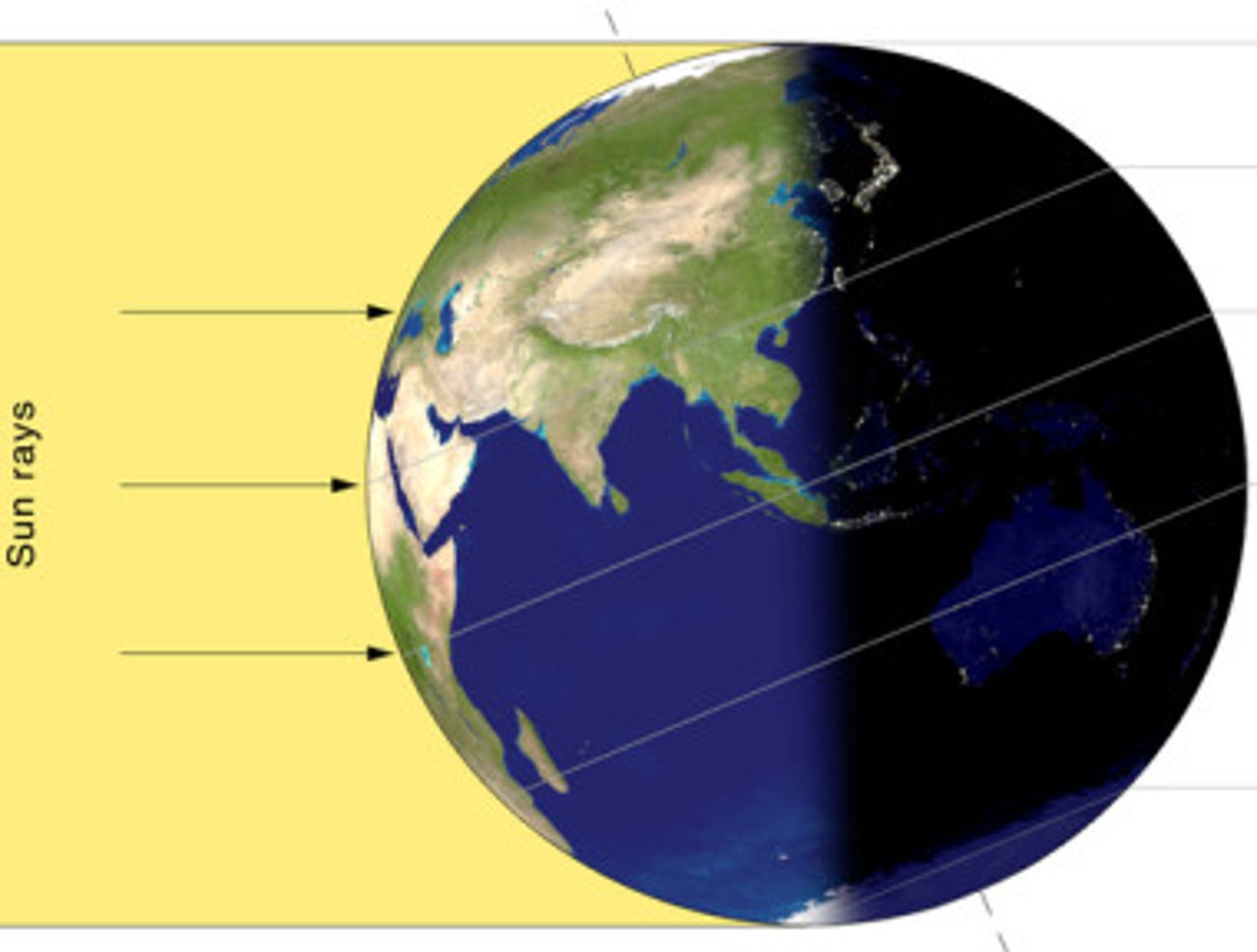
earths rotation
What causes day and night, 24hrs
circle of illumination
The great circle that separates daylight from darkness.
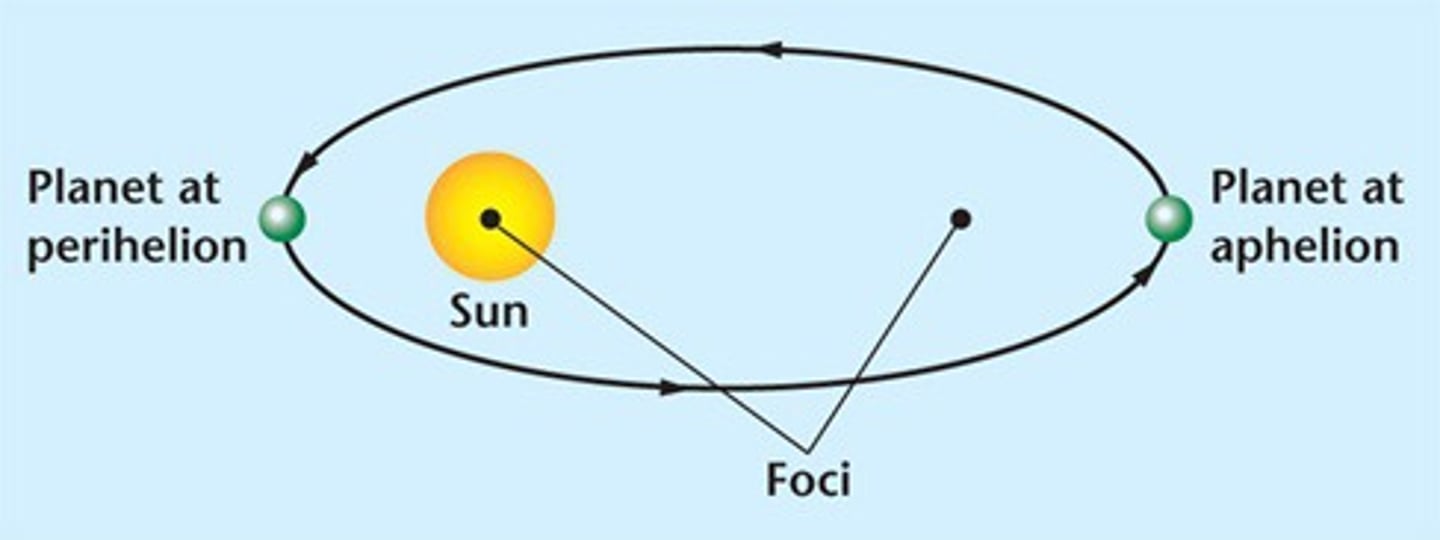
revolution
The movement of an object around another object (earth 365 1/4 days)
Perihelion vs. Aphelion
perihelion- point in orbit closest to the sun
aphelion-point in orbit farthest from sun
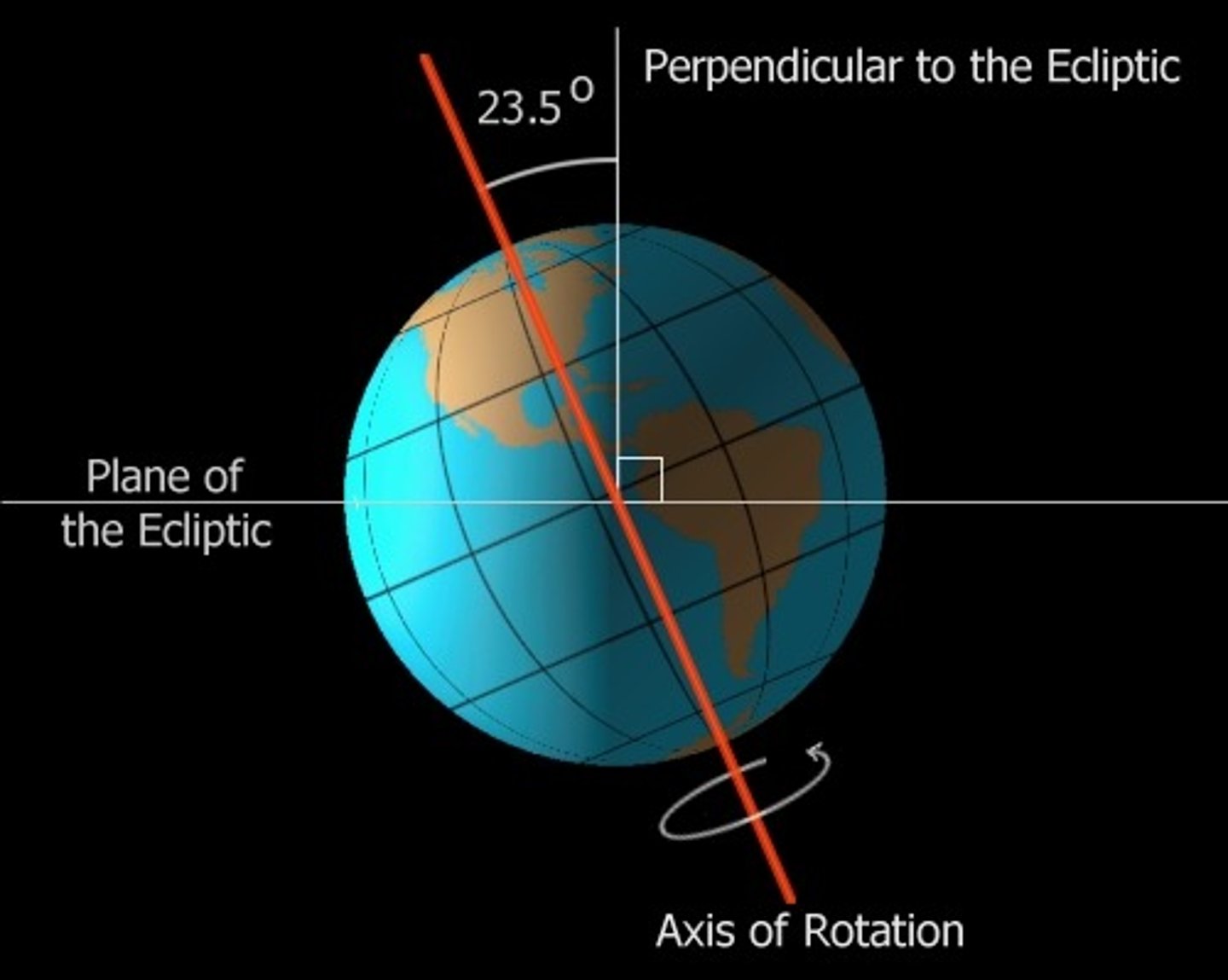
what is earths tilt in degrees
23.5 degrees
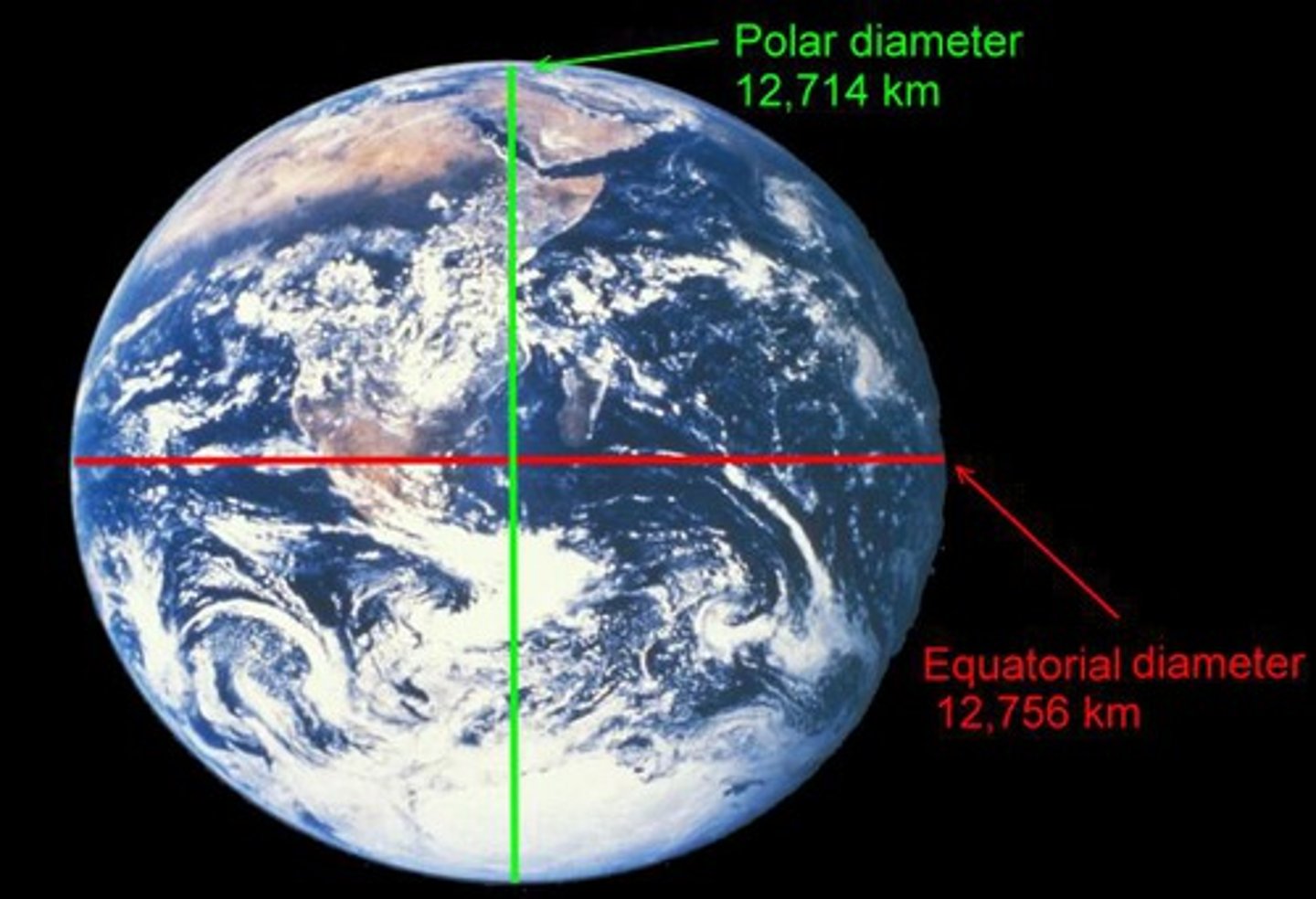
What is the shape of the Earth?
