Atomic Theory
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
What are the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory?
Matter is composed of atoms, (smallest unit of an element that can participate in chemical change)
An element consists of only one type of atom with a characteristic mass.
Atoms of one element differ in properties from those of other elements.
Compounds consist of atoms of two or more elements in small whole-number ratios.
Atoms are not created or destroyed in chemical changes — they are rearranged.
What is the law of definite proportions?
All samples of a pure compound contain the same elements in the same proportion by mass.
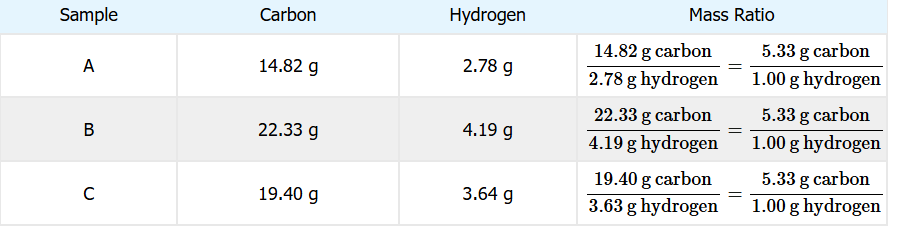
What is the law of multiple proportions?
When two elements form more than one compound, a fixed mass of one element will combine with masses of the other in small whole-number ratios.
Example:
Copper + Chlorine form two solids:
Green solid: 0.558g Cl / 1g Cu
Brown solid: 1.116g Cl / 1g Cu
→ Ratio of ratios = small whole number
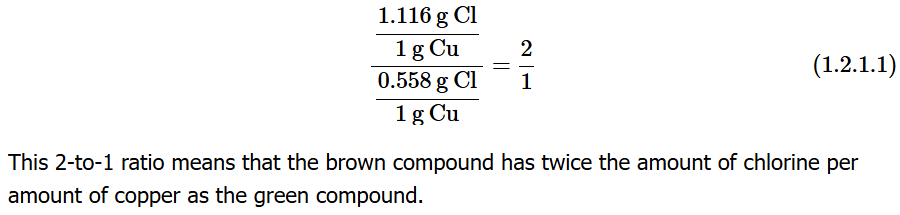
What did the cathode ray experiment discover, and who did it?
It discovered the electron. Conducted by J.J. Thomson.
How was the charge on oil droplets determined by Millikan?
Oil droplets became charged via friction or X-rays.
Droplets fell due to gravity but could be slowed or suspended by an electric field.
By adjusting the field, Millikan calculated the charge on individual drops.
What is the mass of an electron?
9.107 × 10⁻³¹ kg
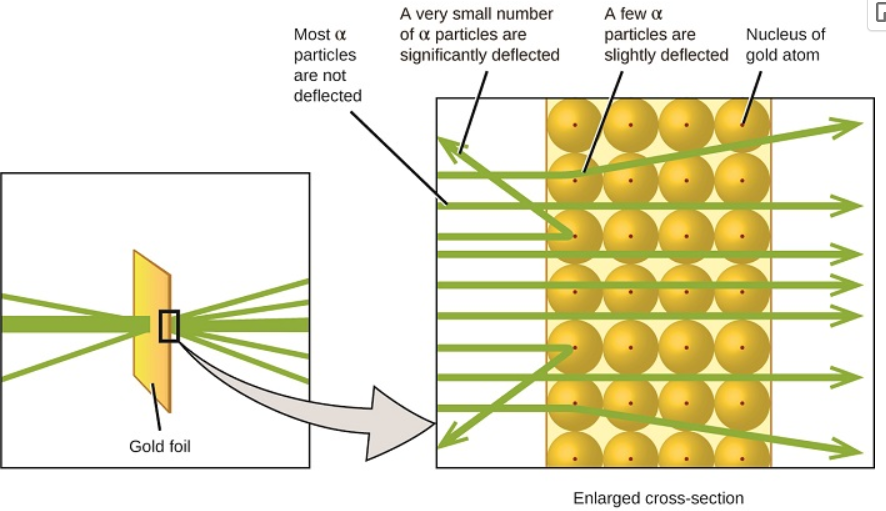
What did Rutherford, Geiger, and Marsden discover with alpha particle scattering?
Most alpha particles passed through foil.
Some were deflected slightly.
A few bounced back → implying dense, positively charged core.
What did Rutherford conclude from the gold foil experiment?
Atoms are mostly empty space.
A small, dense, positively charged nucleus exists at the center of each atom.
What is the mass of a neutron compared to a proton?
Nearly identical; both have approximately the same mass.
How do neutrons explain the existence of isotopes?
Isotopes have the same number of protons (same element), but different numbers of neutrons — leading to different masses but identical chemical properties.