[ANA] LIVER, GALLBLADDER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS, AND SPLEEN
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
91 Terms
Glisson’s capsule
Liver is cmpletely covered by a fibrous connective tissue called
supero-posterior surface; bare area of the liver
This surface of the liver is not covered by parietal or visceral peritoneum and is called?
hepatogastric ligament
Attachment found in the thin part of the lesser omentum
hepatoduodenal ligament
Attachment found in the thick part of the lesser omentum
portal triad (portal vein, hepatic artery, bile duct)
important structures found in the hepatoduodenal ligament
Falciform Ligament
This connects the liver to the umbilicus and divides the liver into the left and right lobes
Coronary Ligament
This is the continuation of the falciform ligament, in which its posterior and anterior leaflet is viewed posteriorly
Triangular Ligament
Found at the junction of the coronary ligament at the lateral side
anterosuperior and posteroinferior
What are the surfaces of the liver
Abdominal wall, pleura
structure anterior to the liver
Transverse colon, Abdominal Esophagus
structure posterior to the liver
Recesses
These are potential spaces created by liver, diaphragm, and inferiorly located kidney where fluid may accumulate
Subphrenic
Recess found between the diaphragm and the superior surface of the liver
Hepatorenal
Recess found between the liver and the kidney
Subhepatic
Recess created by the liver
renal, colic, gastric, duodenal
Enumerate the impressions created by organs near the liver
Lobar Division (Anatomic)
Division created by the falciform ligament that divides the liver into R & L lobes
F: NOT a true division
T/F: The Lobar Division (Anatomic) is a true division of the liver function-wise
IVC’s fossa and gallbladder
The True Division (Functional) is demarcated by the line from which structures
segment IV
This particular portion of the left liver is located in the right lobe, following the anatomical division
T
T/F: The one followed in surgery in terms of liver sections and defining the location of the tumor is the True Division (Functional)
Segments 1-4
Left lobe of the liver contains which segments?
True
T/F: Each segment cannot survive on its own if it does not have these 3 components (portal triad)
Celiac Plexus
Nerve supply of the Liver
Ganglia T7 - T10
SNS innervation of the Liver
Anterior Vagal Trunk
PSNS innervation of the Liver
Portal vein; nutrient-rich
This provides the major blood supply (70%) of the liver and contains what type of blood
superior mesenteric and splenic veins
Formation of the portal vein
hepatic artery; common hepatic artery
This supplies oxygen-rich blood to the liver, which is a branch of which artery?
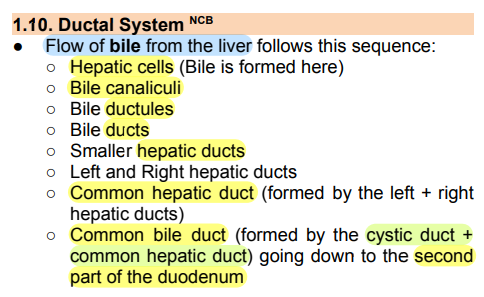
Flow of bile from the liver follows this sequence
inferior surface of the liver
The gallbladder is located in a fossa at the
cystic duct
What suspends the gallbladder
cystic artery; right hepatic artery
blood supply of the gallbladder and its usual origin
cystic vein; portal vein
blood drainage of the gallbladder and where does it drain to
fundus; transpyloric plane
Part of the gallbladder that is very close to the anterior abdominal wall, which also lies at this plane
body
This part of the gallbladder lies in contact with the visceral surface of the liver
Hartman’s pouch
This is a dilatation just prior to the neck the gallbladder and can be a rare congenital anomaly of the gallbladder
cystic duct
The neck of the gallbladder becomes continues with this structure
spiral valves of Heister
The cystic duct is surrounded by which structure that will join the common bile duct
Abdominal wall; inferior surface of liver
structures anterior to gallbladder
transverse colon
structures posterior to gallbladder
common bile duct
The cystic duct surrounded by spiral valves of Heister joins the?
cystic duct and common hepatic duct
Variations in the cystic duct in which it is located at the low junction between which structures
right hepatic duct
Variations in the cystic duct in which it drains into this structure instead of the common bile duct
behind the duodenum
Variations in the cystic duct in which it joins with the common hepatic duct (instead of common bile duct) behind which structure?