oblate spheroid
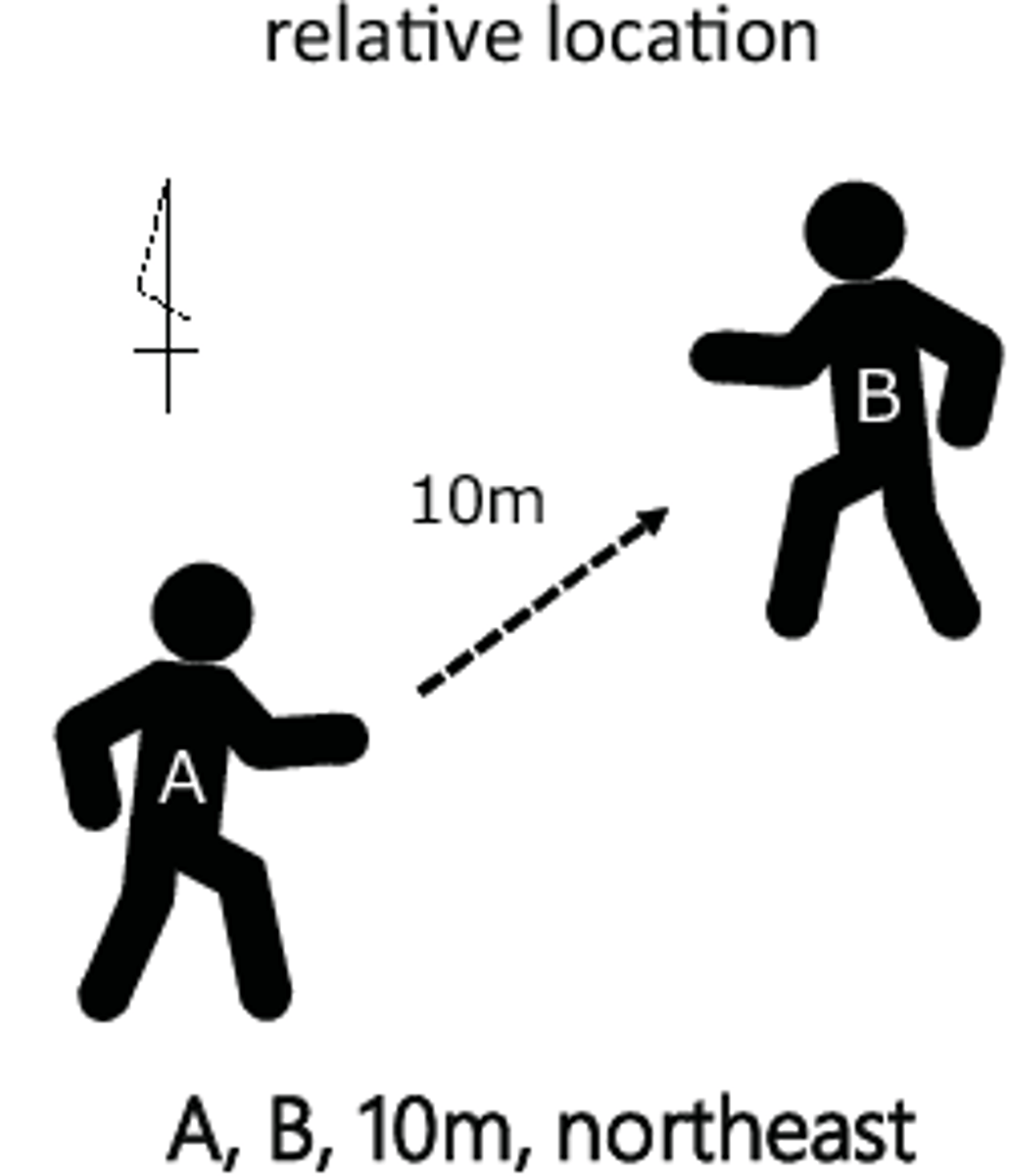
absolute location vs relative location
An absolute location describes a precise point on Earth or another defined space. A relative location describes where something else by using another, familiar feature as a reference point.
cartography
The science of making maps

meridians
Another name for lines of longitude
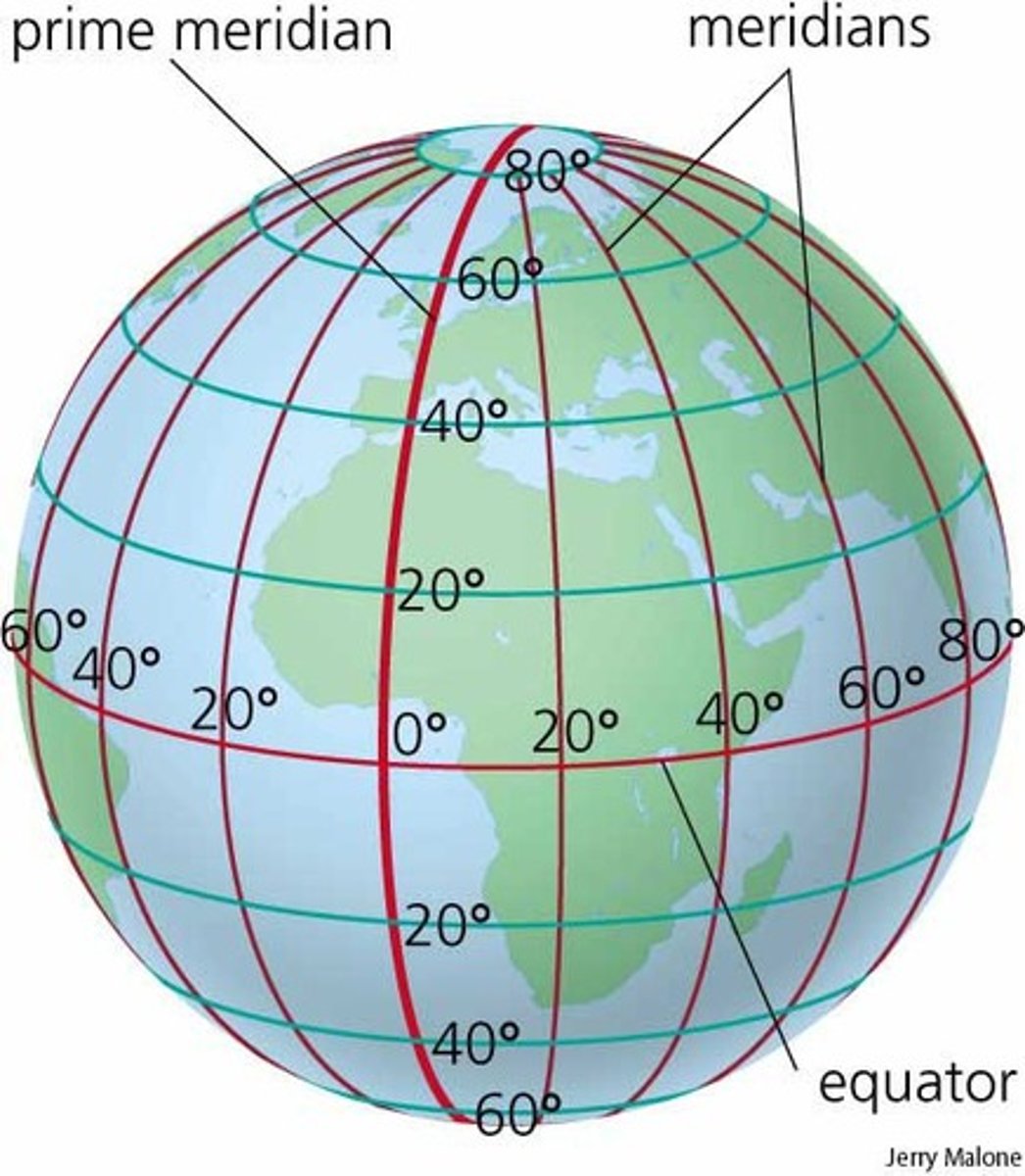
parallels
lines of latitude
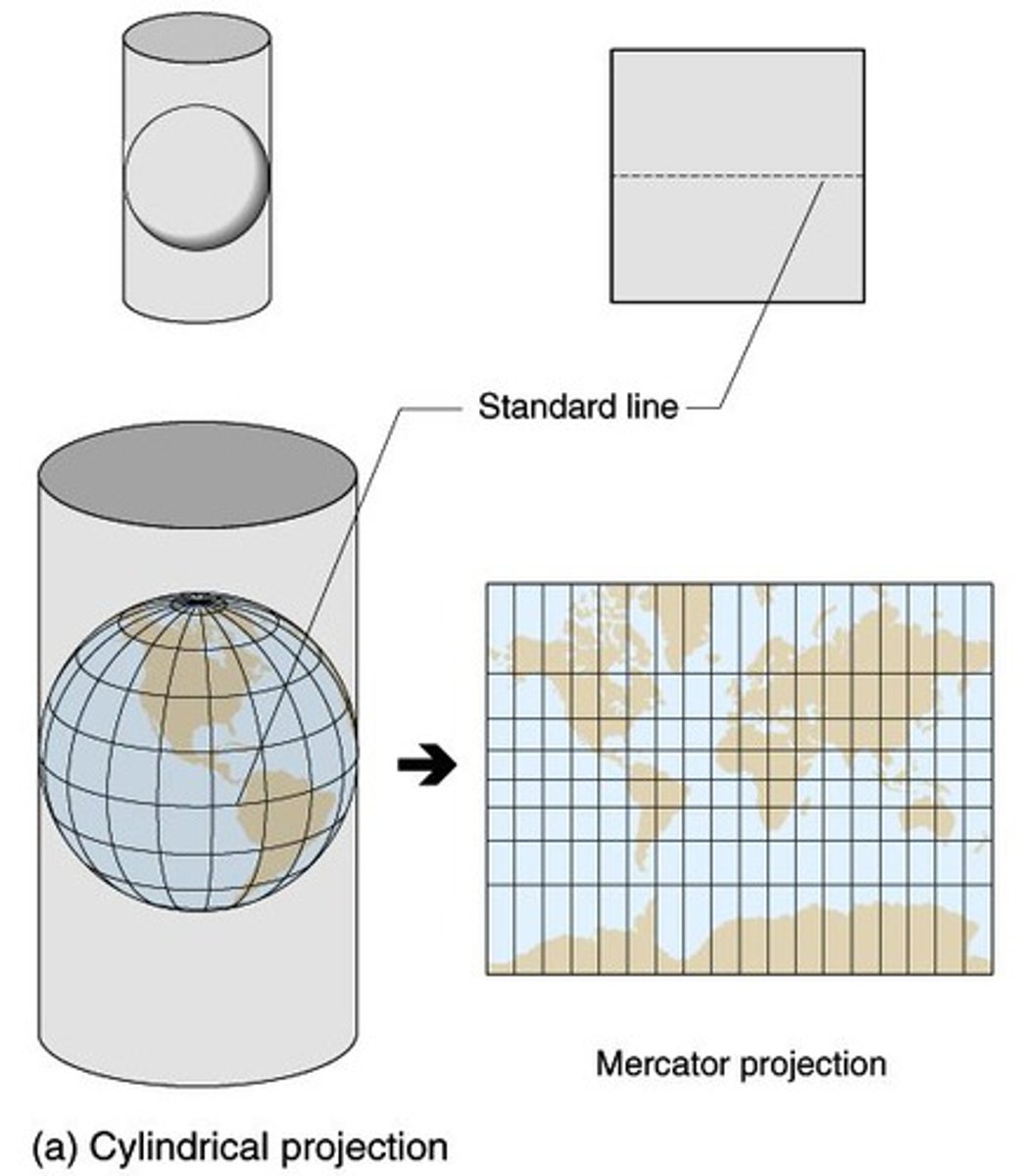
what is a map projection?
a way of representing the spherical Earth on a flat surface
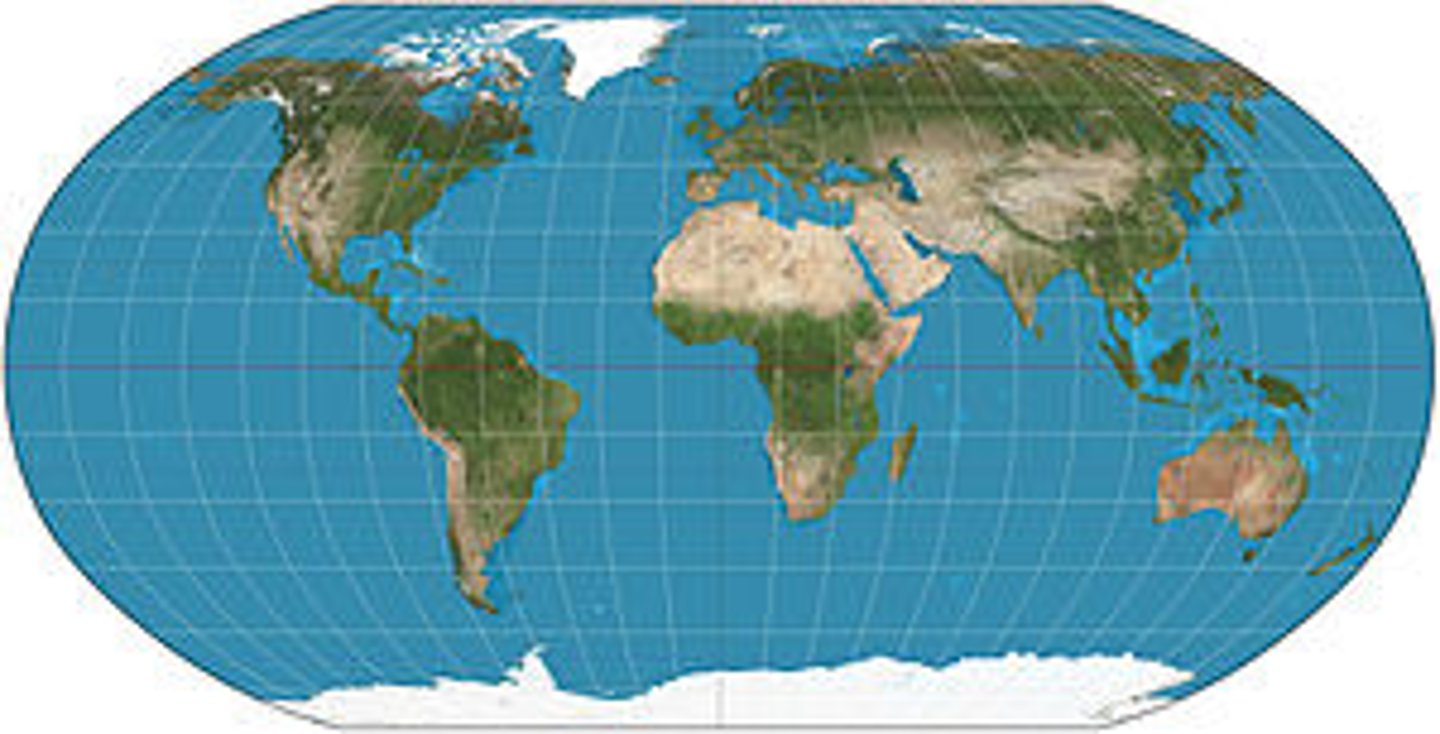
planar projection
a map created by projecting an image of the Earth onto a geometric plane (half of the world on top of one of the poles)
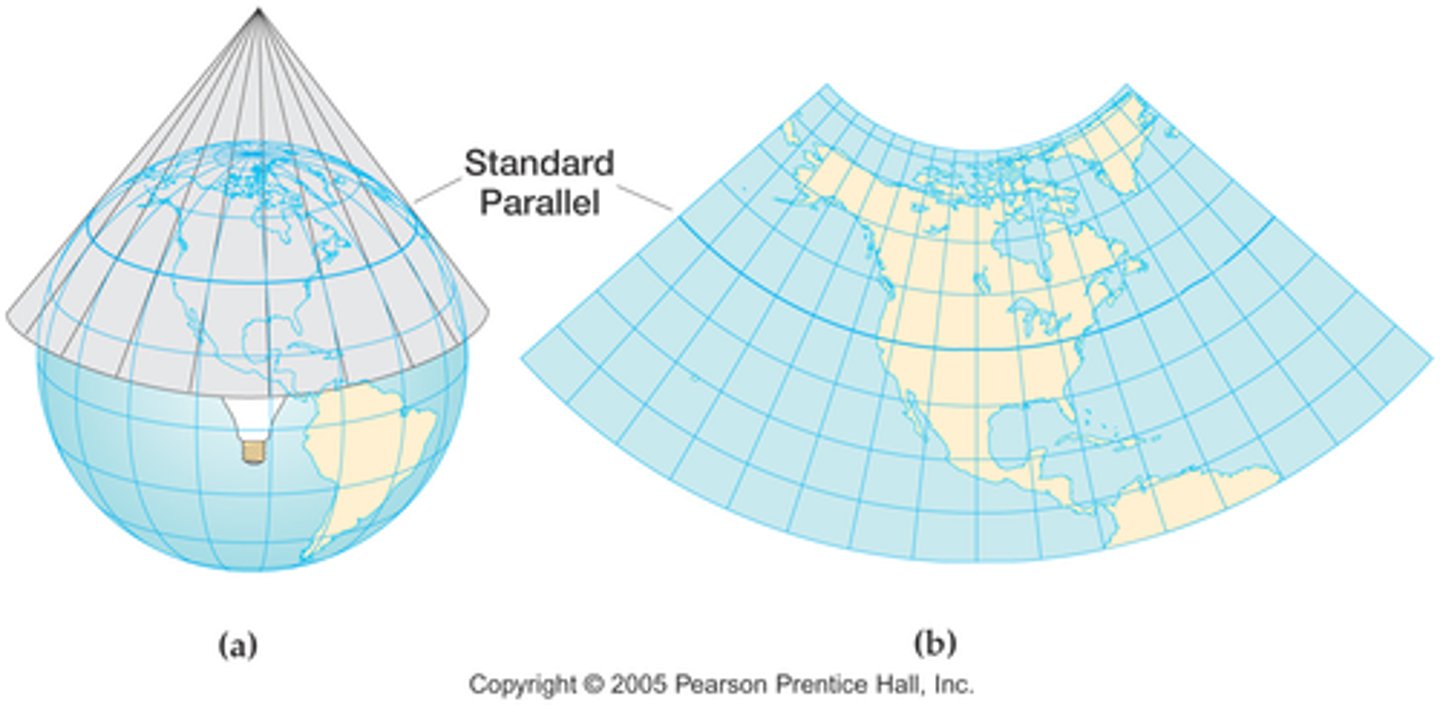
conical projection
The paper is shaped like a cone and contacts the globe only at the cone's base. This type of projection is most useful for middle latitudes.
cylindrical (mercator)
Is drawn with latitude/ longitude all meeting at 90 degree angles
Has accurate directions
The distortions include Greenland (too big), South America (too small) and Antarctica (way too big)
It is used on nautical charts
topographic map
A map that shows the surface features of an area.