Cystohepatic Triangle of Calot
Structure that must be first identified during surgery before dividing anything
Inferior surface of liver, Common hepatic duct, Cystic duct
The Cystohepatic Triangle of Calot is bounded by which structures?
Cystic artery
What is found within the Cystohepatic Triangle of Calot
common hepatic a.
left hepatic a.
multiple cystic arteries
directly from celiac trunk
What are the other variations in the origin of the cystic artery?
Cystic Duct and Common Hepatic Duct
Formation of the common bile duct
right of hepatic artery; anterior of portal vein
Within the hepatoduodenal ligament, CBD is found at the ( ) of the hepatic artery and ( ) of the portal vein
four (4)
The CBD has how many parts?
supraduodenal (1st part)
Location of the first part of the CBD where it spans from its formation down to the superior border of the duodenum
behind D1
second part of the CBD is located
behind the head of the pancreas
second part of the CBD is located
at the medial side of the duodenum
fourth part of the CBD is located
Ampulla of Vater; Major Duodenal Papilla
This is the dilated portion of the Hepatopancreatic Duct, which drains into which structure at the medial wall of D2
Sphincter of Oddi
This surrounds both the CBD and the Pancreatic Duct, which also surrounds the Ampullary and Duodenal Papilla Complex
Epigastric area, LUQ
Location of the pancreas
Left hypochondriac
The tail of the pancreas is located at which region
superior mesenteric vessels
The uncinate process of the pancreas is located posterior to which structure?
formation of the portal vein
The neck of the pancreas lies immediately anterior to?
Tail
This part of the spleen is located nearest to the spleen
Body of stomach, Transverse colon
Structure anterior to the head of the pancreas
IVC, Right kidney, right adrenal gland
Structure posterior to the head of the pancreas
Uncinate process
Structure inferior to the head of the pancreas
Main Pancreatic Duct of “Wirsung”
This structure of the pancreas penetrates medial (posteromedial) border of 2nd part of duodenum and opens through greater duodenal papilla
upper pancreatic head
The Accessory Pancreatic Duct of Santorini drains which part of the pancreas
Union of splenic vein and superior mesenteric vein (SMV)
Formation of the portal vein
behind the neck of the pancreas
Commencement of the Portal Vein
porta hepatis
The portal vein divides into left and right branch at which structure
cystic vein
What is the right tributaries of the portal vein
Paraumbilical Vein of Sappey
This is a left branch/tributary of the portal vein which connects the left branch of the portal vein with the paraumbilical vein/ superficial veins in the abdominal wall
hepatic vein
The normal blood flow leaves the porto-systemic anastomoses via this vessel
SMV
The right lobe of the liver receives blood mainly from the intestine via which vessel
left lobe + quadrate and caudate lobe
blood from the stomach and spleen (Splenic v.) goes to which lobe/s of the liver
Left hypochondriac region
Region where the spleen can be located
fundus of the stomach and diaphragm (between Rib 9-11)
The spleen is found between which structures
Rib 10
Long axis of the spleen lies at which rib
midclavicular line
the most medial extent of a normal spleen is around which structure
Superior, Diaphragmatic/Posterior, Visceral, Inferior
Enumerate the surfaces of the spleen
hilum with the neurovascular structures
The visceral surface of the spleen contains which structure
concave, notched anterior border, irregular
Characteristics of the Visceral surface
convex, smooth
Characteristics of the Diaphragmatic/Posterior surface
Rib 10
The Diaphragmatic/Posterior surface lies along which structure
Gastrosplenic ligament
Attachment of the Spleen that contains left gastroepiploic & short gastric vessels
Splenorenal/Splenicorenal ligament
Attachment of the Spleen that contains splenic vessels
underneath the gastrosplenic ligament
Splenorenal ligament is located at which orientation relative to the gastrosplenic ligament
Splenic artery and vein
Blood supply and drainage of Spleen
Celiac plexus
Nerve Supply of the Spleen