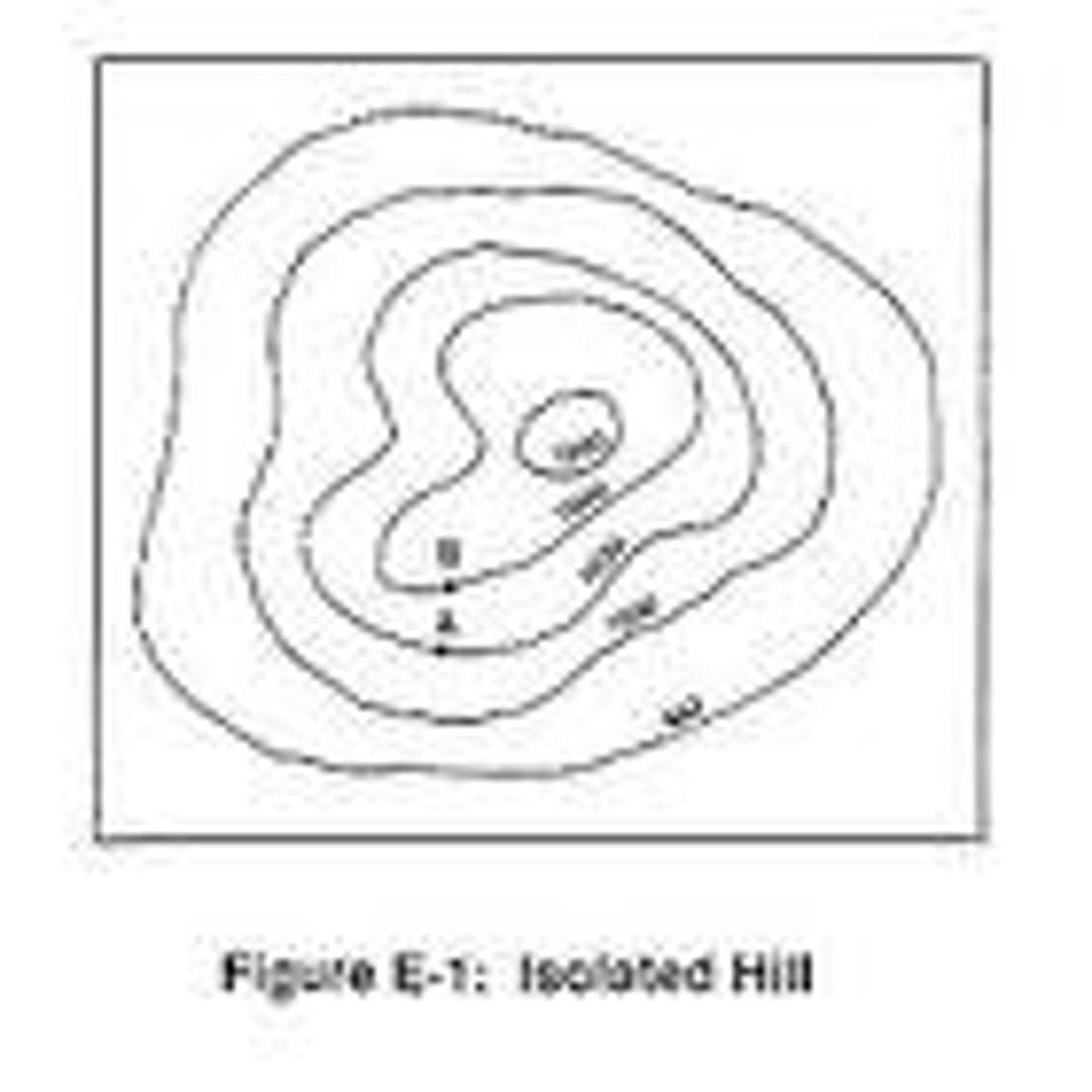

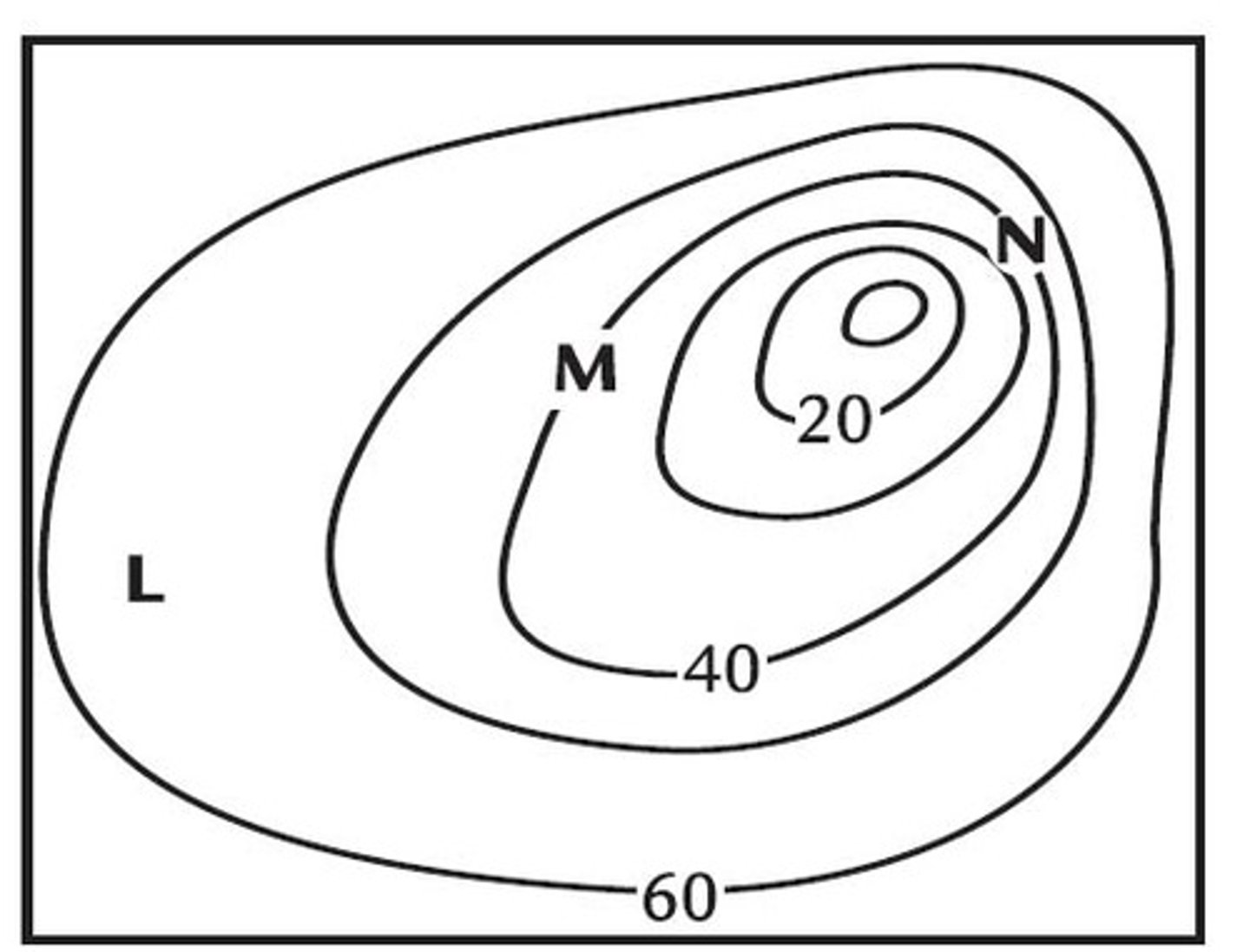
contour lines
lines that connect points of equal elevation
contour interval
the difference in elevation from one contour line to the next
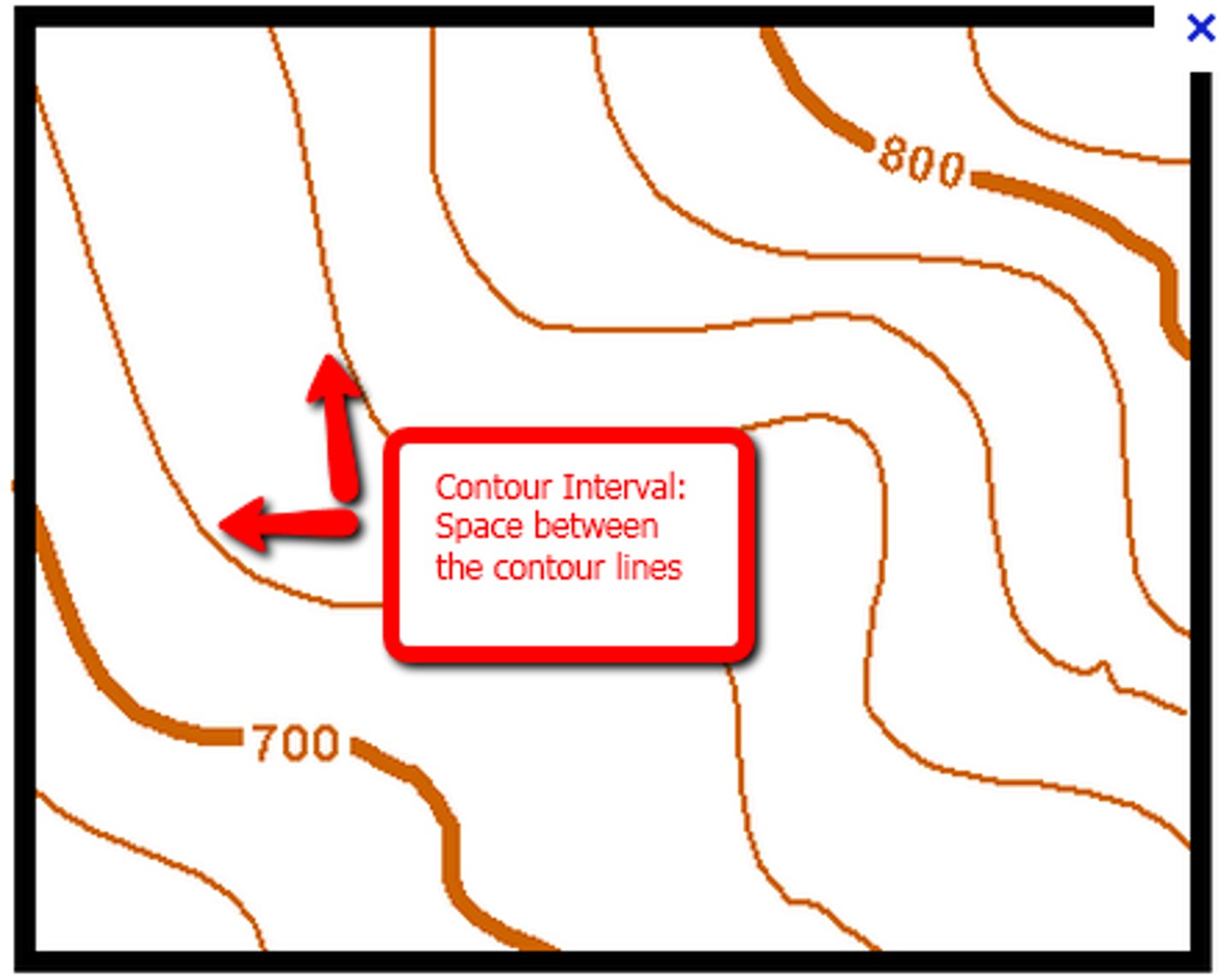
How can you tell a steep slope versus gentile slope on a topographic map?
The lines are close together, this tells you there is a tall drop-off
continuous vs discrete data on a map
continuous data is elevation, rainfall, pollution concentration, and water tables. A continuous surface, generally without sharp or abrupt changes. Discrete features are discontinuous and have definite feature boundaries.
large scale map
Maps that cover smaller areas with greater detail
small scale map
Shows fewer details, and focuses on a larger area (region, world)
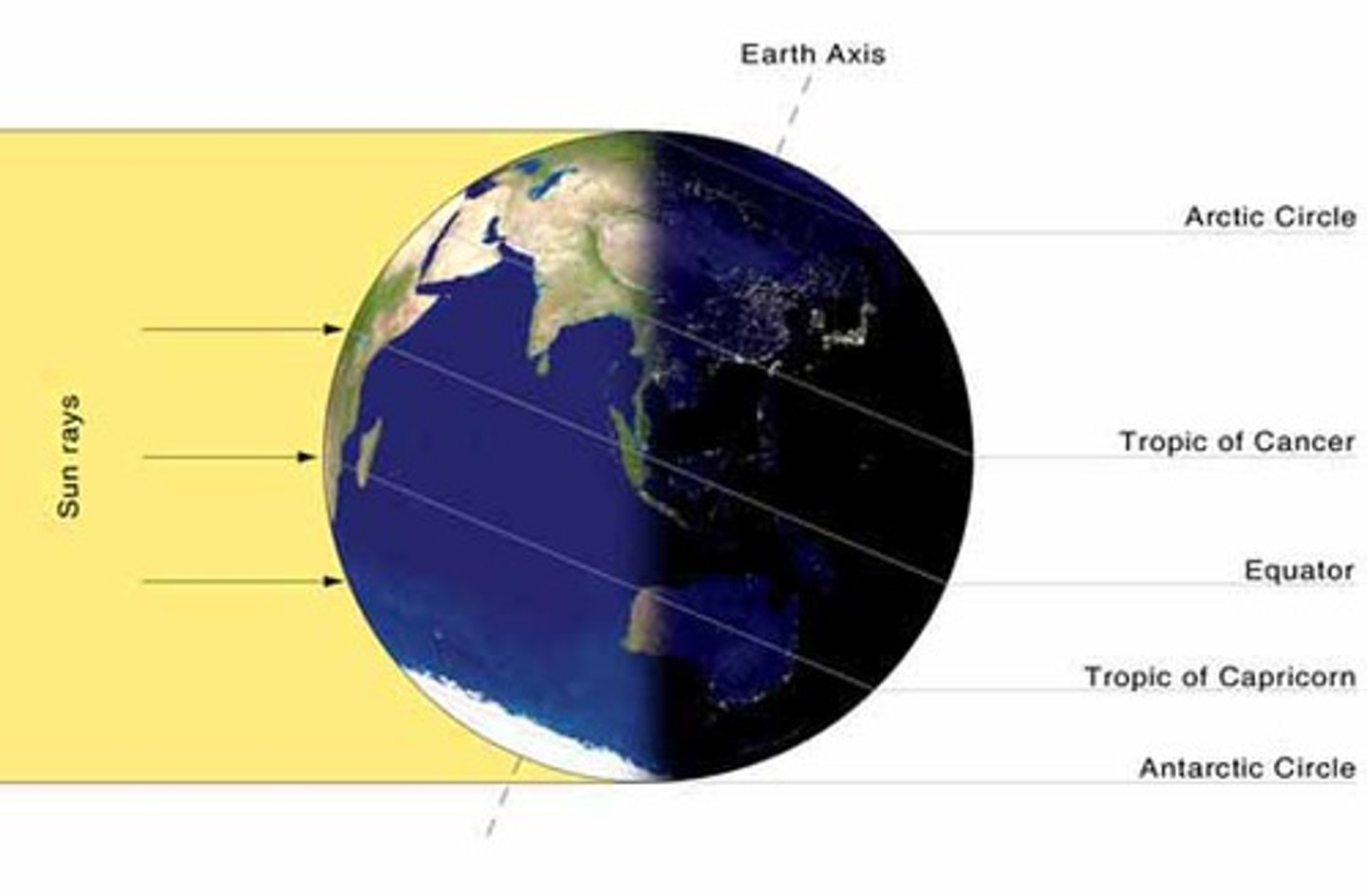
solstices
the longest and shortest days of the year (june 20, December 20)
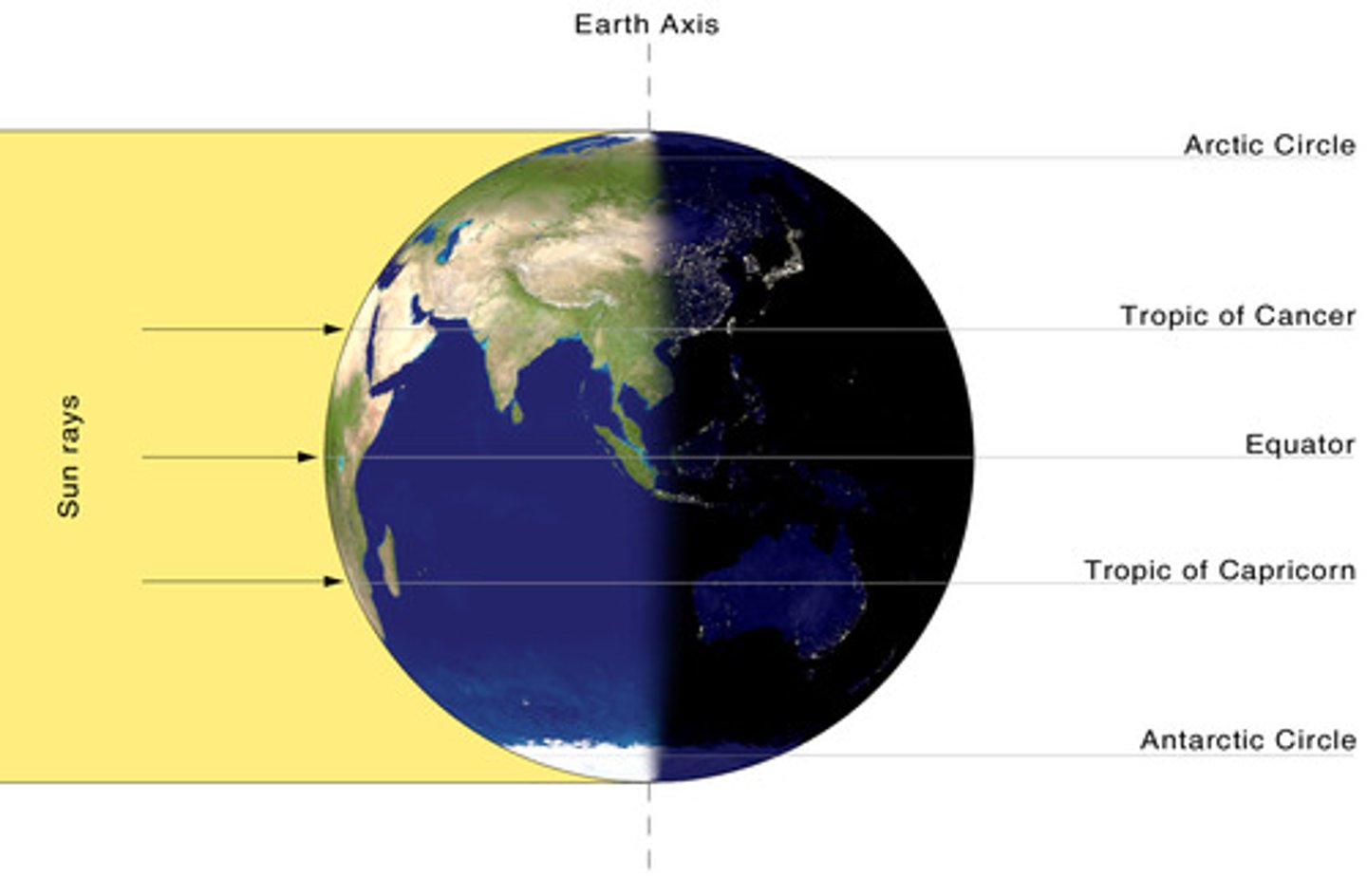
equinoxes
the time or date (twice each year) at which the sun crosses the celestial equator, when day and night are of equal length (about September 22 and March 20).
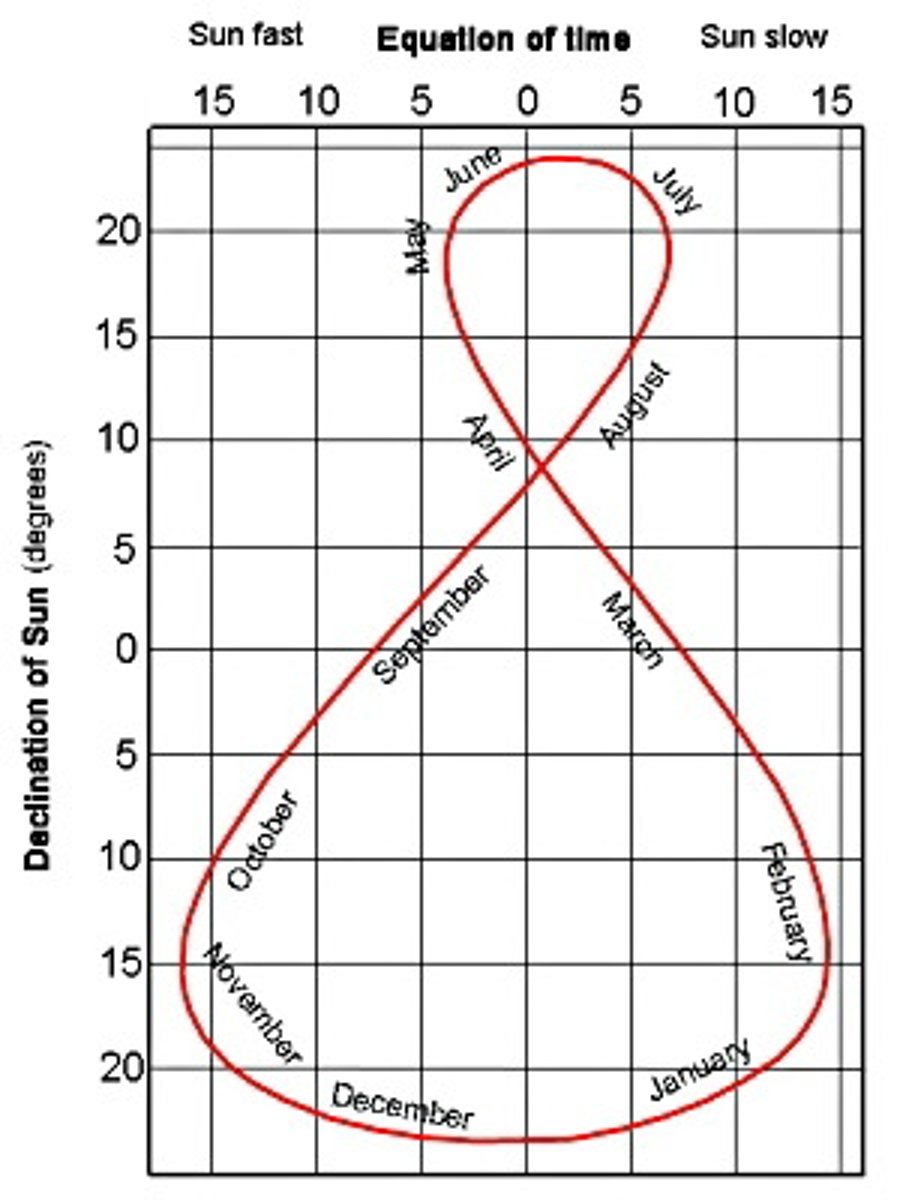
analemma
a diagram that shows the declination of the sun throughout the year
Subsolar Point (Declination of the Sun)
the latitude receiving the vertical rays of the sun
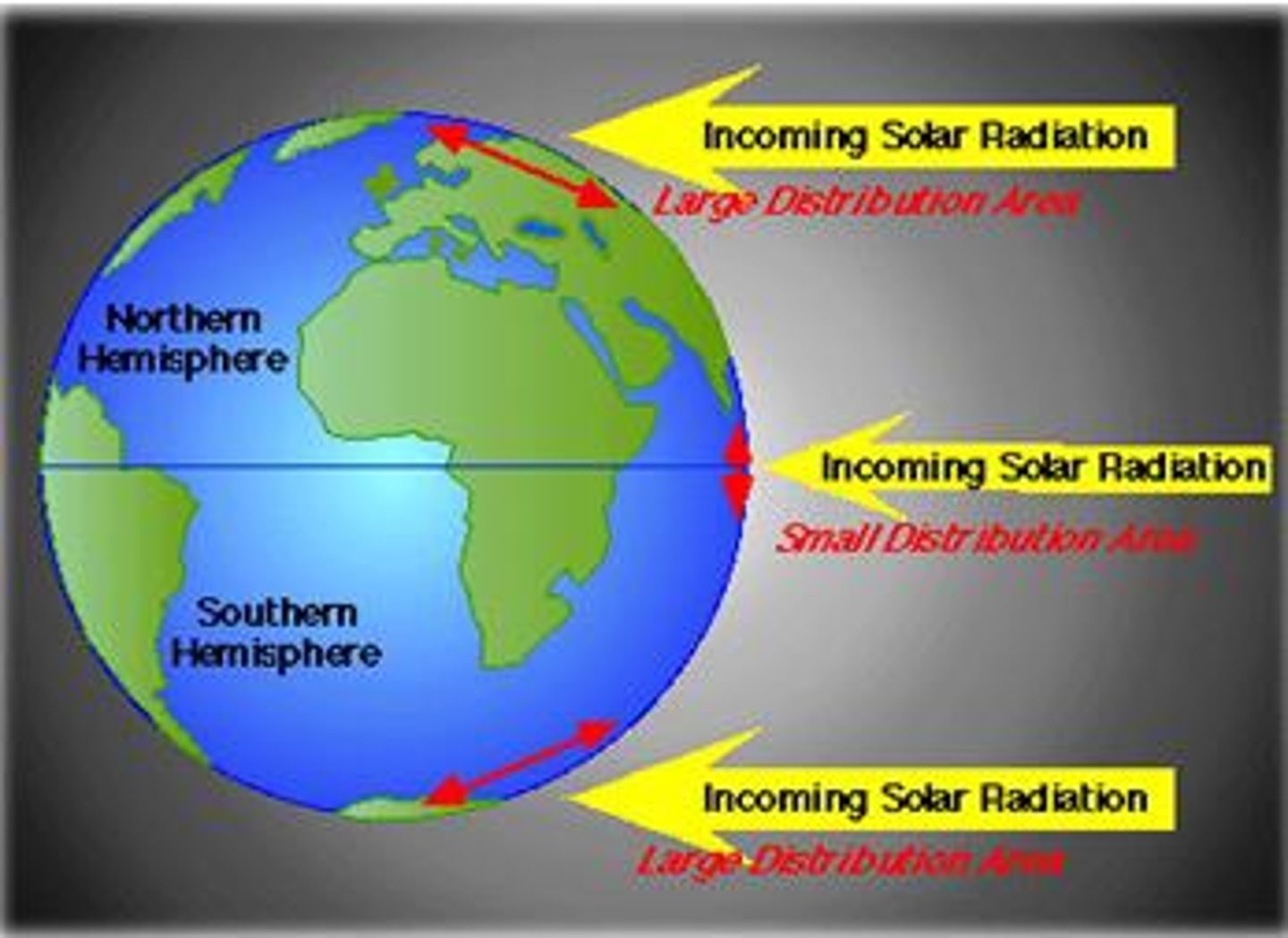
Between what latitudes does the subsolar point (or declination of the sun) migrate?
The subsolar point migrates between the latitudes of the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° North) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° South).
On June 21, an observer would see:
(a) long days and short nights in the Southern Hemisphere
(b) long days and short nights in the Northern Hemisphere
(c) day and night of equal length
(d) none of these
B. Long days and short nights in the Northern Hemisphere
troposphere
The lowest layer of Earth's atmosphere, holds the majority of the atmosphere's mass and water vapor.
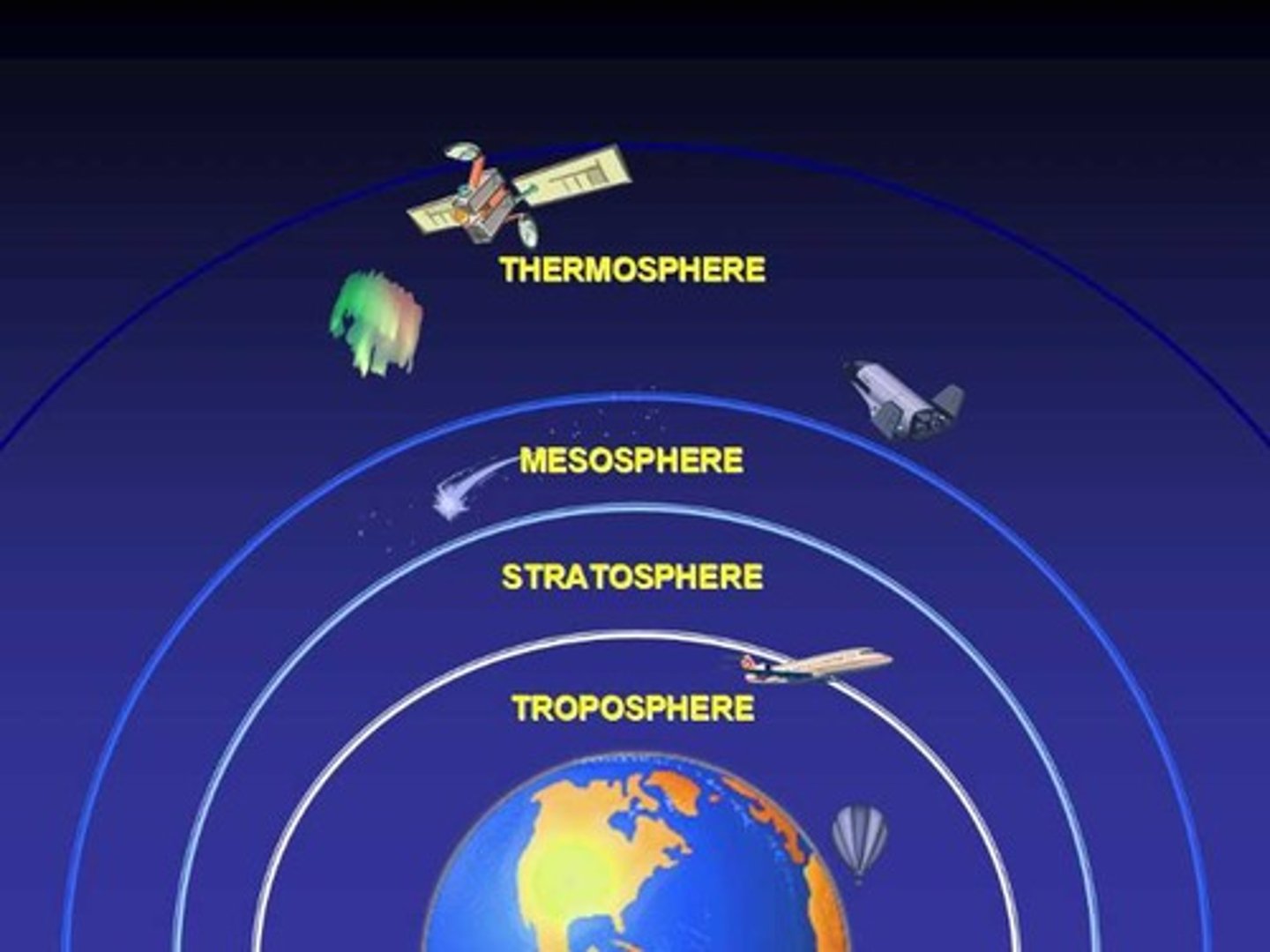
stratosphere
2nd layer of atmosphere; extends from 10 to 30 miles up; location of ozone layer; absorbs 95% of Ultraviolet radiation; temperature increases with altitude increase.

mesosphere
3rd layer of the atmosphere, Coldest
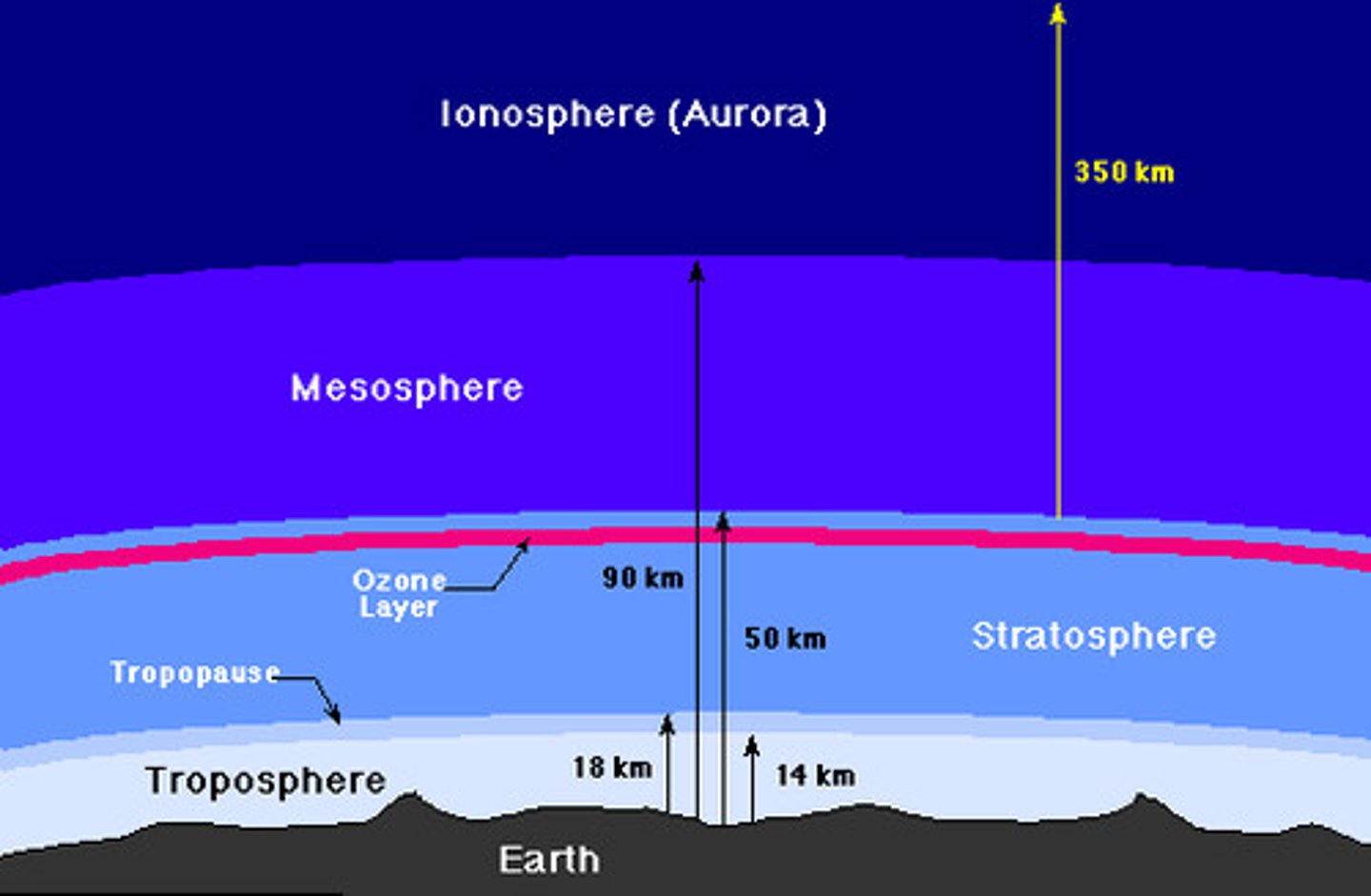
thermosphere
The uppermost layer of the atmosphere, in which temperature increases as altitude increases

constant gas vs variable gas
A "constant gas" refers to a gas in the atmosphere whose concentration remains relatively stable over time and location, like nitrogen and oxygen, while a "variable gas" is one whose concentration fluctuates depending on conditions
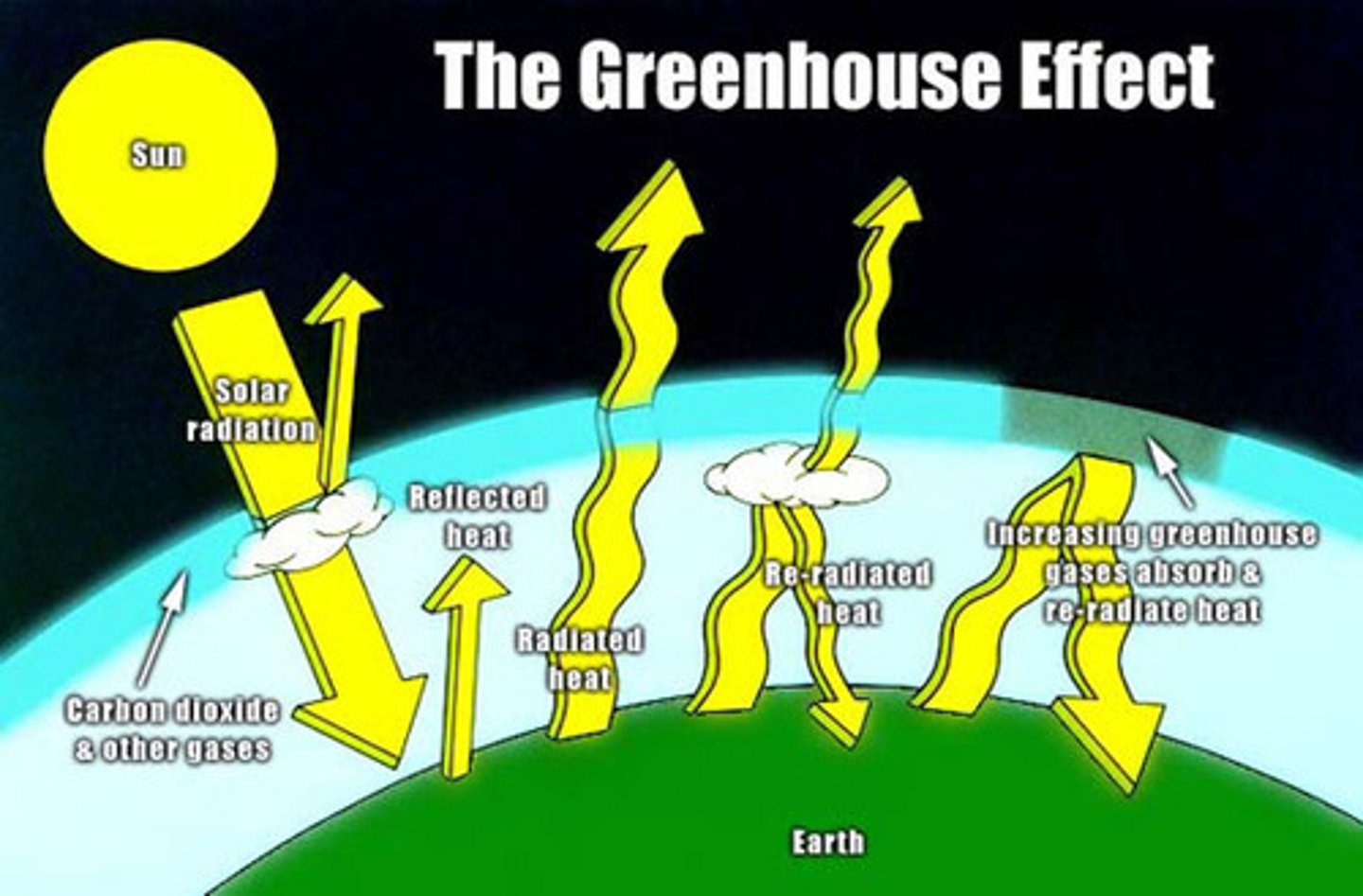
The greenhouse effect
Natural situation in which heat is retained in Earth's atmosphere by carbon dioxide, methane, water vapor, and other gases
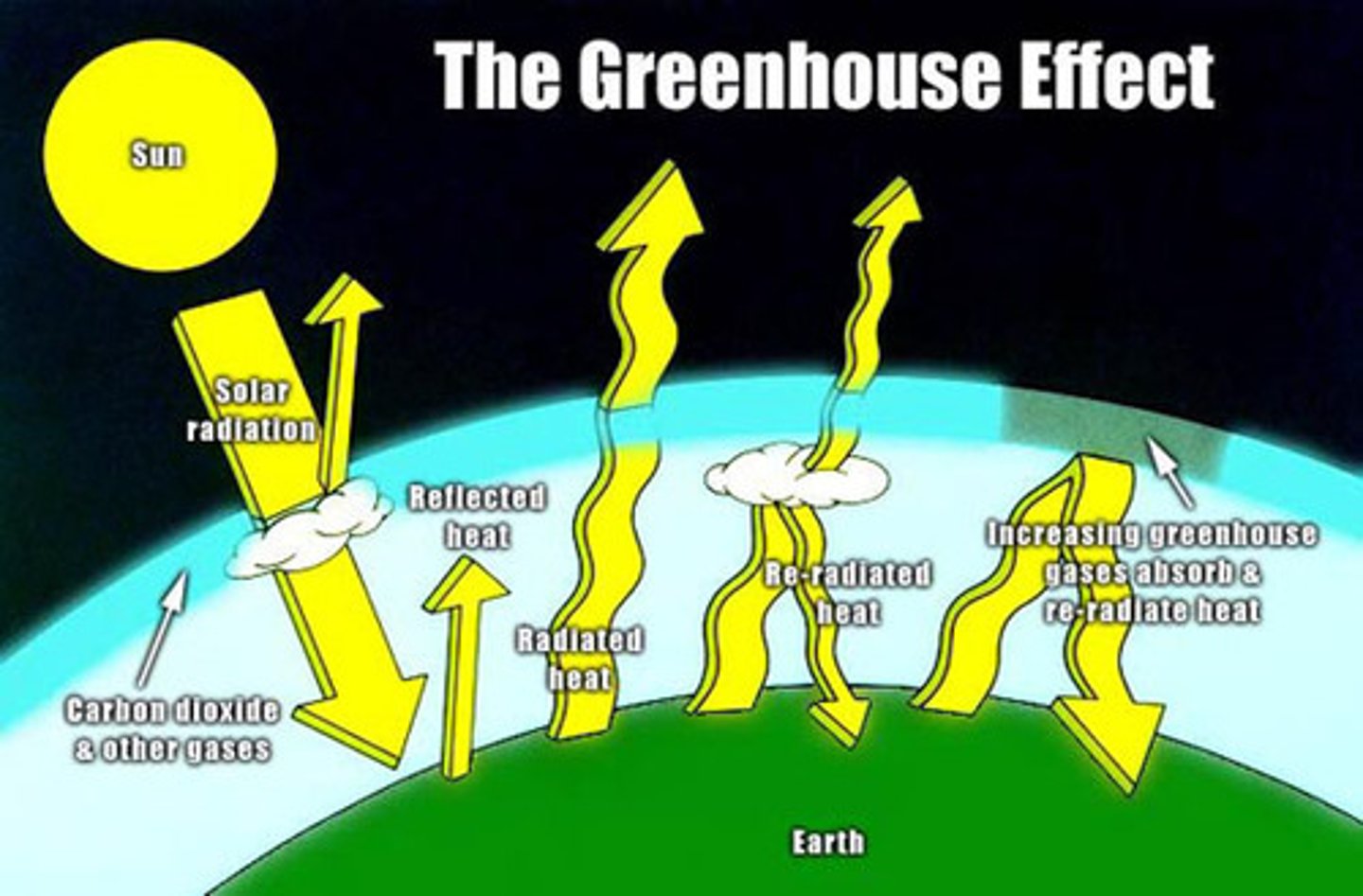
greenhouse gases
Gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, water vapor, and ozone in the atmosphere which trap heat radiating from earth)

electromagnetic radiation
a form of energy that exhibits wavelike behavior as it travels through space
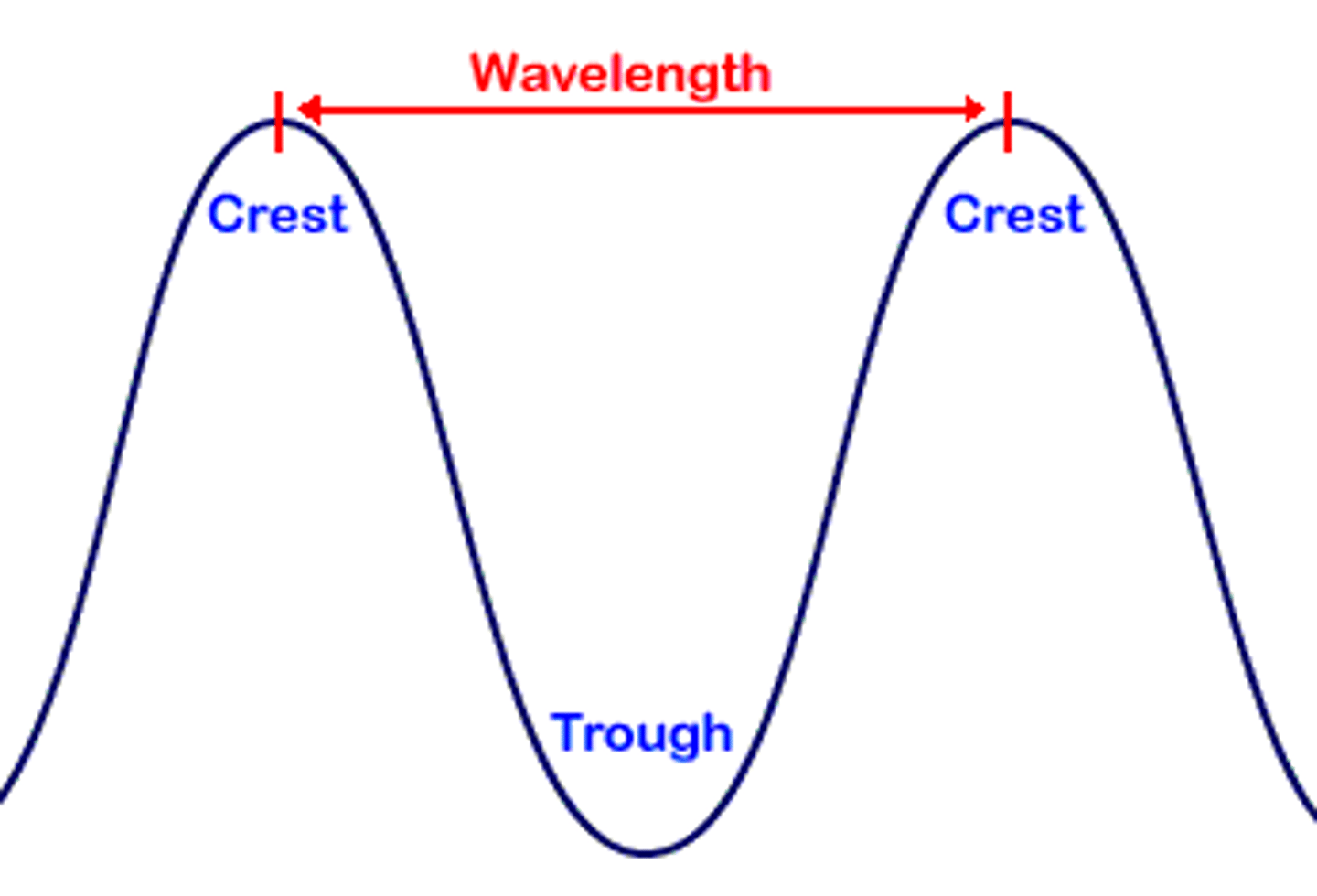
wavelength
Horizontal distance between the crests or between the troughs of two adjacent waves
shortwave radiation
A term most often used to describe the radiant energy emitted from the sun, in the visible and near ultraviolet wavelengths.
longwave radiation
A term most often used to describe the infrared energy emitted by the earth and the atmosphere.
four processes of energy transfer
conduction (touching), convection (transporting heat from hotter areas to colder areas) , radiation, advection (horizontal movement of air)
how does water change state
As energy is is absorbed or released, condensation, freezing, melting, evaporating, sublimation.
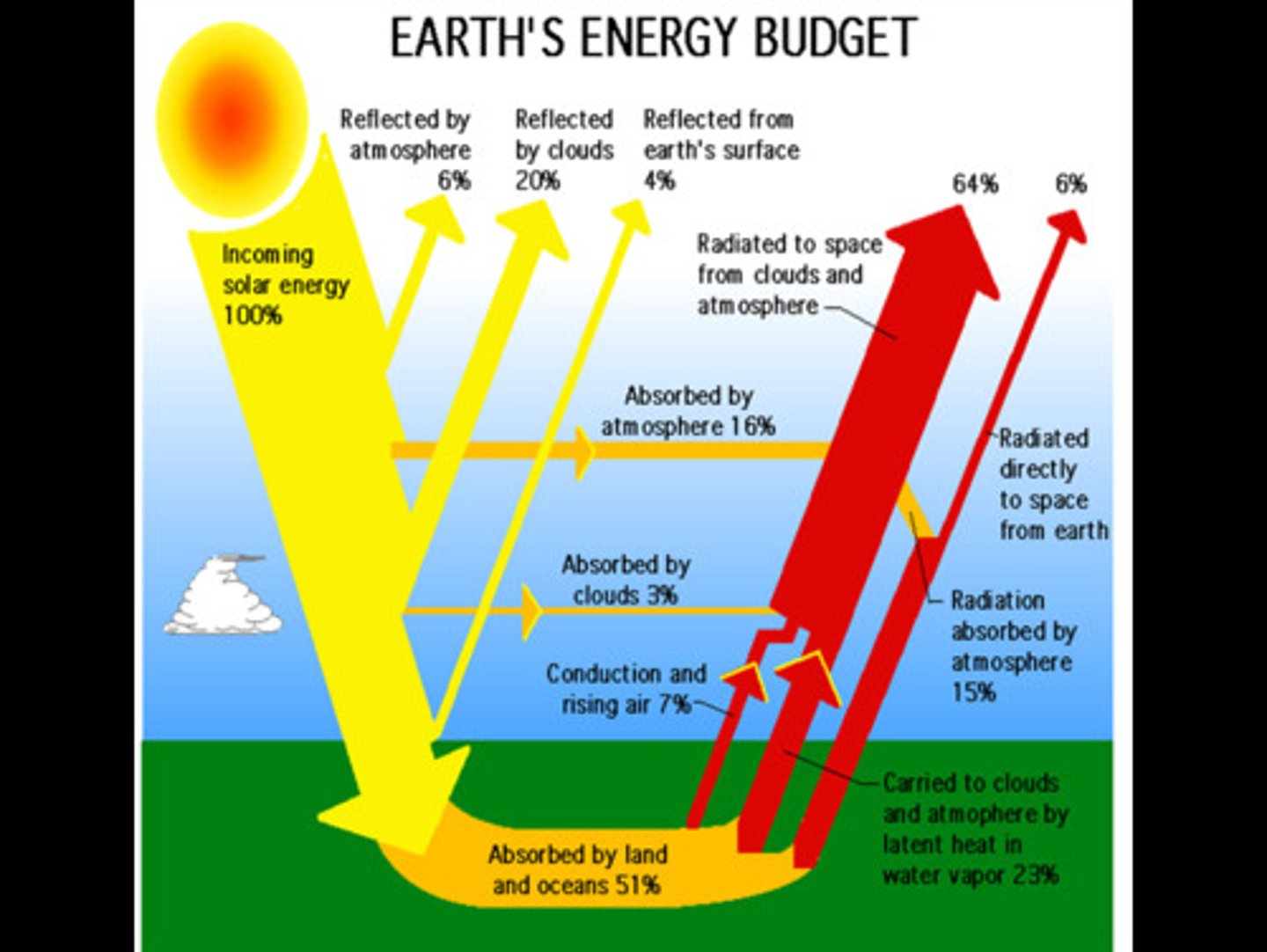
earths energy budget
0-35° both ways has surplus, 35-90° both ways has deficit
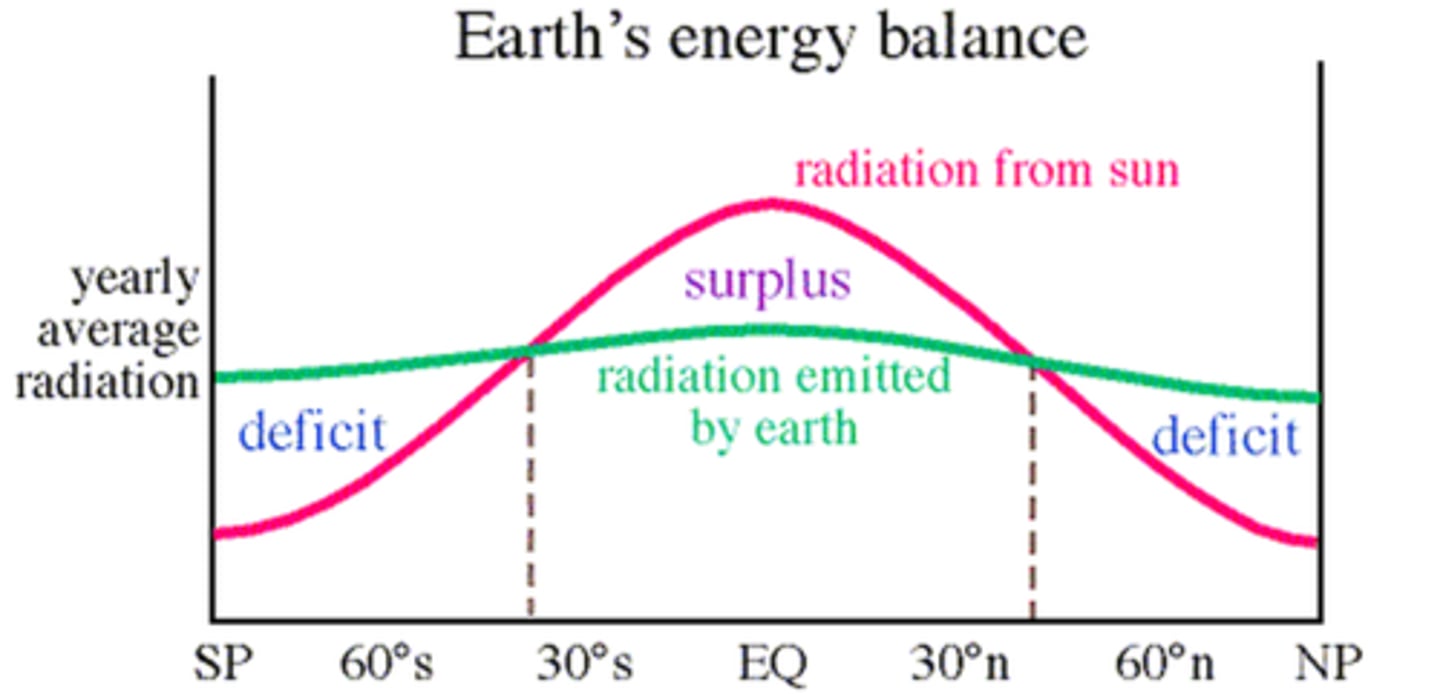
How is the surplus of energy in the low latitudes transferred to higher latitudes?
through the circulation of the atmosphere and oceans
absorption
70% of the suns incoming solar radiation is absorbed by earth, 30% is reflected into space.
reflection
suns radiation is reflected by clouds, ice, snow, and the surface itself
What time of day do maximum temperatures occur at the surface of the Earth?
a few hours after noon due to heat absorption and a delay in temperature rise
six controls of temperature
Latitude (sun angle), land and water distribution, (water holds lots of heats, cools slowly), ocean currents (flowing warm temps to cold keeps earth in equilibrium), altitude (temps increase with altitude), Landform Barriers (mountains block air movement), Human Activities (pollution, cities)
isotherm
Line drawn on a weather map that connects points having equal temperature
temperature gradient
The amount of temperature change per unit of distance.